Using the MCV blood test indicator in a child, knowing its norms and interpretation, you can determine the quantity, quality and level of red blood cells. And also based on the results of this test, various diseases are determined. This test is done in a laboratory using a clinical blood draw, which can be taken from a vein or finger. By deciphering the analysis, the exact diagnosis and type of anemia is established.
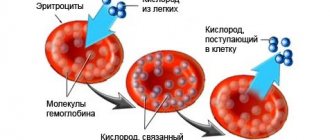
Diseases vary from person to person. And first of all, when a person takes tests, they look at the number and general condition of red blood cells in the blood. After all, they transport oxygen and carbon dioxide with the help of hemoglobin. If red antibodies are detected, then it is necessary to identify a disease of a hematological nature as soon as possible, and even more so if it concerns the body of children.
What is PDW and its importance for the body
PDW in blood testing is a designation for the distribution of blood cells in the bloodstream. Such a blood test is necessary to determine the presence of certain pathogenic processes in humans. Platelets are heterogeneous in nature; both small and large cells are found. There is a somewhat similar meaning - RDW, but it refers to the volume of red blood cells in the bloodstream.
Platelets are an important part of human blood. When a blood vessel is damaged, they accumulate at the site of injury and thereby stop the bleeding.
If there are few of them, the person is in danger of losing a large amount of blood. If, on the contrary, there are more platelets, this can cause the formation of blood clots, which, if they come off, can block the vessel. This is dangerous, since completely blocking the blood flow causes tissue death and, in some cases, death.
Therefore, the PDW indicator is very important - it determines whether the level of platelets in the blood is high or low. If the results are significantly abnormal, together with other tests that are not good enough, this may indicate the presence of serious diseases.
Reasons for lowering PDW
As mentioned above, PDW is looked at from the big picture: symptoms, other tests and examination methods. Reduced PDW levels can result from the following diseases:
- Myelodysplastic syndrome. The abbreviation MDS refers to a range of diseases affecting the bone marrow. As you know, it is in it that blood cells are formed. Therefore, MDS cannot but affect the blood test. This is the only way to detect the disease. The reasons are usually unknown. MDS can occur after chemotherapy or chemical poisoning.
- Leukemia. This disease is also called blood cancer. Cancer cells attack the bone marrow and the normal formation of blood cells becomes impossible. As a result, the patient experiences a decrease in the number of almost all blood cells, and the immune system suffers.
- Metastases to the bone marrow. Any cancer at a certain stage metastasizes. They can affect the brain and spinal cord, as well as other organs. In this case, except for PDW, almost all blood parameters will be reduced.
- Thrombocytopenia. This is an insufficient number of platelets in the blood. This condition itself can be caused by a variety of reasons: bleeding, cancer, etc. It manifests itself in increased bleeding of the gums, hemorrhages, and anemia.
- Radiation sickness. Radiation sickness is a condition of the body that occurs as a result of radioactive radiation of a certain range. The most striking symptoms are low blood pressure, hand tremors, decreased muscle tone, and diarrhea.
- Chronic hepatitis. Despite the scary name, chronic hepatitis is usually mild and does not cause serious liver damage. Blood test results may be abnormal. This is primarily manifested in increased bilirubin.
A timely blood test will be one of the finishing touches in the overall picture necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
Read: Mean platelet volume (MPV) is elevated: causes and treatment
How and under what conditions is it formed?
PDW stands for platelet distribution across blood volume. These are the smallest blood cells, their size is no more than 3-5 microns. The cells themselves are flat and oval in shape, they are transparent and nuclear-free.
Platelets have their own purpose:
- produce reactions in which a blood clot is formed that can stop bleeding in areas of tissue damage (internal and external);
- promote the growth and restoration of blood vessels, provide nutrition with bioactive substances;
- eliminate the inflammatory process along with the delivered immune complexes;
- purification of blood (filtration) from antigens.
Platelets are formed in the bone marrow. Most of them are located in the blood vessels, the smaller part is in the spleen. In this organ (as well as in the liver) the disposal of dead, colorless bodies occurs. The life of platelets is 8-11 days. In this case, the synthesis of new cells occurs without interruption. Both young and old can be present in the blood at the same time.
In total, red cells have several stages of life:
- youth;
- maturity;
- old age;
- irritability;
- degeneracy.
Its size also depends on what stage the platelet is at – the older it is, the smaller it is. Cell volume heterogeneity is also determined by PDW (heterogeneity). If the remaining cells circulate in the blood in their normal volume, minor deviations from the norm do not mean pathology. PDW analysis is performed immediately with MPV, the average red cell volume.
What does PDW mean?
The abbreviation PDW stands for platelet distribution width, that is, their possible fluctuations in volume. In the test form it is designated as the platelet distribution index. These cells are the most microscopic in size when compared with other components of the bloodstream, and do not exceed 2–5 microns.
Platelets are also called platelets, which comes from the English word Platelets, and is associated with their oval, flat shape, which has small protrusions at the edges in the form of thickenings. They are transparent, do not contain a nucleus, and perform several important functions for the human body, including:
- Release of factors that ensure blood clotting and form blood clots in places where the integrity of external or internal soft tissue structures is damaged.
- Production of growth factors aimed at restoring the vascular walls of the bloodstream, saturating them with the necessary biologically active components.
- Transportation of immune complexes to areas of localization of inflammatory processes in order to stop them.
- Filtration of blood fluid from antigens that have ceased to exist as a result of combination with antibodies.
PDW norm table
PDW - in a blood test - is a value that has both its deviation and its norm.
| Patient | PDW standard | Peculiarities |
| Men | 15-17% | |
| Women | 15-17% | During menstruation, blood is not tested. PDW decreases during this period (it varies for each woman). During pregnancy, the values also change - from the norm to 10-20%. |
| Children | 10-14% | During growth and restructuring of the body, values may change, but only slightly. |
The predominance of old and new platelets should not be higher than 10%, otherwise the risk of blood clot formation increases. While a decrease in level can cause large blood losses.
Normal indicators
In people who do not have problems with clotting, regardless of age, the majority of platelets in the bloodstream should be kept in a mature form, because it is at this stage that they are able to fulfill their main purpose - to carry out normal activities aimed at blood clotting. The permissible deviation in the quantitative indicator of mature platelets should not exceed 10%, both in the direction of decrease and increase.
Excessive excess of normal parameters means a high probability of the formation of blood clots, which lead to blockage of blood vessels and then to the development of various pathological processes. And too low platelet counts are a direct path to heavy blood loss, which is no less dangerous for human life and health.
The normal PDW in children under 18 years of age who do not have diseases associated with blood clotting is 10–15%. In adults, this index should not leave the range of 15–17%. Significant deviations from generally accepted parameters in almost all situations are observed as a result of functional disorders of a particular organ or system that require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of high and low PDW
Symptoms of an increase or decrease in PDW in the blood depend on the disease as a result of which the indicator deviated from the norm. This can occur for various reasons; there are quite a few diseases that can cause PDW to decrease or increase.
For example, an increase in the indicator may indicate that a person has anemia. In this case, this will be expressed by pale skin, low blood pressure, weakness, and an enlarged spleen.
If PDW in a blood test is low, then the person often suffers from low blood pressure
A decrease can also mean various reasons, including a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. A deficiency of these elements is expressed in problems of the nervous system, severe hair loss, and a tendency to depression.
PDW: blood test (decoding). Reduced level
- leukemia;
- radiation sickness;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- DIC syndrome;
- viral diseases;
- sepsis;
- use of cytostatics;
- megaloblastic anemia;
- cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis.
Nowadays, it is important to have general concepts about many things. But it is even more important to evaluate your knowledge adequately. Having ideas and deep knowledge are not the same thing. Therefore, you need to understand that PDW is a blood test, the interpretation, norm and meaning of which are well known only to a specialist. The person himself should not draw any serious conclusions about the studies and their indicators; he needs to go to a medical institution.
source
Reasons for promotion and demotion
PDW in a blood test is, figuratively speaking, a means of determining the presence of dangerous diseases. Of course, you cannot rely only on the values of this indicator, however, if the figure deviates greatly from the norm, you should think about other analyzes and a complete check in general.
The reasons for increasing PDW are the following:
- oncological diseases (they quite significantly change the composition of the blood as a whole);
- other inflammations;
- anemia;
- bleeding that occurred after surgery.
An increase in performance does not always mean that there are serious problems. Sometimes the reason may be a simple failure to follow the recommendations before taking the tests. Also, the value may deviate from normal due to taking medications that somehow affect the composition of the blood.
Reduced PDW means few cells in the bloodstream.
Discrepancies from the norm may be caused by the following reasons:
- lack of vitamin B12 and vitamin B9;
- dysfunction of the liver and hematopoietic organs;
- oncology;
- various viruses and infectious diseases;
- taking medications such as cytostatics and others.
Women are not recommended to take tests during menstruation, since all readings will, in principle, differ from the norm, and the platelet volume will be reduced.
However, if the cause of low PDW is not determined, deviations from normal values should not be neglected. Reduced volume can have a detrimental effect on organs, affecting their integrity.
Changes in PDW can occur as a result of poor nutrition, bad habits, or physiological characteristics of a particular organism.
Decoding
Decoding the blood test for PDW is within the scope of authority of the attending physician. Deviations of PDW in women and men from standard values indicate an imbalance between the content of platelets of different sizes in the blood. Changes in PDW are observed in myeloproliferative conditions in which platelet production is increased.
This group of diseases includes the following pathologies:
- Fibrosis of the medulla;
- megakaryocytic leukemia;
- Permanent myeloid leukemia;
- Blood disease polycythemia.
Heterogeneity of the totality of blood plates in size - PDW allows us to determine the following anomalies:
- Diseases accompanied by the body's reactive action on damaging factors;
- Different types of anemia;
- Worm infestations;
- Oncological pathologies;
- Defectiveness of the walls of blood vessels.
The platelet index PDW has diagnostic value in combination with other indicators.
Indications for the study
A referral to donate blood for analysis is issued by a physician. After the examination, he makes a conclusion whether the person should worry about his health or not. Tests and subsequent examinations will either confirm fears or refute them.
The patient is sent to the laboratory, where blood is drawn and the resulting material is examined. This takes time. Then all indicators, including PDW, are written out. With the laboratory tests obtained, the person returns to the therapist, and he examines the results obtained.
The results issued by the laboratory may look like a table in which the data is written down (normal and presence in the patient). It may also specifically indicate whether the person has a disability.
Increase pdw
If the value of the indicator exceeds the permissible value, then this indicates heterogeneity in the volume of platelet particles. This situation has a detrimental effect on the human body and provokes the development of a pathological process. Gradually, as a result, the vessels and capillaries become clogged. Blood circulation is disrupted, as a result of which metabolic processes slow down, and heart attacks are possible in the future.
An increase in platelets may occur in certain cases:
- when diagnosing anemia. This process provokes oxygen starvation, due to which the particles change their volume;
- a high level of concentration of non-nuclear particles is observed in cases where there is bleeding after surgery or certain injuries;
- when neoplasms occur. Such pathological changes contribute to damage to the formed components of the blood. Due to this process, platelets in the blood volume change their normal values;
- The value of platelets increases in the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. Their width is distributed throughout the volume. If this clinical picture is accompanied by an increase in leukocytes, the specialist will diagnose inflammation.
Attention! An increase in the index does not guarantee that an inflammatory process is occurring in the human body.
Deviations from the norm
In the event that the patient does not comply with the recommendations before taking the test, it is possible to change the basic parameters. It is worth remembering that blood sampling occurs in the morning, on an empty stomach. The last meal should be taken 12 hours before the test. Also, doctors recommend not to engage in excessive physical activity; on the eve of the study, emotional and stressful situations should be avoided. In addition, you should avoid taking medications and vitamins if possible.
How is PDW determined?
PDW in a blood test is a value that can change not only as a result of the occurrence of pathologies in a person, but also due to insufficient preparation for the analysis. The volume and distribution of platelets is determined by donating blood from a finger prick. To obtain a more detailed analysis, a sample is taken from a vein.
In order for the result to be accurate, the patient must prepare in advance:
- 1 day before the test, do not engage in physical activity (red blood cells may increase as a result);
- food intake - at least 8 hours ago, it is best to donate blood on an empty stomach;
- For 1 day you should not eat fatty, salty or spicy foods;
- liquid is taken only in the form of water;
- If possible, you should not take medications the day before the test.
Demotion
For a variety of pathologies, making a reliable diagnosis and prescribing adequate treatment helps to record a decrease in PDW.
A drop in the platelet index occurs in the following situations:
- Blood leukemia;
- Exposure to ionizing radio radiation;
- Myelodysplastic syndrome. Dysfunction of the medulla;
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation;
- Diseases of viral etiology;
- Blood sepsis;
- Side effects of cytostatic drugs;
- Blastic anemia, developing as a result of deficiency of folate and cyanocobalamin;
- Chronic hepatitis, liver sclerosis.
Decoding the analysis results
Decoding PDW implies such designations as normal, increased level and reduced.
The norm is considered to be the case when old and young cells are in the bloodstream in almost identical numbers.
An increase in the indicator is an increase in the content of young and old platelets in the bloodstream, and indicates the presence of some kind of problem in the body. Sometimes an increase in PDW and the absence of any symptoms indicates the possible presence of genetic diseases. To check this, a full examination is carried out.
When PDW is reduced, this means that the vast majority of the bloodstream is made up of old cells. This means that there is a problem in the bone marrow and new blood cells are not being produced as before.
The test may also show that the person has very large platelets. Abnormally large cells indicate problems with the immune system. Sometimes cell size depends on heredity - some hereditary diseases affect the size of blood cells.
Studying the material can give the following result – “incomplete”. This means that the platelets clumped together during the counting process. To continue the study, the laboratory technician adds an anticoagulant to break down the cells.
When platelets diverge from their norm, and the reason for the deviation is unclear, an additional study is prescribed, where all materials will be examined in more detail for the presence of malignant processes, infections and other pathologies.
The essence of the analysis and what it shows
To understand what we are talking about, you need to turn to human anatomy and physiology.
Platelets are special shaped blood cells. They ensure its normal coagulation.
The development of cytological structures occurs in special tissues of the bone marrow. This process is called hematopoiesis, and if we talk about platelets in isolation, then thrombocytopoiesis.
Platelets perform their functions for quite a long time. Within 5-12 days. Then they die, and new ones come to replace them.
But this is not a quick phenomenon. Over the course of a short period of time, a shaped cell goes through all stages of life from youth to old age.
After maturation and immediately after leaving the bone marrow, the structure is large. The blood plate is capable of performing its tasks as efficiently as possible.
It takes less time and not as many platelets to close the wound surface. Moreover, adhesion and aggregation occur faster. That is, attachment to the wall of the vessel and accumulation, layering.
Old cells are no longer as active. More of them are needed, and the natural processes themselves proceed slowly and not as well as before. Hence the problems.
Accordingly, if there are more obsolete cytological units, then coagulability will suffer. Its intensity will not be so great that it will be reflected in the coagulogram.
The platelet distribution index or PDW precisely indicates the heterogeneity of cells: that is, the percentage of red plates distributed.
Normally they should be in dynamic equilibrium. Numbers from 1 to 20% are used as values. When young forms of cytological structures predominate, the formula shifts to the right. That is, in a big way. In the opposite case, when there are a lot of old cells, the opposite is true. The number will be lower.
The conditional generalized norm is approximately 15-17%. That is, young forms of platelets should predominate in the bloodstream. This is an indispensable condition for normal coagulation and functioning of the body. Of course, there are differences depending on the gender and age of the patients.
The analysis shows several main violations:
- Thrombocytopathies. A classic pathological process in which the functional activity of red blood platelets decreases. Formally, their number remains normal. This is where the index in question comes to the rescue.
Because the reason is often on the surface and lies in a change in the platelet ratio. The more old cells there are, the worse the body’s functioning is. In critical cases, obsolete structures remain.
- Thrombocytopenia. Different condition. With it, not only the PDW index changes, but also other indicators. The hallmark of the pathological process is a decrease in the number of platelets. It all depends on the primary diagnosis.
- Bone marrow disorders. It’s quite difficult to say exactly which ones. As a rule, with disorders of this kind, the previous named pathologies develop. At the same time, immature hematopoietic cells appear in the bloodstream. Megakaryocytes. They are unable to perform any functions. In this case, it makes sense to conduct a diagnosis. A bone marrow puncture is prescribed.
A blood test for PDW is far from the only necessary test. To tell exactly what is wrong with the patient, auxiliary measures are needed.
For which PDW should you see a doctor?
If the results of a laboratory test show a high or low PDW value, this is a reason to consult a physician. The doctor will examine the available results, and may ask related questions, after which a referral will be issued for other tests.
Do not forget that the reason for the increase may be non-compliance with the rules of preparation for procedures and taking medications. If this is the case for changes in indicators, then the person is sent for a repeat blood draw.
What you should pay attention to when deciphering the results
After receiving the laboratory test results, it is necessary to decipher them correctly, which can only be done by a specialist.
Decoding PDW is of great importance, since this indicator will make it possible to make predictions about the development of the disease and determine the presence of the disease. It is very important to determine PDW for blood diseases and conduct constant monitoring. Indicators are normally considered within the limits:
Various deviations in one direction or another are allowed. When deciphering, the patient’s age must be taken into account, and a comparative analysis with other analysis results is also carried out.
At the moment, PDW has not been studied much, but mainly the indicator provides information about blood diseases and malignant tumors.
A reduced parameter indicates the development of pathological processes in the body, including a lack of iron, which in turn leads to hypoxia of the body’s cells.
How to get PDW back to normal
PDW in a blood test is a value at which it is impossible to accurately determine the diagnosis. Before you begin to bring platelets back to normal, you need to understand why they deviated from their normal state. Therefore, first you should know your diagnosis accurately. Only then does the doctor prescribe the appropriate treatment - a course of medications, hardware therapy, etc.
Special attention is paid to oncological diseases. If the patient has been diagnosed with this, treatment involves special treatment (chemotherapy, radiation therapy, bone marrow cell transplant).
Before using any medication, a person should consult a hematologist. If a child has problems, the pediatrician will prescribe all the necessary medications for treatment.
Medications
If PDW in the blood is low, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Aspirin;
- Clopidogrel;
- Thrombo ACC.
These medications can thin the blood, both for a short time and for a longer period.
When it is necessary, on the contrary, to reduce the indicator, the following drugs may be prescribed:
- Vikasol;
- Dicynone;
- Sedokor.
If a person has undergone a procedure such as chemotherapy, normal PDW is restored by taking hormonal medications.
You should not resort to medications without consulting your doctor - the effects of medications may be unexpected and cause even more problems.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine will not replace full-fledged treatment, but it can be an additional way to get your health in order.
Home remedies are good during a person’s recovery period after surgery.
One of the most popular recipes for restoring PDW levels is a ginger-honey mixture, the recipe for which is very simple:
- Ginger root is ground into a paste and mixed with honey in equal parts.
- The resulting mixture is placed in the refrigerator for 3 days.
- Throughout the entire course (10 days), this folk remedy must be kept in the cold. You should also not heat honey - because of this, all its nutritional properties are lost.
- The product is taken as follows: 1 tbsp. eaten on an empty stomach. It is important to monitor the body’s reaction, since both of these products are strong allergens. To begin with, you should take 1 tsp.
Even before taking folk remedies, you should consult a doctor, as the condition may worsen, allergies and other side effects may occur. If the condition worsens, you should immediately stop taking home remedies.
Other methods
There are quite a few other methods of treating ailments. First, you should note the diet that your doctor may prescribe for a speedy recovery. Depending on which PDW (low or high), products are selected.
So, with a high value, you should pay attention to:
- berries: currants, cranberries, rose hips;
- bitter chocolate;
- lemon, ginger, garlic;
- flaxseed oil and seed.
If the indicators are low, the following products may be added to the patient’s diet:
- eggs;
- red lean meat;
- sesame;
- cereals (buckwheat, rice);
- beet.
Vitamins B12 and C must be present in the patient’s diet - they help restore blood composition. Vitamins can be taken in the form of vitamin complexes, adding them to the diet. Typically, a course of vitamins is 30 days.
Clinics also use hardware therapy in the form of blood purification with a separator apparatus. This device traps blood cells, thereby reducing PDW. Doctors additionally give recommendations so that after recovery you can maintain normal blood counts.
They are quite simple:
- Be sure to consume a sufficient amount of clean water (up to 2 liters);
- avoid physical overexertion; walking and exercise therapy will be sufficient for the patient;
- following a diet that saturates the body with all the necessary elements and improves the condition of the blood;
- reduce the consumption of medications, especially if they were taken thoughtlessly.
These recommendations will help a person maintain normal levels and prevent the recurrence of pathologies.
Deviation from the norm
The PDW norm in the analysis is considered to be 15-17%. A deviation will be considered a figure above and below the specified norm. First, let's figure out what can cause an increase in PDW levels in the blood.
An increase in all platelet indices (and they are always considered together) can be caused by the following reasons:
- Inflammation. To any inflammation in the body, platelets begin to react violently. Their number increases, and accordingly their volume and width also increases. Leukocytes also signal about inflammatory processes. It is not possible to draw a conclusion based on PDW alone.
- Anemia. With iron deficiency anemia, the amount of hemoglobin in the blood decreases. Tissues begin to suffer from lack of oxygen. Platelets do not always respond in this case, but the levels may be elevated for this reason. It is necessary first of all to pay attention to the level of hemoglobin. Anemia can be caused by various reasons: heredity, poor diet, bleeding, blood diseases. Depending on the cause, platelets react differently, which further confirms the need for a full examination.
- Oncology. In various cancers, platelet levels may be low or high, both of which are accompanied by increased cell heterogeneity, i.e., increased PDW levels. More often, the number of platelets is reduced, and the shape and size of the cells vary due to their constant destruction. It has already been proven that platelets to some extent help cancer cells move and form metastases. This may be due to the fact that cancer cells settle and accumulate on blood clots.
- Postoperative period. When surgery occurs, blood loss occurs, after which the body begins the recovery process. Of course, platelets are active, they should form clots that will stop blood loss. Before they begin to stick together to form a blood clot, the cells tend to be heterogeneous in size, which leads to increased levels of PDW.
- Blood loss. The previous paragraph already discussed why PDW increases with blood loss - due to an increase in their activity. Blood loss can also cause anemia, which again leads to increased PDW in the blood.
Norm for children
In children, indicators should also not deviate from the norm for adults.
As with women, parameters may deviate by 1-2% from the accepted norm. This may be due to several main reasons, including active behavior a few minutes before the blood draw, a large dinner the day before the laboratory test, and a small amount of food less than six hours before going to the hospital. If your child is energetic, you should try to calm him down. It usually takes literally 10 minutes of calm behavior to get an accurate result.
If the error of the resulting analysis is more than 2%, you should immediately undergo a re-examination after 5-10 days. If there is any pathology, the PDW readings will begin to increase or decrease. There can be many reasons for this: from simple vitamin deficiency to serious cancer.
During the examination, the child should be protected as much as possible from infection with colds, increase his immunity and create the right diet. This will improve the condition of the blood and help quickly determine the cause of the disorder. In most cases, a deviation from the norm of 5% is easily removable and allows the child to immediately return to normal life.