What is a lung x-ray and how does it differ from fluorography?
X-ray diagnostics, as an independent technique, appeared in 1895. Wilhelm Roentgen patented the rights to the invention of a tube of the same name, which emits microparticles that can penetrate soft tissue. A feature of the described phenomenon remains the different degrees of absorption of the corresponding rays. When a special film is fixed opposite the tube, structures through which the microparticles have passed will be displayed on its surface.
Interesting! Wilhelm Roentgen worked in parallel with Ivan Pulyuy (Ukrainian physicist). Scientists communicated with each other and shared their experiences. However, Roentgen quickly patented the results of his research, which ensured his place in the history of science.
At the end of the twentieth century, the radiation diagnostic method for the first time allowed doctors to see the internal structures of the patient during his lifetime. Over the course of several years, the procedure spread throughout the world, where it was used to determine the causes of coughs, joint pain, bowel movements, and the like. The technique was improved, as were the devices.
In the twenty-first century, radiography is mainly used in traumatology (detection of fractures) and pulmonology (identification of the causes of cough and shortness of breath).
In practice, two main methods are used:
- traditional radiography;
- fluorography of the lungs.
The mechanism for obtaining the image in both cases is the same - the X-ray tube emits particles that pass through the chest organs, and the radiation with different intensities is deposited on the film located on the opposite side of the patient.
The difference between lung X-ray and fluorography lies in the purpose of the procedure and the size of the resulting image. The traditional procedure is used routinely to assess the condition of patients with cough, fever, and other symptoms of respiratory pathology.
Fluorography is a screening method used to detect tuberculosis and large tumors in the chest. The procedure is carried out regularly - once every 2 years for ordinary people. In the presence of harmful working conditions (miners, plant employees), the frequency of examinations increases.
Traditional X-rays of the lungs use films measuring 35 by 35 or 30 by 40 centimeters. In the case of fluorography - 2.4 by 2.4 or 7.0 by 7.0 centimeters.
In addition, during radiography, the patient receives a lower dose of radiation, which is due to the operating features of the devices. Fluorography only helps to detect the presence of pathology. Clarifying the causes of cough and choosing the appropriate treatment method requires the use of traditional radiation diagnostics.
The principle of obtaining fluorography results
The principle of obtaining a fluorographic image is based on the property of human body tissues to absorb or reflect X-rays. Before starting the procedure, the patient takes a position between the radiation generator and the film or digital matrix. At the moment the signal is given, electromagnetic waves are produced by the X-ray tube and, passing through the person, are reflected on the film or fluorescent screen.
How is the image in the photograph obtained? The fact is that human tissue transmits X-rays differently. Thus, dense structures completely absorb them, so nothing reaches their “destination”. These are, first of all, bones. Soft tissues absorb waves only partially, so they appear in gray shades in the image. And the cavities do not interfere with the passage of the signal, so it ends up on the film unchanged.
A fluorogram, like a photograph, is a negative image. Therefore, everything is displayed on it in reverse: the bones are white, and the voids, on the contrary, are black.
How to understand what is wrong? First you need to take a photo. To do this, the patient enters a special cabin, where he leans against the screen with his chest, freed from clothing. The specialist gives the command to hold your breath. At this moment a photo is taken. It explicitly examines changes in the density of lung tissue. Areas where density is increased indicate problems. For example, when connective tissue grows, it displaces healthy lung tissue, causing bright spots to appear on images.
What can you see in the photographs
The final interpretation of lung fluorography is carried out on the basis of the obtained images. On them, the doctor will be able to identify such abnormal processes as:
- adhesions and fibrosis;
- heaviness and radiance;
- scars and layers;
- sclerosis.
In patients with asthma, due to increased tension, the walls of the bronchi swell, which is also conveyed by fluorography.
Formations such as cysts, abscesses or emphysema also cannot hide from the doctor’s eyes.
Who does the decoding and writes the conclusion?
Deciphering an image is not an easy task; it requires certain skills and special knowledge, so this process is the responsibility of a professional radiologist. He writes the conclusion.
Indications and contraindications for X-ray examination
X-rays of the lungs are often used in pulmonology.
The appointment of the appropriate technique is carried out according to the following indications:
- prolonged cough that cannot be treated with traditional methods;
- shortness of breath due to swelling of the lower extremities;
- cough, accompanied by expectoration of purulent sputum and a parallel increase in body temperature;
- suspected lung cancer;
- rib fractures.
Fact! X-ray of the lungs is a routine and safe procedure for the patient, allowing the doctor to monitor the progress of the disease in a particular person. However, there are situations when the use of the appropriate technique is not justified.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- the presence of open wounds of the chest, internal bleeding;
- open pneumothorax.
In each specific case, the doctor independently decides whether to conduct an appropriate examination.
How long to wait for results
The work schedule in the research room is structured in such a way that visitors with coupons are first accepted. Then comes the period of checking the pictures and writing forms. Thus, the reception time is reduced.
The patient learns the results of the government service and receives documents the next day when they are issued. This issue can be resolved in less than 24 hours if you need to quickly receive a description of the results and a certificate.
As an example: undergo digital fluorography, when the corresponding clinic in the city or region has the necessary apparatus and equipment to evaluate the image. This will allow you not to waste time developing the “photo”.
You can also undergo a study at a private medical institution that conducts such diagnostics, and not at your place of residence and registration. In this case, the procedure will cost some money. The price must be found in the relevant clinic.
What diseases or pathologies can be detected by chest radiography and fluorography?
What does a lung x-ray show, and what diseases can be detected with it?
Pathologies that can be properly diagnosed:
- bronchitis. In this case, the visual picture may not change, which is associated with the initial stage of development of the problem;
- inflammation of the lung tissue (pneumonia);
- lung cancer, benign neoplasms;
- tuberculosis;
- effusion pleurisy;
- fibrosis (pneumosclerosis) of the lungs – compaction of the parenchyma with loss of function;
- entry of air, liquid or blood into the pleural cavity - pneumo-, hydro-, hemothorax, respectively;
- emphysema;
- abscess;
- atelectasis;
- progression of alveolar pulmonary edema.
List of diseases that lung fluorography can show:
- Neoplasms in the chest;
- Disseminated form of pulmonary tuberculosis. The appearance of darkening in the lungs on fluorography is one of the possible symptoms of pathology;
- Pneumosclerosis;
- Abscesses, cysts.
Experienced functional diagnostic doctors are able to see other pathological abnormalities in fluorographic images, however, radiography is always required to confirm the diagnosis.
Why is this procedure needed?
In the classic version, fluorography is performed to identify pathologies of any part of the body. However, in practice, this technique is used exclusively for detecting defective lesions in the chest area:
- spots on the lungs, indicating an inflammatory process, tissue destruction due to tuberculosis, malignant tumors, pneumonia;
- anomalies in the location of the heart and pathologies of the heart sac (pericardium);
- tumors, injuries, inflammation and purulent cavities in the mammary glands.
In the vast majority of cases, it is prescribed to check the lungs for dark spots. Preventing the spread of tuberculosis is the main reason why you need to undergo this procedure.
Good to know! Fluorography is most rarely used in the diagnosis of bone fractures in the thoracic region.
Doctors recommend undergoing fluorography as a screening examination, that is, to identify diseases in the absence of noticeable symptoms. It has been proven that this type of X-ray shows even small tuberculosis lesions, making it possible to make a correct diagnosis in the early stages of the disease.
Image quality and diagnostic accuracy
The quality of the resulting x-ray or fluorogram depends on the device on which the diagnosis is carried out. Modern devices work with digital technologies that provide a good final picture.
Important! However, with the availability of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, the quality of information obtained using traditional radiation techniques decreases. The reason is the layering of shadows of all organs during the passage of particles through the tissue. When using tomography, the doctor receives a picture of individual structures. Due to this feature, the diagnosis of cough and other respiratory pathologies increases.
The accuracy of diagnosing pulmonary edema, emphysema, or persistent cough using X-rays depends on the skill of the physician and the individual characteristics of the clinical episode. There are common cases where the lungs appear healthy on film, but in fact the pathology is progressing.
Radiation exposure
If digital inspection is used, its values (EDE - effective equivalent dose) will be from 0.03 to 0.060 mSv (up to 0.002 mSv), with film inspection - 0.15–0.25 mSv (per projection). For comparison: OGK radiography – 0.15–0.4 mSv, fluoroscopy values (within 5 minutes) – 2.5–3.5 mSv, CT – 6–11 mSv.
On average, a person receives about 2.4 mSv of natural background radiation per year (more in mountainous areas, less in plains). If we take into account the radiation received during everyday human activities, the contribution of fluorography once every one or two years will not be so significant.
Some countries are considering a screening program to detect early forms of lung cancer using more accurate low-dose CT scans.
Analysis of research results
A detailed interpretation of radiographs is carried out by a functional diagnostics doctor. However, every doctor has the skills to analyze the appropriate images to navigate the changes occurring in the lung tissue.
Normal for lungs without pathologies
A normal X-ray of the lungs in the presence of a cough is a possible development of events in the early stages of bronchitis. Pathological changes have not yet had time to arise.
Features of a normal radiograph (fluorogram):
- Adequate "rigidity". Normally, three thoracic vertebrae should be visible on the image. An increase in the indicator indicates the “hardness” of the picture, a decrease indicates “softness”;
- Mid-position of the trachea;
- The left border of the heart does not protrude beyond the left midclavicular line, and the right border does not protrude 1 cm from the corresponding edge of the sternum;
- The lung tissue is symmetrically “black” (darkening) with a moderately pronounced vascular pattern, which indicates the normal functioning of the alveoli;
- The junction of the ribs and the diaphragm is free in the image;
- There are no damage to the ribs or visible vertebrae.
These features are the reference points when assessing any chest X-ray. If changes are detected, the doctor indicates this in the conclusion.
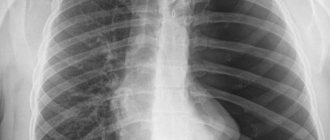
Fluorography image of a healthy person
Below is a picture of a healthy young man who underwent preventive fluorography in order to make sure there were no health problems.
Pathologies - white spots, cavity, small lesions, darkening in the lungs
The appearance of various spots, displacements of organs, and clearing in photographs in patients suffering from respiratory failure, cough and other signs of respiratory diseases are symptoms of pathology.
Possible signs of disease:
- Displacement of the chest organs to one side or the other. Causes: atelectasis, hydrothorax. In the first case, the movement of the structures will be towards pathology, in the second - vice versa;
- Enlargement of the heart and increased vascular pattern. These signs are characteristic of pulmonary edema;
- An isolated increase in the vascular pattern in the area of the apex of the lungs is a possible symptom of tuberculosis. In the absence of timely treatment, the pathology progresses to a disseminated, and then to a cavernous form with the formation of cavities;
- Expansion or deformation of the roots of the corresponding structures;
- The appearance of rich white spots (calcifications);
- Reducing the degree of physiological darkening. The indicated X-ray of the lungs occurs in pneumonia, when local inflammation progresses;
- The appearance of shadows of different shapes and sizes. This symptom may be evidence of tuberculosis or lung cancer on x-ray.
Signs of pulmonary emphysema are enlarged intercostal spaces, a lowered dome of the diaphragm, and increased airiness of the alveoli.
The lungs of a smoker have an enhanced vascular pattern. The roots of the corresponding structures may increase.
Fact! The combination of the symptoms described above allows one to suspect one or another pathology. However, we must remember that to make a final diagnosis, a logical relationship between the clinic and the results of instrumental procedures is important. A complete discrepancy between the indicated points indicates the presence of an error in verifying the causes of the problem (sudden weight loss, cough, fever) in a particular case.
Sometimes it is necessary to take x-rays of the lungs in two projections. Using this technique, areas that cannot be detected during a standard examination become visible.
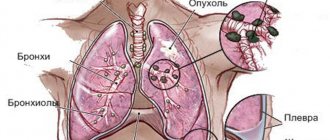
What unhealthy lungs look like photos
Below are images of three patients.
The image clearly visualizes a round neoplasm near the root of the left lung.
The spread of the pathological process is visualized, which partially resembles the “sticking of snow” on the surface of the organs inside the chest.
On the right, fluid is visualized (white area), which puts pressure on the heart, displacing it in the appropriate direction.
Pulmonary edema on X-ray in this case is represented by the symptoms of “butterfly wings”, which indicates the severity and extent of the pathological process.
What it is
Fluorography is a study primarily of the respiratory tract. It is used as a quick method for identifying various diseases of the chest organs.
The name screening implies the ability to detect pathologies at the stage when a person already has a disease, but it is still so underdeveloped. Firstly, it does not produce clinical symptoms. Secondly, it can be identified and treated as effectively and painlessly as possible.
In addition, this is the primary allocation of contingents so as not to waste more expensive medical resources when not necessary. This is why screening was invented.
X-ray and fluorography of the lungs in children
X-ray or fluorography in children is not contraindicated. Sometimes an appropriate examination is performed on newborns to exclude congenital pathology (if there are characteristic symptoms of the disease).
Radiation diagnostics is not used unless necessary. If you do an X-ray of a small child's lungs once, then there will be no problems. However, frequent irradiation threatens to disrupt the normal processes of cell maturation. The child's body is more susceptible to x-rays compared to adults.
Do children get x-rays?
For a child, unlike an adult, x-rays are prescribed with increased responsibility, since the received annual dose should not exceed 1 mSv. This examination is often necessary due to the fact that children are prone to colds, complicated by pneumonia or bronchitis. Other methods - CT scan of the lungs or MRI do not provide complete information and are also much more expensive.
Therefore, with severe symptoms, when you urgently need to take an x-ray and prescribe treatment, there is no longer a choice of which diagnosis is less harmful or better in terms of any specific parameters. The one that is carried out is the one that will help make the correct diagnosis, and often this is radiography. To protect children from unnecessary radiation, the lower abdomen is covered with lead protection and the procedure is performed in modern clinics.
X-ray of a child with bronchitis
Diagnosis during pregnancy and lactation
X-rays of the lungs during pregnancy are not recommended. The reason is the negative impact of the corresponding radiation on the fetus. However, there are situations when the described examination cannot be avoided (cough with hemoptysis, suspicion of a tumor).
Fact! For maximum protection of the child, women shield their belly. The essence of the procedure is to wear special lead aprons. The metal blocks X-rays, which reduces the risk of negative consequences. Routine use of the corresponding technique is not permitted.
When to start panicking and the main nuances
There is no need to panic at all. Regardless of the results of the x-ray, an emotional breakdown only aggravates the patient's condition. However, you cannot reassure yourself if there is serious pathology in the photographs.
Changes in radiographs that require special attention:
- the appearance of ring-shaped shadows or spots;
- sharp darkening of one lung against the background of increasing symptoms of respiratory failure;
- the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity.
These symptoms are the first to alert doctors. However, the presence of other pathological changes also requires verification and selection of adequate therapy.
Frequently asked questions from patients
Below are answers to the most frequently asked questions from patients who need x-rays.
Are X-rays of the lungs and fluorography harmful?
In 98% of cases, the corresponding studies used to diagnose the causes of cough or other respiratory pathology do not pose a threat to human health. The dose that the patient receives in 1 procedure is too small to have a negative effect on the body.
How often can fluorography and x-rays of the lungs be done?
The frequency of fluorography for an ordinary citizen is 1 time every 2 years. If there are factors that increase the risk of developing pathology - once every 12 months. If necessary, this figure may increase. X-ray of the chest organs is performed according to indications.
Fact! The maximum permissible safe dose of radiation that a person can receive through diagnostic procedures is 150 mSv per year. After undergoing a fluorography and chest x-ray session, a person receives 0.8 and 0.4 mSv, respectively.
In a year, a patient can theoretically have 187 fluorographs and 375 radiographs. That is why it is pointless to worry about the harm of episodic diagnostic procedures.
X-ray or fluorography of the lungs, which is better?
To identify the cause of cough in a patient undergoing hospital treatment, a conventional chest x-ray remains more effective. Fluorography is used for occasional screening and detection of hidden diseases in people without clinical manifestations. However, to clarify the results obtained, conventional radiography is prescribed.
Will fluorography show pneumonia?
On the fluorogram you can see the characteristic symptoms of the inflammatory process, but with its severity. In the early stages, the problem may go unnoticed.
Does fluorography show lung cancer?
If there is a large malignant neoplasm inside the chest cavity, fluorography will be able to detect its presence.
How to check the lungs other than fluorography?
In addition to fluorography and x-rays, the following methods are used to assess the functional activity and structure of the respiratory system:
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- spirography;
- bronchoscopy.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe auxiliary procedures.
Where to get a lung x-ray and who prescribes it?
An X-ray can be taken to determine the causes of cough or other symptoms of respiratory pathology in almost any clinic or hospital. An appointment for the appropriate procedure is given by a therapist or pulmonologist if indicated.
What is a digital x-ray and how do you read it?
Digital x-ray is a subtype of the conventional procedure. The difference lies in the features of the sensors, which detect radiation after passing through the chest organs. Recording is carried out not on film, but on special media that allows you to display the image on a computer screen, followed by printing on paper. The images are decrypted according to the scheme described above.
Is it possible to x-ray the lungs at home?
Fact! X-rays are not performed at home. The reason is the unsuitability of the apartment or private housing to carry out the corresponding procedure. To carry out high-quality diagnostics, it is necessary to have a large apparatus, a special protective room in the walls of which lead is sewn up and the like.
Fluorography remains more mobile. There are special cars with built-in beam installations. Thanks to this design, it is possible to screen for tuberculosis or cancer in settlements where there are no outpatient clinics with appropriate equipment.
Is it possible to eat before fluorography?
Eating or eating before the X-ray examination is not contraindicated. The products do not have a negative impact on the reliability of fluorography results.
How much does an x-ray cost?
If you have an official doctor's referral, X-rays to verify the cause of cough in public medical institutions are free of charge. However, if a person wants to undergo an examination on his own without the appropriate documents, then the price of the procedure ranges from 1000 rubles, depending on the characteristics of the clinical case, the number of projections, etc.
How often can you do it
The frequency of fluorography is determined by the patient’s condition. When figuring out how many times fluorography can be done and how often the examination needs to be done, one should take into account the clinical picture and the form of the inflammatory process.
The acceptable rate is 1-2 times a year. In this case, the radiation exposure will be minimal and harmless.
More frequent sessions are necessary for the following groups of people:
- Employees of hazardous enterprises or people who are constantly in contact with patients with tuberculosis. These include TB doctors, correctional colony employees, etc.
- Patients with a number of chronic diseases that negatively affect the body's protective functions. These are diabetes mellitus, AIDS, hepatitis and other lesions.
- People serving time in prison.
If complications develop, a re-examination must be performed, but such diagnostics are often prohibited.