Having learned about the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, a woman does not immediately realize what a difficult path she will have to go through. She will have to register with the antenatal clinic, take many different tests to monitor her health, and visit the offices of different doctors. But, besides all this, she will need to undergo a medical genetic examination in order to identify or refute congenital pathologies in the child in the womb. This examination includes a Down test during pregnancy. In this article we will tell you what this examination is, why you should do it, and what to do if the result is positive.
About Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality characterized by the presence of an additional 47 chromosome.
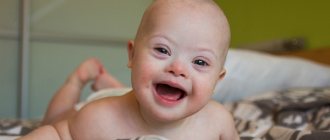
Children with Down syndrome differ in appearance. They have a puffy face, an upturned nose, and a constantly open mouth due to a large tongue that cannot fit into it.
They lag behind their peers in physical and mental development.
There are no medications for the “extra” chromosome. This problem can affect any married couple, regardless of social status, age and standard of living.
Factors influencing the development of chromosomal abnormalities:
- the age of the future parents is approaching forty years;
- there is a family connection between mom and dad;
- one of the parents had similar diseases in the family;
- poor lifestyle, especially drug use;
- lack of vitamins.
Pathological factors are indicative and cause a pregnant woman to fall into a group at increased risk of the disease.
To date, the reason leading to the presence of an extra chromosome has not been established.
Until recently, it was not possible to identify pathology in pregnant women. But due to the rapid development of high-tech methods in the field of medicine, an analysis was developed. Prenatal screening is a “triple test” that allows you to identify an abnormality in the set of chromosomes.
The disease is studied by geneticists and cytogeneticists.
What to do if the fetus has Down syndrome
If, during testing, the doctor diagnoses Down syndrome, then the future parents will have to make a difficult decision. This pathological condition cannot be treated either in the womb or after birth. When such a disease is detected, there are only two options: to have an artificial abortion or to carry and give birth to a sick child.
According to doctors, an abortion in such a situation can be done at any stage of gestation, since the doctor cannot refuse this procedure due to a serious diagnosis. Parents must make the right decision on their own without instructions or recommendations from a doctor. The gynecologist has no right to interfere with the family’s decision and dissuade them from making one or another decision.
When future parents learned that a screening test showed extra chromosomes, the main thing is not to draw hasty conclusions. First of all, the first tests may be false, so additional diagnostics of fetal development need to be carried out. The girl needs to undergo additional tests to identify a chromosomal defect.
A screening examination cannot always give a 100% correct result, since even machines and doctors can make mistakes. It is recommended to visit several geneticists and consult about this
It is important to remember that reliable data when undergoing laboratory procedures can be obtained using new modern equipment. Therefore, after conception, a girl is recommended to have her first scheduled ultrasound scan using a modern device in a good hospital.
If your doctor prescribes a referral for additional procedures, you should undergo them. They will give more information about the fetus and identify whether there are any health risks.
When is the test performed?
An analysis to detect chromosomal pathologies is carried out at the end of the third trimester.
From 11 to 13 weeks of gestation, a pregnant woman must donate blood for three types of hormones and undergo an ultrasound examination.
The combination of two tests allows you to expand the picture of the pathology and take appropriate measures.
It is important to note that the first trimester is a “natural” selection for the fetus, therefore, if severe fetal malformations are detected, termination of pregnancy is proposed.
Questionable results are confirmed by non-invasive diagnostic methods, which confirm or refute the diagnosis with 98% accuracy.
Pregnant women make their own decisions, after consulting with a geneticist and comparing the risks of pathology.
Children with Down syndrome require specialized care and treatment. Sometimes the underlying pathology is combined with defects of the heart muscle, respiratory and nervous systems.
Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of chromosomal abnormalities, in particular Down syndrome?
Of course, there are no recipes for such problems, but you can significantly reduce the risk of their occurrence: plan your pregnancy, lead a healthy lifestyle, consume enough folic acid and multivitamin complexes.
In addition, take the necessary tests in a timely manner and undergo an ultrasound examination. These simple (and also mandatory!) procedures will help keep you and your unborn baby healthy. They reduce the risk of diseases and genetic pathologies.
Composition of the analysis
As mentioned above, to establish a diagnosis, a triple screening test is performed, which includes:
- Ultrasound examination of the fetus.
- Blood tests, namely hormones.
If the results are questionable, amniocentesis, cordocentesis or villus biopsy is performed.
The first two indicators are mandatory types of research. For this reason, gynecologists strongly recommend registering for pregnancy before the 12th week of gestation.
The main screening is carried out no later than 13 weeks. If non-invasive manipulation is necessary, no later than 20 weeks, ideally from 16 to 18 weeks.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the proven and “old” ways to detect fetal anomalies. Ultrasound is performed in combination with biochemical parameters.
Subsequently, the data is entered into a special program, where a blood test is performed and the risk or percentage of the pathological phenomenon is established.
The method is informative, but may be unreliable (approximately 20% of false positive results).
During an ultrasound examination, the following indicators are determined:
- Fruit size. With a chromosomal abnormality, the size of the fetus is significantly below the permissible norm.
- Rapid heartbeat, sometimes the cardiac system has serious developmental defects.
- Deterioration of the bony base of the nose and enlarged collar zone. These two indicators are fundamental, since all “sunny children” have an expanded collar area with signs of swelling, and an absent or too small nose.
Ultrasound examination reveals fetal hypotonia and possible pathology of the renal system. There is often echogenicity in the intestinal buds.
In severe situations, the fetus may not be viable and die in the first trimester.
Blood biochemistry
The blood collects for 3 types of hormone: hCG, AFP and free estriol:
- free b-hCG is a hormone produced by the chorion. It grows rapidly in the presence of chromosomal pathology, however, the concentration of the hormone is not taken into account separately, but is compared with other indicators.
- AFP is a specific protein that decreases in Down syndrome. Alpha-fetoprotein is synthesized in the liver and is a fundamental test for the presence of fetal abnormalities.
- Free estriol is the third screening test that is reduced to extremely low results. Estriol can drop sharply, in which case we are talking not so much about a possible genetic pathology, but rather about fetal abnormalities that are incompatible with life.
- As an additional test, PAPP-P, a protein produced by the placenta, is monitored.
Blood must be donated in the first half of the day on an empty stomach, and an ultrasound scan is performed either on the day of blood donation or the next morning.
To obtain reliable results, you should not neglect the simple rules for collecting venous blood.
Prenatal diagnosis
The first screening is carried out at 11–13 weeks of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the first trimester will include:
- Ultrasonography.
- Determination of human chorionic gonadotropin levels.
- Study of PAPP-A content in the blood.
The second screening is carried out at 15–22 weeks of pregnancy. It consists of:
- Ultrasonography.
- Determination of alpha-fetoprotein value in maternal blood.
- Study of the content of human chorionic gonadotropin and estriol, as well as inhibin A.
For pregnant women who are in a group with an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, it is recommended to undergo invasive diagnostic techniques:
- Chorionic villus biopsy.
- Amniocentesis.
- Cordocentesis with fetal karyotyping.
- Consultation with a medical geneticist.
Ultrasonography
Today there are certain markers of Down syndrome in the fetus. Ultrasound signs of the disease are visible changes in the development of the baby.
Main markers of pathology:
- Increasing the thickness of the collar space. It is located in the place where the future neck and lower part of the back of the head are formed. An indicator of the likelihood of a fetus having Down syndrome is a thickness of the nuchal translucency exceeding three millimeters.
- Absence of nasal bone.
- Short tubular femoral and humeral bones.
- Signs of the absence of various parts of the intestine.
- Anomalies in the structure of the frontal lobe of the brain and cerebellum.
But not one of them is one hundred percent. Only summary ultrasound signs make it possible to conduct a consultation and prescribe invasive research methods.
Laboratory data
This type of examination consists of a blood test for Down syndrome. Determining the content of human chorionic gonadotropin is a reliable diagnostic method. This substance is also called the pregnancy hormone. Refers to indicators of successful pregnancy.
When human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels increase by more than 2 MoM, the doctor prescribes a double or triple test for the woman for a more accurate diagnosis of Down syndrome during pregnancy.
The double test consists of examining the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin and PAPP-A (pregnancy-associated protein) in the first trimester. When the hCG content increases to more than 2 MoM, and the PAPP-A value is less than 0.5 MoM, with up to 90% confidence, they indicate a pathological pregnancy.
This is possible when:
- Down syndrome.
- Threatened miscarriage.
- Frozen pregnancy.
The triple test consists of examining the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein and estriol at 15-22 weeks of pregnancy.
Down syndrome is characterized by the following changes in their concentration in the blood of a pregnant woman:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin is more than 2 MoM.
- Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is 0.5 MoM.
- Free estriol less than 0.5 MoM.
- Inhibin A more than 2 MoM.
The triple test is not a mandatory diagnostic measure. But it is recommended to carry it out in the following cases:
- Mother's age is more than 35 years.
- Presence of people with Down syndrome in the family.
- Unfavorable course of previous pregnancies - miscarriages.
- Presence of patients with genetic pathologies in the family.
- If the mother suffered a serious illness during pregnancy.
Invasive methods
These studies make it possible to accurately determine the development of genetic pathologies in the fetus.
Chorionic villus biopsy is a study in which part of the chorionic villi tissue is obtained from the placenta. This area is identical to the genetic material of the fetus. The procedures are performed under ultrasound control and using anesthesia.
Amniocentesis is the study of amniotic fluid. The material is collected through small punctures in the abdomen. The accuracy of this method reaches 99%.
Cordocentesis is a procedure for collecting cord blood. Diagnosis is carried out under ultrasound guidance. The material is collected through punctures in the abdomen or cervix.
If there are signs of Down syndrome based on ultrasound, laboratory tests and invasive techniques, the attending physician gathers a consultation. After making a decision, the pregnant woman’s medical meeting explains the risk of giving birth to a sick child. In this case, the terms of termination of pregnancy are extended to twenty weeks for medical reasons.
Invasive fetal chromosome analysis
High-tech methods make it possible to establish a diagnosis with almost one hundred percent probability.
Minimally invasive diagnostic methods include:
- Amniocentesis. is carried out for mothers who are at risk of having a child with genetic disorders, as well as with disappointing results of the first screening. Amniocentesis is a study of amniotic fluid to determine the level of ACE. The procedure is performed in a hospital setting. Under the control of an ultrasound sensor: a needle is inserted into the anterior wall of the abdomen and amniotic fluid is collected in a volume of no more than 15 ml. Laboratory testing establishes the concentration of AFP. Its decrease confirms the preliminary diagnosis.
- Cordocentesis is the removal of fetal blood from the umbilical cord. Cordocentesis is the 100th result of intrauterine examination. During the procedure, the obtained blood is subjected to a thorough analysis, which reveals not only a chromosomal mutation, but also a number of other diseases. The procedure is quite expensive and is accompanied by the risks of placental abruption and spontaneous miscarriage.
- A no less accurate result is obtained with chorionic villus biopsy. The material for the study is chorionic villi, obtained by introducing special mirrors into the vaginal cavity.
A cytogeneticist is examining the material. In most cases, the methods are microscopic in nature.
Who should get tested?
Any woman can get tested for Down syndrome in her child to make sure her child is healthy. But usually they don’t just take a Down test, but undergo a routine examination during pregnancy, which may show that the child is not entirely healthy.
Risk group
There are also women who are at risk.
- We decided to have a child after 35 years. The older the expectant mother, the greater the risk of giving birth to a baby with Down syndrome. Not only the age of the mother plays a role here, but also the age of the future father.
- The child's parents were close relatives.
- Before this pregnancy, there were spontaneous miscarriages or stillbirths.
- Parents were in contact with chemicals, exposed to radiation, and worked in hazardous industries.
- They took medications that cause mutations in genes.
- Both lead unhealthy lifestyles.
Karyotype analysis
It is worth taking a karyotype test before pregnancy. What it is? Karyotypes are combinations of chromosomes. This study can be carried out at any age. A karyotype analysis should show that a woman is 46XX, and a man is 46XY. If there is a deviation from the norm, then there may be problems with conceiving a child, with bearing it, deformities and developmental pathologies are possible. A karyotype test may be performed on an adult to determine whether their children may have genetic diseases. Then it's a blood test. Or a study is carried out during pregnancy to make sure that the fetus does not have chromosomal pathologies. In many countries, a karyotype test is taken before marriage.
Results and risk groups
The obtained data is loaded into a special computer program, which compares the results with normal indicators and displays the probability as a percentage.
Fetal pathologies can be low, threshold or high.
For example, the result is as follows: 1:100, 1:150, 1:200. The data is a threshold: one in 100, 200 or 150 will be diagnosed with a chromosomal abnormality.
A low ratio is a ratio of 1:350 or higher. If there is an increased risk of Down syndrome, a consultation with a geneticist is carried out.
The possibility of additional examinations is established. The issue of termination of pregnancy is being resolved.
Be that as it may, responsibility for subsequent actions falls on the mother's shoulders.
The risk group is represented by pregnant women who:
- complicated gynecological history;
- there are similar cases of pathology in the family;
- the mother's age is above 35 years, and the father's is 40 or older;
- addictions;
- addiction.
The pathology can be diagnosed in any baby, even born to a famous or rich couple.
The likelihood of having a child with Down syndrome is zero if blood counts and ultrasound examination of the fetus are normal.
Pregnancy with a fetus with Down syndrome: a gift or a sentence
Not all young parents are able to accept the news of their special child as a given. Unfortunately, the vast majority are inclined to have an abortion if their moral convictions allow it.
Many emotions overwhelm parents: fear of the unknown, enormous self-pity, doubt, uncertainty. The statistics are sad: along with abortions, sick children are abandoned in the maternity hospital. Only a small percentage accepts a child as a precious gift from above.
Parents who did not give up and were not afraid of difficulties will have difficult work. It’s a pity, but modern society is still “saturated” with Soviet times, when sunny children were isolated and kept away from “normal” kids.
Today, the vast majority avoid these guys, considering them strange and not like everyone else. The collective attitude towards such children is far from tolerant, and prejudices and echoes of the past do not allow us to accept them and help them establish themselves in society.
Prognosis for a positive result
A positive result means that a child with genetic abnormalities is developing in the mother's womb. The data must be confirmed by invasive diagnostic methods.
Future parents must be prepared for the birth and upbringing of a “sunny baby.” It would be a good idea for mom to consult a psychologist.
Children with Down syndrome have disabilities in physical and mental health. Initially, the prognosis for all babies is the same.
Development, learning and adaptation to normal life depend on the level of treatment and adaptation with the help of parents and surrounding loved ones.
Diagnostic features
During pregnancy, Down syndrome cannot be diagnosed safely and at the same time with a high probability. Of course, this can be done with a high degree of probability if you undergo many tests, but women need to decide whether they need the result in principle.
Reasons for the uselessness of prenatal diagnostics:
- Causes significant harm to physical health - some tests for Down syndrome during pregnancy are taken using a syringe that is inserted through the mother's abdomen, such manipulations can harm the baby (and also harm the baby), and even cause a miscarriage.
- Attempts to identify Down syndrome and signs of this disease during pregnancy cause significant psychological harm to the mother in any case - if the child is sick, the mother may be persuaded to have an abortion, resistance to infanticide can lead to conflict situations, and carrying a child knowing that he is sick is psychological trauma for a mother she doesn't need at all. If the child is healthy, but the diagnosis is incorrect, then psychological experiences can harm both him and the mother, and after birth such a baby falls under unnecessary suspicion; instead of just being a welcome joy, he can be tested for months for the presence of a non-existent disease.
- Detection of Down syndrome during pregnancy - tests, screenings, tests, ultrasound cannot diagnose the disease with one hundred percent probability, and are often erroneous and therefore useless.
Harmful Invasive Diagnosis
Prenatal screenings for Down syndrome are unnecessary and can be harmful to the physical and psychological health of mother and baby. In addition, they cost a lot of money, which can be used for the development of a newborn baby or to provide better conditions for a pregnant mother. Of course, the worst thing is that such studies are not done in order to “just know” and not for the treatment of the baby, as is often presented, but precisely in order to continue such information earnings in the form of termination of pregnancy, or abortion, this For some reason they prefer to avoid the word. When talking about abortion, in order to persuade the mother to commit murder, doctors often call the child the formless word “fetus.” It has gotten to the point where murder is colloquially called “cleansing,” probably in order to psychologically distance oneself from this great sin.
How deviations are determined
There are several methods that allow one to determine with varying accuracy the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. Moreover, the more complex the diagnosis, the more reliable results can be expected. However, there is a certain risk of complications due to medical intervention.
Amniocentesis: examination of amniotic fluid
For a long period, amniocentesis was used to diagnose an extra chromosome in the fetus.
The procedure involves puncturing the woman's abdomen with a thin needle, through which amniotic fluid is drawn. Based on a study of its composition, conclusions are drawn about the presence of a hereditary disease. The fetal liver produces a special protein (AFP, alphafetoprotein), which enters the amniotic fluid. If the protein level is below normal, this indicates abnormalities (the fetus has an extra chromosome). Amniocentesis is performed only if the expectant mother is at risk (mature age of the woman in labor).
Chorionic villus biopsy is the most accurate result
This test allows you to reliably determine whether the fetus has a chromosomal abnormality or not. The procedure is carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine. A special probe with a speculum is inserted through the woman's vagina, with the help of which a thin flagellum of chorionic villi is removed. The cells of the placenta contain precise information about the structure of chromosomes and their number, which also makes it possible to determine the sex of the child.
Auxiliary screening tests for identifying hereditary pathologies
There are also additional tests that are used to diagnose an extra chromosome in the fetus. The AFP protein enters the amniotic fluid and then into the blood of the pregnant woman. Therefore, analysis of the venous blood of the expectant mother is also successfully used. Blood diagnostics for chronic human gonadotropin (hCG) and alpha-fetoprotein testing are carried out at 10–13 and 16–18 weeks, respectively. However, these studies are not accurate, they do not guarantee 100% reliability of the result.
We also recommend reading the article methods for diagnosing pregnancy in the early stages. From it you will learn what other tests the pregnant woman needs to undergo, what they will show, and also how they can help prevent certain developmental pathologies.
During pregnancy, signs of Down syndrome can be more or less accurately diagnosed by ultrasound, which is performed at 14 weeks. The main symptoms of deviations are:
- smaller fetal size compared to existing standards;
- presence of heart disease;
- violation of skeletal formation;
- expansion of the collar space (if it exceeds 5 mm from the norm);
- echogenicity of the intestine;
- one artery in the umbilical cord instead of two;
- increased fetal heart rate;
- dilation of the renal pelvis;
- the presence of a choroid plexus cyst in the brain;
- cervical folds (signal the accumulation of subcutaneous fluid);
- absence of the nasal bone or its shortening.
However, it should be understood that in the early stages it is impossible to reliably talk about the presence of pathology only on the basis of ultrasound data. About 20% of false positive results are noted. The most complete picture can be obtained through a comprehensive examination of a woman: ultrasound, blood test for hCG, AFP, free estriol, plasma protein A. This approach provides only 1% of false positive results.
By the end of the 5th month of pregnancy, a definitive diagnosis can be made. A child with Down's pathology has a distinctive appearance; some signs during pregnancy will be shown by an ultrasound machine, others will become noticeable after birth:
- slanted eyes;
- wide lips;
- reduction in the size of the upper jaw;
- flat, wide tongue with a longitudinal groove;
- round head, sloping forehead;
- saddle nose;
- flat face;
- small chin and mouth;
- low-set ears, attached lobe;
- wide short neck;
- sparse hair with straight, soft hair;
- funnel-shaped (or keeled) shape of the chest;
- short crooked little finger;
- wide feet and hands (on the palms there is a single four-fingered transverse groove);
- shortened limbs;
- significant changes in internal organs;
- improper growth of teeth.
How screening is carried out during pregnancy: rules for performing the study
First of all, a woman needs to donate venous blood on an empty stomach for biochemical analysis. After blood collection, the pregnant woman undergoes an ultrasound scan performed by a doctor specializing in genetic research. The screening procedure is performed using high-class equipment.
Screening for Down syndrome can be performed transvaginally or abdominally. The first study is carried out by inserting a special attachment of an ultrasound machine into the vagina. 30 minutes before the examination, the woman needs to drink 500 ml of water. The second diagnosis is performed in the same way as the first. The only difference is that a pregnant woman does not need to drink large amounts of liquid. The third examination is performed abdominally and does not require special preparation.
After the procedure is completed, the doctor acquaints the pregnant woman with the results obtained. If screening indicators deviate from the norm, genetic consultation is recommended. In some cases, a slight deviation from normative values indicates the possibility of having a child with a pathology. Compliance of the results with the standards is an indicator of the healthy progression of pregnancy.
What tests are included in screening?
A comprehensive diagnosis of downism during pregnancy includes a blood test and ultrasound diagnostics. During gestation, the protein component of the blood changes in the body. There is a connection between blood components and the presence of developmental abnormalities in the child. A change in protein levels accompanies a normal pregnancy, so medical specialists take into account the period at which the study is carried out.
Ultrasound examination includes examination of the fetal collar zone. Each child has a small amount of fluid in this area, the level of which can be determined using ultrasound. There is a relationship between fluid levels and the risk of having a child with Down syndrome. The discovery of swelling during the study of the collar space indicates the likelihood of downism and heart defects.
The study of body systems using ultrasound radiation allows us to identify structural abnormalities of the fetus. The study is able to detect some possible defects. The degree of diagnostic accuracy depends on the type of test, the experience of the medical specialist and the equipment.
When is the examination done?
Screening is carried out once every trimester. The first examination is performed in the first trimester of pregnancy, more precisely at 11-13 weeks; diagnosis at a longer period is uninformative. The biochemical test is aimed at clarifying the level of hCG and PAPP-A. This analysis is called the “Double Test” and allows you to find out the likelihood of having a child with Down and Edwards disease. Screening using ultrasound equipment and a biochemical test make up a comprehensive triple test for the first period of pregnancy.
Screening examinations during pregnancy in the second trimester are performed between 16 and 18 weeks. At this stage, it is possible to measure a larger number of indicators than in the previous period. Biochemical diagnostics can identify abnormalities in the structure of the spine, anencephaly, downism, and Edwards syndrome. A combined examination of the second trimester combines a biochemical test and ultrasound.
At 32-34 weeks, the third screening is carried out, including an ultrasound examination of the fetus, recording the baby’s heart rate, and Doppler measurements. A set of diagnostic methods is used to assess the general condition of the fetus.
What is screening
The examination is a complex of diagnostic procedures, including ultrasound diagnostics and analysis of venous blood for hormonal components. The most common method is to conduct the study every trimester. Routine ultrasound is a mandatory procedure, and full screening for Down syndrome falls into the category of additional studies.
Doctors prescribe a full range of diagnostic procedures in the following cases:
- mother's age exceeds 35 years;
- heredity is burdened with genetic pathologies;
- pathologies of previous pregnancies;
- infection with an infectious disease in the first trimester;
- use of medications that negatively affect the fetus;
- presence of bad habits;
- work in hazardous conditions.
Early detection of developmental anomalies makes it possible to correct genetic diseases and relieve symptomatic manifestations. If severe pathologies are detected, the woman may be offered termination of pregnancy according to doctor's indications.
Causes
The cause of the syndrome is the appearance of an extra copy of chromosome 21, and it can be copied completely, then trisomy occurs, or individual sections of the chromosome can be copied, then a translocation variant of the disease occurs. The genetic norm is 46 chromosomes, the syndrome occurs when there are 47 chromosomes.
Trisomy 21 was first explained by the French pediatrician Jerome Lejeune, defining the disease as a genetic defect. He studied Down syndrome - how to determine how to cure patients with this disease. He also condemned the use of his invention for prenatal research, which was done for the purpose of abortion. His position aimed at protecting life from the moment of conception cost the scientist the Nobel Prize (this is unofficial, but subjectivity is also present in the Nobel Committee). Pope John Paul II appointed the scientist who was able to recognize the patterns of development of the disease as the first president of the Papal Academy of Life.
Now in Rome the case for the canonization of Jerome Lejeune is being considered, his words in defense of life deserve special attention today: “Human genetics can be summed up in this basic credo: In the beginning there is a message, and there is a message in life, and the message is life. And if the message is a human message, then life is a human life.” It doesn't matter what genetics a person has. The main thing is that this is human life, which must be valued equally; discrimination against people for any reason, including health reasons, must be prevented.
Lejeune also said: “The enemies of life know that in order to destroy Christian civilization, they first need to destroy the family at its weakest point - the child. And among the weakest, they must choose the most vulnerable - a child whom no one has yet seen, a child who is not yet known and not loved in the usual sense of the word, who has not seen the light of day, who cannot even cry with grief.” It is important not only to identify the disease, but also to accept the person into society; the mother needs to avoid termination of pregnancy despite personal difficulties, medical instructions and pressure from relatives.
Jerome Lejeune
The disease does not depend on any external factors, but the following dependence on the woman’s age has been statistically discovered:
- between 20 and 24 years of age, the statistical probability of having a child with a genetic defect is approximately 1 in 1500 or 0.07 percent, that is, less than one tenth of one percent;
- respectively, from 25 to 35 years - 1 to 1000 or 0.1 percent;
- 35 - 39 years old - approximately 0.5 percent or 1 in 200;
- Women over 45 years old may well give birth to a healthy child, but the risk of the syndrome at this age is significant - about 5 percent of babies are likely to be born with an extra 21st chromosome.
It is possible that with age, the genetic material in men also becomes weaker, but this depends very much on health and lifestyle. The deterioration of hereditary genetics strongly depends on the way of life and bad habits, so you need to lead a moral and healthy way of life, and this will have a positive effect not only on your immediate offspring, but also on the health of future generations.
People who already have Down syndrome have a high chance of having children with the genetic disorder, up to 50 percent. Most women can have children, most men are infertile, but not all, there is still a small percentage of fertile people, it is difficult to determine this possibility. Therefore, people who already have the genetic defect do not necessarily need to know how to avoid pregnancy, they just need to abstain from sexual intercourse in general. If pregnancy occurs, anything can happen, it doesn’t matter whether the fetus has Down syndrome or not, the baby’s life must be saved, given the opportunity to be born and helped to live a full life. Society should help parents in raising both sick and healthy children in such families.