0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.02
898
Leukocytes
Man exists in an ocean of microorganisms invisible to the human eye. Every second, along with food, air, water, they enter his body. It is unlikely that a person would be able to live for a long time if natural defenses – the immune system – did not stand in the way of viruses, bacteria, fungi and other harmful microorganisms.
It is a collection of organs, tissues and cells responsible for destroying foreign agents that have entered the body.
The most important component of the immune system are leukocytes. They are called white blood cells, although under a microscope they appear purple-pink.
Types of leukocytes
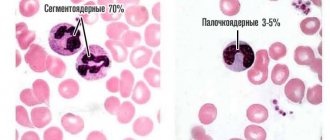
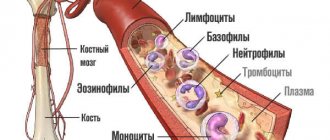
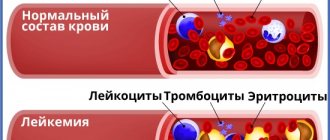
There are five types of leukocytes:
- neutrophils;
- lymphocytes;
- monocytes;
- eosinophils;
- basophils.
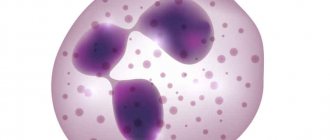
Basophil in the blood
Why does the body need basophils?
Basophils (basophilic granulocytes) are the largest leukocytes in size, but at the same time, quantitatively they are inferior to other leukocytes. The factory for the continuous production of basophils is the bone marrow. First they enter the blood, where they circulate for several hours, then move into the tissues and remain there for 8 to 12 days.
Basophils perform the following functions.
- Actively participate in the fight against allergens.
- Actively counteract helminths.
- Block various toxins in tissues.
- They help other white blood cells move through the walls of capillaries to the location of the harmful agent.
- Responsible for the growth of new capillaries.
- Maintains normal blood flow in small blood vessels.
Causes of basophilia
The number of basophils normally ranges from 0 to 1% of all leukocytes. In children, the norm changes with age:
- in newborns the norm is 0.75%;
- under one month of age – 0.5%;
- in infants the norm is 0.6%;
- in children under 12 years of age – 0.7%.
If basophils are elevated in a child, this is a serious reason to visit a doctor.
An increase in basophils in a child’s blood (basophilia) can signal a number of diseases, including severe ones.
Food allergies
- Often, increased basophils in the blood of children are caused by food or drug allergies.
- An increase in the number of these white blood cells can provoke insect bites and food poisoning.
- Basophils in a child increase with blood pathologies:
- acute leukemia;
- chronic myeloid leukemia;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- vera polycythemia.
- The level of these leukocytes increases in some infectious diseases (varicella and natural pox, helminthiasis).
- Other diseases may be responsible for the increased content of basophils in children:
- hemolytic anemia (red blood cells are destroyed faster than they are formed);
- ulcerative colitis (chronic inflammation of the colon mucosa);
- myxedema (reduced production of thyroid hormones);
- nephrosis (pathology of the kidney tubules);
- chronic sinusitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses).
- Basophils may be elevated due to treatment with certain hormonal drugs.
Changes in the number of basophils in the blood
Basophils are counted along with the rest of the leukocytes that make up the leukocyte formula. All leukocyte cells are taken as 100%, from 0.5 to 1 of which are normally occupied by basophils. When the number of basophilic granulocytes increases above 1%, basophilia occurs. This condition is typical for such pathological conditions as:
- the final phase of acute inflammation;
- decreased thyroid function;
- lymphogranulomatosis (malignant disease of lymphoid tissue);
- spicy ;
- malignant formation in the lungs;
- diabetes;
- jaundice in acute hepatitis;
- allergic reactions;
- taking medications containing estrogen;
- hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells;
- some viral infections;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Most often, an increased number of basophils in a child is observed with various chronic diseases, with allergies of any origin and with malignant blood diseases.
The opposite of basophilia is called basopenia.
Basopenia accompanies bone marrow diseases and a number of endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, Cushing's disease).
What should parents pay attention to?
There are no clear signs of basophilia; they depend on the reason that caused the cells to exceed the norm. However, parents should pay attention to the following signs:
- a prolonged but slight increase in the child’s body temperature;
- redness and rashes on the skin;
- complaints of itching;
- lacrimation;
- cough;
- swelling;
- complaints of joint pain;
- enlarged spleen.
The causes of basophilia can only be accurately determined by a blood test.
How to properly donate blood for analysis
How far the number of these leukocytes is outside the normal range can only be answered with certainty by a blood test. However, the correct procedure for taking blood for analysis is very important. The diagnosis and determination of optimal treatment depend on the result of the analysis.
Blood for analysis is taken either from a vein or from a finger, always in the morning. You should not eat breakfast, since eating changes the content of basophils and other leukocytes in the blood. In the morning you can drink water, but still. The last meal should be nine hours before the visit to the medical facility. Heavy and fatty foods are not recommended the day before the procedure.
The situation with infants is more complicated. The child must be fed at least 1.5-2 hours before blood sampling.
If you are taking medications and there is no way to temporarily stop them, you should tell your doctor about this.
Elevated basophils in a child - video
Normal levels of these cells differ between children and adults. Their number is, in principle, very small - less than 1% of the total number of leukocytes, but its determination plays an important role in diagnosing the pathological condition.
The number of basophils in a blood sample can be expressed in both absolute and relative terms. The absolute number directly means the number of cells, the normal value is 0.01-0.09 x 109 g/l. The relative indicator is a percentage of the total number of leukocytes, taken as 100%.
The norm depends on the age of the child. So, in a newborn it is 0.75%, which may seem to be an increased amount compared to older children: in a baby after a month, the level of basophils decreases to 0.5%, in children after a year it reaches 0.7%. But it should not be higher than 1%.
If the analysis shows that the absolute or relative content of basophils in a child is increased, then this should in no case be ignored. You should immediately visit a doctor to find out the causes of this disorder - as stated above, they can range from very harmless to very dangerous, requiring immediate treatment.
The opposite condition may also occur - a decreased level of basophils in a child, called basopenia. This is typical for:
- Endocrine diseases;
- Bone marrow diseases;
- Acute infections.
- To normalize the level of white cells, the main task is to find out what caused their increase. This pathology is overcome by treating the underlying disease that causes changes in the blood. The patient may also be prescribed vitamin B12, which has a positive effect on hematopoietic processes. They can prescribe both a dosage form of the vitamin (tablets, injections) and a diet with a high content of foods rich in B12. These include mainly animal products: dairy products, meat and eggs.
- An abnormal level of white cells can also be observed in a healthy person with some iron deficiency or anemia. This condition is corrected by including iron-containing foods in the diet or taking iron supplements. Also, these white blood cells may increase when taking certain medications, such as estrogen-containing ones. Their elimination will lead to normalization of blood cell levels naturally.
In this video, you'll learn more about the differential blood test, which measures the number of white blood cells (including basophils) in a sample. The role of each type of leukocyte is revealed, what indicators correspond to the norm and what its violation indicates.
A blood test helps to obtain accurate information about the condition of the body. It is important that all indicators are normal. Now you know about the significance of this type of cell such as basophils, what function they perform, what a deviation from the norm indicates, and what needs to be done when violations are identified.
Basophils in a child’s blood test are determined as part of the leukocyte formula (it is also called a leukogram), therefore such cells in the analysis form are presented as a percentage of all leukocytes. The normal content of basophils in a child of any age, whether a newborn, a preschooler or a teenager, is considered to be 0-1%. If we take into account the absolute number of such cells, then the norm will be 0.01-0.065 x 109/l.
When children have elevated basophils, it is called basophilia or basophilocytosis. In this condition, the absolute number of basophilic leukocytes will exceed 0.2 x 109/l.
How far the number of these leukocytes is outside the normal range can only be answered with certainty by a blood test. However, the correct procedure for taking blood for analysis is very important. The diagnosis and determination of optimal treatment depend on the result of the analysis.
Blood for analysis is taken either from a vein or from a finger, always in the morning. You should not eat breakfast, since eating changes the content of basophils and other leukocytes in the blood. In the morning you can drink water, but still. The last meal should be nine hours before the visit to the medical facility. Heavy and fatty foods are not recommended the day before the procedure.
The situation with infants is more complicated. The child must be fed at least 1.5-2 hours before blood sampling.
Laboratory testing occurs by counting basophilic white blood cells under a microscope along with other cells. In a child, the level of basophils in the blood may be higher than the prescribed values due to the active growth of the circulatory system, because they take part in normalizing blood flow and creating new capillaries.
| Age | Basophil content in blood test, % |
| Up to 1 month | 0,8 |
| From 1 month to 2 years | 0,5 |
| 4 years | 0,8 |
| 6 years | 0,6 |
| 10 years | 0,5 |
| Adults | 0-1 |
Doctors say that a slight increase in values may be normal, linking this with the characteristics of the body. However, it is necessary first of all to understand the reason for the deviation from the accepted indicators. Particular attention is paid to infants, because their immune system is imperfect, and diseases can develop rapidly.
Pediatricians are no less concerned about the reduced level of basophils in the child’s blood (basopenia). This condition is typical for disorders of bone marrow function or metabolism during the rehabilitation period after chemotherapy.
A slight decrease indicates an allergic reaction or stress. A serious decrease in them indicates an inflammatory process in the body, such as pneumonia. It is important to consider the level of basophils in conjunction with other blood parameters and symptoms, because basopenia itself does not indicate a disease. That is why deciphering the analysis should be entrusted to a child health specialist.
The increased level of basophils returns to normal after the primary disease is cured. During therapy, the indicator must be monitored - for this, blood tests are regularly taken.
If a change in basophil levels is caused by taking a medication, it must be discontinued. After some time, your blood counts will return to normal.
In newborns, the upper acceptable limit of the BASO indicator is 0.75%. As children grow, the norm of basophils in children changes and is:
- in a two-week-old baby - 0.5%;
- from 2 weeks to a year - 0.4 - 0.9%.
After a year, normal BAS values for both children and adults are considered to be between 0% and 1%. And the absolute amount of BASO abs in children from 1 year of age and adults lies in the range of values from 0.01*109/l to 0.065*109/l.
The condition when basophils are elevated is called basophilia. Absolute basophilia, when BAS abs is 0.21*109/l and higher, is extremely rare in children. And if a similar test result appears in a child, it is necessary to re-examine the blood.
Treatment of basophilia
A blood test shows the relative and absolute content of basophils. Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines the reasons for the increased content of basophils in the child’s body and prescribes a course of treatment.
Primary diseases
You cannot get rid of basophilia without curing the disease that caused it.
- In severe cases, for example, with leukemia, a course of treatment is prescribed by an oncohematologist. This could include chemotherapy, radiation, or even a bone marrow transplant.
- If basophilia has become the body’s response to pathogenic pathogens, then drugs are prescribed depending on what kind of infection is in the body.
- In case of allergies, appropriate antiallergic treatment is carried out.
Decrease in the number of basophils
- It is possible to reduce the level of basophils in the blood and tissues if you stop taking medications that cause increased synthesis of these leukocytes. However, you should not refuse prescribed medications without consulting your doctor.
- You can reduce the number of basophils in the body by consuming foods rich in iron. These include:
- seaweed;
- peas;
- dried mushrooms;
- buckwheat;
- beans;
- dried apricots;
- apricots.
- To reduce basophils in the blood and tissues, vitamin B12 deficiency must be eliminated. It is found in the following natural products:
- beef liver;
- beef;
- pork;
- lamb;
- eggs;
- milk;
- cheese;
- cod;
- mackerel.
Sources of vitamin B12
When adjusting a child’s menu, it is necessary to take into account his age and consult with a nutritionist.
Additional information on the topic can be obtained from the video:
How to return basophils to normal
Only by identifying the reasons for deviations of basophils from the optimal level can we influence their normalization. Timely treatment of the underlying disease stabilizes the blood composition. To prevent basophilia and basopenia it is necessary:
- fill your baby’s diet with foods containing: vitamin B12: dairy products, eggs, lean meat. There is a lot of vitamin in soy milk;
- iron: liver, fish, red meat, greens;
If the cause of the deviations lies in taking certain medications, then stopping them will normalize the situation.
Constant monitoring of basophil levels will help prevent many diseases. Timely prescribed therapy will ensure a quick recovery for the baby.
Date: 11/05/2016.