Baby teeth and molars - what's the difference?
The differences between temporary and permanent are the following characteristics:
- The roots of baby teeth are shorter, widely spaced and angled. This is explained by the need for the formation of molars;
- the enamel of temporary teeth is bluish, it is much thinner, and therefore more susceptible to the development of caries;
- The child’s milk teeth are smaller than the molars;
- The number of some teeth is not equal to the number of others. There are fewer temporary ones, because some elements of the series immediately grow as radicals;
- the tissue of baby teeth is poorly mineralized;
- temporary teeth grow vertically, and the crowns of permanent teeth are directed outward (towards the lips and cheeks).
When is an x-ray indicated in childhood?
An x-ray of the child’s baby teeth is scheduled the day before treatment. The doctor resorts to this measure to make sure that the upcoming therapy will not harm the process of formation of permanent teeth.
Specific indications for radiography include:
- the presence of carious lesions and other destructive processes;
- the appearance of jaw anomalies;
- diagnosing abscesses;
- the need to control impacted teeth and the natural change of temporary elements to molars;
- Carrying out bite diagnostics;
- inappropriate condition of the root system of temporary teeth.
More often, the procedure is resorted to in case of delayed growth of permanent elements of the series.
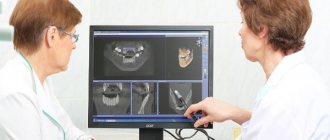
Types of x-rays when examining children
Depending on the goals of the study, there is a need to obtain one or another type of x-ray. Among them:
- targeted radiographs - show one or a pair of teeth and nearby soft tissues;
- panoramic image of the jaw - displays a picture of the dentition along with the rudiments of the radical elements;
- 3D images are three-dimensional images of the entire jaw (upper, lower row) or a section of it.
The difference between panoramic and targeted radiographs
The difference between a panoramic X-ray and a targeted X-ray is the area of study. In the first case, the object of study is the jaw row, in the second - a specific area of the child’s gums, jaw or oral cavity.
Sight shot
Panoramic shot
In the process of targeted radiography, the beam tube is brought closer to the soft tissues. A successful shot shows one or two elements adjacent to each other.
3D modeling in negative
We are talking about a procedure carried out using innovative equipment that allows one to obtain a 3D image of the jaw row or its area. Such an image helps to determine the location of pathological canals, areas of the root system, and fillings. A study is scheduled on the eve of endodontic therapy and implantation.
3D
Modern methods of X-ray diagnostics
Ultrasound is a study of internal organs, which is carried out using ultrasonic waves.
It is carried out in real time and in 2D or 3D images. That is, you can not only see the organ, but also watch its contractions or some movements in it. Ultrasound diagnostics helps not only to look at organs for the presence of tumors, but also to see disturbances in blood circulation. This is important when studying blood vessels and their functioning. The method is also informative in diagnosing diseases of the thyroid gland and brain. X-ray is a study based on the passage of x-ray waves through human tissues and organs. This image is recorded on a special film. A very simple and accessible technique. Although now they mostly use more informative methods. This examination is superficial.
Explanation of X-ray
X-ray of the jaw is a research method using electromagnetic waves, widely used in dentistry, sports medicine and traumatology.
The procedure is carried out in private diagnostic centers and regular hospitals, and in the first case, digital equipment is most often used, which involves a lower radiation dose.
- carious lesion;
- inflammatory processes in the gums, tooth roots;
- dislocations and damage to bone tissue;
- foreign objects;
- malignant neoplasms and cysts;
- accumulation of liquids;
- developmental pathologies caused by genetic diseases;
- abscesses;
- cracks in the dental canals;
- gum diseases.
You cannot take x-rays without a doctor’s referral, since only a doctor can determine whether you need exactly such a diagnosis and what type of examination to undergo (upper or lower jaw, panoramic, etc.).
The procedure is prescribed:
- before bone grafting and prosthetics;
- in preparation for implantation;
- if you suspect cancer;
- to confirm the connection between ENT pathologies and dental diseases;
- as part of the diagnosis of periodontitis, root fractures, caries in hidden areas;
- with incorrect positioning of the tooth joint;
- in case of injury.
There are relative contraindications for x-rays of the jaw - during pregnancy and age less than seven years. At the same time, it happens that you cannot do without pictures, and then the doctor may recommend this type of examination.
Radiography is a fairly old method of examination, but despite the fact that today there are MRI and CT scans, x-rays are often performed today. And the reason for this is not only the cost of the procedure.
Compared to other diagnostic methods, jaw x-rays have the following advantages:
- the ability to obtain data that cannot be obtained during a routine inspection;
- The patient receives the results of the study as quickly as possible, so that he can immediately begin treatment;
- the ability to take pictures in different projections;
- the procedure lasts only a few seconds, this usually does not cause discomfort to patients, although the diagnosis requires maximum immobility from the patient;
- safety for the body (subject to diagnostics using modern equipment).
If for any reason you need an X-ray of your jaw, our clinic is what you need. Regardless of what pathology you have, our specialists will conduct the most informative diagnosis in the shortest possible time.
Thanks to the most modern equipment, we will carry out the most accurate diagnosis with minimal risk to health.
X-rays are examined in two different ways:
- Interproximal x-ray shows the edges of the jaw. Such a study effectively helps to detect the problem of hidden caries and pathologies of wisdom teeth.
- Occlusal x-ray is a method that is used to study specific areas of the jaw.
In addition to the standard method of performing an orthopantomy (imaging the entire jaw), there is also a targeted X-ray effect on the tooth. In this method, an x-ray film wrapped in thick, opaque paper is placed behind the tooth. Using a special X-ray tube, one specific tooth is x-rayed.
- Radiovisiography is one of the methods of x-ray diagnostics, in which the matrix of the device itself is located directly at a specific tooth. This modern type of digital x-ray allows the doctor to obtain a high-resolution image directly on a computer monitor and study it in detail. This method is one of the safest. However, it is not used in all clinics, since this technology is expensive.
- CT (computed tomography) is the safest x-ray method. It is recommended for use by children and pregnant women if necessary. The procedure does not take more than 30 seconds. At the same time, an x-ray of the lower jaw, upper jaw and the area adjacent to them will be taken.
X-ray examination for diagnostic purposes has virtually no contraindications. The only contraindications (with the exception of pregnancy) are severe oral bleeding and the patient being in a serious or unconscious condition.
All kinds of methods are developing at great speed, so there is practically no need to worry about their imperfections. Specialists offer several types of procedures for their patients:
- Palatal photograph. It is the most popular, its essence is that it can be used to examine certain areas - the maxillary joint, part of the upper or lower teeth. That is, it gives a specific result that interests the doctor and the patient.
- Panoramic X-ray. Helps determine the condition of the entire row of teeth, as well as the position of the jaw joint. At the same time, it is used not only for fractures or dislocations, but also for a general assessment of the “picture”.
- Periapical radiography. Determines the condition of the tissues around the tooth and its root. A very significant procedure for identifying incipient diseases.
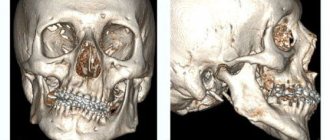
- 3d photo. The most convenient option for the doctor, as it shows a three-dimensional image of the jaw, which allows you to monitor the course of treatment. Accurately detects diseases such as maxillary sinus cysts.
- Bitewing snapshot. The patient squeezes the film between the teeth, so the dentist can determine whether any deviation is present. This technique usually refers to pediatric radiography.
All this is available to anyone, and the benefits of x-ray diagnostics are becoming more and more important over time. The problem of dental diseases is very relevant now, so experts strive to optimize treatment procedures.
Using X-rays, you can clearly visualize the temporomandibular joint.
Compared to X-rays, modern jaw CT algorithms result in less radiation exposure, which allows the dentist to re-prescribe a CT scan if dynamic monitoring of the condition of the treated tooth is necessary.
We suggest you read: Snot during teething in children
CT is a fairly high-quality diagnostic method. Computed tomography is the ideal method for diagnosing intraoral changes. To improve the quality of diagnosis, specialists use image enhancement with a contrast agent.
The duration of the procedure is several minutes when using the latest generation equipment. Innovative devices have been installed in the medical, ZAO, Central Administrative District. These clinics can perform 3D modeling using software applications that build 3D images based on tomograms.
1. Pathology of the facial part of the skull; 2. Hidden caries;3. Condition of the oral cavity before implantation;4. Traumatic damage to the upper and lower jaw;5. Anomalies in the development of the skeletal system;6. Arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint;7. Dystopia of the head;8. Assessment of the condition of the sinuses;9. Presence of cysts, foreign bodies inside the sinuses; 10. Definition of fistula tracts;11. Benign, malignant tumors; 12. Retention, cleft palate;13. Quality of canal filling.
Computed tomography of the jaw is prescribed before planning dental operations. After the manipulation, dynamic monitoring of the intervention status is required. Cone-beam tomography is also prescribed for these purposes.
In medical clinics in Moscow (ZelAO, North-Eastern Administrative Okrug, ZAO, South-Western Administrative Okrug, VAO, TAO, NAO) and the Picasso Center, CT scans of the jaw are prescribed according to strict indications. Not every person can be prescribed radiation diagnostic methods. The main contraindication to the examination is pregnancy. Ionizing radiation can cause abnormalities in the genetic apparatus, since radiation affects cells with active growth.
Under the influence of radiation, a teratogenic effect occurs on fetal tissue, which increases the likelihood of not only developmental anomalies, but also changes that are incompatible with life.
3D and 2D CT scans (separated by red line)
Another contraindication to the examination is the patient’s weight over 200 kilograms. The diagnostic table of an X-ray machine can withstand such a mass.
• Contrast computed tomography is contraindicated during breastfeeding. The substance passes into milk and is therefore dangerous to the health of the baby. Complete release of contrast from the body occurs after 48 hours; • Contrast should not be performed in case of renal failure. The contrast is delayed, which increases its pathological effect on other organs.
The situation provokes severe allergic reactions; • In cases of severe coma or shock, diagnostic manipulations cannot be performed on a computed tomograph, especially with contrast. Only for emergency indications is an examination carried out to identify a hematoma or brain tumor.
Comparative characteristics of tomography of the jaw with radiography. In addition to low radiation exposure, CT visualizes even small cavities and clefts. The study allows us to obtain a three-dimensional model that clearly shows the structure of the jaw.
When performing radiography without contrast, cracks and tumors can be visualized. During the examination, 2 projections are performed - lateral, direct, which allow obtaining more diagnostic information, but at the same time the radiation dose to the patient increases.
Features of the procedure
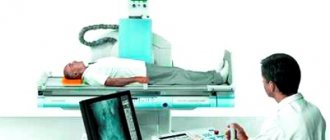
To x-ray the jaw of a child with baby teeth, a film or digital device is used. The equipment is placed in a specially designated room, where the photo laboratory is also located.
The algorithm of action for the specialist and the patient is as follows:
- Before the procedure, the child needs to remove metal items (watches, jewelry, glasses, etc.).
- A special protective apron is put on the patient’s body, into which lead plates are sewn. Thus, the child’s internal organs are protected from the adverse effects of x-rays.
- The subject is asked to press a plastic plate with his teeth. The patient's lower jaw should be pressed tightly against the septum of the device. During the examination, the patient is required to remain motionless.
- The plates of the X-ray equipment begin to move around the child's head. This process takes no more than 20 seconds.
At the end of the examination, the panoramic image is printed on paper or transmitted electronically.
The principle of intraoral radiography (sighting) is somewhat different. The patient is seated on a chair and a protective apron is used. After the child opens his mouth, the specialist installs a film or matrix inside the examinee’s oral cavity. The doctor then places the machine's tube near your mouth. The duration of the procedure is no more than 60 seconds.
The result of the x-ray examination is saved on the computer. This makes it possible to further monitor the dynamics of the clinical picture.
Indications for use
There is no clear list of symptoms when one should sound the alarm due to the individual characteristics of the human body. But, if problems begin with limited functional mobility of the lower jaw and connecting joint, then this is a reason to seek help.
Among other generally accepted signs, pain syndrome in a given zone is distinguished. Moreover, this can be either an acute pain that occurs when performing a certain movement, or an aching pain syndrome.
You also need to pay attention to:
- facial asymmetry;
- clicking and other sounds when chewing food;
- tinnitus;
- dizziness.
If you notice at least one of the above symptoms along with joint pain, you should immediately contact a traumatologist or maxillofacial surgeon for advice.
X-rays are also taken to determine the extent of damage to functional deviations that are caused by:
- dislocations;
- subluxations;
- fractures.
When a patient undergoes surgery, even if it is an ordinary plastic surgery, it is still impossible to do without an image. More serious reasons for visiting an x-ray office may be the following diseases at different stages of development:
- rheumatism;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- malocclusion.
Moreover, the sooner the victim contacts the attending physician, the more effective subsequent treatment will be, based on the detailed information received.
The issue of X-ray safety for children
Any X-ray radiation, including in the dental industry, carries a certain degree of danger to the patient’s health. Research in the field of medicine confirms the possibility of developing acute radiation sickness when exposed to increased radiation. However, X-ray equipment is not enough to provoke it.
X-raying of a child’s primary teeth can be safe if the examination schedule and radiation safety standards are followed.
The permissible annual exposure rate, according to regulatory documentation, is 5 mSV (millisievert). In the case of small patients, as well as pregnant and lactating women, this figure is halved.
Dental radiography is characterized by minimal mZV indicators. With digital X-rays, the amount of single exposure is 0.01-0.03 mSv. In this case, the permissible single dose is 0.1 mSV. The development of radiation sickness is discussed only when this figure increases by (0.7 ZV).
X-rays are often prescribed periodically, for example, as part of a long therapeutic course. How often can dental x-rays be taken? According to WHO, if 5-6 such procedures are carried out during the year, the radiation background of a small patient will not be disturbed. However, one should not lose sight of the factor of the presence of its own background radiation in the area in which the child lives. For example, for Moscow this figure is 20 µSV.
There is no official evidence that chronic doses of irradiation to the oral cavity (for example, long-term therapy) result in the development of cancer.
Is it possible to refuse x-rays for a child?
The child's parents have the right to refuse x-rays. However, responsibility for making such a decision rests entirely with them. Such diagnostic methods are not always able to provide a complete picture of the condition of the patient’s oral cavity.
Without X-rays, the doctor cannot arrange prosthetics. If you refuse the procedure, the planned treatment becomes impossible.
Radiography of baby teeth for children is included in the list of the most informative diagnostic methods. This procedure helps to assess the condition of the row elements, nearby soft tissues and identify the rudiments of permanent teeth without harm to the child. For diagnostic purposes, panoramic, targeted and 3D images are created. Digital X-ray is recognized as the most efficient and safe diagnostic tool.
Photos of the jaw
Help the project, share your review 
Join the discussion of the article:
Site search
Recommendations
Sangviritrin - instructions for use of the solution and indications for use for dental problems
Mouth spray: the best formulations with prebiotics, their cost and application features
Falimint - reviews, instructions for use and expert assessment of effectiveness
Stomatofit - complete instructions for use, dosage, selection of analogues and price comparison
Ketorol for toothache - reviews of use and effectiveness. Cost and dentists’ opinions about the medicine
Antibiotics for flux: the most effective remedies and tips on choosing medications for children and adults
Metrogil denta - analogues, advantages of use, composition features and indications for use
Periodontocide - means for prevention, release form, methods of application and indications for use
Medicine for teeth - rating of the best remedies for eliminating pain and relieving swelling. Doctors' advice and cost of the most effective drugs
Medicine for gums - the most effective gels, ointments and tablets for relieving pain and discomfort
Blue for stomatitis - methods and features of using the medicine for children and adults
Cholisal is a dental gel for gums and oral cavity. Price and instructions for use
Kamistad gel - instructions for use, features of use, composition, indications and contraindications
Lincomycin - instructions for use, cost, reviews from patients and doctors
Ointment for gums - the choice of the most effective healing and anti-inflammatory agents
Ibuprofen - clinical practice, instructions for use and safety tips
Pain after wisdom tooth removal - possible complications and duration of pain after removal
Removal of a wisdom tooth - indications, features and main stages of the removal operation
Toothpicks - benefits, harm and tips for choosing safe toothpicks from the best materials
Bone dental implantation – myths and truth about bone tissue augmentation. Step-by-step description of the operation
Sections
Most read on the site:
A tooth hurts at night The sky in the mouth hurts Vitamins for teeth Inflammation of the gums Inflammation of the tooth Gel for gums Herpes in the mouth Dental hygiene Gorpils Dekasan Dental floss Tartar Plaque Ibuprofen Irrigator How to choose a mouthwash How to brush your teeth Kamistad gel Bleeding gums Medicine for gums Medicine for teeth Cavity treatment mouth Lincomcin ointment for gum metrogil denta nystatin swollen upper lip whitening paste gums gums periodontocide Prevention Pomic in the mouth Solution to the oral cavity of Sinki sinky from stomatitis spray spray stomatophytite dentistry in the gums, ultrasound halitosis Hepilor Holisal Crunches the jaw Itchy teeth Cleaning gums Splinting teeth Mouth ulcers
Copyright © 2020 ZubkiExpert.Ru is a leading online portal about dentistry. Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment! Home | Sitemap | Dentist consultation