general information
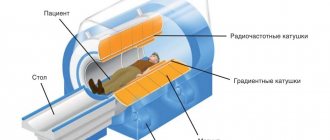
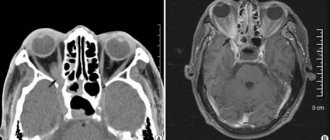
When X-rays pass through, the radiation is partially absorbed by human tissue, depending on the density. Special sensors detect this weakening and transmit information to the computer. The software forms a three-dimensional image of the tissue under study and produces the result in the form of layer-by-layer black and white images of the studied area with a step of 1 mm in different projections. Recently, a more accurate type of CT has become widespread - multislice computed tomography with a slice pitch of 0.5 mm.
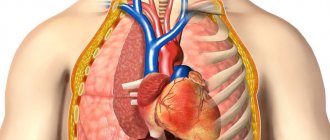
Chest tomography provides the diagnostician with maximum information about the pathologies of the internal organs, skeletal system, blood vessels and helps determine the choice of current treatment methods. CT scan of the thoracic region allows you to accurately localize various anomalies in the condition and structure of the spine.
Possible risks when scanning children
When planning a CT scan to study a specific pathology in your child, remember that there are certain risks:
- The likelihood of developing cancer due to excessive radiation (if the child has to undergo CT scans more than once).
- The likelihood of a serious allergic reaction to the injected allergic drug.
- The likelihood of complications in the child from general anesthesia and sedation.
Computed tomography is usually prescribed for children to visualize injuries and tumors. In such cases, the benefit of early diagnosis is considered justified. The harm from ionizing radiation in this case is much less than the danger posed by such pathologies.
If your child is referred for such testing, do not refuse because of the potential harm from x-rays. Think about the fact that thanks to this research method, the doctor will receive important information about the structure and functioning of all his organs and systems.
Indications and contraindications for diagnosis
Chest CT is indicated in the following cases:
- skeletal bone injuries;
- impaired mobility and pain in the joints of the shoulder girdle and spine;
- suspicion of intervertebral hernia;
- cartilage inflammation;
- osteoporosis;
- suspicion of developmental anomalies of the spinal column;
- suspicion of the presence of foreign objects in the stomach, esophagus, respiratory tract (especially in children);
- suspicion of the presence of benign or malignant tumors, metastases;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment in cancer patients;
- pneumonia, pulmonary tuberculosis, foci of darkening in the lungs of unknown etiology;
- pathologies of the mediastinal organs, bronchi, trachea;
- abscesses, pleurisy, fluid accumulation in the lungs or pleural cavity;
- the presence of parasites in the respiratory system, monitoring the effectiveness of healing the body from them;
- abnormalities in the development of the chest organs and skeletal system;
- enlarged lymph nodes of unknown etiology;
- systemic diseases (scleroderma, lupus), sarcoidosis, lymphogranulomatosis;
- heart disease, aorta, heart defects, heart attacks;
- cardiosclerosis of heart vessels;
- preparation for surgical interventions, adhesions after operations;
- pulmonary embolism;
- emphysema;
- atherosclerosis, thrombosis and other vascular pathologies;
- ischemic disease;
- violation of the structure of the mammary glands;
- esophageal stenosis, bleeding;
- to clarify an already made diagnosis, if other methods do not provide a reliable picture of the disease.
A CT scan of the chest is recommended for shortness of breath, symptoms of heart failure, persistent and untreatable cough, and pain of unknown origin in the chest area.
Absolute contraindications to CT OGK:
- pregnancy due to the teratogenic effect of ionizing radiation;
- lactation;
- pain, inability to lie still during the examination (with involuntary twitching of individual muscles or parts of the body);
- patient weight more than 130-150 kg (depending on the design of the device).
Relative contraindications to CT with contrast:
- allergy to the components of the contrast agent (iodine, seafood);
- thyroid diseases;
- severe heart failure;
- severe general condition of the patient;
- severe liver and kidney failure;
- myeloma (oncological disease of the blood system);
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- severe forms of asthma.
For children under 14 years of age, CT is contraindicated and is performed only for life-threatening conditions.
The decision to perform a tomography is made only by the doctor, taking into account the potential benefits and harms to the patient.
Contraindications
Before the study, the patient informs the doctor about the existing allergy to iodine if contrast is expected to be used. Chest tomography is absolutely contraindicated in the following cases:
- Pregnant women throughout the entire period of gestation.
- A person's weight over 120 kg makes research difficult.
Relative contraindications for the procedure:
- allergy to iodine;
- children under 12 years of age;
- multiple myeloma;
- diabetes;
- breastfeeding period. If the tomography is performed on a nursing mother, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding the baby for 2 days.
- chronic renal failure;
- patients suffering from claustrophobia;
- epilepsy;
- people suffering from neurological diseases cannot stand still during a session. However, the procedure can be performed after the administration of sedatives.
How to prepare for a chest CT scan?
No preparation is required for a chest CT scan. Electronic devices and metal objects must be removed before the examination. Young children, mentally unstable patients, and people with claustrophobia have to use sedatives or even anesthesia before the examination. When using contrast, it is recommended not to eat for 6-8 hours before diagnosis and not to drink for 1-2 hours. After a CT scan with contrast, you need to drink more fluids so that the drug is eliminated from the body faster.
Analysis of the CT results of the OGK is carried out after diagnosis by a radiologist within 1-2 hours.
Preparation for the procedure
With the exception of the situations described in partial contraindications, there is no need to look for an answer to the question of how to prepare for the examination. Be sure to take your personal passport for the procedure, as well as a referral, if the selected clinic requires it. Please note that you should definitely notify your doctor of any previous examinations of this kind and how you handled them. It is important to go to the CT scan only in comfortable shoes and clothing. Pay special attention to ensure that there are no metal inserts on it, this is important.
Before the procedure, you must remove all metal objects from yourself.
As for the procedure involving contrast, in such situations preparation is still necessary. The basic rule is that it is forbidden to eat food approximately 8-10 hours before your appointment, that is, you simply should not eat in the morning. It is also important not to drink liquid 2 hours before, because it can also adversely affect the result. When the contrast agent is introduced, the process of the procedure itself will begin, which will be controlled by a specialist.
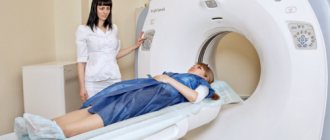
How is a chest CT scan performed?
To conduct a CT examination of the chest and mediastinum, the patient is placed on the mobile table of the scanning device and secured with special belts and pillows. If necessary, the medical staff administers contrast. The table is then moved inside the tomograph. The patient must remain completely still throughout the procedure. For a thoracic CT scan, the patient must lie on his back; if necessary, the doctor may ask him to turn to his side. The device makes a whistling noise during the procedure.
Using Contrast
A chest CT scan without contrast may not be sufficiently informative. A chest CT scan with contrast provides clearer images of the pathologies being examined. A contrast agent for examination is administered intravenously:
- for CT - by medical personnel;
- For MSCT, bolus contrast is used - the drug is injected with a special syringe-injector at a strictly defined speed. With MSCT, scanning is carried out several times at certain intervals. This type of contrast is optimal for studying vascular pathologies, and veins and arteries separately.
CT scan with contrast is ideal for diagnosing neoplasms, determining the shape and size of the tumor, and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
Radioactive iodine preparations are usually used as contrast.
How long does the study take?
A CT scan of the chest cavity without contrast lasts 5 minutes, with contrast – 15-30 minutes.
Chest CT scan: what does it show?
A chest CT scan clearly shows:
- damage to the skeletal system (cracks, fractures), wounds, foreign bodies;
- abscesses, inflammation;
- heart disease, aorta;
- hemorrhages, bleeding;
- abnormal development of internal organs;
- oncological diseases;
- benign tumors;
- inflammation of cartilage tissue, intervertebral hernia;
- diseases of the lymph nodes;
- esophageal stenosis;
- pneumonia, darkening of the lungs.
Tomography with contrast clearly visualizes vascular pathologies, atherosclerotic plaques, very small tumors, heart attacks, hematomas.
In women, a chest CT scan gives a complete picture of changes in the mammary gland, the presence of heterogeneous lumps, cysts, and inflammation.
Associated diseases
Tomography reveals diseases associated with occupational hazards, for example, silicosis.
Possible risks
Computed tomography of the thoracic region is dangerous due to the effects of ionizing radiation on human tissue.
How many times a year can you do it?
A CT scan of the ribs and sternum can be performed once a year. In case of emergency, the study can be performed up to 3 times a year at intervals of at least 4 weeks.
What is the radiation dose?
The radiation dose received from a thoracic CT scan is 10 mSv. The radiation exposure generated by radiation is cumulative. The recommended radiation dose from x-ray examinations is 15 mSv per year.
Features of MSCT
Computed tomography is not associated with discomfort or pain.
The patient lies down on a sliding table located inside the tomograph. The movable surface of the table is located directly under the device. At this time, the doctor conducts research and manages the work of the tomograph from the next room, while simultaneously maintaining contact with the patient.
The study lasts about 15 minutes; when a contrast agent is introduced into the body, its duration increases to half an hour.
Advantages of the method
Computer diagnostics has many advantages over other methods:
- allows you to take layer-by-layer images in different projections and visualize the area under study on a computer;
- high resolution allows you to study internal organs, blood vessels, lymphatic system, and neoplasms in the smallest detail;
- Thoracic CT can be performed in a few minutes, which makes it possible to use the method in life-threatening situations, especially in cases of trauma, heart attacks, and pulmonary embolism;
- it can also be used in the presence of implants, vascular stents, pacemakers, tattoos;
- CT provides clearer images of the tissues of the heart and lungs - organs that are in constant motion - than MRI.
Unfortunately, such an examination is not recommended for children and pregnant women due to the danger that radiation exposure poses to a child.
Use in pediatrics
Computed tomography of organs and tissues of the chest cavity is harmful for a rapidly growing and immature child’s body, therefore, before reaching 14 years of age, the procedure is performed only in extreme cases, when the need for a correct diagnosis outweighs the risk of radiation:
- for injuries;
- if foreign bodies enter the respiratory tract or are swallowed;
- if neoplasms are suspected;
- for pneumonia, tuberculosis.
To obtain high-quality images for a small child, a chest CT scan can only be performed under general anesthesia.
What changes does a CT scan diagnose?
X-ray computed tomography technology reveals the following changes in organs, soft tissues and bone structures:
- inflammatory processes of a specific, nonspecific nature and their complications;
- tumor formations of benign, malignant origin, metastases;
- cavitary formations in the lung parenchyma of parasitic origin;
- violation of the integrity of anatomical structures;
- abnormal position, structure of organs;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- fluid in the pleural cavity, cardiac sac;
- adhesive process;
- the presence of pathological passages connecting the trachea and bronchi with the esophagus;
- foreign bodies that entered the body through natural means or through a hole in the chest.
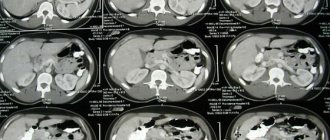
Lung pathology
A tomogram of the lungs reveals infiltrative changes in the parenchyma, areas of compaction, decay cavities, and collapse of the organ.
CT is prescribed for the diagnosis of pneumonia, tuberculosis, granulomatous diseases, congenital developmental pathologies, and post-traumatic changes.
Norm
Peripheral cancer of the left lung with decay
The use of iodine contrast allows one to evaluate the structure of the mediastinum and the condition of the pulmonary vessels. In lung cancer, contrast enhancement is used to determine the involvement of neighboring structures in the tumor process and characterize the blood supply to the malignant focus.
Pathology of the heart and blood vessels
Computed tomography is performed to assess the condition of the heart muscle, valves, and identify blood clots in the cavities of the heart.
Vascular imaging reveals stenosis, calcification, atherosclerosis, and anomalies of the coronary arteries. Angiography shows the caliber, diameter of the vessel, dissection, pathological dilatation, rupture of the aorta, blockage of the pulmonary artery by blood clots.
CT scan of the cardiovascular system is indicated for patients with symptoms of coronary insufficiency, acute vascular diseases that threaten the patient’s life.
Pathology of the thymus
When scanning the thymus, the structure, density, contours, size, and position of the gland are assessed. The method verifies organ hyperplasia from tumor lesions.
In case of malignant formation of the thymus, it reveals cystic changes and necrosis in the lesion, germination into the heart sac, pleural cavity.
CT is used to diagnose thymoma, carcinoid, cyst, and thymic hyperplasia.
Pathology of the lymphatic system
When examining intrathoracic lymph nodes using CT, the doctor receives information about their number, size, contours, and structure.
The condition of the surrounding fiber is assessed. Pathological changes are detected in the form of inflammatory foci, calcifications, and increase in size.
X-ray tomography is prescribed if a tuberculous process, lymphogranulomatosis, or metastatic lesion from the primary site is suspected.
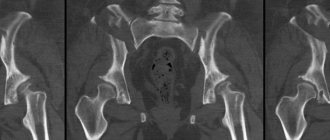
Pathology of the ribs, spinal column
Computed tomography of the bone structures of the chest reveals a violation of the integrity of the ribs, sternum, vertebrae of a traumatic nature (fracture), degenerative processes, and tumor lesions.
Metastatic lesions of L3, L4. Common osteochondrosis, spondylosis.
Norm
CT scanning of the ribs and thoracic spine is prescribed for injuries, herniated discs, suspected tumors, and metastases in bone tissue.
What is the price?
The cost of a chest CT scan depends on many factors: the reputation of the clinic and the reputation of the doctors, the type of tomograph, the list of services included in the price list (sometimes the price of the service does not include a decoding of the results). When choosing a clinic, you cannot be guided only by price - you may come across not very conscientious or unqualified staff, and the procedure will have to be redone. The cost of a CT scan is higher than that of a conventional X-ray examination and lower than that of magnetic resonance imaging, but when choosing, you should not take into account only cost-saving criteria; the feasibility of the choice is determined by the doctor.