Feces are “waste materials” that are produced during the digestion of food. By its color, smell and consistency, one can judge the activity of the digestive tract, as well as identify certain violations in this process. If suspicious inclusions appear, for example, white spots in the stool, this indicates the presence of serious health problems. Such impurities are not considered normal, therefore, if you notice such a deviation, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo a thorough examination.
What do white streaks in stool indicate?
White-streaked stool may indicate intestinal pathology
Particles of mucus are definitely present in the stool. If a person is healthy, then these whitish discharges in the stool may not be noticed. White veins may indicate the development of certain abnormalities and pathologies. These secretions consist of leukocytes and epithelial cells.
The appearance of white veins may be associated with eating large quantities of bananas, oatmeal, and cottage cheese. In infants, this may be due to the immaturity of the fermentation system. If the white grains look like cottage cheese or sour milk, then this is a sign that the baby is overeating. The remains of undigested food are passed out along with the feces. White lumps without any impurities may indicate lactose intolerance.
In adults, white streaks and mucus enveloping the stool indicate damage to the distal parts of the intestine - and constipation is often observed.
If mucous discharge is observed along with small white grains, this indicates a pathology of the large and small intestines.
Possible diseases that are caused by white plaque in the stool:
- Intestinal candidiasis
- Perirectal fistula
- Dysbacteriosis
- Colitis
With intestinal candidiasis, white spots are an accumulation of fungi. Whitish dots in combination with mucus can be observed with mucous colitis or while taking antibacterial drugs. In many cases, dead worms - pinworms - can be mistaken for white veins.
Signs of streaks in stool
White streaks in stool are a sign of intestinal infection or helminthic infestation
White spots in the stool that resemble grains, lumps or grains are the remains of undigested food. If a person feels well and there are no other signs, then treatment is not required in this case.
If white veins are associated with a fungal disease, then the patient may feel discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen, the consistency of the stool changes, diarrhea appears, and health worsens.
Also, against the background of changes in stool, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Slight increase in body temperature
- Light yellow diarrhea
When a helminthic infestation appears, the child becomes restless and capricious, and sleep is intermittent. If a child has mucus, foam and blood in his stool along with white lumps, he should consult a pediatrician.
If there is an infection in the body, the child looks unhealthy. At the same time, the complexion changes, during defecation the baby bends his legs and cries. With symptoms of an intestinal infection, the child is hospitalized in a hospital.
Causes and Effects
Blood elements can be observed in large or moderate quantities, or it can be released in drops or form veins. In order to find out the cause of bleeding, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the quantitative indicator of the discharge, but also to its color. It can be bright scarlet, dark, almost black. And, depending on the color, the reason lies in various pathologies.
The appearance of blood in the stool can be caused by various pathological conditions.
Table. Blood color and related diseases.
| Color | Probable Causes |
| Red regular | Painful formations in the rectum, pathological conditions of the colon. |
| Red dark | Stomach diseases. |
| Scarlet | Intestinal pathologies, such as UC, intestinal diverticulosis, infections. |
| Red bright | Hemorrhoidal formations. |
| Black-red | Ulcerative and other lesions of the gastroesophageal tract, pathological processes in the esophagus. |
When an alarming symptom appears, you should definitely pay attention to what the blood looks like.
Important! The higher the pathological process occurs in the body, the further the source of blood is from the anus, the darker its color.
Bloody impurities can be bright red or dark burgundy
Diseases and pathological conditions in which blood discharge is present in the stool may be as follows.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Stomach cancer.
- Duodenal ulcer.
- Bowel cancer;
- Worms.
Classification of helminths
- Esophageal carcinoma.
- Infectious diseases.
- Internal injuries to various parts of the intestine.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the stomach or esophagus.
- Polyps in the colon.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome with ruptures in the esophagogastric zone.
Stages of development of hemorrhoids
- Scarring of liver tissue.
- Intestinal tuberculosis.
- Taking medications that reduce blood clotting.
In addition to the likely presence of the disease, blood in the stool is dangerous because its excessive leakage can cause anemia, which will require medical intervention and the prescription of iron supplements, or (depending on the degree of drop in hemoglobin) blood transfusion.
Causes of blood in stool
Blood in stool “by gender”
Fecal bleeding may differ according to “gender characteristics.” In men, the most common causes are:
- injury to the rectal area;
- cracks in the rectal cavity;
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- oncopathology.
Hemorrhoids can be distinguished from fissures usually due to the presence of sagging nodes from the anus
Liver cirrhosis is accompanied, in addition to bleeding, by the following symptoms:
- feeling of constant nausea;
- bitterness that is felt in the mouth;
- itching of the skin;
- intolerance to certain products;
- rosacea (star-shaped formations of reddened subcutaneous vessels) on the abdomen.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis in men
For women, all of the listed causes of bleeding are also likely, but specific ones are added to them, which men do not have:
- last stages of pregnancy;
- the presence of varicose veins in the perineal area;
- endometriosis;
- oncology of the genital organs.
Endometriosis
Hidden bleeding in oncology is one of the most common causes of the phenomenon. The most common is intestinal cancer, but other oncopathologies are also found throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Their symptoms are as follows:
- aversion to food, aversion to it;
- severe constant fatigue;
- intestinal pain;
- pale skin;
- permanent intestinal disorders;
- increase in gases in the intestines;
- heavy stomach;
- inability to have a complete bowel movement.
Gases in the intestines
Sometimes, having discovered elements of blood in the stool, a person is afraid without reason. There are a number of factors that can give stool a color similar to that observed when there is blood in it, but are not pathological. The following substances and products are coloring:
- beets are all from it;
- red hot pepper;
- fresh and cooked tomatoes;
- Activated carbon;
- iron supplements.
But in all other cases, having found elements of bleeding, you need to make an appointment with a doctor who will prescribe a stool test for occult blood.
Fecal occult blood test
Video: Blood in a woman’s stool, a man’s, what could it be?
Diagnostics
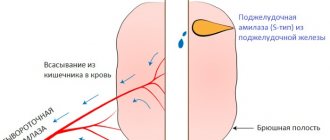
To identify the inflammatory process in the intestines and determine the cause of whitish inclusions, an instrumental study is carried out.
The patient must undergo a stool and blood test, where an increase in white blood cells can be detected. Stool examination is of great importance in children, which is divided into several groups: macroscopic, microscopic, bacteriological and chemical.
A coprogram or general stool analysis allows you to determine the condition of the digestive system, large and small intestines.
After receiving the results, the doctor will be able to accurately determine the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is necessary to carefully prepare for the analysis, as this directly affects the result:
- Before collecting stool, you should urinate and perform hygiene procedures. The perineal area should be wiped well so that urine and water do not get into the stool. After all, all this can lead to an erroneous result.
- To collect feces, you can purchase a special container at the pharmacy. It must be clean and dry. Place cling film over the toilet seat and after defecation, collect the feces in a prepared container.
- The amount of material collected for research should be 5 g. It should be delivered to the laboratory within two hours. It is not recommended to store feces for a long time.
- If the feces were collected in the evening, then the container with the contents must be placed in the refrigerator or other cool place.
Blood in the stool as a symptom of the disease
The mere presence of blood does not imply an indication of a specific ailment. Rather, it is a general symptom that can hide many problems. Moreover, even hidden bleeding that occurs for a short time and is not very profuse, which stops on its own after some time, does not at all mean the cessation of the disease.
Stool with blood in an adult can take on a different character.
Important! In all cases when blood is found in the patient’s stool, even in fragmentary form, it is necessary to conduct an examination and determine the cause of its appearance.
It should be noted that not in one hundred percent of cases blood means a disease of any internal organ. Sometimes this can be irritation of the mucous membrane, and even simple staining of the stool by a food product consumed the day before, which the patient mistook for bloody streaks (beets, for example, have a similar effect). But still, in most episodes, the actual presence of blood, even in latent form, in the stool, signals a serious illness, including malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal system.
You need to understand that blood in the stool is not the disease itself, but a sign of it and a very alarming one.
By the way. There are two options for detecting blood hidden in a patient's stool. Or he discovers it on his own and goes to the doctor with this problem. Or, having taken a stool test for something else, he learns from the results that blood was detected in the laboratory.
In the first case, which is observed much less frequently, in order to begin to pay close attention to the quality of his stool, the patient needs something to encourage him to do so. For example, if any symptoms occur (diarrhea, constipation, intestinal pain). In this case, it is possible to detect blood with the naked eye, although it is hidden. In the second case, which is the most common, there are no other symptoms, and the doctor informs the patient about the presence of a problem, prescribing additional tests.
Blood from the anus may come out during bowel movements in large quantities or appear a little, drop by drop.
Bloody stools are not as common as you might think. But the possibility of finding traces of blood hidden in the stool can occur in a patient of any gender and any age.
Treatment: basic drugs
Medications for the treatment of intestinal pathologies
Depending on the cause of this symptom, treatment is prescribed:
- If the presence of white spots in the stool is associated with a fungal disease, then antibacterial and antifungal drugs are prescribed, which include substances such as Clotrimazole and Fluconazole. In addition, the doctor will prescribe medications against intestinal dysbiosis.
- If the white lumps in the stool are worms, then anthelmintic drugs are used for treatment. To avoid possible infection with worms, the hygiene of the infant should be improved. It is important to iron the baby’s underwear on both sides, after each bowel movement, wash the bottom with soap and lubricate it with baby cream.
- If a baby has white lumps due to lactose intolerance, the doctor will prescribe lactose-free formulas and recommend products that reduce the amount of this enzyme in mother's milk.
- To restore normal intestinal function, drugs are used to eliminate the inflammatory process. For mucous colitis, antiseptics are used to improve the patient's condition. To normalize the enzyme environment of the intestinal mucosa, drugs such as Festal, Pancreatin, Mezim, etc. are used.
- During treatment, the patient must follow a diet. The diet should contain a large amount of fiber: vegetables, fruits, dried fruits, bran, etc. For a while, you should limit the consumption of butter, strong tea, coffee, and carbonated water.
Features of treatment
What to do if white spots appear in the stool of an adult? First of all, it is necessary to establish the reason for the deviation. Only after this can adequate, effective therapy be prescribed:
- Fungal infections of the intestines are treated with antifungal drugs. Fluconazole and Nystatin are most often prescribed orally. Together with antifungal agents, medications are used to prevent the development of intestinal dysbiosis.
- Worm infestation is treated with anthelmintic drugs. They are prescribed taking into account the presence of which particular parasite began to excrete feces with a white coating in an adult or child. Zentel, Pirantel, Vormil, Vermox - all these products are very widespread and are freely available. But taking them without a doctor’s prescription is strictly prohibited.
- If the cause of such a disorder lies in celiac disease, the patient is prescribed a special diet. Products containing gluten are excluded. Hypolactasia (lactose intolerance) is treated by avoiding dairy products. If it was diagnosed in an infant, then under such circumstances special dairy-free formulas are used.
- Enzyme preparations (Festal, Mezim, Pancreatin) are used to eliminate the deficiency of enzymes produced by the pancreas.
In fact, the list of medications for the presence of white seeds in stool is much longer. However, as well as diagnoses in which this deviation is observed. In addition, some diseases can be treated through surgery, and not just with medications. Therefore, self-medication is categorically unacceptable, because it not only will not help, but can even harm.
Blood
Finding blood in feces is always a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. It can be a manifestation (often the first):
- colon cancer;
- inflammatory autoimmune bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease);
- large benign neoplasms (for example, polyps);
- pathologies of the rectum and anus (fissures, ulcers, hemorrhoids, proctitis, etc.)
- ischemic colitis (caused by pathology of the vessels feeding the intestines);
- intestinal angiodysplasia;
- blood coagulation pathology;
- infectious damage to the intestine (for example, dysentery, amoebiasis, intestinal tuberculosis, etc.);
- drug damage to the intestine (due to taking antipyretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.);
- helminthic diseases (ascariasis, trichocephalosis, etc.).
The amount of blood can vary: from barely noticeable streaks to several glasses. Sometimes, instead of stool, when the patient has a bowel movement, only blood or blood with mucus comes out. The color of the blood reflects the location of the source of blood loss. Scarlet fresh blood is characteristic of a “low” location (anus, rectum, sigmoid colon or descending colon). Often it is located on top of the feces. Dark blood (especially if mixed with fecal matter) or blood clots indicate a “high” localization, that is, the pathological process is in the right side of the colon or small intestine.
An admixture of greenish or yellowish pus in excrement is always a sign of a serious inflammatory process. It appears when:
- infectious colitis;
- proctitis;
- autoimmune inflammatory processes in the colon (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's colitis);
- diverticulitis;
- breakthrough of abscesses into the intestine;
- disintegration of a malignant tumor (this happens in advanced stages of the disease).
Therefore, pus in the stool is also considered an alarming signal. Self-medication for these diseases is ineffective and can result in dire consequences.
Causes of “thick blood”
Speaking in the language of specialists, blood thickening leads to a deterioration in its rheological properties. That is, blood flows slower and more difficult. It can become thicker for various reasons. As a rule, this condition is accompanied by:
- violation of hematocrit;
- increased hemoglobin;
- an increase in the number of red blood cells;
- decreased elasticity of red blood cells and their deformation;
- aggregation (sticking together) of red blood cells;
- acceleration of blood clotting (due to an increase in the amount of fibrinogen);
- an increase in the amount of paraproteins (specific proteins that appear in the plasma during myeloma).
Common causes of blood thickening:
- Coagulopathies. This is a group of diseases in which blood clotting occurs. These include autoimmune, genetic and coagulopathies of toxic origin.
- Liver diseases. The liver is involved in the production of proteins responsible for blood clotting. And some diseases can increase or decrease the synthesis of these substances, which affects blood viscosity.
- Oncological diseases. Malignant blood diseases cause an imbalance between the plasma and cellular components of the blood.
- Dehydration. There can be many reasons leading to dehydration. The most common one is not drinking enough water. Diarrhea, severe and prolonged vomiting, taking diuretics, and poor absorption of water by the body also lead to dehydration. But regardless of the reason, the result is always the same - the substance in the vessels becomes thicker.
Slime
A healthy intestine always contains cells that produce mucus. It is necessary for the timely passage of feces through the intestines. Therefore, a small amount of clear mucus in feces can be found normally. In addition, small specks or lumps of mucus are common in the stool of breastfed infants. They are associated with excessive fat content in mother's milk, which the still weak digestive enzymes of the child's body are not able to cope with. However, a large amount of mucus and its yellowish or brownish color are often manifestations of:
- increased intestinal motility;
- infectious diseases (salmonellosis, typhoid fever, dysentery, etc.);
- inflammatory processes in the intestines of non-infectious origin (diverticulitis, etc.);
- helminthic diseases;
- neoplasms;
- cystic fibrosis.
In addition, mucus can be a companion to constipation and a harbinger of exacerbation of chronic autoimmune intestinal diseases (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
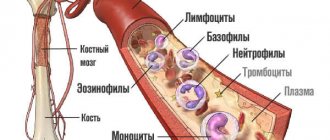
List of diseases affecting the blood
If you list all the blood diseases, the list will be huge. They differ in the reasons for their appearance in the body, the specifics of cell damage, symptoms and many other factors. Anemia is the most common pathology affecting red blood cells. Signs of anemia are a decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin. The reason for this may be reduced production or large blood loss. Hemoblastoses - most of this group of diseases is occupied by leukemia, or leukemia - blood cancer. As the disease progresses, blood cells transform into malignant tumors. The cause of the disease has not yet been clarified. Lymphoma is also an oncological disease; pathological processes occur in the lymphatic system, and leukocytes become malignant.
Myeloma is a blood cancer that affects the plasma. Hemorrhagic syndromes of this disease are associated with a clotting problem. They are mostly congenital, such as hemophilia. It manifests itself as hemorrhages in joints, muscles and internal organs. Agammaglobulinemia is a hereditary deficiency of serum plasma proteins. There are so-called systemic blood diseases, the list of which includes pathologies affecting individual systems of the body (immune, lymphatic) or the entire body as a whole.
Leftover food
Some types of food cannot be completely digested, so the presence of seeds, poppy seeds, bones, fragments of dense peel, veins and cartilage of meat, and fish bones should not be a cause for concern. Digestive enzymes are not able to cope with such coarse fiber and connective tissue.
You should be wary if there are traces of meat, eggs, cottage cheese, or fat in the stool. Their presence reflects a severe deficiency in the formation of enzymes necessary for digestion. This happens when:
- widespread and severe atrophy of the gastric mucosa;
- inhibition of the production of pancreatic juice (a consequence of pancreatitis or removal of part of the pancreas);
- intestinal enzyme deficiency.
Also, food residues in feces are observed with accelerated intestinal motility (irritable bowel syndrome).
Classification of blood diseases:
The key point in the development of the disease is pathology at one of the levels of hematopoiesis.
The range of diseases that can be detected includes:
Anemia:
- deficiency anemia (iron deficiency, B12 deficiency, folate deficiency);
- hereditary dyserythropoietic anemia;
- posthemorrhagic;
- hemolytic;
- hemoglobinopathies (thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, autoimmune, etc.);
- aplastic anemia.
Hemorrhagic diathesis:
- hereditary coagulopathies (hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, rare hereditary coagulopathies);
- acquired coagulopathies (hemorrhagic disease of newborns, deficiency of vitamin K-dependent factors, DIC syndrome);
- hemostasis disorders of vascular and mixed origin (Rendu-Osler disease, hemangiomas, hemorrhagic vasculitis, etc.);
- thrombocytopenia (ideopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, alloimmune purpura of newborns, transimmune purpura of newborns, heteroimmune thrombocytopenia);
- thrombocytopathies (hereditary and acquired).
Hemoblastoses:
- myeloproliferative diseases;
- myelodysplastic diseases;
- myelodysplastic syndromes;
- acute myeloid leukemia;
- B-cell neoplasms;
- Histiocytic and dendritic cell neoplasms
Pathologies of the circulatory system are characterized by changes in the quantity of blood elements, their quality, structure and shape with a parallel decrease in their functions. Diagnosis is quite complicated, since a deviation from normal blood counts can occur with almost any other disease of the body. A diagnosed disease requires immediate medical intervention and changes in diet.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have impurities in your stool, contact your gastroenterologist. If this is not possible, the primary diagnosis will be carried out by a general practitioner or family doctor. After clarifying the diagnosis, the patient may be scheduled for an examination by a proctologist, oncologist, surgeon, hematologist, or infectious disease specialist. For diagnosis, the qualifications of the endoscopist and the equipment he uses are very important.
Video version of the article:
Watch the video on the topic: analysis of feces in a child, rules for collecting and storing biomaterial.
The secretions of the human body are a kind of compass indicating the state of its health. Feces are a kind of mirror that reflects the functionality of the digestive system and its organs. In some cases, the homogeneity of feces may be disrupted by various inclusions that differ in appearance. Feces with white grains may turn out to be a completely harmless phenomenon - or evidence of internal pathology. Let's look at what suspicious white formations may indicate.
Preparing for analysis
In order for the reaction to protein to be correctly determined in the laboratory, it is necessary to follow the rules for the preparation and collection of feces for coprograms, which will be similar for both children and adults.
Thus, correct preparation includes:
- Before taking tests, inform your doctor about taking certain medications.
- During the initial visit, inform the clinician about traveling to other countries - this is necessary, because infection of the gastrointestinal tract with certain viruses, bacteria or protozoa is typical for individual regions.
- a ban on the use of feces that have already been in contact with water or urine, detergents or other chemicals.
Types of inclusions and assumptions regarding their origin
White inclusions in stool are not always a sign of dysfunction of organs or pathological changes in them. However, with such a “bell” it won’t hurt to make observations.
Foreign inclusions may look different:
- In the form of lumps and smaller grains.
- In the form of veins or worms.
- Resembling tiny white dots and a ball.
Based on their origin, such inclusions can be divided into several groups; their appearance can be justified:
- Certain foods, respectively, something white in the feces is a harmless phenomenon that does not require urgent measures to eliminate the problem.
- Helminthic infestations can manifest themselves in a similar way, and in this case treatment is necessary.
- White inclusions may indicate disturbed microflora and inflammatory processes occurring in the intestines.
If we are talking about pathological phenomena, they are accompanied by other symptoms, thanks to which the presumed diagnosis can be clarified. Below we will look at possible reasons that change the appearance of stool.
Damage to all blood cells
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. A rare genetic disease. Caused by the destruction of blood cells by lymphocytes and macrophages. The pathological process occurs in various organs and tissues, resulting in damage to the skin, lungs, liver, spleen, and brain.
- Hemophagocytic syndrome caused by infection.
- Cytostatic disease. It manifests itself as the death of cells that are in the process of dividing.
- Hypoplastic anemia is a decrease in the number of all blood cells. Associated with cell death in the bone marrow.
The appearance of light inclusions in the background of power supply
The most harmless option is to eat certain foods. This could be cartilage from meat products, accidentally consumed egg shells, and pharmaceutical drugs can manifest themselves in a similar way. In this case, we can advise one thing - you should carefully monitor your own diet, exclude problematic elements from the menu and observe whether the nature of your bowel movements changes.
A more serious reason why white spots are observed in the stool of an adult is lactose deficiency. This disease is quite rare and is formed due to a lack of enzymes designed to break down milk sugar. The main group of patients are children under three years of age, while in adults the problem is diagnosed in approximately 8.9% of cases.
You can suspect the presence of lactose deficiency based on the following signs:
- Liquefied stool, diarrhea due to high osmotic pressure.
- Pain in the lower abdomen of a spasmodic nature.
- Bloating, constipation, but no gas passing.
- The appearance of feces in the form of dense lumps with white particles.
- Rarely, vomiting occurs in white masses with a pungent sour-milk odor, with particles of undigested food.
Negative symptoms in this pathology always appear after meals.
Treatment
Blood diseases develop very quickly, so treatment must begin immediately after diagnosis. Each disease has its own specific characteristics, so treatment is prescribed in each case differently. Treatment of cancer diseases such as leukemia is based on chemotherapy. Other methods of treatment are blood transfusions, reducing the effects of intoxication. In the treatment of blood cancers, stem cell transplants obtained from bone marrow or blood are used. This newest way to fight the disease helps restore the immune system and, if not overcome the disease, then at least prolong the patient’s life. If tests make it possible to determine which infectious blood diseases the patient has, the list of procedures is aimed primarily at eliminating the pathogen. This is where antibiotics come to the rescue.
Presence of helminthic infestation
White grains in the stool that appear in an adult or a child may indicate the presence of a helminthic infestation. The most common causes of the pathological condition are failure to comply with hygiene rules - ignoring hand washing, eating fruits and berries directly from trees and bushes without first washing. Parasites penetrate the human body through the consumption of untreated water and insufficient heat treatment of meat and fish.
Most often, pinworms or roundworms penetrate the human body. The infestation may go undetected for some time, but white eggs in the stool that look like tiny dots indicate the presence of worms. However, due to their size, the eggs may go unnoticed, but adults, resembling white thin threads, also come out with feces.
You should pay attention to whether there is movement. Over time, other symptoms develop:
- Itching appears in the anal area, when there is irritation around the posterior opening; in females, unpleasant sensations may also appear in the vagina.
- Insomnia develops.
- Enuresis is possible.
- In a dream, when the body is infected with worms, the victims grind their teeth.
- Unreasonable irritation and anxiety appear.
- Less commonly, sporadic pain is noted in the abdominal area, and vomiting appears.
- Generalized skin rashes or eczema may occur.
- Soreness of muscles and joints is possible.
Why is condensation dangerous?
Blood viscosity often increases in pregnant women. In this case, this process plays a natural role of protection against possible bleeding and miscarriage. Also, the fluid in the vessels of women becomes thicker immediately before childbirth. This is how nature protects the expectant mother from severe blood loss. But excessive thickening during pregnancy can be dangerous both for the woman (promotes thrombosis, thrombophilia, varicose veins, leukemia) and for the fetus (damage to the vascular bed).
As for newborns, their blood is much thicker than that of adults. But that shouldn't be a concern. The baby needs time to adjust to life in a new environment. In the first hours after birth, hemoglobin in the baby’s body can reach 200 g/l. But already in the first few days of life, these numbers will begin to decline. Almost half of the hemoglobin will be destroyed in the first day and the thickness of the baby’s blood will decrease.
It’s a different matter for adults whose blood has become thick for various reasons. They should not expect the indicators to return to normal on their own. This condition can be dangerous to health.
Often, thickening is accompanied by increased formation of blood clots, which can clog blood vessels, preventing normal blood flow. If a blood clot blocks a vessel in the heart or brain, a heart attack or stroke may occur, possibly with death.
If the substance has become viscous, but the number of platelets has decreased, this condition leads to circulatory problems in the body and increases the risk of bleeding. In some cases, hypercoagulability syndrome accompanied by a reduced platelet count is a symptom of cancer.
If increased viscosity is not treated, this condition can provoke hyperosmolar coma and intracerebral hemorrhage, which has a high risk of death.
Formation of candidiasis
White lumps in stool can appear as a result of the development of candidiasis in the body, or, simply put, thrush. The disease is accompanied by the formation of a cheesy coating on the intestinal wall and when feces pass through the organ, white inclusions enter them. In addition, a number of other signs arise:
- Soreness appears in the area of the intestinal tract of an aching or pulling nature.
- Burning around the anus.
- Skin irritation and redness, peeling.
- Loss of appetite or its noticeable deterioration.
- Rumbling in the stomach and pain in its lower sections.
In some cases, with candidiasis in the stool of an adult, not only white dots, lumps or flakes are observed, but also bloody impurities. The temperature with this pathology rarely rises, much more often remaining normal.
Decoding the results of the occult blood test
Depending on how the test was carried out and what the internal regulations of the laboratory are, you will receive an answer in 1-6 days. From the description of the methods for conducting this study, it is clear that its results cannot be expressed in an exact digital equivalent: in a benzidine and guaiac test, the reagent is either colored or not - only the speed and intensity of the coloring differs. As for the enzyme immunoassay and fluorescent tests, everything is clear here too: the second strip either appears or not, and the glow is either present or not.
As an example, let’s look at the decoding of the results of a fecal occult blood test using the Gregersen method (benzidine test):
Development of dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis is a phenomenon that can be observed in both adult patients and children. This condition refers to an imbalance between beneficial and opportunistic bacteria in the body.
Dysbiosis often occurs in children who are transferred to artificial feeding, but in adults, an incorrectly selected diet can lead to the same problem. The disease can be caused by taking antimicrobial drugs, exposure to hormonal and radiotherapy, as well as radiation and chemistry.
Dysbacteriosis often becomes a side effect of infectious lesions of acute or chronic course; it develops against the background of helminthic infestation and with deterioration of the immune system.
White streaks are found in the stool; adults and children may experience:
- diarrhea;
- change in color of stool;
- dyspeptic disorders - loss of appetite, feeling of nausea, vomiting attacks;
- there is a decrease in body weight;
- allergic reactions, cramping abdominal pain are possible;
- due to a lack of vitamins, the skin dries out, turns pale, stomatitis may develop, and problems with hair and nail plates appear.
Another sign indicating the presence of dysbiosis is the appearance of mucus in the stool.
Indications
Clinicians identify a number of clinical signs that are indications for conducting a coprogram to detect protein in the stool. Since such a disorder often causes gastroenterological pathologies, the symptoms will be corresponding.
Thus, among the manifestations there are:
- violation of the act of defecation, which is expressed in constipation or diarrhea, as well as in the alternation of such symptoms.
- rapid loss of body weight.
- an increase in temperature, which is accompanied by pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
- the appearance of pathological impurities in the stool, namely blood and mucus.
- intestinal dysfunction.
- attacks of nausea and vomiting - while vomiting will not always bring relief.
- a clear expression of the characteristic rumbling sound.
- pain syndrome.
- weakness and fatigue.
In children, an indication may be such a sign as delayed development, both physical and psychological - this can be affected by some diseases.
Inflammatory processes in the large intestine
If white balls or lumps appear in the stool, you can suspect an inflammatory process occurring in the area of the large intestine. If you monitor your stool, you will notice that such inclusions appear regularly over several days.
Given the heterogeneity of the structure of such lumps, it can be assumed that we are talking about leukocytes huddled together.
Such balls are either a sign of open inflammation or indicate leukoplasia of the intestinal mucous layer - a very dangerous malignant pathology. Accordingly, the best solution would be to contact the clinic to clarify the diagnosis.
Common causes
Let's look at what pathologies can cause blood clots in the stool and how to detect them. After reading this article, you will understand how dangerous this symptom can be and that only an experienced specialist will help eliminate this manifestation. Therefore, do not hesitate, consult a doctor as soon as possible, because the presence of blood streaks in the stool already indicates that the process is neglected.
The reason may be:
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- Colon polyps;
- Malignant oncopathology;
- Diverticulitis;
- Internal hemorrhoids;
- Proctitis;
- Worm infestations;
- Intestinal infections.
White lumps in infants' stool
By and large, the reasons for white inclusions in stool in children are the same as in adults. An exception may be infants, taking into account the peculiarities of feeding. The fragile digestive system of infants may have difficulty accepting new food products and problems are observed until complete adaptation occurs. But until this moment, light lumps can be observed quite often.
Important. Perhaps the reason is not in the menu, but given the fact that diseases in the baby’s body can develop very quickly, it is better to get qualified advice and help.
Why might a child have black strings in his stool?
As you can see, most often the appearance of such threads in a child’s feces is associated with iron. When his body is fully formed and is capable of completely breaking down, digesting and assimilating complex or heavy substances that come with food, these phenomena will stop.
In the meantime, it can be considered completely normal if black strings, grains or undigested pieces of food are found in the diaper, especially if this happened after the introduction of a new infant formula with a high iron content. This is within the age-related physiological norm and does not require treatment; You should also not exclude this product from your baby’s diet.
Sometimes a one-year-old baby's stool color may change to black or black-green. This is again connected with his diet - the introduction of fruits and especially berries with intense color, such as blueberries, blackberries, red and black currants, and cherries. Juices and vitamins also contain a lot of iron, which is oxidized under the influence of gastric juice and gives stool an unusual color. Once you find out the reason for this, you should not exclude them from your diet.
This is what an undercooked banana looks like
Very often the cause of this problem is bananas, which have a fibrous structure, so the black strings are most likely just undigested banana fibers.
Black threads, as well as various kinds of inclusions, grains, grains or grains of black sand are collectively called black dots. Sometimes it can just be raspberry, currant, kiwi seeds, grape seed particles, poppy seeds, etc.
Here are the traces the most common fruits leave in baby stool:
- Banana - thin black threads or dots like a poppy seed;
- Persimmon, kiwi - the same points;
- Chblocks, pears - black threads.
How to get rid of suspicious inclusions
To do this, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of their appearance, and, accordingly, a medical examination will be required.
As for treatment, therapeutic regimens are based on the diagnosis:
- If the problem is caused by a fungus, antimicrobial and antifungal agents are prescribed. Most often they contain Fluconazole and Clotrimazole. At the same time, medications are prescribed to prevent intestinal dysbiosis.
- In case of helminthic infestation, it is recommended to take anthelmintic drugs, which are taken against the background of enhanced hygiene.
- If you are lactose intolerant, avoid taking dairy products. Special mixtures are prescribed for infants.
- To restore the functionality of the intestines, it is necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs.
- The presence of mucous colitis requires the use of antiseptics.
- Normalization of the enzyme environment is carried out using Festal, Mezim, Pancreatin.
Very often, medications are taken against the background of a diet in which the amount of fiber consumed is increased and fatty, spicy, smoked foods and carbonated drinks are abandoned.
Classification of nosebleeds
Bleeding from the nose (scientifically called epistaxis ) is a developmental anomaly in which blood bleeds from the vessels of the nasal cavity. The danger of such a condition may include large blood losses, which threatens human life and health. According to statistics, about 20% of all patients with epistaxis turn to ENT doctors for emergency help. 80-85% of patients are diagnosed with problems with the hemostatic system. About 85% of cases of epistaxis are a symptom of diseases of the organs and systems of the body, and in 15% of cases the causes of the phenomenon are pathologies of the nasal cavity.
Types of nosebleeds are determined by their abundance:
- Minor hemorrhage - a few milliliters of blood flows from one nostril. Hemorrhage can be stopped quickly with the right help. Negative aspects of the condition are fear, confusion, discomfort.
- Moderate hemorrhage - about 300 ml of blood flows from the nose in adults. The consequences of excessive blood loss are lightheadedness, weakness in the body, spots before the eyes, thirst, rapid pulse, pale skin, shortness of breath, and ringing in the ears.
- Profuse (massive, severe) bleeding is dangerous for humans. Blood loss can be more than 300 ml. Medicine has recorded cases when the volume of blood flowing from the nose was more than a liter. The consequence of the condition can be hemorrhagic shock, accompanied by loss of consciousness, a significant decrease in blood pressure, and insufficient blood circulation in the organs.
Nosebleeds are distinguished as anterior (blood comes out through the nostrils) and posterior (blood goes down the back wall of the nasopharynx). Anterior hemorrhage is rarely profuse, does not threaten the life and health of the victim, and can be stopped independently. Posterior bleeding is characterized by excessive profuseness and can be stopped only with the help of doctors.