What is the essence of the analysis?
The surface of the mucous membrane and the lumen of the human intestine are populated by various microorganisms, which include bacteria and fungi. Some species are necessary for the normal course of digestion processes; some microorganisms should not normally be present or their minimum amount is allowed.
Based on these criteria, there are 3 main groups of microorganisms that populate the intestines:
- Opportunistic microorganisms. Represented by a small number of microorganisms. Normally, their development is suppressed by normal microflora, as well as local immunity factors. Under certain conditions leading to a decrease in the protective properties of the mucous membrane, the number of cells of representatives of opportunistic (opportunistic) microorganisms increases, which leads to the development of an inflammatory reaction and pathological process.
- Pathogenic microorganisms. Normally, they should not be in the intestines. Their appearance and subsequent vital activity lead to the development of the disease. Sometimes, when the properties of microorganisms are weakened, as well as certain individual characteristics of the immune system, bacterial carriage is possible. This is a condition when pathogenic microorganisms are present in the intestines and are released into the external environment, but there are no signs of a pathological process (disease).
- Normal microorganisms are necessary for the normal functional state of the intestine. They perform a number of important functions, which include protecting the mucous membrane, improving the digestion process and digestion of cellulose through the production of certain enzymes, the synthesis of B vitamins in the large intestine, and the formation of feces.
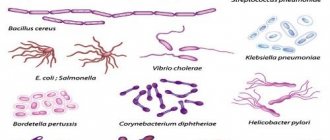
Table 1. Representatives of the intestinal microflora: normal, opportunistic and pathogenic bacteria.
| Normal | Opportunistic | Pathogenic |
|
|
|
Most bacteria, representatives of normal and opportunistic microflora, are determined during the study of stool analysis for UPF. The principle of the laboratory research method is to inoculate biological material (stool) on special nutrient media. Colonies of microorganisms grow on them and are identified. Colony counts (CFUs, or colony-forming units) are then performed, followed by determination of the number and ratio of different types of bacteria.
Read on the topic: How to test stool for pathologies at home?
Stool analysis for OPF (opportunistic pathogenic flora): what is it, preparation and testing
Symptoms of acute intestinal infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms manifest themselves in the form of nausea, fever, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
In severe cases, dehydration occurs and dangerous complications develop.
The presence of pathogens can be detected, as well as their sensitivity to antibacterial drugs can be determined by stool culture for the presence of pathogenic intestinal flora.
In the laboratory, microorganisms are grown on nutrient media.
Purpose of analysis
The goal pursued by the doctor when prescribing a bacteriological examination of stool is to establish the true cause of pathological processes in the intestines.
The choice of treatment tactics that guarantees the patient’s complete recovery depends on the result of the analysis.
By inoculating stool for pathogenic flora, the presence of pathogenic microorganisms is detected, which excludes the development of the disease for other reasons.
Established deviations from the norm, which confirm the infectious nature of the pathology, eliminate the need for additional diagnostic measures. The doctor has the opportunity to formulate antimicrobial therapy on an individual basis, taking into account the results of the study. Bacterial seeding is prescribed for:
- diagnosis of acute intestinal infections;
- pathogen identification;
- determining an effective drug for therapy;
- evaluation of treatment results.
Actually, stool culture for flora is a microbiological study of human biological material, performed in vitro (outside the patient’s body) in laboratory conditions.
The raw materials presented for analysis are placed in a special nutrient medium.
Biological materials are kept in special conditions at a certain temperature for a certain time necessary for the growth of microorganisms.
The identified pathogenic flora serves as material for the next stage of diagnosis - an antibiogram. Thanks to the antibiogram, the degree of sensitivity of dangerous microorganisms to the effects of bacteriophages and antibacterial drugs is established.
Disgroup analysis - what is it?
A person can get a referral to do this research, but what is it? Feces for the disgroup include a study using bacterial culture of the patient’s intestinal microflora.
It is usually carried out when there is a suspicion of an intestinal infection or if there is a sick person in the family and it is necessary to monitor the condition of cohabitants.
Disgroup analysis helps determine the lack of enzymes involved in digestion in the large intestine, which are produced by intestinal flora. This opens up the possibility of diagnosing dysbiosis if it is present.
To carry out bacterioscopic analysis, a small amount of biomaterial is required. Place it on a nutrient medium and wait for the microorganisms to begin multiplying. Next, the resulting material is placed under a microscope and the pathogenic environment the doctors encountered is studied. Sometimes the polymerase chain reaction method is used for bacteriological examination of a smear.
- What does an immunologist treat - what diseases. Treatment of adults and children by an immunologist
- Apple puree: recipes
- Chicken with mushrooms in sour cream sauce: recipes with photos
Object of study
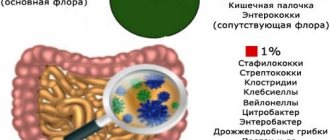
For a healthy person, colonization of the intestines with yeast-like fungi, bifidobacteria, bacteroids, E. coli, cocci, and lactobacilli is the norm. Together they form a unique microflora that contributes to:
- strengthening the wall of the large intestine;
- protecting the colon from harmful influences;
- decomposition of fiber from food;
- synthesis of biologically active substances;
- production of substances that ensure normal functioning of the immune system.
The selection of colon contents required for culture of pathogenic intestinal flora has sound reasons. The small and large intestines are divided into a certain number of subsections with characteristic microflora.
The composition of the microbiota of the small intestine adjusts bile and gastric juice. Bile and stomach acids, as well as enzymes, allow only a small number of microorganisms to exist in the small intestine.
In the large intestine, a completely different picture is observed, allowing the microbiota to be defined as:
- aerobic and anaerobic (needing and not needing the presence of air);
- specializing in a certain type of broken down substance (for example, preolytics are responsible for protein conversion);
- beneficial, opportunistic and pathogenic.
The normal composition of the microbiota involves the proximity of every hundred bifidobacteria cells with one lactobacilli cell, a dozen E. coli cells, and one cell of another microorganism (for example, enterococcus). The degree of activity of each type directly depends on the state of the body.
Standards are approximate only and may vary depending on age and lifestyle
Deviations from the norm cause:
- allergic reactions;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- oncological and infectious diseases;
- age;
- working conditions;
- nutritional features.
There are no unimportant details in the study
During sowing of stool, they are checked for disgroup. It is performed if there are epidemiological indications, or for preventive purposes.
When a pathogenic pathogen is identified during a disgroup test, antibiotic therapy is used. This type of analysis is also needed in order to identify what phenomena in the human body are lacking for normal digestion.
In children, diagnosis for disgroup most often shows that there is not enough lactose enzyme in the stool. Investigation is necessary when young children show the first signs of diarrhea. In children, the disease is much more severe than in adults.
If diarrhea begins in an infant and he does not receive medical care within 24 hours, the disease is fatal.
Using a stool test for the intestinal group, doctors can detect dysentery in a patient. However, you need to know: in some cases, if people have this disease, the Shigella that causes it may not be detected in their stool. To diagnose dysentery, a person is examined for the presence of symptoms accompanying this disease:
- elevated temperature;
- abdominal pain;
- the presence of blood in the stool.
Rotavirus infection in its symptomatic picture may be similar to dysentery.
The same study of stool, which becomes watery during the disease, but no blood or mucus is observed in it, can detect rotavirus infection in a person.
Rotaviruses should be absent in the stool of a healthy person. If they are detected, urgent use of antibiotic therapy is required.
101analiz.ru
Culture results
The performed bacterial culture reveals the presence of truly harmful bacteria belonging to the dysentery and typhoparatyphoid group, or bacteria belonging to the opportunistic pathogenic flora (UPF).
Interpretation of the results confirms or refutes the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
The growth of intestinal pathogenic bacteria involves determining sensitivity to the effects of antibacterial drugs.
Source: https://diagnost-mk.ru/endoskopiya/posev-kala-na-upf.html
How to take the test correctly?
The reliability of the obtained test results for opportunistic flora is determined by the correct preparation of the patient, containers, direct collection of biological material and its storage. Typically, detailed recommendations regarding preparatory measures are given by the doctor during a consultation after prescribing the appropriate study.
Be sure to read:
Bifidobacteria: concept, functions and sources of beneficial microorganisms
Preparing for the test
Before collecting stool for analysis for opportunistic microflora, it is important to follow a few simple recommendations:
- Avoid drinking alcohol, fatty fried foods, sweets, and foods that enhance fermentation processes in the intestines a few days before collecting stool.
- 3 days before the study, it is advisable to stop taking medications (the possibility of taking medications is discussed with your doctor individually). Antibiotics, regardless of the route of entry into the human body, lead to the death of some intestinal microorganisms, which can cause unreliable test results for UPF (see more about how antibiotics affect microflora).
- You should not collect feces directly after an enema, the use of rectal suppositories, or after using sorbent preparations. Sorbents are a group of drugs that bind and remove toxic compounds and various microorganisms from the intestinal lumen with feces.
- Before defecation, it is recommended to toilet the perineal area with clean water without using detergents.
In infants, it is not recommended to introduce complementary foods before collecting stool. Preparatory measures for collecting stool for analysis of UPF in older children are not fundamentally different.
Preparing containers
To obtain reliable results of stool testing for opportunistic microflora, it is important to prevent various microorganisms from entering the material from the outside. Therefore, sterile containers must be used to collect material.
- The pharmacy sells special disposable sterile plastic containers for collecting stool.
- It is allowed to use small glassware (glass jars for food, preserves). They should first be thoroughly washed with clean water and then boiled for several minutes. This will destroy microorganisms on the walls of the dishes.
Collection of material
Feces for analysis of opportunistic microflora are collected after a natural act of defecation. It is not recommended to collect feces from the toilet, so it is better to defecate on a prepared clean sheet of paper, polyethylene, or in a dry vessel. Stool collection is carried out using a clean wooden spatula or a disposable plastic spoon. A small volume of material, which should not exceed 1/3 of the container, is placed in a sterile container and screwed on with a lid. A direction with passport data must be attached to the container with the material taken for research. In children, feces are collected with a spoon from diapers or nappies.
Be sure to read:
How to eat if you have an intestinal infection?
Material storage
Quite often, feces taken for examination cannot be immediately delivered to the laboratory. It can be stored in a cool place at an air temperature of +3 to +5° C. The duration of such storage should not exceed 8 hours. The ideal option is to deliver the collected material to the laboratory within a period of time not exceeding 3 hours.
Advantages of cyst formation in protozoa
The main task of cystogony is to preserve the population of a particular type of microorganism and its maximum distribution in nature, while the reproductive function for some species is considered more secondary. Some microbes are able to replace the formation of cysts for further sexual division.
Advantages of cyst formation in protozoa:
Many single-celled creatures, entering the human body, cause various diseases. It is quite difficult to detect them by examining the biological material of a patient. Most often, their presence is indicated by cysts found in the stool.
The most common classes of protozoa, cystic forms of which can be found in feces:
- flagella;
- rhizomes;
- coccidia;
- ciliated;
- ciliates;
- sporozoans.
Violation of the living conditions of pathogenic microorganisms gives impetus to the formation of a protected form, which will be able to survive in the air and will subsequently reach its new host. Therefore, protozoa can only be detected in feces in the form of cysts. Their presence will indicate a pathogenic influence and the possible development of a particular disease.
Decoding indicators
The interpretation of the results of a stool test for opportunistic microflora includes indicators of the number of certain types of bacteria; it is presented in the form of a table:
| Intestinal microorganism | Age, years | Content standard |
| Bifidobacteria | From 0 to 1 year | 1010 and above |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 109 and above | |
| Lactobacilli | From 0 to 1 year | 106-107 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 107-108 | |
| Escherichia coli (total) | From 0 to 1 year | 107 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 108 | |
| Enterobacteria lactose-negative | From 0 to 1 year | 104 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 105 | |
| Enterococci | From 0 to 1 year | 105-107 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 105-108 | |
| Bacteroides | From 0 to 1 year | 107 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 108 | |
| Staphylococcus saprophytes | From 0 to 1 year | Under 104 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | Under 104 | |
| Clostridia | From 0 to 1 year | Under 103 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | Less than 105 | |
| Candida | From 0 to 1 year | Under 103 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | Under 104 | |
| Peptostreptococci | From 0 to 1 year | 103-105 |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | 109-1010 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | From 0 to 1 year | No |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | No | |
| Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli | From 0 to 1 year | No |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | No | |
| Proteus | From 0 to 1 year | No |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | No | |
| Pathogenic fungi | From 0 to 1 year | No |
| Children over 1 year old and adults | No |
Be sure to read:
The benefits of inulin and sources of its content (foods, dietary supplements)
The interpretation and subsequent prescription of treatment, if necessary, is carried out by the attending physician.
Read on the topic: How to restore intestinal microflora at home
Principles of treatment for changes
Changes affecting the results of stool analysis on the UPF are usually manifested by an increase in the number of various opportunistic bacteria above the normal level or the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, complex treatment is prescribed, which may include several areas:
- Antibiotic therapy is used to suppress the activity of opportunistic microflora (according to indications) or to destroy representatives of pathogenic flora.
- Probiotics are preparations that contain viable bacteria from representatives of normal flora, mainly bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
- Prebiotics are drugs that stimulate the activity of beneficial bacteria by containing essential substances.
- General recommendations, including a diet with the exclusion of foods that enhance fermentation processes in the intestines. Preference is given to fermented milk products, as well as plant products containing fiber.
The duration of complex treatment is determined by the doctor individually. Typically, after a course of therapy, control laboratory tests may be prescribed, including stool analysis for UPF.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Taking a stool test for dysbacteriosis + interpretation
- Culture for intestinal dysbiosis: details of the analysis
- Bacteriological culture (tank culture) of feces: essence, preparation and analysis
- Preparing and submitting a stool test for dysbacteriosis in infants
- Klebsiella in the intestines: danger of bacteria, symptoms and treatment (drugs, diet)
- Enterobacteriaceae in a child’s stool: is it dangerous and how to treat it?
- Klebsiella in the stool of a baby: symptoms, treatment and prognosis for the child
- Yeast fungi were found in a child’s stool: is it dangerous and is treatment necessary?
- How to take a stool test for the intestinal group?
- Analysis of stool for disgroup: essence, preparation and delivery of analysis