Types of X-ray diagnostics
There are two main X-ray examination techniques:
- Fluoroscopy (otherwise called x-ray transillumination) ─ X-rays, passing through an intensifying apparatus, are displayed on the monitor screen. The advantage of this type of diagnosis is that the study takes place in the present tense. The structural features and functions of the organ, as well as the features of the movement of contrast through it, are assessed.
A significant disadvantage of fluoroscopy is the relatively high radiation dose compared to radiography.
- Radiography is the projection of the object being studied using x-rays onto a special film.
For x-ray examination, depending on its purpose and area of conduct, various x-ray contrast agents can be used (for example, oil or water suspensions of iodine preparations for bronchography).
These types of diagnostics differ in the method of execution; the patient’s preparation is similar.
X-ray with functional tests
This type of research is done when it is necessary to examine the most mobile parts of the spine - cervical or lumbar. The indication for its implementation is severe pain in a certain part of the spinal column. It is best to take several pictures at once in different projections - both sides (left and right), as well as the back. Tests are carried out in three body positions.
- Lying bent or straightened. In the first case, the patient lies on his side, with his head resting on his arm bent at the elbow. The legs are bent at the knees and pulled towards the stomach. In the extended position, one arm is bent and placed behind the head, and the other touches the edge of the table. It is important to maintain lumbar lordosis.
In general, such tests are selected for a particular patient on an individual basis, depending on the indications. The most important condition is the opposite direction of the body position. Functional examination is usually carried out in a familiar x-ray room.
X-ray of the back is one of the most commonly used diagnostic methods. It is important to carefully prepare for this study in order to obtain the most reliable images. Otherwise you will need to do them again.
Doctor's tactics
Before prescribing any examination to his patient, the doctor interviews and examines him, carefully reads his anamnesis and medical history. Having put forward a hypothesis about a possible disease, the doctor may resort to x-rays as one of the ways to confirm it.
The doctor gives the patient a referral for an x-ray
In this case, it is important to be guided by the principles of necessity and sufficiency ─ to use only those methods and diagnostic methods that will be sufficient to determine the disease, but not unnecessary.
Before moving on to diagnosis, it is important to explain to the patient the purpose of the study, the reasons why this particular method was chosen and not another, and also explain what the preparation consists of.
Contraindications
Any x-ray examination has a number of contraindications:
- Children under 15 years of age.
- Pregnant women.
In pregnant women, X-ray radiation can negatively affect the development of the fetus, and in children it can cause disruption of the growth and development of organs and systems.
The doctor may insist on conducting an examination if it is impossible to use other methods to verify the diagnosis.
During the upcoming x-ray examination, it is necessary to remember that there are basic principles of preparation for it in order to conduct a high-quality diagnosis.
Is it possible to do x-rays and fluorography for pregnant and nursing mothers?
Often girls are concerned about the question of whether it is possible to do fluorography and x-rays during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnancy is a contraindication for X-rays and fluorography. This is due to the negative effects of X-rays on the fetus. However, in some cases, an x-ray may be performed (fluorography is not prescribed for pregnant women). It is prescribed when the life of a pregnant woman is in danger. In this case, the benefits to the woman outweigh the risks to the fetus.
Consequences of X-ray examination during pregnancy:
- In the first trimester, this diagnostic procedure should not be performed, as it can cause a miscarriage;
- In the second trimester, irradiation provokes the development of congenital malformations of various organs;
- In the third trimester - can lead to complications during childbirth.
Fluorography is carried out in the first days after childbirth to identify tuberculosis in a woman. After the procedure, it is recommended to express a portion of milk, after which you can continue to feed the baby.
General principles of preparation
X-ray technician helps the patient to take the correct position
- It is necessary to free the area under study from clothing as much as possible.
- The examination area should also be free of dressings, patches, electrodes and other foreign objects that could reduce the quality of the resulting image.
- Make sure that there are no various chains, watches, belts, hairpins if they are located in the area that will be studied.
- Only the area of interest to the doctor is left open; the rest of the body is covered with a special protective apron that screens out X-rays.
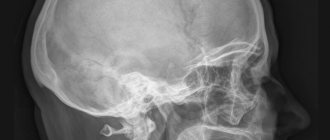
X-ray of the skull, spinal column and joints
Both an overview and a targeted image of the area of interest to the doctor can be prescribed.
There is no preparation for x-rays of the skull and several parts of the spine: from the cervical to the thoracic.
With x-rays of the lumbar and sacral spine, examination of the pelvic bones, as well as x-rays of the hip joints, the patient is prescribed a diet and bowel cleansing, all of which is described in detail in preparation for the examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
No preparation is needed to examine joints and limbs.
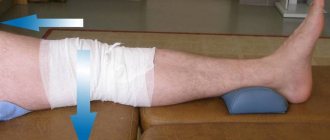
Radiography is widely used in traumatology
Expert advice
Experts advise patients to remove foods such as dairy products, vegetables and fruits, beans, and brown bread from their diet a few days before the x-ray. After all, they are the ones who contribute to increased flatulence and can negatively affect the quality of x-rays.
Before going to the clinic for an x-ray of the lower back, you need to take several tablets of activated charcoal three times a day three days before the procedure. To make the patient feel more calm and remain motionless during this procedure, experts recommend drinking valerian root a couple of days before the x-ray. You need to take sedatives three times a day, 15 drops at a time.
You should not eat before the x-ray. The last meal should be at least 19 hours before the x-ray. Experts also strongly recommend doing two enemas before x-raying the lumbosacral spine, one in the evening and the second in the morning before visiting the hospital. On the day when the patient is scheduled for x-rays, you should not drink, eat, or smoke. Even if you are a heavy smoker, you will have to be patient if you do not want to redo the x-ray several times.
If you follow these simple recommendations from experts, then the diagnosis and x-ray of the lumbosacral spine will be clear, and doctors will be able to determine from the first time what exactly is bothering you from the image. Also, if good images are available, doctors will be able to immediately begin treating patients.
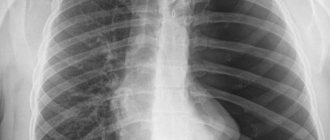
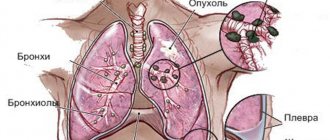
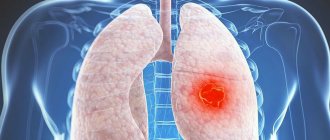
Chest x-ray
- Plain radiography of the chest organs allows you to diagnose pathological changes in the skeleton, lung tissue, the condition of the pleural cavity, and assess the size and shape of the shadow of the heart and adjacent vessels.
There is no need to prepare for this study.
- Bronchoscopy and bronchography make it possible to obtain X-ray images of the trachea and bronchi after the administration of contrast. Needed for studying parts of the lungs that are inaccessible to endoscopy, when diagnosing various bronchopulmonary diseases and/or planning surgical intervention.
As a preparation, if there is sputum, the lungs should be cleared of it, for example, with the help of expectorants prescribed in advance before the study. On the day of the study, it is forbidden to eat or drink.
Is it possible to eat and drink before fluorography and x-rays?
Fluorography can be performed at any time of the day. The result will not be affected in any way by the consumption of food and liquid. Since a fluorographic image shows organs in a pile of cells, food cannot distort the result. The image shows the lungs, heart, large and medium bronchi, aorta and diaphragm, but the esophagus and stomach are covered and not visualized.
X-rays can also usually be taken after eating and drinking. However, if a contrast agent is used, the examination is carried out on an empty stomach. You should also not drink for at least 60 minutes before an x-ray with contrast. X-rays of the stomach, duodenum, and large intestine are also performed on an empty stomach.
X-ray of the breast
X-ray examination of the mammary glands (mammography) allows us to identify pathological changes in the glands, mainly of a tumor nature. Prescribed according to indications by a gynecologist, oncologist or other specialist.
As a screening method, it is used for early diagnosis of breast cancer in women over 40 years of age.
No preparation is required for a breast x-ray.
Mammography is recommended to be taken at the beginning of the menstrual cycle from days 5 to 12
Is it possible to smoke before fluorography and x-rays?
Heavy smokers may have a question: is it possible to smoke before an x-ray examination? To answer this question, you need to understand what fluorography and x-rays show. The image shows the pattern of the lungs, which changes in the presence of various lung pathologies.
If a person smokes daily for many years, then certain changes occur in his lungs. And they will be visible in the photo. But these pathological changes can also occur in a person who does not smoke and has never smoked. Therefore, based on the results of X-rays and fluorography, it is impossible to say unambiguously whether a person smoked before the examination or not.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that smoking before the examination does not affect the result.
X-ray of the digestive organs
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity gives a general idea of the condition of the gastrointestinal tract in the patient. Allows you to diagnose intestinal obstruction, the presence of free gas (if there is perforation of a hollow organ).
No special preparation is required.
- X-ray of the esophagus. Without a contrast agent, it is needed to search for foreign bodies.
Most often, a study with contrast is necessary ─ to assess the motor function of the organ, determine the presence of possible narrowings or expansions, neoplasms, hiatal hernias.
Preparation for fluoroscopy includes ingesting the required volume of contrast agent before the examination.
- An X-ray of the stomach and duodenum shows the size and shape of the stomach, its motor activity, the presence of defects in the mucous membrane, neoplasms, and stenoses.
A few days before the study, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes dishes and foods that cause increased gas formation. The study is carried out on an empty stomach.
X-ray of the stomach is performed on an empty stomach
The day before the examination, a cleansing enema is given or a laxative is prescribed. It is possible to use enterosorbents.
- X-rays of the large intestine show the size and position of the intestine, as well as its motor function.
During irrigoscopy, a barium suspension is administered rectally and fluoroscopy is performed. A combination of barium suspension and air is possible (double contrast technique).
Preparation is similar to preparation for the examination of the stomach and duodenum.
How to prepare for an X-ray examination
An X-ray examination is carried out to identify the disease, clarify the location of the pathological process and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
The internal organs and tissues of a person, depending on their anatomical structure, have different densities, therefore, when X-rays pass through, the degree of their absorption is reflected in the contrast of the resulting image.
The natural contrast in x-ray examination is air, bone and fat tissue. Organs containing such tissues are clearly visualized. In other cases, for example, in order to make hollow organs “visible”, it is necessary to administer a contrast agent. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to obtain their graphic image.
But in any case, in order for the contrast and visibility of a tissue or organ to be as close as possible to “anatomical” indicators, high-quality preparation for the study is required.
Preparation for x-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT)
1. Preparation for gastric examination
- The study is carried out on an empty stomach, and you need to completely refuse food 6-8 hours before the study;
- 3 days before the study, you should give up hard-to-digest foods such as legumes, mushrooms, pickles, olives, brown bread, etc. Plus, you need to stop drinking alcoholic beverages 2-3 days before the test.
- on the eve of the study, you need to limit smoking, consumption of spicy and fiery foods;
- It is advisable to conduct the study in the morning (before 11.00);
- before the study, you should not
eat food or take tablets (with the exception of patients with diabetes), or drink (even a sip of water); It is advisable not to brush your teeth to avoid liquid entering the stomach.
2. Preparation for the examination of the small intestine
- It is necessary to limit food intake after 19 pm.
- 2-3 days before the test you should avoid foods that cause gas formation. These are legumes, vegetables and fruits, black bread, fresh milk, herbs, etc.;
- 2-3 days before the study you need to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and limit smoking;
- It is advisable to conduct the study in the morning (before 12-13 pm).
3. Preparation for examination of the colon (irrigoscopy and irrigography)
- It is necessary to limit food intake after 7 pm; a light breakfast is recommended in the morning;
- 2-3 days before the examination, you should avoid foods that contribute to gas formation. It is recommended to switch to boiled meat, fish, omelets, cereals, etc. It is advisable to take an infusion of chamomile and thyme on the eve of the test;
- The study is recommended to be carried out in the morning (before 12-13 pm);
- Before the study, it is recommended to cleanse the colon in any of two ways:
Cleansing enema
On the eve of the examination - at approximately 16.00 - it is advisable to take a mild laxative with plenty of water. This could be 30 g of petroleum jelly (or castor) oil or the drugs Regulax, Bisacodyl, etc. It is advisable to consult a doctor first.
In the evening, after dinner, at approximately 19.00, you need to give an enema with boiled water at room temperature using an Esmarch mug (1.5 liters of water). Perform the enema while lying on your left side. In the morning - 2 hours before leaving the house - repeat the enema.
Colon cleansing by taking Fortrans powder orally
The dosage of the drug depends on the patient's weight. One powder dissolves in 1 liter. boiled water at room temperature and drink in small sips for 1 hour.
If the patient’s weight is up to 60-65 kg, then it is necessary to take 2 powders (the evening before the test), dissolved in 2 liters. boiled water at room temperature for 2 hours. And in the morning - 2-3 hours before leaving the house - give a cleansing enema, as described above.
If the patient’s weight is from 70 to 80 kg, then on the evening before the test it is necessary to take 3-4 powders, which dissolve in 3-4 liters, respectively. water and taken within 3-4 hours. In the morning - 2-3 hours before leaving the house - a cleansing enema is performed.
If the patient’s weight is more than 80 kg, then it is necessary to take 4 powders in the evening according to the scheme described above, and in the morning - perform a cleansing enema.
Preparation for x-ray examination of the urinary tract (excretory and survey urography)
- before the study, it is necessary to limit food intake after 7 pm; in the morning, a light breakfast is required, which may include porridge, white bread with cheese, hard-boiled egg, tea, etc.;
- 3 days before the test, exclude foods that stimulate gas formation: legumes, vegetables and fruits, brown bread, fresh milk, herbs, etc.;
- Do not take saline laxatives;
- In the evening, it is recommended to take Fortrans orally (as described above);
- It should be borne in mind that if you have an allergic reaction to iodine or iodine-containing drugs, the study is contraindicated.
Preparation for examining the patency of the fallopian tubes (hysterosalpingography), as well as for radiography of the lumbar spine, is the same as for examining the urinary tract (described above).
Preparation for fluorography (lung examination) is not required.
You can learn more about the indications and contraindications for a particular study, as well as the nuances of preparing for it, from an ON CLINIC radiologist.
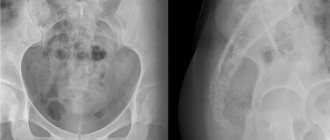
X-ray of the urinary system
Patient preparing for x-ray examination of kidneys and urinary tract
- Survey radiography of the kidneys and urinary tract helps to form a general impression of the shape and position of the kidneys, the condition of the ureters, and determine radiopaque stones.
- Several types of urography (excretory, retrograde) provide more information than the previous study.
As preparation, the diet already described above and laxatives on the eve of the study are prescribed.
Preparation for radiography and fluoroscopy is quite simple, and if performed correctly and with high quality, it allows the doctor to obtain the most informative results.