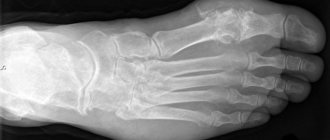
No person is insured against damage and injury. In addition, there are certain parts of the body that are at greatest risk of developing various pathologies. One of these is the ankle joint. Dislocation, swelling, pain and other unpleasant symptoms serve as an alarming signal indicating the need to seek medical help in the near future.
Before starting treatment, specialists will prescribe the patient to undergo diagnostic procedures. A timely examination will help identify the cause of the pathological condition of the ankle joint. MRI is an ultra-modern and most informative research method that provides a detailed picture of internal structures and an assessment of the condition of muscles and soft tissues. It is quite difficult to establish an accurate diagnosis without tomography. In addition, the causes of the development of pathology can be a variety of factors.
Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging for joint pathology
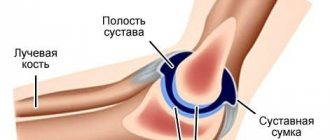
An MRI scan of the ankle has a significant advantage over other types of examination. Its advantages lie in the ability to obtain high-quality images, which allows specialists to detail the image with a certain accuracy. In the conclusions of a diagnostician, you can find an objective assessment of the condition of bones, muscles, soft tissues, and ligaments. During the procedure, specialists have the opportunity to visually examine the characteristics of blood flow in a specific clinical case.
For complex injuries and damage to the leg, magnetic resonance imaging is the only type of examination that guarantees an accurate result. In addition, an MRI of the ankle joint does not take much time: the scan lasts about 20-30 minutes, when using contrast - no more than an hour. The procedure for the patient takes place without any side effects and is absolutely painless, so upon completion the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. MRI is a non-invasive method that allows you to look inside the human body and get maximum information about its condition.
Following the provision of first aid for an ankle injury, the victim is sent for diagnosis. The examination is prescribed by a surgeon or traumatologist. Without prior MRI, it is impossible to carry out surgical treatment, and therefore tomography is mandatory for patients for whom surgical intervention is indicated.
Alternative Methods
MRI is an effective but expensive technique. It also has a number of contraindications, so patients are first prescribed an x-ray or ultrasound of the ankle. Using ionizing radiation or ultrasonic waves, pathologies of joints, muscles, bones, ligaments and tendons can be detected.
Ultrasound or MRI - which is better?
Ultrasound has no contraindications and is prescribed even for pregnant women and children. The peculiarity of the procedure allows you to examine an active child or a patient with a neurological or psychosomatic disease.
Ultrasound examination allows us to examine the condition of soft tissues and ankle joints from different projections. The structure and integrity of visualized objects is assessed. The vessels are also described, inflammation and displacements are recorded. When a tumor is detected, the ultrasound specialist records its size, location and contents. To confirm oncological pathology, it is necessary to undergo an MRI. The image received on the screen is deciphered immediately. The patient receives pictures and measurements after the diagnosis.
How does MRI differ from CT?
Computed tomography is intended to identify pathologies of bone tissue, congenital and acquired abnormalities of organ development, and determine the condition of blood vessels, tendons, and ligaments. The tomograph uses x-rays to obtain images. It is dangerous for humans, so CT scanning more than twice a year is not recommended. Contraindications are pregnancy and children under 6 years of age.
Tomography is prescribed after x-ray to clarify the diagnosis. The procedure is also carried out in a device that resembles a cylinder. The patient is placed on the couch and the leg is secured in one position. A full scan takes up to 15 minutes, so in emergency situations a CT scan is often prescribed.
Indications for an MRI of the ankle
Other indications for undergoing a research procedure include the following conditions and illnesses:
- the presence of neoplasms of unknown histology (if a benign or malignant tumor is suspected);
- fractures and dislocations of the ankle joint;
- sprains, ruptures of ligaments and tendons;
- pain syndrome of unknown etiology in the lower limb;
- swelling and limited mobility of the foot;
- pinched nerve in the foot.
In addition, the most common reason for undergoing an MRI is certain chronic diseases. For example, tomography is recommended for arthrosis or arthritis of the ankle joint, the symptoms and treatment of which require periodic monitoring by qualified doctors. The study allows us to identify problems even when other research procedures have shown questionable results, including those associated with circulatory disorders in the limb.
Thus, magnetic resonance imaging is a comprehensive diagnostic method, to notice the development of the pathological process in its early stages and begin to eliminate deviations as early as possible.
What does it show
What does an MRI of the ankle show?
Norm:
If the ankle joint is normal, then during imaging on the MR machine, the radiologist will see a clear shape and structure of this part of the body, the absence of circulatory disorders, signs of enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of neoplasms and the inflammatory process in soft tissues and cartilage.
Deviation from the norm:
MRI diagnostics with high accuracy allows us to identify the following diseases and degenerative processes in the ankle:
- Intrauterine anomalies of joint structure.
- Deformations, malformations and functioning of the joint.
- Fractures and cracks.
- Rupture, sprain.
- Dislocation.
- Soft tissue bruises and hematomas.
- Accumulation of fluids, including blood, inside the joint.
- Damage due to improper surgical intervention.
- Infectious lesion.
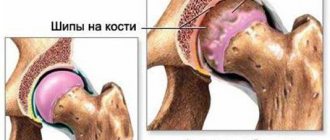
- Arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteophytes.
- Damage to the cartilage capsule, abrasion of cartilage tissue.
- The presence of benign and malignant tumors.
- Penetration of metastases from the outside or formation of metastases from the affected joint.
Timely diagnosis of the disease allows minimizing side effects and maximizing the restoration of joint mobility and function. If you suffer from discomfort in the ankle area, therapy does not give the desired result, or you experience excessive physical stress on your legs, spend a little time and money on an MRI. As they say: it is better to be overly cautious and make sure that the joint is in good condition, than to be underprotected and find yourself in a situation where it is impossible to fix anything.
Contraindications and precautions
Despite the safety of the procedure, in some cases it is still recommended to refrain from MRI. A technique for examining the body that involves the introduction of a contrast agent, as a rule, has more contraindications than a standard scan. Patients with a history of a tendency to allergic reactions should be especially careful when undergoing the diagnostic procedure. During pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding, the administration of a contrast agent is unacceptable even in minimal doses. Gadolinium, which is part of it, negatively affects the functioning of the kidneys, so it is not advisable to resort to this diagnosis for people suffering from renal failure.
Due to the peculiarities of MRI of the ankle joint and the principle of operation of the equipment, it is important to adhere to other restrictions:
- The patient's weight should not exceed 120 kg.
- It is better to conduct research for people suffering from claustrophobia or mental disorders in an open-type tomograph.
- The study is not carried out on patients who have metal structures in their bodies. Whether it is a heart valve, a pacemaker, an insulin pump, a prosthesis, or just a piercing, any iron elements can distort diagnostic results.
- When the couch is immersed in the chamber, the patient's body is tightly secured with restraint straps to avoid involuntary movements.
Can MRI be done in childhood?
This research method is extremely rarely used in children, for a number of reasons. In addition to the harm from the contrast agent, there are other points that prevent the procedure from being performed at such an early age. Maintaining motor immobility, which is required during magnetic resonance imaging, is often an impossible task for children.
If there is an urgent need for diagnostics, the child is examined under general anesthesia. That is why it is more advisable to perform an MRI only in cases where the expected benefit from the diagnosis outweighs the potential risk to the baby’s health.
Information content of the procedure: what will an MRI show?
If the ankle joint is swollen, but the cause of the pathology remains unknown, an MRI is prescribed in 90 percent of cases. Due to the versatility of the study, doctors receive detailed information about the condition:
- bones, since tomography allows you to visually examine the lower parts of the tibia, partially the calcaneus and talus;
- ligamentous apparatus - tendons and ligaments that are susceptible to tears and sprains even without heavy physical exertion are often the cause of long-term pain;
- muscles - to confirm or exclude an inflammatory or infectious process of the soft tissues of the lower leg and foot;
- cartilage tissue - with timely detection of areas of increased wear, cracks and other defects, the patient has every chance of preventing arthritis of the ankle joint.
Symptoms and treatment of most pathologies discovered during the diagnostic procedure require a serious approach and further monitoring by specialists. This method of examining a limb is also used if cystic or oncological formations are suspected.
In addition to the fact that an MRI of the ankle joint shows the presence of diseases, the procedure may be prescribed to the patient in order to monitor the effectiveness of the current treatment, as well as after its completion.
Contraindications
MRI is the safest method for diagnosing the ankle joint, but it also has its limitations.
Contraindications to MRI are divided into absolute, when exposure to magnetic fields can harm health and negate diagnostic results, and relative, when changing the conditions allows the examination to be carried out with minimal or no risk.
MRI is strictly contraindicated in the following cases:
- Implanted pacemaker or defibrillator.
- Electronic middle ear implants.
- Ferromagnetic implants for fixing complex fractures.
- Metal hemostatic clips.
- Foreign objects made of metal (bullets, fragments).
Relative contraindications for which magnetic resonance imaging is still possible:
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- Obesity.
- Body dimensions exceeding the volume of the tunnel of a closed tomograph.
- Claustrophobia and/or anxiety disorders.
- Convulsive syndrome, tremor.
- Permanent makeup or tattoo applied with metallic ink.
Contraindications to the use of a contrast solution to increase the efficiency of the study are discussed separately. The patient's condition may permit conventional MRI and may respond unfavorably to contrast administration.
How to properly prepare for a joint diagnosis?
If the patient was sent for the study for the first time, he certainly does not need to worry. Worried about the upcoming procedure, many are vying for answers on how to do an MRI of the ankle. In fact, no special preparation is required to examine this part of the body. The patient can go for an ankle scan by appointment immediately after receiving a referral from the attending physician. If intravenous administration of gadolinium is necessary for MRI with contrast, it is advisable to come to the session a little earlier, since additional time will be required for the distribution of the substance throughout the body, and on an empty stomach.
Using Contrast
An MRI of the ankle with contrast is used if a malignancy is detected. A direct indication for the procedure is an elevated tumor marker. To do this, blood is donated to check for the presence of a certain protein produced by the body.
When medical gadolinium is injected into a vein, its distribution throughout the body’s circulatory system occurs within 15-20 minutes. As a result, the tomograph takes pictures with illuminated areas that are a tumor. Based on the results, the radiologist and the attending physician can determine the extent of the lesion, the stage of the cancer, and the depth of growth of the tumor into adjacent soft tissues and muscles.
The contrast agent is safe for the body, but toxic if the dose is exceeded or the kidneys are unable to remove the metal, so this type of MRI is contraindicated in renal failure. An allergy test is also performed before the examination. Tomography is not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers and infants.
If during the scan you feel unwell, nauseous, or have a metallic taste in your mouth, contact your radiologist via two-way communication. The procedure should be stopped until the condition improves.
What is an ankle exam?
The procedure itself usually does not cause any difficulties. Briefly, the progress of the research can be described as follows:
- Before entering the office, the patient removes all metal objects, including jewelry, costume jewelry, and turns off his mobile phone.
- In early pregnancy, scanning the ankle without administering a contrast agent is allowed, but before the procedure it is necessary to warn the doctor about the special situation of the patient being examined.
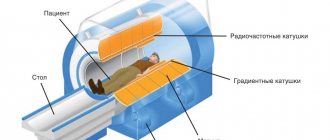
- Next, the patient will be asked to lie on the tomograph couch, the specialist will tightly fix the arms, legs, and head using belts and bolsters. To reduce audibility (the device is quite loud), the patient may be given headphones.
- After this, the table is moved into the chamber at such a distance that the patient’s foot and lower leg fall directly under the torsion path of the tomograph ring.
Research results and their interpretation: what to do next?
The procedure will not affect the sensations of the patient in any way, even if his ankle joint is swollen. The progress of the study will be monitored in the next room by a doctor who can be contacted at any moment and stop the scanning process in unforeseen circumstances.
Upon completion of the examination, the doctor will give the patient the results of the procedure. There is no need to independently look for the causes of pathologies and assess the severity of damage to the ankle joint: the attending physician will decipher the study indicators.
Features of the procedure
Radiation is not used in magnetic resonance imaging, so the procedure does not harm the body. MRI is performed without any unpleasant sensations, does not cause negative consequences and, according to indications, is performed even in childhood. There is no need to prepare for an MRI of the ankle; the procedure can be performed on the day of your visit. A study using a contrast agent is done 4-5 hours after a meal, but preferably on an empty stomach.
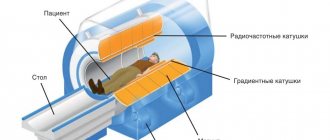
To increase the information content of the MRI, the patient should remain still. Therefore, the area being examined – the patient’s leg – is fastened with special straps to the retractable couch of the device before the examination. The patient lies down on it after removing clothing and accessories that may contain metal, as well as clothing from the examination area.
Afterwards, the diagnostician turns on the tomograph, sets the parameters for examining the ankle joint and retires to the next room, where the control panel of the device and the medical staff’s workstations are located. The couch automatically moves inside the tomograph, and the device begins to scan the ankle. The tomograph is well lit and ventilated from the inside, and is also equipped with a built-in microphone so that the patient can communicate with the doctor. If discomfort occurs, he may ask you to interrupt the procedure.
The duration of an MRI of the ankle joint is from 30 minutes to an hour if contrast is used in the study. The doctor calculates its volume based on the patient’s weight and injects it into a vein before the MRI or during the examination.
What main diseases does tomography reveal?
Based on the diagnostician’s conclusion and based on the symptoms described by the patient, the specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. In case of a fracture, bruise of soft tissues or partial rupture of the ligaments of the ankle joint, the patient will receive complex treatment, consisting, as a rule, of a course of restorative medications and physical therapy exercises. If a neoplasm is detected, to determine its exact nature, the patient is sent for a biopsy to undergo histological examination of the tissue samples taken.
The most common pathologies that can be detected by MRI of the ankle joint are the following:
- arthrosis and rheumatic diseases (including infectious diseases, gout, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis);
- damage to joint capsules, ligament ruptures and sprains;
- hemorrhage in the joint;
- rupture of the syndesmosis (more often due to ankle dislocations between the fibula and tibia);
- anomalies of embryonic development;
- chondrosarcoma – cancer of the articular bones;
- synovioma is a malignant tumor of the synovial membrane.
Which is better: MRI or CT? What's the difference between them?
When choosing a diagnostic method, in most cases doctors prefer MRI. In some cases, computed tomography may be an alternative. It is difficult to definitively determine which type of ankle scan is better and more effective, since the purpose of both procedures largely depends on the indications.
Thus, CT scan follows the principle of radiographic examination, i.e. illumination of a part of the body with rays. Accordingly, this type of diagnosis is more effective for pathological changes in bone tissue. In a CT scan, the bones will be depicted using white shadows, and the remaining cavities will be indicated in a dark color. This marking is effective for identifying the site of a fracture, cyst, or foreign body.
To see the condition of the ankle muscles, it is preferable to use an MRI. Scanning the joint itself, the ligamentous apparatus and the surrounding soft tissues will be more revealing than a computed tomography scan.
What is an MRI of the ankle?
MRI of the ankle is a study that consists of layer-by-layer scanning and determination of changes that occur in cells. This is a reliable and informative diagnostic method that provides high accuracy and detail. Diagnostics are carried out under the influence of electromagnetic waves in a constant magnetic field. The examination is prescribed to identify abnormalities, inflammation, injuries and tissue destruction. The procedure is non-invasive and safe, performed in hospitals and outpatient settings.
How often can joints be scanned using MRI?
Despite stereotypical thinking and ideas about the dangers of magnetic resonance imaging for human health, this type of diagnosis is absolutely safe for the body. If there are no contraindications and all necessary precautions are taken, there is no need to worry: the study cannot negatively affect the course of the disease or worsen the patient’s general condition. Unlike radiography and CT, MRI can be done much more often. Meanwhile, the decision on the need for diagnosis and the frequency of the procedure is made exclusively by a specialist.
How does the procedure work?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint consists of many steps: organization, patient preparation, scanning, interpretation and obtaining results.
The organization includes working with documentation:
- Checking documents for undergoing MRI according to the social quota, that is, free of charge.
- Or draw up an agreement for paid diagnostics.
- Registration of a patient's card.
- Making payment.
Preparing the patient for the procedure consists of many nuances:
- Questioning, examination and familiarization with the results of laboratory tests in order to establish possible contraindications.
- Changing into more comfortable clothes or a disposable hospital uniform.
- If the study is accompanied by contrast enhancement, the patient is weighed to calculate the required dosage of the drug.
- The doctor also selects the most optimal composition, taking into account the state of health.
- The nurse provides instructions on safety precautions and basic behavior during the procedure and answers questions.
Performing a scan:
- The patient is helped to sit on a pull-out couch.
- The body is secured with soft fixations to ensure immobility during the diagnostic period.
- If necessary, an additional coil is installed in the ankle joint area.
- The couch transports the patient into the scanning chamber or under the modular scanner of an open tomograph. The device starts working.
- If necessary, the procedure is interrupted to introduce a contrast solution. Then the study is resumed.
- After completing the diagnosis under anesthesia or using contrast, the patient should spend some time under the supervision of staff in order to, if necessary, stop side effects. In the meantime, the radiologist will prepare a description.
Decoding and obtaining results:
- If the specialist is very busy, the completion of the report may take until the next day. Most often, patients receive results within 30-60 minutes.
- In some specialized MRI centers, a radiologist may conduct a short consultation to help the patient decide on further actions.
- Individual medical institutions can send examination results to the patient’s email or publish them in his personal account on the clinic’s website.
How much does it cost to undergo an MRI of the ankle in Russia?
Another point worthy of attention is the cost of MRI of the ankle joint. It is not easy to say for sure how much diagnostics cost in Russia, since prices for the procedure may vary significantly in different regions of the Russian Federation. On average, the cost of tomography fluctuates around 4000-5000 rubles. If they have a compulsory health insurance policy, patients still have the opportunity to undergo the procedure free of charge at their place of residence. Details should be clarified with the attending physician or the insurance company that issued the policy.