This question is asked quite often when prescribing this type of research. The answer to this is, in general, simple - a standard urine sample for general analysis of 50 - 100 ml will completely satisfy the laboratory technician. For children, slightly different rules apply, differing significantly depending on their age - from 5 to 50 ml. However, the quality of the results of such an analysis depends not only on the amount of urine tested, but on how prepared you are for collecting the sample and on the quality of this procedure itself.
How much urine is needed for analysis?
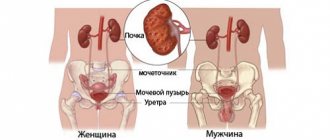
Depending on what diagnostics are prescribed to you, the collection method and the amount of material examined may be different. Thus, the volume of urine for general urine analysis in an adult and a child can differ significantly. What can we say about newborn babies?
Most often, a person does not think about how much urine is needed for a urine test, and fills the jar to the top. However, this is not always required. Let's try to figure out how much urine is needed to analyze different types of urine.
What standard is needed for qualitative analysis?
For a mature person, the optimal amount of urine is within 80 ml. This indicator varies somewhat depending on the type of analysis, age and physiological characteristics of a particular organism.
Norms for a mature organism
In a general urine test, approximately 80 ml of liquid should be considered optimal. The minimum volume required for a guaranteed reliable result is 50 ml, and there is no need to donate more than 100 ml, so the norm is 50 - 100 ml.
For baby
Having been born, the child’s body begins to actively rebuild the functioning of its systems towards an autonomous existence and in the first days secretes very little fluid, so taking a test from him is quite problematic. At one time, a newborn produces 5–10 ml of urine, which makes it extremely difficult to collect it in sufficient quantities. You need to collect at least 5 ml of liquid. With such a quantity, analysis, although very difficult, is possible.
Child under 1 year
Within one and a half to two months after birth, the amount of urine excreted increases to approximately 20–50 ml, so it becomes possible to collect a full volume of 35–50 ml for analysis with convincing information content. The minimum amount for this age is 10 ml.
General research
This study involves collecting a morning portion of excreted fluid. In this case, the entire material must be placed in the jar. Normally, a person secretes from 100 to 200 milliliters of fluid in the morning.
For diagnostics, 80-130 milliliters will be enough. If your container is significantly smaller than the allocated volume, then it is worth collecting the urine in a separate container and then pouring the required part.
Parameters and norms studied
The urine parameters to be studied and their norms are determined by clinical diagnostic medicine. In the standard form, some indicators are indicated in Latin. Knowing the abbreviation, reading the final protocol will not be difficult.
Organoleptics
The list of the main organoleptic properties of urine includes:
Hyaline casts in urine - what does this mean?
- Color. In its normal state it has a light yellow (straw) tint. The color of urine is influenced by the frequency of urination. With intense emptying of the bladder (pollakiuria), urine becomes lighter; with olakiuria (decreased diuresis), it becomes amber in color. The non-pathological reason for the shift in color indicators is the peculiarities of the diet (frequent consumption of beets, asparagus, etc.). A red tint to urine indicates severe hematuria (the presence of a large number of red blood cells - erythrocytes) in the urine. This gives reason to assume inflammatory processes, injuries to the ureters, kidneys, bladder, and the presence of cancer. The color of Porter beer indicates liver pathology. Green impurities appear in the presence of purulent-inflammatory processes.
- Specific gravity or density (SG). For the analysis of an adult, the regulatory framework is 1.010–1.022 g/l. The indicator reflects the degree of urine saturation. Hypersthenuria (high density) accompanies dehydration. Hyposthenuria defines a non-sugar type of diabetes, a decompensated stage of kidney disease.
- Smell. Shouldn't be harsh. When assessing the smell, attention is paid to strong impurities of feces, acetone, and rotten fish.
- Foaminess. Foam on the surface of urine is characteristic of liver disease.
- Transparency. Normally, it is close to absolute. The transparency of healthy urine is guaranteed to remain clear for several hours. The cause of cloudiness is salts (phosphates, urates, oscalates), a large number of epithelial cells, and protein.
Possible change in urine color
Physico-chemical characteristics
Seven indicators are subject to study, and four of them should not be present in the urine of a healthy person. In the analysis form you can read the Latin designation “Neg” or the Russian designation “Absent”.
Table of normal values and causes of deviations
| Indicators | Abbreviation | Norm | Deviations |
| acidity | RN | 4–7 units | A neutral acidity reaction (5-6 units) is considered good. Alkalosis, or alkalinization of urine, occurs when phosphate stones form in the urinary organs or due to bacteriuria (bacterial infection). Acidosis (acidification of urine) can be caused by inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and bladder, chronic alcoholism, nephrotuberculosis |
| protein | PRO | ≤ 0.033 g/l | PRO urine analysis reveals proteinuria - a pathological excess of protein, characteristic of inflammatory diseases (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.). In women, proteinuria can develop against the background of vulvovaginitis. |
| glucose (sugar) | G.L.U. | ≤ 0.8 mmol/l | glucosuria - an increase in the concentration of glucose in urine means a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, characteristic of diabetes mellitus, chronic pancreatitis, and cirrhosis of the liver. |
| hemoglobin | HB | Neg | Hemoglobin is a blood protein with the function of providing the body with oxygen. It is found in red blood cells and should not be present in urine. Hemoglobinuria indicates the pathological destruction of red blood cells during sepsis, heart attack, anemia, and bleeding of internal organs. |
| ketone bodies | KET | Neg | ketonuria (the presence of toxic ketones in the urine) indicates a failure of metabolic processes. Occurs as a complication of diabetes, chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis, alcoholism, thyrotoxicosis |
| bilirubin | BIL | Neg | bilirubinuria accompanies diseases of the hepatobiliary system |
| urobilinogen | URO | 5-10 mg/l | if urobilinuria (increased pigment levels) is detected, then there are serious pathologies of the liver and bile ducts. |
Microscopic sediment of biofluid
Microscopic examination of sediment includes:
- red blood cell count (BLD);
- identification of cylinders;
- urine LEU (leukocytes or white cells) analysis;
- identification of epithelial cells;
- detection of fungi, bacteria, parasites.
The LEU and BLD indicators have gender differences associated with the anatomical structure of the external genitalia of women and men. There are five types of casts (protein compounds); the presence of a minimum amount of only hyaline casts is allowed in the urine.
Reference values and reasons for increasing indicators
| Parameter | Norm | Deviations |
| LEU | male -≤ 3; women-≤ 6 | leukocyturia (increased LEU) is a sign of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.) and chronic infections. |
| BLD | men - 1-2 women - ≤ 3 | hematuria accompanies damage to the kidneys, bladder and ducts, glomerulonephritis, certain diseases of the genital area (colpitis, endometriosis, prostatitis, adenoma) |
| epithelium | ≤ 10 units | an increase in number indicates kidney and bladder diseases |
| hyaline casts | no more than 20 | cylindruria may indicate inflammation of the renal apparatus |
| red blood cell casts | Neg | are determined by thrombosis of the renal veins, nephrotuberculosis, and renal infarction. |
| granular cylinders | Neg | found in pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis |
| epithelial casts | Neg | characterize necrosis, the presence of infections, intoxication |
| waxy cylinders | Neg | a sign of severe renal pathologies |
| fungi, bacteria, parasites | Neg | the presence of pathogens in the TAM indicates corresponding infections (bacterial, fungal, helminthic) |
Unsatisfactory results of microscopy of urine sediment are the basis for prescribing a detailed study - the Nechiporenko test. When deciphering the final data, the doctor takes into account how much the indicators deviated from the norm, as well as their changes in relation to each other.
Important! You should not self-diagnose. Only a doctor can correctly decode the analysis results.
Research on Nechiporenko
How much urine do you need? To analyze urine according to Nechiporenko, the laboratory assistant separates one milliliter of liquid from the entire volume. This is the amount required to determine the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and casts. However, this does not mean that you can bring a few drops of urine to the laboratory.
To study material according to Nechiporenko, you need to donate from 50 to 70 milliliters of liquid. In this case, the portion of urine should be medium. This means that the first stream of liquid should be released into the toilet. After this, the material is collected in a jar. You should also finish urinating in the toilet.
Preparing for analysis
To get the most reliable results from a urine test, you need to prepare for it.
Before the study, you do not need to change your usual drinking regimen, but you must stop drinking mineral water
The day before, you should avoid foods that can color urine (blueberries, blackberries, cranberries, beets, carrots), this also includes synthetic vitamins. In addition, strong tea and coffee, large quantities of mineral water, excessively spicy and salty foods, smoked foods, and alcohol are not recommended. You should adhere to your normal drinking regime, i.e. do not drink more or less liquid than usual. In addition, the day before the study, it is advisable to avoid excessive physical and mental stress, as well as sexual contact.
The test result may be affected by some medications (diuretics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.), for this reason, before the study, you must agree with your doctor about the possibility of discontinuing them.
If it is necessary to collect urine from a newborn or infant, it is convenient to use a urinal bag specially designed for this purpose, which is sold at the pharmacy.
It is recommended to take a urine test at least a week after cystoscopy or removal of the urinary catheter.
Research on Zimnitsky
How much urine do you need to collect to conduct this test? Zimnitsky's analysis involves diagnosing fluid that is released during the day. In this case, the main condition is to collect material every three hours. Absolutely all portions are collected in sterile containers. A healthy person produces from one to two liters of urine during the day. Therefore, you should fit approximately 150-300 milliliters of liquid in one container.
To carry out diagnostics, the laboratory assistant extracts about 10 milliliters of urine from each jar. It is in this scope that the research is carried out. From this we can conclude that only 80-100 milliliters of collected material is needed for diagnosis.
About the types of laboratory testing of urine
In addition to OAM, there are other types of urine testing that differ in the technology for collecting biomaterial, the method of laboratory study, and the reason for the purpose. There are urine tests performed:
- to determine renal pathologies - Nechiporenko test;
- assessment of the performance of the kidneys and heart - Zimnitsky test;
- identifying dysfunctions of the urinary, urinary and endocrine systems of the body - daily biochemical urine analysis;
- quantitative determination of calcium - Sulkovich's test;
- assessment of renal reabsorption function and excretion stability - Rehberg test;
- detection of pathogenic bacteria and activation of opportunistic microflora - BAC-seeding.
Specific studies are designed to study tumor markers (Bence Jones protein, PSA, C-125, AFP, etc.). Pregnancy can be determined in the early stages based on data from an analysis of the level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
OAM and urine biochemistry are basic purposes. Based on their results, the issue of the need to conduct additional tests is decided. All types of urine tests require compliance with the conditions of preparation, collection, storage and transportation of biological fluid. The time of the analytical procedure depends on the complexity of the study. General clinical analysis is prepared faster than others.
Reference! An independent rapid analysis takes several minutes, but its results do not have the accuracy of a laboratory test and can be decoded erroneously.
Test to determine glucose, protein and creatinine levels
How much urine is needed for this type of diagnosis? A person should collect one to two liters of material. In this case, there is no need to deliver the entire volume to the laboratory. Diagnosis involves collecting all the secreted fluid, which is placed in one large container. After this, you need to separate 100 milliliters from the resulting volume and deliver them to the laboratory.
During the study, doctors do not use the entire dose received. They take about a third of the volume and carry out diagnostics. It is worth noting that for each test you need to take the specified dose. So, if you are assigned to test your urine for the presence of glucose, then 100 milliliters of the daily norm is given. Each additional study involves adding the specified portion.
Containers for collecting urine
A container for collecting urine must be prepared in advance. Some laboratories provide disposable plastic containers for urine collection upon request or when scheduling a test. In other cases, they can be purchased at a pharmacy. The advantages of special containers designed specifically for collecting urine are that they are completely ready for use, easy to use, and have a tight lid.
The day before the test, it is advisable to avoid excessive physical and mental stress, as well as sexual contact.
If it is not possible to purchase a disposable container, the material can be collected in a glass jar with a capacity of 100–250 grams with a tight-fitting lid. Such a jar must first be prepared: thoroughly washed, then sterilized with steam or boiling water, and dried. Household plastic containers should not be used to collect urine, since they cannot be properly disinfected at home, and in addition, the material from which they are made can react chemically with urine.
Amount of child's urine for diagnosis
Unlike adult norms, the baby’s portion of fluid secreted may be significantly smaller. So, if a person needs to collect 100 milliliters for a general analysis, then 20-50 will be enough for the baby. Remember: the laboratory assistant cannot refuse you an analysis due to the fact that there is not enough material.
If the study needs to be carried out on a newborn, then the portion may be even smaller. Babies in the first month of life can urinate only 10 milliliters at a time. This amount of liquid will be quite enough for diagnosis. Only in some cases can a doctor prescribe collecting two different portions of material in one container.
How long are the results of tests for HIV and syphilis valid?
The shelf life of a blood test for HIV and AIDS is 6 months, for syphilis - 3 months. Blood is prepared for hidden infections for 4-10 days.
Each clinic sets its own limitations on the validity of the tests performed. So, to undergo a medical examination and provide a certificate to the military registration and enlistment office, the validity period should not exceed 14 days, otherwise it will become irrelevant.
To understand how valid clinical blood tests are, you need to take into account the level of equipment of the laboratory, the specifics of the study being conducted, the requirements and capabilities of the clinic.
The degree of equipment of modern clinics and the availability of new equipment play an important role in the timing. In emergency cases in surgery, oncologists, for example, to conduct an urgent course of chemotherapy for a fee, can provide answers within 1 day or even after 2-3 hours. In public clinics, the study takes an average of 5-6 days.
Blood has a unique composition, and it is one of the suitable materials for identifying the condition of any organ or system in the body. The analysis allows you to identify abnormalities during pregnancy in women or infants when carried out immediately after birth
The reliability of the information received about the functioning of a particular organ, the state of hormones and tissues in the body depends on the expiration date, which is important, for example, for women before undergoing IVF. Failure to meet deadlines can lead to distortion of information, incorrect diagnosis, and exclusion of the child from receiving vaccinations.
The validity period of the tests is limited, so you need to contact your doctors in time to get a transcript and advice, otherwise the tests will have to be retaken when the expiration date expires.
Requirements for collecting material
Before collecting material for laboratory research, parents should familiarize themselves with a number of rules, violation of which may distort the result. The requirements for collecting urine from children are as follows:
- Evening or daytime urine is not suitable for general analysis;
- at least four hours must pass between the last urination and the collection of material;
- collection is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach;
- You should first clarify how much urine is needed for a particular analysis;
- It is forbidden to collect urine in a pot;
- Do not squeeze liquid out of a diaper or nappy;
- Do not pour several portions of urine into one glass;
- Only a sterile container is used;
- it is necessary to collect urine from the first morning urination immediately after the baby wakes up;
- before collecting urine, hygiene procedures are carried out without using soap;
- It is recommended to collect an average portion of urine, since primary urine contains a larger number of bacteria.
What is a biochemical blood test
The biochemical method of studying blood is a technique that has been successfully used in medicine for about a hundred years. The first biochemistry tests were not like modern comprehensive blood tests; they included only one parameter, for example, total protein. LHC is a type of testing that is rarely prescribed immediately, without preliminary research. Absolute indications for its use include hereditary diseases, gestation, and autoimmune diseases. A BAC can also be prescribed at the discretion of the doctor, if there are no objections from the patient.
Typically, a BAC is prescribed after the preliminary stages of a clinical examination, for example, a complete blood count, have given reason to suspect that the patient has a pathology. A biochemical blood test can provide information for confident identification of any disease and identify dysfunction of the organs of the human body. In line with the general therapeutic examination of the patient’s health status, a general LBC is prescribed. If this type of biochemical analysis cannot provide answers to the questions posed, a LHC with advanced parameters is prescribed. The choice of additional values of the second type of LHC depends on the opinion of the diagnostician.
The table below shows the values of the expanded BAC with norms for children of different ages and adults (men and women).
Minimum amount of urine
The smallest volume of biomaterial is:
- for a newborn - 5 ml;
- for a child up to one year - 10 ml;
- after a year - 50 ml.
The accuracy of diagnosing diseases in children is influenced not only by the volume of collected material, but also by the universal sampling rules.
To carry out diagnostics successfully, it is better to use sterile containers, and collect the required amount of urine for analysis from the child under hygienic conditions. The question arises: how long can the material for analyzing a child be stored? Urine can be stored for no more than 2 hours, and it is not stored under the influence of high and low temperatures. If all conditions are met, the research results will be correct.
source
When is it shown?
A urine test is prescribed:
- To all people who are experiencing a painful condition. Also for those who have kidney and urinary tract disease.
- When conducting a preventive examination, a urine test is also prescribed. This is necessary in order to see whether there are any inflammatory processes in the body or not.
- When assessing the current condition of a person, when diagnosing him with any illness.
- A number of diseases that a person has suffered require testing after some time in order to make sure that a relapse has not begun. For example, streptococcal infection.