Features of dental x-rays for children
Previously (about 10-15 years ago), x-rays of baby teeth were not a common procedure. Some parents even believed in the myth that baby teeth have neither a root nor a nerve, so the causes of toothache must lie somewhere on the surface, that is, on the crown. This is absolutely not true, and childhood toothache can be caused by the same reasons as in an adult (more on this below).
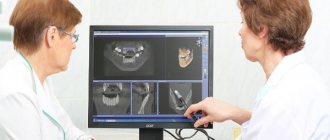
When asked whether children undergo dental x-rays, we can confidently answer that yes, they do. Moreover, to accurately diagnose the problem and build the correct treatment plan, this is necessary. Another thing is that preference should be given to relatively safe types of x-ray examination, for example, digital.
There are several recommendations for parents to listen to when going for an x-ray with their child:
- You need to come to the clinic in advance so that you have time to psychologically prepare your child for the procedure. You need to tell him that the x-ray will not cause any pain, so you shouldn’t be afraid of it.
- The child's clothing should be loose, easily removable and without complex metal decorations.
- As for girls, you need to give them a simple hairstyle, without using metal pins, bobby pins, etc.
Who should I go to with the photo?
Most often, the results of an X-ray of a child’s jaw are required by the dentist, so he sends the child for examination to establish or clarify the diagnosis.
However, in some cases, an x-ray examination of the oral cavity may be prescribed by an otolaryngologist.
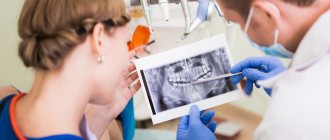
To correctly decipher the result obtained, special knowledge is needed, so studying it may require the participation of several specialists.
Having received the result, parents and the baby must show it to the doctor who referred the child for this procedure. Based on the image, the specialist will determine whether the patient needs treatment. If pathology is detected, the doctor will determine the degree of its development and location.
Types of X-rays for children
Like adults, children may be prescribed different types of x-rays.
Sight radiograph
A targeted radiograph is performed using a special digital visiograph. A specific problematic tooth or several adjacent ones (maximum 4) are removed.
Panoramic radiograph
The panoramic image shows the entire oral cavity: the upper and lower dentition, teeth that have not yet erupted, and the jaws. It also affects the sinuses. An orthopantomogram (this is what a panoramic image is called) is often prescribed to young patients when it becomes noticeable that their teeth are erupting incorrectly: with an inclination, rotation, and so on. In this case, X-rays help to understand whether there is an anomaly in the development of the jaw bone. There are cases when, after the loss of baby teeth, permanent teeth do not appear for a long time. An x-ray will help identify the cause of this deviation.
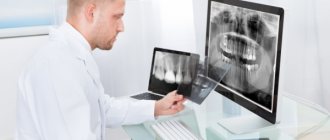
Decoding the results
The finished images must be deciphered by a specialist. It is possible that several doctors will be present during the decoding, for example a radiologist
, dentist, otolaryngologist.
The photographs are used to assess how symmetrically the teeth and jaws are positioned. If a focus of any pathology is detected, it is important to determine its exact location and size.
When diagnosing a jaw fracture, you need to determine its complexity, consider whether there are fragments and how they are located.
If a tumor-like neoplasm is detected, it is important to assess its size, consider its boundaries (clear or blurred), and determine its location.
What will be in the photo
There are two types of shots: panoramic and targeted.
The difference between them is that a panoramic image will show the entire dentition on both jaws, while targeted radiographs record the condition of a separate area of the oral cavity, jaw or gums. During a targeted X-ray, the beam tube is close to the problematic soft tissues, and 1-2 nearby teeth appear in the image. The panoramic image reflects the condition of the lower and upper jaws, the localization of tooth germs and the location of the roots. You can estimate how many teeth have already appeared and what condition the rudiments are in.
Thanks to such an image, it is possible to prevent possible problems with the bite: if the image shows that one of the teeth lies unevenly in the jaw and there will most likely be a delay in eruption, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment. It is easier to get rid of the problem at the stage of its appearance than to waste time and money on expensive braces in the future.
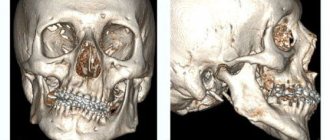
With the help of modern installations, it is possible to obtain a 3D image of the jaw, which will reflect the location of all fillings, roots and pathological canals. This procedure is usually performed before starting endodontic treatment and when planning to install an implant. Such a photo will cost more, but in some cases you cannot do without it.
What unformed root tips look like on an x-ray
In unformed tips, the length of the root is almost normal, the walls are parallel to each other. The wide root canal ends in a funnel-shaped extension. In the area of the apex, the periodontal fissure merges with the growth zone, which incompetent specialists sometimes identify as a pathology.
Throughout the entire length of the root and at the apex, a compact plate of the socket wall is differentiated. This picture is typical for the upper central and lateral incisors in 8-year-old children, for the lower central incisors in 6-year-old children, as well as for the lower lateral incisors and first lower molars in 7-8 year old children.
Indications for testing
To determine the extent of caries damage
Children's teeth are susceptible to caries. We cannot assume that caries of baby teeth is not dangerous, since they will fall out anyway. Pathology can spread to permanent teeth even before they erupt. Therefore, it is very important to identify caries and carry out effective treatment.
To identify periodontitis and pulpitis
Periodontitis (tooth root pathology, pulpitis) is an inflammation of the pulp where the nerve is located. It is clear that such diseases cannot be detected during the initial examination, because they are hidden in the tooth itself or inside the gums. The child’s main complaint is pain in his baby teeth, and the ability to identify its cause is through an X-ray photo.
When planning endodontic treatment
Endodontic treatment is a set of procedures aimed at preserving a tooth. When emerging caries causes complications, such as pulpitis or periodontitis, the doctor needs to perform therapeutic manipulations inside the tooth. To understand how much pathology has affected the tooth, what percentage of it is destroyed, you need to take an x-ray.
To assess the condition of the permanent tooth buds
An assessment of the condition of the permanent tooth buds is also required before endodontic treatment. It is necessary in order to understand whether the permanent teeth have been affected by pathology and how close they have already descended to the milk teeth.
To diagnose and determine treatment regimens for pathologies of occlusion or teething
At an early age, it is still relatively easy to correct an incorrectly formed bite or correct the position of erupted teeth. This can be done using braces or other special systems. However, to begin orthodontic intervention, you need to understand how serious the pathology is. X-rays help with this.
To determine the reasons for the delay in the appearance of permanent teeth
If a child does not have baby teeth before one year of age, the doctor may order an X-ray to predict their appearance. Of course, such a developmental pathology as adentia (when there are simply no rudiments of baby teeth) is extremely rare, but it is still worth excluding it completely and understanding how soon the first tooth can appear.
Baby teeth and molars - what's the difference?
The differences between temporary and permanent are the following characteristics:
- The roots of baby teeth are shorter, widely spaced and angled. This is explained by the need for the formation of molars,
- the enamel of primary teeth is bluish, it is much thinner, and therefore more susceptible to the development of caries,
- A child’s baby teeth are smaller than his molars,
- The number of some teeth is not equal to the number of others. There are fewer temporary ones, because some elements of the series immediately grow as radicals,
- the tissue of primary teeth is poorly mineralized,
- temporary teeth grow vertically, and the crowns of permanent teeth are directed outward (towards the lips and cheeks).
How is research conducted?
Panoramic dental x-rays are done for children, just like for adults:
- The child stands inside the orthopantomograph.
- He clamps the plastic tube between his teeth and keeps his lips closed.
- The device blade is moved as close to the patient as possible.
- A picture is taken (while the device rotates around the child’s head). This takes no more than 20-30 seconds, during which you cannot move or breathe.
A targeted photograph is taken as follows: the child sits on a chair and approaches the device.
Next, he wraps his mouth around the digital sensor and clenches his teeth. A picture is taken (takes a few seconds); during this process you cannot move or breathe. To protect the body from exposure to x-rays, a special apron is worn.
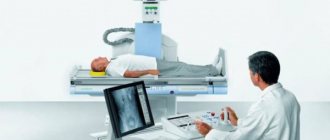
How do you do an X-ray of a child's head?
Many mothers are afraid when their children (especially under the age of 3 years) are prescribed x-rays.
Almost everyone knows about the harmful effects of ionizing radiation, so such anxiety among parents is completely justified. It must be said that when photographing the head, the child’s body is reliably protected by a lead apron or vest, and the radiation exposure received during the procedure is not so great as to seriously affect the growth and development of the child’s body. The quality of the images largely depends on how still the child was during the scan. To minimize his movements, fixing straps are used. To prevent the child from worrying, relatives are allowed to be in the office. If the child is small or very restless, he is given sedatives.
Contraindications
If there is bleeding
Bleeding in the mouth, caused, for example, by problem gums, can affect the quality of the X-ray image. First, the doctor must prescribe hygiene procedures that can stop the bleeding, and only then send for x-rays.
If you feel unwell
If your child is sick, has a fever, or simply feels unwell, you should not take him for an x-ray. It is better to postpone this procedure until complete recovery.
Method of performing an X-ray of a child’s skull
Children from one year old are seated in a chair and secured. There should be no metal pins or headbands in your hair - this can distort the picture of the disease. The body must be reliably shielded with protective equipment. The thyroid gland is covered with a protective collar.
If the baby's parents are present during the x-ray, they also need a protective apron. The time of the procedure and the quality of the image depend on how immobile the regime is observed. After the procedure, to neutralize the negative consequences, the child should drink plenty of fluids.
Features of an X-ray of a newborn's skull
A very young one-month-old child who is unable to stand and sit independently may also be sent for an X-ray of the skull if there are special indications. Such patients are placed on the work table of the X-ray machine, areas of the body that are not to be photographed are covered with a lead apron, and the limbs are secured with special belts.
Possible problems
At the moment the molars appear, certain dental problems are possible. In order to take timely measures to eliminate them, parents must have an idea about them.
A situation is possible in which baby teeth do not fall out in a timely manner, or they have fallen out, but molars have begun to appear in their place. The reason for this must be determined by the dentist, who must be visited without delay. A general x-ray is usually taken to show the degree of development of the molars.
We suggest you read: How to pull out a molar tooth at home yourself
Among the options for the lack of eruption of molars in due time can be indicated:
- Hereditary predisposition, which is the cause of a possible delay in the appearance of molars. If the x-ray shows that the process of forming the rudiments of teeth is underway, then you will just have to wait a little for their appearance.
- Adentia. Disturbances in the processes of formation of tooth germs during the intrauterine development of a child, inflammatory processes can lead to a similar pathology - the absence or death of tooth germs. The solution is prosthetics.
The first time after teething, the tooth is poorly protected from caries and the effects of various bacteria. This is explained by the low degree of enamel mineralization at the initial stage. Almost nothing interferes with the development of caries; tooth tissue is destroyed, pulpitis occurs, with the subsequent risk of its transition to periodontitis. Severe pain, changes in body temperature and deterioration in well-being may occur.
It is highly advisable not to let the situation get worse, not to cause severe pain, but to visit a dentist as soon as painful sensations appear. If a child is predisposed to caries, it is better to carry out preventive procedures, for example, fissure sealing. The folds on the chewing surface are covered with a composite material that protects such natural cavities from the accumulation of food debris in them, the development of bacteria, and inflammatory processes.
In the worst case, you can lose a tooth.
Teeth grow crooked
A common situation is when the molar has already begun to erupt, but the baby tooth does not want to fall out. The result is that the new tooth seeks alternative growth paths, which leads to its displacement and change in the direction of growth. Hence the malocclusion and the alignment of the dentition. Treatment by an orthodontist will be required.
If this situation occurs, you should not remove or loosen a baby tooth yourself; you should visit a doctor.
An alarming symptom of the presence of diseases (caries, etc.) in the oral cavity, or there are problems with the entire body (connective tissue diseases, diabetes, etc.). A visit to the doctor is mandatory.
This is necessary to develop a strategy for restoring a lost tooth. This is necessary for the proper growth of the remaining teeth and the formation of the maxillofacial system. Considering that the jaw tissue is still in the process of growth, prosthetics are only possible temporary, which must be adjusted as the jaws develop. Permanent prosthetics will be available only after their formation is completed.
Injuries
The first few years after teething, teeth are at increased risk of injury from impact. Sports injuries, falls, and blows can lead to chipping of parts of the tooth and cracks. Be sure to contact a dentist who will restore the lost part with modern materials.
Is it possible to refuse x-rays for a child?
The child's parents have the right to refuse x-rays. However, responsibility for making such a decision rests entirely with them. Such diagnostic methods are not always able to provide a complete picture of the condition of the patient’s oral cavity.
Without X-rays, the doctor cannot arrange prosthetics. If you refuse the procedure, the planned treatment becomes impossible.
Radiography of baby teeth for children is included in the list of the most informative diagnostic methods. This procedure helps to assess the condition of the row elements, nearby soft tissues and identify the rudiments of permanent teeth without harm to the child. For diagnostic purposes, panoramic, targeted and 3D images are created. Digital X-ray is recognized as the most efficient and safe diagnostic tool.
Sources
- https://afrodita-spa.ru/diagnostika/rentgen/vidy-diagnostiki-rentgena-zubov-rebenka
- https://cordiacardio.ru/rentgen/foto-detskoj-chelyusti.html
- https://medfenik.ru/rentgen-detskoj-chelyusti-do-poteri-molochnyh-zubov.html
- https://martinka.ru/dopolnitelnye-uslugi/rentgen-molochnykh-zubov-rebenka/
- https://iDiagnost.ru/issledovaniya/rentgen/kak-podgotovit-rebenka-k-rentgenu-molochnyh-zubov
- https://osnimke.ru/zuby/rentgen-molochnye-zuby.html
[collapse]