What is the coccyx and its functions?
Before you learn how to do an X-ray of the coccyx
, you should become more familiar with the functions of this part of the spine. It is a rudimentary organ, which during the process of human evolution stopped developing into a tail, since there was no such need. The tailbone looks like the curved tip of the spine and consists of three to five vertebrae. It is attached to the sacrum via a joint with a cartilaginous disc, and the joint itself is so mobile that the coccyx can tilt back during childbirth.
Muscles are attached to the front of the coccyx, which are involved in ensuring the functioning of the genitourinary organs, as well as the intestines. The coccygeal plexus is also located here, thanks to which signals from the organs of the pelvic area are sent to the brain. The main load from sitting falls on the tailbone.
Contraindications for the study
The harm caused by X-ray radiation to the body during an examination is minimal, but it exists. Moreover, radiation accumulates in the body. Therefore, it is important not only to monitor the frequency of x-ray examinations, but also to identify contraindications to diagnostics.
The radiation dose for radiography of the spine in two projections is no more than 1.5 mSv, which is equal to the natural radiation received over 6 months.
Full text of the article:
Radiography is not prescribed for patients:
- during pregnancy;
- under the age of 15 only in cases of extreme necessity;
- for obese people – diagnosis is uninformative.
When is an x-ray of the coccyx prescribed?
An X-ray of the coccyx is a prerequisite for diagnosing the cause of pain and other symptoms noted by the patient.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment using palpation and questioning.
X-rays are mandatory in the following situations:
- a person cannot bend or fully straighten his back;
- there was a strong aching pain in the lower back;
- problems with urination appeared;
- the lower back muscles are constantly tense;
- the patient notes the spontaneous occurrence of “lumbago” in the spine;
- long sitting causes the patient severe discomfort or is impossible.
Preparation for an x-ray of the coccyx may also be necessary if pain in the pelvic organs appears after an injury. This is explained by the fact that the nerve endings of the coccyx are connected to these organs.
What can diagnostics show?
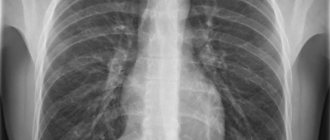
It is important to find out what an x-ray of the tailbone shows and what problems doctors can diagnose based on its results. The image will show the vertebrae and their spinous processes. By carefully examining the images, the doctor will be able to identify:
- fractures, bone integrity disorders, dislocations;
- discrepancy between the articular surfaces of the coccygeal joint, complicated by dislocation;
- presence of osteochondrosis;
- tumor processes and metastases in the coccyx;
- deformation of the connection of the coccyx with the sacral region;
- osteomyelitis;
- developmental defects.
#!RentgenSeredina!#
What will an x-ray show?
The image helps to visualize those pathologies that are not visible to the naked eye. One can only guess about damage to the coccyx, but the final diagnosis is made solely taking into account the data from radiographic images in several projections. Screening data shows:
- dislocation of elements in the sacral region;
- cracks;
- fractures;
- osteochondrosis;
- cysts;
- hernia formation;
- injury;
- inflammatory processes;
- metastases of oncological tumors;
- osteomyelitis;
- deformations;
- foci of osteoporosis.
In most cases, doctors make a diagnosis based on the results of an x-ray. For example, a fracture of the coccyx is clearly visualized and leaves no doubt. If the doctor is dissatisfied with the results of the study, because the suspected pathology did not show up in the image, then the doctor will recommend using alternative diagnostics.
How to prepare for an X-ray of the coccyx?
It is important to learn how to prepare for an x-ray of the coccyx, since following all recommendations will allow you to obtain the highest quality image. A few days before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude any gas-forming foods from the diet, since gas-filled intestinal loops transmit x-rays less well.
You will also need to do an enema before taking an x-ray of the tailbone. It is done twice. The first - in the evening of the day before the diagnosis, the second - a couple of hours before the x-ray. In the case of an urgent examination, only an enema is performed to cleanse the intestines before the examination. The examination is also performed on an empty stomach, and before the examination, medications that suppress gas formation may be prescribed.
Common causes of coccyx fracture
The coccyx is an integral component of the musculoskeletal system, thanks to which the load is evenly distributed over the pelvic area. There are various reasons for this pathology and it is mainly observed when the buttock area is damaged. Injury can occur when there is ice and when athletes do not follow jumping technique.
In addition, the following factors can provoke a tailbone injury:
- Generic activity. If the fetus is large enough or is not presented correctly, as it moves through the birth canal, the woman experiences a displacement of the sacrococcygeal joint.
- Accidents on the road. In such a situation, the victim may be diagnosed with various types of injuries, including a fracture.
- Severe injury. When this type of injury occurs, the patient's external vertebral structure is destroyed.
Too much monotonous exposure to the coccygeal area can provoke bone displacement. With frequent movements with shaking and other circumstances, there is a high probability of injury and these are mainly cracks. The cause of the damage may be osteoporosis, that is, a violation of the strength of bones when calcium and elastic fibers are washed out of it.
How is an X-ray of the coccyx done?
It is important to remove all metal objects and decorations so that they do not affect the quality of the photo. To begin the diagnosis, the patient will be asked to lie on a table and assume a certain position. As a rule, several basic styling is used:
- direct projection - first you need to bend your legs at the knees and hip joint so that you can take a picture of the sacrum, then straighten your legs to take a picture of the tailbone;
- lateral projection - the patient lies on his side, hands behind his head, knees slightly bent;
- oblique projection – rarely needed, the doctor selects the position individually.
Having learned how to do the coccyx x-ray procedure, you don’t have to worry that it will cause discomfort and unpleasant sensations. After the diagnosis, the patient will be asked to wait outside the office while the doctor makes a transcript.
What is determined during the procedure?
An X-ray examination of the sacral area allows us to determine the presence of injury or pathological process. Typically, the results of such diagnostics are:
- Bruises - the sooner an x-ray is taken in this case, the better. Usually after it a severe hematoma is formed, which does not resolve on its own and requires a minor surgical operation. This will eliminate the possibility of severe inflammation or suppuration. The image allows the doctor to determine the severity of the blow and the severity of its consequences for the patient.
- Dislocation of the sacrum is another unpleasant possible diagnosis that indicates deformation in the area. It usually manifests itself as a pronounced visual displacement, pain when pressing, swelling and a crunching sound when moving.
- Fracture is considered the most dangerous diagnosis, as it can be open or closed. In the first case, the pain is almost unbearable, in the second, the clinical picture is blurred, depending on the complexity. If the tailbone is covered with a thick layer of tissue, an additional CT scan will be required to accurately examine the fracture. On an x-ray it will be visible as a thin black stripe against the background of light bone.
Injuries often occur from falls on ice, birth injuries, being hit in the area with a heavy object, or falling from a bicycle. The process may also reveal pathological abnormalities in the coccyx, which include neoplasms, osteochondrosis, hernia, inflammation, or others.
Indications
X-rays of the sacral spine are prescribed in many cases:
- neoplasms in the vertebrae;
- leg muscle cramps;
- injuries received;
- pain in this area;
- numbness and paresthesia in the legs;
- assumption of protrusions and rheumatological symptoms;
- the need to carry out such diagnostics before and after surgery;
- osteoporosis;
- infectious diseases affecting the spine;
- osteomyelitis;
- congenital pathologies;
- spondylolisthesis;
- radiculitis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- monitoring treatment.
When using X-rays, it is impossible to examine soft tissues and diagnose muscle strain.
Among spinal pathologies, sacral diseases are the most painful. Therefore, it is important to diagnose them correctly. Today, new research methods are becoming widespread, but fluoroscopy remains one of the most popular diagnostic methods, since devices for its implementation are available in many medical institutions. X-ray of the sacral spine requires preliminary preparation of the subject. It is not indicated for all patients and is carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
- Indications
- Contraindications
- What does it show?
- How to prepare?
- How do they do it?
- Pictures
- Decoding the results
- What are the side effects?
- Actions after the procedure
- What is the price?
- Where to do it?
- Conclusion
Rehabilitation period
The recovery period after this injury lasts up to one and a half months. In case of severe injury, it lasts up to three months. After the patient’s bone damage heals (if this fact is confirmed by an x-ray), rehabilitation after the fracture begins. How long it takes for a coccyx fracture to heal depends on the degree of injury and the type of damage. And also the patient himself, how carefully he follows the doctor’s recommendations.
The following methods are used:
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- massage.
Close attention is paid to the patient's nutrition. The diet should contain sufficient amounts of easily digestible protein, calcium and magnesium so that the tailbone bones heal faster.
It necessarily includes the following products:
- seafood;
- cottage cheese;
- fish;
- milk;
- persimmon;
- nuts;
- veal;
- chicken meat.
The patient should drink at least one and a half liters of fluid daily.
Exercise therapy and massage
There are no direct exercises to develop range of motion in the coccyx area. Their main task is to strengthen the lumbar muscles and pelvic floor structures, improve blood circulation of the pelvic organs. Exercise therapy to restore the coccyx begins immediately. While the patient is on bed rest, he is recommended breathing exercises and gymnastics in a lying position. After the third week, the range of movements expands. A complex of exercise therapy is developed by a rehabilitation physician for each patient. It depends on the patient's condition.
Lumbar X-ray – why is it important?
The lower back is the part of the back that experiences significant stress every day. The vertebral region supports most of the entire human body. Plus, given the low mobility of modern people, the load on the lower back is much greater than before, and the muscle corset, which also helps to keep the torso in an upright position, weakens without exercise.
The lower back experiences serious stress
This is why the spine begins to hurt more often in the lumbar region than in other parts. In some cases, pain in this part of the body signals the development of serious pathologies that only a doctor can handle. Unfortunately, a person sometimes seeks help late, when the disease has already developed, and treatment becomes much more difficult than if the patient had come to a specialist at the first symptoms.
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine
Prices for lumbosacral corset
Decoding of received images
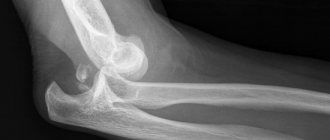
Normally, the coccyx consists of 3-5 fused vertebrae, which are distinguished by some mobility and the presence of nerve endings in them. Visualization of changes in bone tissue, traumatic damage to bone discs and surrounding soft tissues is not allowed on the images. The coccyx has a beak-like shape in pictures, from its first vertebra there are processes known as coccygeal horns - they connect to the sacral horns and form the coccygeal-sacral joint, which should be movable.
A fracture of the coccyx on X-ray, as well as its dislocation, are identified as the most common deviations that occur after strong falls in this area. Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of this part of the spine often occur, which are characterized by changes in the structure of bone tissue. Deviations noticeable on x-rays include cysts, synovitis, hernias, protrusions, and fistulas. X-rays can detect the presence of foreign bodies in the area being examined, such as bone fragments remaining after previous injuries.
The higher the density of the tissue, the lighter it appears on an x-ray. Bone tissues are visualized especially clearly, since they practically do not transmit ionizing X-ray radiation of such intensity. The same applies to abnormal structures, such as tumor formations - they are able to stop radiation much more noticeably than normal soft tissue. X-rays of the coccyx and sacrum are performed mainly to determine the condition of the bone structures. To assess the soft tissue surrounding this part of the spine, alternative diagnostic methods are used (for example, magnetic resonance imaging).
Features of the structure of the coccyx
The coccyx is the lower portion of the spine, which may have three to five fused vertebrae . They are arranged in the form of an inverted pyramid with the base at the top and the apex at the bottom.
The first vertebra is endowed with modified upper articular processes, the so-called coccygeal horns. Its lateral surfaces have rudimentary (non-functioning) transverse processes. The remaining vertebrae do not have such processes.
Under what circumstances should x-rays not be taken?
This method of radiation examination of the coccyx is prohibited for women during pregnancy and persons under 14 years of age. If a neoplasm is suspected, adolescents should undergo an MRI. Overweight patients are not given x-rays because the images are unclear. Many people know how to do an X-ray of the coccyx, but not everyone knows that there are contraindications to the procedure. It is not recommended to carry out self-diagnosis in private clinics without a doctor’s prescription, as this can harm the patient’s general health.
Signs of a coccyx fracture
The symptoms of fractures and cracks are very similar. However, signs alone may not be enough to determine the diagnosis. The main symptom of a broken tailbone is sudden pain at the site of injury. The pain is especially severe during the first few days after injury.
In addition, the victim may experience certain symptoms when the coccyx is fractured:
- injury to the epidermis and adjacent tissues;
- bleeding;
- discomfort when walking;
- tissue swelling;
- hematomas in the area of injury;
- discomfort when trying to empty the intestines;
- pain during rectal examination.
After a fracture, children and adults may experience slight tissue swelling or a hematoma. When the intestine is injured, bloody impurities may appear in the stool and the urge to go to the toilet becomes more frequent. With such a pathology as an open fracture of the coccyx with displacement, bone fragments are observed.
Possible complications and consequences of a fracture
The most common complication of a broken tailbone is coccydynia. It manifests itself as persistent and severe pain in the coccyx area. It develops due to the formation of callus, fibrous hematoma, compression of nerve endings and damage to the periosteum of the coccyx.
Complications of a coccyx fracture in women include disruption of labor. It is associated with the formation of a clinically narrow pelvis as a result of impaired mobility in the sacrococcygeal joint. Common consequences of a fractured coccyx include disruption of the bowel movement and pain during bowel movements. Symptoms of the consequences of a coccyx fracture in women and men include pathologies of sexual function, as the nerve plexuses innervating the pelvic organs are damaged. Migraine also develops after an injury to the coccygeal bones due to a violation of the shock-absorbing functions of the spinal column. The consequences of a fractured tailbone in a child are the same as in an adult.
Recovery prognosis
It is quite difficult to give a prognosis for recovery after a fracture of the coccyx . Most likely, this can only be done by a specialist who observes the picture of the disease and treatment. The process depends on many factors.
These include the severity of the injury, the course of treatment, the rehabilitation period, etc. If the fracture is not too complex and the victim has completed a full course of treatment and rehabilitation, then, as a rule, the tailbone heals properly, the pain goes away, and the ability to work fully returns. But at the same time, for some time you can only do light work.
Diagnostics
Only a traumatologist identifies a fracture and makes a diagnosis after conducting a series of studies. He examines the victim and asks him about the circumstances of the injury.
It does the following:
- When examining a patient, the doctor examines the coccygeal area. Detects the presence of swelling and hematoma. When pressing on the upper part of the tailbone, the pain intensifies.
- An x-ray of the coccyx is prescribed in the lateral (with legs bent) and direct projection.
- Computed tomography is considered the most informative method for coccyx injuries. With its help, even the smallest fractures are determined.
- MRI - prescribed to detect damage to soft tissues, blood vessels and nerve plexuses in this area.
A vaginal examination is performed in women to determine the crepitus of fragments at the site of injury. In men, a rectal examination is performed for the same purposes. If the pain syndrome is severe, it is not performed, since manipulation increases the pain.
First aid for a fracture
If the area of the coccyx is severely damaged, it is necessary to provide the person with all possible assistance until a specialist arrives and the patient is admitted to a medical facility. The condition can be alleviated by taking the following measures:
- After an injury, it is necessary to lay the person horizontally on a hard surface, preferably on his side. In case of unconsciousness and bouts of vomiting, this position will help prevent choking on vomit.
- The patient’s position must be fixed with available materials, and it is recommended to place fabric rollers under the curves of the body. During a fracture, it is important that the spine is in its natural position and that no load is placed on the tailbone.
If the patient is conscious and the swallowing reflex is preserved, it is allowed to take a drug with an analgesic effect.