Before answering the question: “what should be the platelet rate during pregnancy?”, we note that pregnancy is a special time for a woman. As a rule, it is a happy time, associated with the fulfillment of the highest destiny of a woman’s destiny.
A woman has to be more reasonable, more responsible, wiser and stricter with herself. Because you need to think not only about your health, but also about the health of your unborn child. And therefore, receiving the result of the next clinical blood test in her hands, her eyes curiously examine the lines with still incomprehensible symbols, words and meanings - HCT, MCH, MPV, PLT, LYMP%, RBC, leukocytes, eosinophils, hematocrit norm, platelet norm - What is this? what do these numbers mean? Is everything okay with my health? are there any deviations? Is there a threat to my unborn child?
We hope that the material presented in this article will help partially satisfy women’s curiosity by popularly explaining the meaning of one of the parameters of a general blood test - the number of platelets in the blood. We will also tell you what these formations are, what function they perform, what they are responsible for, what the platelet level should be during pregnancy, what deviations from the normal platelet level indicate - such knowledge cannot be useless.
Platelets
Platelets are called nuclear-free, spherical plates of blood. A platelet (in Greek θρόμβος means clot, and κύτος means cell) is not quite a full-fledged cell, a kind of protein formation focused on performing a specific function in our body. This is what a platelet looks like in the photo:
Genesis and morphology of platelets
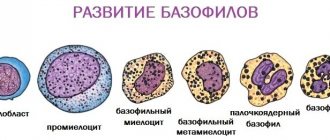
Platelets, like other blood cells, are formed in the red blood marrow. They bud from the cytoplasm of giant cells - megakaryocytes, being part of their cytoplasm. A platelet lives for 5-11 days; its lifespan is determined by the characteristics of the biological environment and the state of human health. During this time, the platelet goes through 3 forms of existence - young, mature, old. There are also forms that reflect pathological and situational states of platelets, for example, “degenerative” and “irritable.”
The purpose of platelets in the human body
In its mature form, the platelet is much larger in size compared to its other forms. Only when mature is it able to fulfill its main purpose - to participate in the processes of regeneration (healing) of damaged body tissues and blood clotting.
The mechanism of platelet function
In the normal (non-activated) state, the platelet is a lump of neutral cytoplasm. At the moment of activation, it changes its shape and becomes “sticky”. Thanks to this, platelets can attach to the edges of damaged tissue or vessels, forming a kind of ring of platelets around the perimeter, which over time (depending on the size of the damage, but normally 8-10 minutes) fills towards the center.
The platelet barrier is called the “primary plug” by doctors. Next, the process of hemostasis continues with the protein deposited on the primary plug - fibrinogen. The resulting compound activates blood clotting factors, which transform the primary plug into a secondary one - the fibrin protein. After a certain time, the damage is eliminated, the fibrin plug disintegrates, and fibrin breakdown products are absorbed by macrophages.
A few words about platelet activation: the platelet membrane in an inactivated state is covered on the outside by phosphatidylcholine molecules, and on the inside by phospholipid molecules. Only phospholipid molecules have the ability to be “sticky”. During activation, phospholipids, due to the phenomenon of osmosis, pass through the platelet membrane to the surface, making it “sticky”. Activation of platelets is not retroactive; once it occurs, it changes the properties of the platelet forever.
What are platelets
Platelets are blood cells involved in the clotting process.
Platelets are thin discs of blood that have the unique ability to clot blood. When wounds or cuts occur, they stick together, forming clots that clog blood vessels and prevent blood loss. As a result of this process, a crust forms on the surface of the skin, and if removed, bleeding may resume.
In addition to participating in blood clotting, platelets help protect the body from attacks by harmful viruses and bacteria. They actively participate in the formation of immunity and are constantly updated.
The lifespan of platelets is no more than one week. Old cells are destroyed in the spleen, giving way to new blood disks.
Clinical blood test - platelet standards during pregnancy
Clinical, also known as “general” blood test, is the most common of all blood tests. Almost any civilized person is familiar with this type of analysis.
With a frequent and long history of use in clinical medical research, a complete blood count may vary in form, parameters and values.
This is what a standard general blood test form looks like:
In a non-standard form, it may look different, some of its parameters can be changed, but what can never be changed is the symbols. For platelets they are as follows:
Now regarding platelet standards in general. The data is shown in the table below by category - children, men, women. You can be sure that the platelet rate in the blood of men and women is different - in women it is slightly lower in both the lower and upper limits. In children, initially high platelet levels decrease over time.
From the data in the table, which displays the norms during pregnancy by trimester, it is clearly seen that the level of platelets is more or less stable during the first 2 trimesters and changes dramatically in the 3rd trimester.
Pathological conditions associated with high/low platelet count in the blood
In medical terminology, any deviation from the normal limits of platelet content in the blood is called “thrombocytopathy”. If the pathology values are below the lower limit of normal, this is thrombocytopenia, if above the upper limit, it is thrombocytosis. Disorders associated with the functionality of platelets are called “thrombasthenia.”
A lack of platelets in the blood can cause blood clotting to decrease and even with a small cut a person can lose a lot of blood - several times more than with normal platelet levels. This pathology occurs after long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), for example, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin).
An excessive number of platelets in the blood is also very dangerous for the body. At the slightest disturbance in the human biological cycle, platelets will stick together into fibrin clots and clog blood vessels, reducing their permeability. This situation is fraught not only with a general deterioration in health, but also with more complex clinical manifestations - a brain vessel blocked by a blood clot may burst, hemorrhage will begin, followed by a heart attack or stroke. Extensive, that is, with profuse hemorrhage, a heart attack or stroke - this means death in 99.9% of cases.
Thrombocytopenia during gestation
A lack of platelets in the blood indicates that a woman:
- there is a viral infection;
- lack of iron in the body;
- an autoimmune disease develops;
- allergy or allergic reaction;
- lack of B vitamins;
- there is internal hemorrhage;
- consequences occurred after long-term use of diuretics, sulfonamides and NSAIDs.
Thrombocytopenia manifests itself in the form of spontaneous bruises, abrasions, bleeding gums, and abnormally long bleeding, for example, from the nose.
The third trimester is the time when the threat of thrombocytopenia is most likely. The most negative consequence of thrombocytopenia for a pregnant woman can be pathology of fetal development.
Thrombocytosis during gestation
Elevated platelets during pregnancy will indicate:
- acute bacterial infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- presence of cancer (leukemia, tumors of internal organs);
- hormonal imbalance;
- a woman taking corticosteroids;
- woman drinking strong alcohol.
The appearance of venous networks, nodules and expansions on the surface of the skin (particular attention should be paid to the legs) will be indirect evidence of the onset of thrombocytosis in the body of a pregnant woman.
An increased level of platelets in a woman’s blood can lead to the formation of blood clots in the circulatory system of a pregnant woman’s placenta, which in the first semester will mean spontaneous termination of gestation, that is, miscarriage.
Establishing a diagnosis and prescribing treatment for such serious disorders in the body as thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia must be entrusted to a specialist.
Taking a blood test is a mandatory test throughout the entire pregnancy period. Any deviations should alert the attending physician. However, it is not uncommon for minor changes in one or two parameters to be a variant of the norm. Under what conditions are platelets low during pregnancy and when should you be concerned?
Platelets are small blood cells responsible for coagulation and the ability to regenerate damaged tissue. During pregnancy, platelets play a significant role in the normal functioning of the placenta; their normal level contributes to the flow of nutrients from the mother’s bloodstream to the fetus. The normal platelet count during pregnancy ranges from 180-380 thousand/µl. Minor deviations from these indicators do not cause concern among doctors. However, a persistent significant increase or decrease in parameters necessitates diagnosis.
It should be remembered that a single analysis will never give a complete picture of your health status. A low level of platelets is often recorded due to improper collection, long-term storage of material, or insufficient nutrition. Also, the results can be affected by severe stress, poisoning, excessive physical and psychological stress of a pregnant woman. To talk about pathology, you should donate blood at least 2-3 times.
If the platelet level is fixed below 130-140, this may indicate the presence of serious diseases:
- ARVI or inflammatory process;
- HIV infection;
- endocrine disorders;
- internal bleeding;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- lupus erythematosus;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- leukemia or other blood diseases.
However, most often the situation looks much more banal. Low platelets during pregnancy are determined by:
- late gestosis;
- some types of allergic reactions;
- lack of vitamins and minerals (in particular folic acid and zinc);
- use of certain medications.
In addition, in late pregnancy there is a physiological decrease in platelets to 140 thousand/μl. For an accurate diagnosis, a woman will need to undergo several specific tests, and possibly resort to instrumental examination methods. Having ruled out all pathologies, the doctor prescribes corrective nutrition and the use of multivitamin complexes and dietary supplements.
Significance of this analysis
Blood is a “vehicle” through which oxygen and nutrition are supplied to the baby. Therefore, all changes in the condition of the child or mother can be determined by blood.
When registering, the doctor writes out a number of directions for laboratory tests. Here is a list of what blood tests are taken during pregnancy when registering and the periods for taking them again:
- Complete blood count – 16-22 weeks of pregnancy, 24-28 weeks, 32-36 weeks,
- For blood group and Rh factor,
- Biochemical analysis – 10-14 weeks, 16-20 weeks, 24-28 weeks,
- For glucose – 22 weeks,
- Coagulogram - blood clotting (22 weeks, 32-36 weeks).
- For HIV – 24-28 weeks, 32-36 weeks. ,
- For hepatitis B and C – 24-28 weeks, 32-36 weeks. , – 24-28 weeks, 32-36 weeks,
- On RW – the presence of antibodies to syphilis. (24-28 weeks, 32-36 weeks),
- For TORCH infection (antibodies to toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus infection, rubella and two types of herpes simplex virus).
- Check for STDs - sexually transmitted diseases.
From the list you can immediately see which blood test is taken most often in pregnant women - a general one. And this is no coincidence, it gives a clear clinical picture, with its help you can determine the cause of deviations from the norm. It is rented out at least 4 times. It is also called clinical.
Symptoms and consequences
To identify pathology, it is not necessary to wait for routine diagnostics. A woman may suspect this problem based on how she feels and some external manifestations.
Thrombocytopenia is indicated by symptoms such as:
- hemorrhages under the skin - expressed in the appearance of bright scarlet spots (usually on the legs and arms), directly under the epidermis layer under the influence of mechanical action;
- the formation of hematomas - and bruises form in various places for no good reason;
- bleeding gums and nose;
- the appearance of black stools;
- uterine bleeding;
- the appearance of a small rash of tiny bruises.
In addition, the pregnant woman’s well-being significantly worsens, weakness and dizziness are possible, and dyspeptic manifestations are likely. If you pay attention to the accompanying syndromes in time and identify the disease, it will be easy to increase the level of platelets in the blood, the treatment will have a good effect and prevent the development of dangerous complications. Otherwise, the consequences may be irreversible.
In an advanced form of the disease, with a significant decrease in indicators, it is possible:
- development of fetal hypoxia;
- intrauterine developmental delay;
- frozen pregnancy;
- miscarriage and premature birth;
- the occurrence of heavy bleeding during childbirth.
The risks are very high, so it is important to identify the cause of thrombocytopenia in time and eliminate the negative factor.
Possible consequences
An increase in platelet count can cause such complications
:
- risk of miscarriage;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- severe toxicosis;
- phlebeurysm;
- thrombosis of the extremities;
- risk of heart attack and embolism
(in case of blockage of blood vessels or rupture of a blood clot).
Thrombosis is a very dangerous condition. And if it occurs, the pregnancy is urgently terminated for health reasons
Therefore, it is important to undergo tests in a timely manner in order to diagnose the problem in time and begin treatment.
The last time platelet levels are checked is just before delivery to decide on the method of delivery.
Treatment methods for thrombocytopenia
How to increase platelet levels in the blood? In the vast majority of cases, no specific treatment is required. The blood completely restores its composition after eliminating the underlying disease that caused changes in the analysis. Since the dominant cause of decreased platelets in pregnant women is viral and bacterial infections, to improve the indicators, it is necessary to cure the disease and wait for the recovery period. If the number of platelets does not return to normal for a long time or there is a chronic disease that causes their constant decrease, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy.
The basis of treatment is a special diet. For thrombocytopenia, it is necessary to provide a diet with sufficient calorie content and a high amount of nutrients. Your daily diet should include foods high in vitamins and minerals:
- fresh vegetables and fruits (apples, beets, cabbage),
- eggs (1 piece per day),
- legumes,
- mushrooms,
- nuts,
- meat and fish products with reduced fat content,
- dairy and fermented milk products,
- seafood and seaweed,
- all types of greens.
It is not recommended to adhere to diets that limit the nutritional and energy value of the diet, reduce the consumption of healthy fats and refuse organic foods. At the same time, smoked meats, fast food, canned food and foods that are highly likely to provoke the development of allergies (chocolate, citrus fruits) are not recommended. Such nutrition will provide the body with a sufficient amount of vitamin C, iron, folic acid, zinc, vitamin B12 and other valuable microelements.
A pregnant woman must maintain an adequate drinking regime with a sufficient amount of clean water, compotes, fruit drinks and weak herbal teas. Consumption of caffeinated drinks and cocoa is not recommended.
However, with pathological thrombocytopenia, diet alone will not be enough. For severe allergic reactions, corticosteroids and immunoglobulins may be needed to increase platelet counts. Critically low rates require hospitalization and intravenous administration of drugs. For bleeding of any etiology, the doctor can prescribe hemostatic agents in any form. Among them: aminocaproic acid, sodium etamsylate, calcium chloride, etc. The choice of drug is made exclusively by the attending physician, with mandatory consideration of possible risks for the unborn child. Self-medication is unacceptable. In winter and spring, a course of specialized multivitamin complexes is recommended. In especially severe cases, a blood transfusion procedure is required.
Treatment
The first thing you should do if you detect low platelets is to consult your doctor and undergo additional examinations. The tactics and treatment regimen depend on the true cause of the phenomenon. prednisolone
is used for thrombocytopenia , but this steroid hormone has many side effects, and during pregnancy, treatment differs markedly from standard therapy.
If the reason why platelets are reduced lies in an infectious disease, it should be treated. If we are talking about ARVI or influenza virus, then the blood composition will normalize after the woman finally recovers, without therapy at all.
Treatment will not be needed if the number of blood platelets has decreased due to medications taken by the expectant mother. Simply stop taking these medications and your blood composition will return to normal.
If the state of platelet deficiency is associated with disorders of the thyroid gland or kidneys, then the woman is referred for consultation to a nephrologist or endocrinologist. Together with the gynecologist, these specialists will have to plan a treatment regimen for the underlying disease.
Special medications that have the ability to increase blood clotting are rarely prescribed, since in principle they are not intended for use during pregnancy. If the decrease in blood platelets is critical, then the woman is hospitalized and coagulants are administered to her in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor. This is especially true when there are only a few days left before giving birth.
Both at home and in the hospital, women are advised to take vitamin complexes.
She should also be more careful about her diet. Products that increase blood clotting are bananas, apples, chicken and quail eggs, meat and fish, and fresh herbs.
with autoimmune thrombocytopenia face the most difficult treatment
. They are prescribed hormonal drugs (glucocorticosteroids) in a hospital setting. In some cases, if the pregnant woman’s condition is threatening, donor blood transfusions may be performed. This helps, at least temporarily, to increase the number of blood platelets and increase the body’s defenses.
When treating with hormones, they most often start with Dexamethasone, gradually moving from therapeutic doses to prophylactic ones until the platelet count is normalized or approaches the existing norm.
If hormonal therapy cannot raise the number of blood platelets, injections of human immunoglobulin are prescribed. The expectant mother will receive several injections during her pregnancy, with only 1 injection in each course.
In the most severe cases, when proper nutrition and hormones are powerless, a woman can, for health reasons, undergo laparoscopic surgery to remove the spleen, because it is in this organ that most of the platelets die. The puncture is small; the splenectomy itself is performed under general anesthesia.
To learn how to increase platelets at home, watch the following video.
Carrying a child is a difficult time in a woman’s life, which, unfortunately, can be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. These include nausea, anemia and low platelets during pregnancy.
Elevated platelet count
Along with a reduced level of platelets, pregnant women often experience a reverse pathology called thrombocytosis, when more than 400 thousand platelets per microliter are recorded in the blood. Elevated platelets during pregnancy are often diagnosed with dehydration, severe toxicosis, impaired drinking habits, and poor nutrition. The condition is characterized by the formation of blood clots within the choroid plexuses.
Among the causes of thrombocytosis are:
- genetic failures;
- autoimmune diseases;
- phlebeurysm;
- haemorrhoids;
- severe allergic reactions;
- blood diseases;
- oncological diseases;
- latent and chronic infections;
- taking medications that increase blood clotting.
Thrombocytosis is especially dangerous in the third trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus is growing rapidly and the need for nutrients increases. Due to increased blood viscosity, blood clots may form in the vessels of the umbilical cord, which can lead to severe forms of oxygen and food starvation in the unborn baby. There is a high risk of premature birth and the appearance of a child with various congenital pathologies.
Conditions where platelets are physiologically elevated during pregnancy are quite rare, so treatment with diet alone is impossible. With proven thrombocytosis, the doctor prescribes medications that thin the blood, as well as drugs aimed at curing the underlying disease that caused the development of the disease. Therapy has an integrated approach and is characterized by a long duration. To achieve a positive effect, constant monitoring and prevention are required.
A normal platelet level is a necessary condition for comfortable pregnancy and easy childbirth. If platelets are low during pregnancy or a significant increase is recorded, emergency drug therapy and a special diet are required. This will help get rid of unwanted consequences and maintain the health of mother and child.
Every girl needs to know what her platelet count is during pregnancy. Their number should be approximately 150-400 thousand/µl. The level of blood cells may change during pregnancy, but this indicator does not depend on the trimester.
Vitamin C Blood test flaxseed oil Prevention Grapefruit for the intestines during pregnancy special nutrition vitamins
Specialists are required to refer women for a blood test. It is one of the must-haves for expectant mothers. An unpleasant pathology can provoke miscarriage due to antiphospholipid syndrome. That is why the disease requires surgical treatment, and during pregnancy you need to know how to reduce platelets in the blood.
But too low a cell level often causes serious bleeding. During spontaneous labor, the baby may experience internal bleeding. Moreover, there is another danger: the child will die due to a cerebral hemorrhage.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia from occurring during gestation, women only need to follow a few simple rules. Basic preventive recommendations:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- strengthening the immune system;
- avoidance of taking medications for no apparent reason - only vitamin complexes are allowed;
- compliance with the drinking regime;
- Regular visits to the obstetrician-gynecologist and compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions.
The outcome of platelet abnormalities depends on the underlying cause. In any case, refusal of medical care will lead to the development of complications that can end sadly for both the mother and the fetus.
Causes of increased cell number
When platelets are low during pregnancy, the doctor diagnoses thrombocytopenia. This condition is characterized by:
- fragile vessels;
- increased likelihood of internal bleeding.
Often small bruises appear on a woman’s body that do not disappear for a long time. The nose begins to bleed and the gums bleed. This phenomenon is due to the following reasons.
- Lack of folic acid.
- Severe forms of autoimmune and endocrine pathologies.
- Taking diuretic, antirheumatic, antibacterial medications.
- Severe form of late toxicosis.
- Allergic reactions.
- Consequences of viral or bacterial infectious diseases.
When platelets are very low during pregnancy, proper treatment is necessary. It is advisable to consume foods high in vitamin C:
- bell pepper;
- apples;
- black currant;
- cabbage.
Proper nutrition with vitamins C
Low platelets during pregnancy are especially dangerous in the last trimester.
Why does the cell count increase?
An increased number of blood cells also does not bode well, since it is dangerous for the blood to thicken. Sometimes during pregnancy, platelet hyperaggregation develops in any trimester. In this case, their number reaches 400 thousand/µl.
Platelet aggregation during pregnancy is a very important indicator that reflects the ability of blood platelets to stick together. Therefore, to control the number of cells, you need to regularly undergo a medical examination and take all prescribed tests. When blood vessels are damaged, blood cells receive a signal from the body, after which the blood plates stick together at the site of damage and close the gaps.
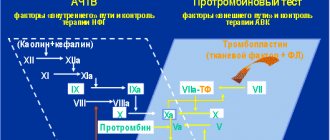
In order to determine the rate of platelet aggregation during pregnancy, a coagulogram is performed. This is a study of blood plasma using special substances that provoke adhesion. They are called inductors. The analysis is carried out in laboratory conditions. Normally, when blood plates interact with the active substance, aggregation is 30-60%.
Take a blood test to check your platelet level
Doctors identify several causes of elevated platelets that occur during pregnancy. These include.
- Pathologies that provoke an increase in cell concentration.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Dehydration due to loose stools, frequent vomiting, and low fluid intake.
Sometimes a woman’s indicators are slightly elevated, but their decrease is not necessary, since this condition does not cause concern. However, when the results of a coagulogram reflect an increased number of blood platelets, it means that some harmful changes are observed in the body.
When an increased platelet count is observed during pregnancy, the likelihood of spontaneous miscarriage increases significantly in any trimester.
If your platelet level is slightly elevated during pregnancy, it can be lowered without the use of medication. You just need to adjust your menu.
There are a number of products that thin blood plasma:
- garlic;
- tomato juice;
- Apple vinegar;
- linseed, olive oil.
Drink tomato juice for prevention
Treatment and prevention of pathology
When expectant mothers experience hyperaggregation of blood cells, only a hematologist should be treated. First of all, it is necessary to treat the exact condition that caused the spike in platelet levels during pregnancy. The specialist will individually select the medications that the woman needs.
If during pregnancy in the 1st-3rd trimester the level of platelets increases, you can bring them back to normal with the help of diet. The diet should include:
- a large amount of iodine (buckwheat, persimmon, caviar, seafood);
- magnesium and calcium (rice bran, avocado, dark green vegetables, dairy, soy products);
- flaxseed oil, olive oil.
Thinning blood plasma with flaxseed oil
If you plan to correct an elevated platelet level during pregnancy, you need to exclude chokeberries, walnuts, pomegranates, and bananas. These products only increase blood viscosity. To avoid “thickening” of the blood, you need to drink about 2 – 2.5 liters of liquid. Give preference to sour drinks.
Most often, doctors recommend paying attention to your diet rather than resorting to medication. Eat foods with iron, vitamin B12, folic acid, zinc, vitamin C. Your menu should be rich in eggs, legumes, dried mushrooms, oysters, mussels, liver, red meat, liver, fish, cereals, nuts, oranges, tangerines, herbs , chocolate, peanuts, seeds, apricots, cabbage, rose hips, black currants, strawberries, raspberries, citrus fruits, pomegranates, grapes, herbs.
Be sure to exclude smoked products, dishes with citric and acetic acid. During pregnancy, such products help increase the level of platelets in the blood.
Very often, deviations from the norm occur due to liver problems. Sometimes a woman does not know that her blood cell levels are abnormal and continues to lead a normal life. However, this pathology requires treatment with special medications to restore liver function.
To avoid high or low platelet levels during pregnancy, preventive measures are necessary. First of all, it should.
- Watch your weight.
- Eat properly.
Do not overuse salt, strong tea and coffee. Be sure to treat diseases of infectious and viral origin, since they can cause serious consequences. Also find out whether it is harmful to have frequent ultrasounds for pregnant women.
Attention!
The information published on the website is for informational purposes only and is intended for informational purposes only. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice! The site editors do not recommend self-medication. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician! Remember that only complete diagnosis and therapy under the supervision of a doctor will help you completely get rid of the disease!
To avoid complications while carrying a baby, you need to register with the antenatal clinic on time and regularly carry out scheduled examinations. When reading a blood test, low platelets during pregnancy are often detected.
Platelets are microscopic blood platelets produced by the bone marrow. These elements play an indispensable role in blood clotting and perform the most important protective function of the body.
Diagnostics
An increase and decrease in platelets in the blood is detected only during a general clinical analysis. For such a study, capillary or venous biological material is required. Interpretation of the results is within the competence of the hematologist. To obtain accurate information, it is recommended to carry out the test on an empty stomach and in the morning.
Taking blood from a vein for OAC
However, the data from this diagnostic method are not enough to establish the root cause, which could indicate why high or low platelets occurred during pregnancy. To detect the etiological factor, patients should undergo a comprehensive examination.
Primary diagnostic procedures:
- studying the medical history - helps to establish the main pathological source;
- collection and analysis of life history - the clinician must be provided with complete information regarding the course of pregnancy, addiction to bad habits and taking any medications;
- a thorough physical examination, which involves assessing the condition of the skin;
- a detailed survey of the patient - drawing up a complete symptomatic picture and determining the degree of severity of external signs characteristic of any variant of the problem.
To establish a definitive diagnosis, you may need:
- specific laboratory tests;
- instrumental procedures;
- consultations with specialists from various fields of medicine.
The diagnostic program is prescribed on an individual basis.
Normal blood platelets in the body
The lifespan of these small blood cells is 7-10 days. During pregnancy, female organs begin to work at an increased pace, and this reduces the lifespan of platelets. The volume of blood circulation increases, which also affects the normal level of blood platelets. If before conception their number in healthy women fluctuates between 150-400 thousand/µl, then during pregnancy this number decreases slightly.
- Platelets during pregnancy are calculated individually. But when the blood level drops below 140 thousand/µl, we can talk about the development of thrombocytopenia. This is a serious disease that poses a threat to the expectant mother.
- The peak of the disease occurs in the last trimester of pregnancy; during this period, the female body is especially vulnerable.
- Low platelets can lead to severe bleeding, complicating childbirth. Doctors must do everything possible to stop it and save the mother and child.
To confirm this diagnosis you need:
- take a general blood test;
- do a coagulogram;
- collect the entire anamnesis.
Then you should make an appointment with a hematologist. Only he can increase the level of blood platelets by prescribing the correct treatment, individually selecting medications for each woman.
Why do pregnant women have a special norm?
Indicators of a general blood test (CBC) change during pregnancy, and this is clearly demonstrated in the table. The values in it also vary depending on the timing of gestation. Decoding the answer received from the laboratory will help to understand whether everything is normal with the health of the expectant mother.
Why do test standards change during the period of waiting for a child? Blood, a special circulating liquid tissue, participates in all metabolic processes of the body. It carries oxygen and nutrients to all cells. Pregnancy is a special period in a woman’s life, including in terms of physiology.
The heart adapts to the birth of a new life, changing its rhythm and even position. Blood pressure drops in mid-gestation, then returns to its original values. New standards are applied to assess health status. Blood tests in pregnant women are also assessed based on other parameters.
After conception occurs, the volume of peripheral blood of the expectant mother begins to gradually increase. Blood is needed to nourish the uterus and placenta. From here, the third circle of the circulatory system begins to form, where blood flow will steadily increase as the embryo grows and develops.
The plasma volume increases by at least a third of the original volume, and the number of red blood cells changes very little. And these are not all the changes that are observed in the UAC.
Why does the platelet count decrease?
The platelet rate during pregnancy may decrease slightly in any trimester. This is due to physiological changes. If pregnancy occurs without complications, the level of blood platelets does not decrease significantly.
- Poor blood tests are observed in women with toxicosis developing in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- The pathological condition causes a serious complication - preeclampsia, which is characterized by nausea, vomiting, high blood pressure and headache.
The lifespan of platelets is significantly reduced when the body lacks vitamins. Anemia leads to a decrease in the number of blood platelets in the blood. To avoid it, you need to take multivitamins prescribed by your doctor and diversify your diet.
Doctors believe that the culprits for the decrease in platelet levels are:
- viral infections;
- allergies;
- violation of the blood coagulation system;
- lack of follates.
Sometimes the appearance of the disease is influenced by external factors. The disease can be provoked by uncontrolled use of blood thinning medications. Therefore, they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor and not exceed the recommended dose.
If blood tests were normal before pregnancy, most likely after the baby is born, the platelet level will recover and the disease will cease to bother you.
The importance of platelets for a pregnant woman
Platelets are platelets of blood that are necessary for normal blood clotting and stopping bleeding. Also, these blood elements perform a protective function in the body. Platelets are produced in the bone marrow.
The level of platelets can be determined using a blood test, which a pregnant woman should take in the morning on an empty stomach. For a non-pregnant woman, the norm is 150-400 thousand/µl
During pregnancy, the indicator may change; the individual characteristics of the body are of no small importance here.
If the pregnant woman is healthy, platelets may decrease slightly. Doctors attribute this to the fact that blood elements are quickly destroyed, because a pregnant woman has increased peripheral blood circulation (the amount of blood in the body increases).
Platelet aggregation
When examining a blood test, the most important indicator that needs to be monitored is platelet aggregation.
Aggregation is a process that allows platelets to stick together. When the integrity of the blood vessels is compromised, bleeding begins. Blood plates accumulate in the area of the injury and connect with each other, closing the gap.
To check coagulability, you need to do a coagulogram. If the readings are 30-60% when blood comes into contact with the inducer, there is no need to worry.
When the test shows a lower level, the ability of platelets to connect is reduced, and bruises and bruises often appear on the woman's body. Hypoaggregation leads to heavy bleeding, which can start from a simple finger cut.
If aggregation indicators are increased, it means that the patient is developing platelet hyperaggregation during pregnancy.
This is a dangerous condition that leads to the formation of blood clots in the veins and arteries. The prerequisite for this is severe dehydration. In the first trimester of pregnancy, fluid loss can be caused by constant vomiting due to toxicosis.
Hyperaggregation in the early stages often leads to miscarriage, so it is very important to get tested on time and inform your doctor about the slightest changes in your condition.
Red blood cells during pregnancy, ESR during pregnancy
The number of red blood cells begins to increase at 8-10 weeks of pregnancy and by the end of pregnancy it increases by 20-30% (250-450 ml) relative to the normal level for non-pregnant women, especially in women who took iron supplements during pregnancy. Among pregnant women who did not take iron supplements, the number of red blood cells may increase only by 15-20%. The lifespan of red blood cells decreases slightly during normal pregnancy.
The level of erythropoietin during normal pregnancy increases by 50% and its change depends on the presence of pregnancy complications. An increase in plasma erythropoietin leads to an increase in the number of red blood cells, which partially meet the high metabolic oxygen requirements during pregnancy.
In women who do not take iron supplements, the average volume of red blood cells decreases during pregnancy and in the third trimester averages 80-84 fL. However, in healthy pregnant women and in pregnant women with moderate iron deficiency, the average volume of red blood cells increases by approximately 4 fL.
ESR increases during pregnancy, which has no diagnostic value.
Treatment of elevated levels
When they are slightly enlarged, the hematologist prescribes a special diet. It should include foods containing large amounts of vitamin C.
- You should eat plenty of fruits and vegetables. Every day you need to make salads from fresh cabbage, bell peppers, and include seafood in your diet.
- It is useful to prepare fresh juices from black currants, green apples and tomatoes.
- To reduce blood thickness, you need to regularly drink 1 tsp. flaxseed or olive oil and do not forget to add garlic and onions to your food.
For mild treatment of hyperaggregation, it is recommended to eat small portions at least 5 times a day. It is imperative to saturate your body with clean water. To feel normal, you need to drink about 2 liters a day, squeezing a few drops of lemon juice into a glass.
Along with the diet, it is useful to carry out simple physical exercises and walk more.
If platelets are very high and the risk of blood clots is very high, the doctor will prescribe special medications that help thin the blood. It is also advisable to try treatment with homeopathic remedies. They are also prescribed by a hematologist, based on the results of the examination and the general condition of the mother and unborn child.
Treatment
In medicine, there are many forms of thrombocytopenia, so you cannot prescribe treatment yourself; it is necessary that this be done by an experienced doctor.
If a low platelet count during pregnancy occurs as a result of an infection entering the body, then everything should return to normal after recovery from it.
If the problem arose as a result of taking some medications, then the solution is very simple and clear - stop using them.
If the problem arose due to a malfunction of the internal organs that are responsible for the production of hormones and antibodies (kidneys, liver, thyroid gland), then the doctor will prescribe treatment that will help restore the normal functioning of these organs.
If the problem is related to a lack of some vitamins in the body, then following the basic principles of the diet can help. Not many people know about this, but in vain, because pregnant women should not include smoked and canned foods, or anything that contains acetic and citric acid, in their diet. A list of what expectant mothers must eat: fresh vegetables, fruits, nuts and berries, legumes, meat, fish, mushrooms, eggs.
The disease is an autoimmune type, in which the body itself prevents the production of new platelets and destroys old platelets.
In this case, the treatment will also be special:
- The doctor will prescribe corticosteroid drugs, angioprotectors and immunoglobulins.
- Prescribe a special diet.
- In some cases, blood transfusions are prescribed.
Low platelets during pregnancy are very dangerous for the body, so if any of its symptoms are discovered, you need to seek the help of a specialist who will understand the causes and accompanying treatment.
The importance of timely diagnosis and treatment
Prevention
To prevent the development of thrombocytopenia in a pregnant woman, it is important to adhere to certain rules:
- exclude all factors that can negatively affect the immune system;
- before planning a pregnancy, get all the necessary vaccinations against ARVI, rubella, chickenpox and other viral infections;
- refuse certain medications even in the initial stages of bearing a child;
- adjust your diet.
To prevent thrombocytosis, the following preventive measures are taken:
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- exclusion from the menu of foods that can increase blood viscosity;
- taking more fluids and food that thins the blood.
It is necessary to monitor the platelet count throughout pregnancy. Therefore, it is so important not to neglect regular examinations by specialists and testing.
Why platelets are low during pregnancy - what to do
A low level of platelets in the blood of pregnant women is caused by a cell content of less than 140 thousand/μl. If the results of the analysis reveal an indicator below normal, this means that a critical situation has arisen, which threatens the opening of bleeding during childbirth. A decrease in cellular elements in the blood occurs for a number of reasons:
- autoimmune diseases;
- HIV infection, AIDS;
- lupus erythematosus;
- oncological diseases;
- viral pathologies.
In the later stages, a low amount is accompanied by toxicosis, which is dangerous due to the formation of gestosis. But often a deficiency is caused by malnutrition, as a result of which the body does not receive all the necessary vitamins and microelements.
You can quickly increase the level of cells in the blood by following your doctor’s recommendations, which are aimed at preventing colds, limiting stressful situations and stopping taking medications that reduce the levels.
Also, you should eat foods that increase platelets in the blood, these include berries and fruits with large amounts of vitamin C (black currants, rose hips, raspberries), while citrus fruits, smoked and canned foods are excluded from the diet. It is important to diversify your diet with foods that contain zinc and vitamin B.
If there are few cellular elements and they are rapidly falling, then drug therapy will be required with a preliminary diagnosis of the cause of the pathology. Treatment involves the use of hormonal glucocorticosteroids, immunoglobulins to stimulate the immune system; if therapy is ineffective, plasma transfusion is possible.
The indicator is normal
The platelet count in a pregnant woman is an important indicator that should always be monitored. During pregnancy, it can decrease due to the fact that there is an increase in blood volume and the formation of a placental circle of blood flow. The average volume considered normal in pregnant women is approximately 140-340 thousand/µl.
The indicator depends on the timing of pregnancy. Normal platelet count in blood:
- 1st trimester – 170-340 thousand/µl;
- 2nd trimester – 160-330;
- 3rd trimester – 140-320.
After childbirth, some changes are observed in the female body, the main task of which is to reduce blood loss. This occurs due to increased coagulability. After the postpartum period ends, all indicators return to normal .
What tests are needed?
To control the composition of the blood, certain laboratory tests are carried out. Only after the biological material has been fully studied is a diagnosis made: low or high platelet levels in a pregnant woman.
Diagnostics consists of conducting examinations such as:
- general examination of the patient by a gynecologist, therapist or hematologist;
- blood test to determine the number of blood platelets, ferritin and serum iron levels;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs.
If necessary, an additional bone marrow biopsy may be prescribed.
Sometimes situations arise in which there is low coagulation or a tendency to form blood clots, despite a positive blood test. In this case, the patient is sent for a coagulogram.
This research method determines the level of cell aggregation, that is, their ability to connect with collagen. Normally, this figure should be from 30 to 60 percent.
To obtain the most accurate results, you need to be well prepared before submitting the material for analysis. It is important that blood sampling is carried out on an empty stomach . For a couple of days, it is recommended to avoid taking medications that can negatively affect the number of platelets in the blood.