Disgroup analysis - what is it?
With vomiting and prolonged diarrhea, it is possible that there is an infectious disease that is prone to serious complications. A disgroup is an enteropathogenic group that includes diseases such as dysentery, salmonellosis, one type of typhus, and others. If they are not treated in a timely manner, among complications doctors identify intoxication of the body and death.
In order to reliably identify intestinal infections, promptly identify dysbiosis, candidiasis or enterobiasis, and speed up the long-awaited recovery process, it is important to know what a disgroup is and what part such tests take in collecting anamnesis data. During pregnancy, a characteristic smear is also prescribed, especially if the expectant mother constantly complains of indigestion, poor appetite and flatulence. This rule also applies to children who, from birth, are at risk of intestinal infections.
When and how to take a smear for disgroup
If it is impossible to take stool during a bowel movement (and diarrhea and enemas are unacceptable for this analysis), then the medical professional will use a tampon. It will be used to take a swab from the anus for analysis.
The procedure of taking a smear is unpleasant, but it is in demand in the case of a difficult natural bowel movement of the patient. Before performing it, you should avoid taking antibiotics, giving rectal suppositories, and enemas. Before taking a smear, your healthcare provider will ask you to lie on your side, pull your knees toward you, and spread your buttocks. A special cotton swab will be inserted to a depth of about 4 centimeters into the rectum and made several rotational movements. After this, the swab will be placed in a test tube with a special medium.
Stool analysis for disgroup
Analysis of stool for disgroup is widely used to identify acute and chronic intestinal infections and dysbiosis. If symptoms of an intestinal infection appear, such a study is extremely necessary.
Signs of intestinal infection: general weakness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, frequent loose stools with pathological impurities, malaise, abdominal pain, fever, headaches and muscle pain.
These symptoms may occur with salmonellosis, shigellosis, amebiasis, rotavirus infection and other intestinal infections. When analyzing the disgroup, it is possible to identify the pathogen and select an effective treatment.
Intestinal dysbiosis (dysbiosis) in children is manifested by the following symptoms: bloating, flatulence, alternating diarrhea and constipation, bad breath, nausea; an allergic reaction that has not previously occurred. Signs of dysbiosis may appear after antibiotic therapy and disappear after the use of probiotics.
To collect stool, use a clean, dry glass jar with a lid or a disposable container. In addition, it is necessary to prepare a bedpan and a pot (you should first treat it with any disinfectant, rinse thoroughly several times with running water and rinse it with boiled water).
In the morning, before collecting stool, you should carry out a hygienic washing procedure. It is necessary to wash the external genitalia and perineum of the child with warm boiled water, pouring water in the following sequence: pubic area, external genitalia, perineum, anus area in the direction from the urethra to the anus. Wipe the skin dry in the same sequence and direction. Feces for research should be collected during spontaneous bowel movements. When collecting stool for examination, it is not recommended to use laxatives. The stool for analysis should not contain any admixtures of urine or menstrual fluid.
Before collecting the test, the child should urinate into the toilet, then perform a natural bowel movement into a potty or bedpan, then collect the stool.
Stool collection for analysis is carried out with a spatula or a special spoon, which is attached to the container. For analysis, 1–2 teaspoons of stool is needed. The container is filled approximately 1/3 full. If there are impurities of pus, mucus or flakes in the stool, then these areas should be selected for collecting material. Areas with blood should not be taken, since the blood contains bacteriostatic substances that inhibit the growth of microorganisms in nutrient media.
If the stool is watery, you can collect the material using a pipette. In the container, its thickness should be at least 2 cm. When collecting feces from a small child, you can take feces from clean linen. The stool collected for analysis is delivered to the laboratory no later than 2 hours. F is clearly indicated on the container.
I.O. of the child, date of birth, date and time of collection of material. Sometimes rectal swabs are used for testing and are taken by a nurse, laboratory technician, or doctor. To collect them, disposable rectal swabs on a rod in sterile packaging are used.
The child is placed on his side, his legs are brought to his stomach, his buttocks are spread with his hand. The nurse inserts a tampon into the anus to a depth of 2–4 cm. Using rotational movements for several seconds, she collects material from the walls of the rectum, removes the tampon and places it in a container with a special medium. The sample must be delivered to the laboratory within a maximum of 2 hours. In children with loose stools, a disposable soft catheter can be taken to collect material: one end is inserted into the rectum, and the other end is lowered into a container.
When performing this analysis:
- determine the presence of bacteria and protozoa;
- carry out inoculation of feces on nutrient media;
- identify the pathogen;
- determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to drugs.
Test results are expected in 1–7 days. To ensure the reliability of the analysis, stool should be taken at the first symptoms of the disease, before starting antibiotic treatment. If pathogenic microorganisms are found in the stool, but the child does not have any symptoms characteristic of an intestinal infection, then we can say that he may be a potential carrier of the disease. Under certain conditions, he may become ill himself. In any case, such a carrier is dangerous for others.
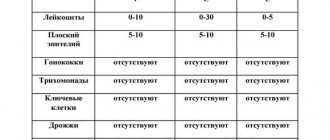
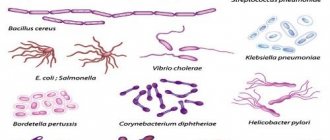
There should normally be no pathogenic microorganisms in feces. The causative agents of shigellosis are Shigella, the causative agents of salmonellosis are Salmonella, the causative agents of cholera are Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of amoebiasis is Amoeba, and the causative agent of balantidiosis is Balantidium.
For intestinal infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms, additional diagnostics and a blood test are performed to identify antigens to these microorganisms.
In addition to identifying intestinal infections, stool analysis is carried out to identify dysbiosis and determine its degree. If an opportunistic microorganism in feces is detected in a titer of more than 105 CFU/g, it is believed that it was the cause of the pathological symptoms.
In a healthy person, 15 groups of microorganisms are identified in the feces: eubacteria, bacteroides, enterococci, bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, Klebsiella, clostridia, etc.
By assessing the growth of bacterial flora on nutrient media, it is possible to identify the causative agent of the disease if:
- growth is insignificant on a liquid medium, but not on a solid medium, these bacteria are not the cause of the pathological condition;
- the growth of a certain type of bacteria of 10 colonies on a dense medium - it is possible that they caused dysbacteriosis;
- the number of microflora colonies is 10–100 – there is a high probability that this microflora caused the disease;
- If the number of bacterial colonies is more than 100, then these bacteria are the causative agents of the disease.
What does the analysis reveal?
The microflora of the human intestine is diverse, including both essential bacteria and opportunistic bacteria that can cause disease under certain conditions. It is important not only the fact of detection, but also the relationship with other representatives of the microbial association.
Detection of pathogenic microflora confirms the diagnosis of intestinal infection. After this, it becomes clear which antimicrobial agent the patient needs to take in order to be cured. The same study is repeated after completion of the full course of treatment to monitor its effectiveness.
To understand the components of the human intestinal microflora, consider the table below.
| Normal microorganisms | Pathogenic microorganisms | Opportunistic microorganisms |
|
|
|
- A group of normal microorganisms is an essential component of the intestinal microflora of a healthy person. These bacteria provide local immune protection, maintain pH at a normal level, and participate in the absorption, breakdown and digestion of all nutrients. Without this group of microorganisms, the full functioning of the digestive canal is impossible.
- A group of opportunistic microorganisms occupy the area of the intestinal mucosa according to the principle of functional antagonism. That is, while they are present, there is no free space for pathogenic microorganisms and they cannot settle in the human intestine. It is important not only their presence, but also a certain ratio: they should not dominate the normal microflora. When their number increases significantly, conditions are created for the occurrence of intestinal disease.
- Pathogenic microorganisms are absent in the body of a healthy person. These microbes cause various damage to the digestive canal and the entire body as a whole. Examples are presented in table form.
Be sure to read: Undigested food in a child’s stool: why does it appear and what does it mean?
| Pathogen | Name of the disease |
| salmonella (Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi) | typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever |
| other salmonella | salmonellosis |
| Shigella | dysentery or shigellosis |
| Vibrio cholerae | cholera |
| dysenteric amoeba | amoebiasis |
| balantidium | balantidiasis |
| Giardia | giardiasis |
The result of the study for the disgroup is assessed in combination with other tests and the general condition of the patient.
Indications for analysis
Disgroup analysis is used to diagnose intestinal infections and dysbacteriosis. Most often it is prescribed when the patient has characteristic signs of an intestinal infection. These signs include: nausea and vomiting, frequent loose stools, abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite and general weakness.
To prescribe the optimal treatment regimen, the doctor needs to know exactly the causative agent of the infection. Many intestinal pathologies: salmonellosis, dysentery, rotavirus infection have a similar clinical picture, so the type of infection can only be reliably determined using laboratory stool analysis. If dysbacteriosis is suspected, the specialist will also refer the patient for this examination - it will help confirm or refute this diagnosis.
Signs of dysbiosis are chronic flatulence, constant diarrhea and constipation, bad breath, and sudden intolerance to certain foods.
Analysis price
The cost of a smear depends on the reputation of the clinic and the city where the laboratory test was performed. In the provinces, such a service is much cheaper, as are the prices for tablets at the pharmacy. In St. Petersburg and Moscow, prices are approximately the same, generally affordable for patients. When performing a smear, timeliness and proper preparation for laboratory testing are important so that repeated laboratory testing and unplanned waste do not arise.
Approximate prices for disgroup analysis in the capital are detailed in the table below, and are acceptable for patients who need to check the composition of the intestinal flora and eliminate the risk of the development and spread of pathogenic pathogens. So the prices are as follows:
| Clinic name | Cost of services, rubles |
| Eden on Arbat | 200 |
| World of Health | 300 |
| Women's Health Center | 350 |
| Vicky Honey | 400 |
| Vita | 500 |
| He's a clinician | 650 |
Rules for collecting stool
Stool collection for analysis must be carried out in compliance with certain rules. This will allow you to get the most reliable results. If you are taking medications, be sure to tell the doctor who ordered the test: you may need to stop taking the medications for a while. A few days before the test, you should not use laxatives, rectal suppositories, activated charcoal, vaseline and castor oils.
You also need to know that material obtained after a cleansing enema is not suitable for analysis. It is recommended to collect stool in the morning, since it is advisable to provide it for analysis no later than 2 hours after receipt.
Before bowel movement, you should urinate to avoid urine getting into the test material. It is more convenient to purchase all the supplies necessary for collecting stool at the pharmacy.
The finished kit includes a clean and sealed plastic container along with a spoon. The volume of material sufficient for analysis is about 2 such spoons. If you plan to use another container, wash and dry it thoroughly before use.
Material obtained after a cleansing enema is not suitable for analysis. To get the most accurate results possible, stool should be collected from several places. If it contains mucus, flakes, pus or other uncharacteristic inclusions, these also need to be submitted for analysis. At the same time, blood impurities in the stool should be avoided, since they can complicate the procedure for studying the material.
For the same reason, women are not recommended to have stool tested during menstruation. If you have watery stools, you should collect the stool using a pipette. The amount of material should be such that its layer in the container is about 2 cm. Sometimes independent stool collection is not required, and the necessary material is obtained using a rectal smear. During the procedure, the patient lies on the couch on his side with his legs pulled up to his stomach. A laboratory technician, nurse, or doctor uses a customized rectal swab to collect stool. For diarrhea, a flexible catheter is used to collect biomaterial, which is inserted directly into the rectum.
How to take the test correctly?
The information content of the stool analysis result depends on proper preparation for the study. If questions arise, they should be asked to your doctor to avoid false positives or false negatives.
Preparing for the test
It starts 3-4 days before the actual test. At this stage of preparation, the patient needs to:
- stop using laxatives (including petroleum jelly and castor oil), antimicrobial agents, antidiarrheal drugs, sorbents;
- stop using enemas and rectal suppositories;
- do not undergo an x-ray examination of the digestive canal with a barium mixture, since the x-ray contrast agent takes a long time to be eliminated;
- interrupt your diet for a while, especially if it involves eating only plant foods, juices and significantly limiting the amount of food you eat.
To prepare for a stool test for the disgroup, the patient should:
- eat balanced and regularly;
- observe drinking regime;
- Empty your bowels regularly.
If the above is observed, a person will not have problems collecting material for research.
Preparing containers
There are 2 options for delivering feces to the laboratory: in a factory container and in a home remedy.
The easiest way is to buy a container at your nearest pharmacy. A neat plastic jar, often with a mark on the side indicating to what level it should be filled. There is space on the lid or side to enter patient and study information. The factory container is equipped with a tightly screwed lid, which avoids the spread of unpleasant odors and spillage of the collected material.
It is entirely acceptable to use a home remedy - a glass jar. Before use, you must thoroughly rinse the jar to remove foreign substances and boil for 15-20 minutes without additional reagents. The lid undergoes the same treatment. After boiling, both the jar and the lid dry naturally without wiping with a towel.
Collection of material
The ideal time to collect material is morning. Only in exceptional cases is it allowed to study the material collected in the evening.
- Before bowel movement, prepare a clean vessel covered with paper or a disposable plate.
- Bowel movement occurs naturally.
- Feces are collected directly into the prepared vessel (plate), and not from the surface of the toilet.
- For disgroup analysis, portions of stool are selected from different areas using a spatula or a disposable spoon; areas containing blood and mucus are not suitable for testing.
- The container is immediately tightly sealed and signed.
For diarrhea, stool is collected with a pipette or tube directly from the intestines. The amount of feces sufficient for research is 80-100 g.
In case of constipation, the material is collected by a medical professional using a tampon. The patient lies on his side and spreads his buttocks with his hands. The medical worker inserts a tampon into the anus to a shallow depth and gently passes it along the mucous membrane. He takes out the swab and places it in a test tube with transport medium.
How and for how long can the material be stored?
It is advisable not to store the collected material for research for more than 2 hours. In some cases, it may not be possible to deliver the material immediately after collection. Then the container is placed in the refrigerator (not in the freezer) on the middle shelf. Storage is allowed for no more than 6-8 hours. To improve storage in the laboratory, you can purchase an analysis container with a special preservative.
Methodology
During the analysis, the material is examined under a microscope to determine the presence of bacteria or protozoan microorganisms. The laboratory assistant also inoculates the stool, placing it in special nutrient media.
This allows you to grow colonies of bacteria, analyze the intensity of their reproduction and identify the causative agent of infection or dysbacteriosis. Growing colonies of bacteria takes time, so test results are not immediately available. The research process can take from 1-2 days to a week.
Scraping for enterobiasis, how to do a smear test
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
When health-related inconveniences appear, a person immediately runs to the doctor to find out the problem. And in most cases this is the right choice. For example, if enterobiasis is suspected. If there is even the slightest reason to suspect this disease, the doctor, be it an infectious disease specialist or a therapist, sends his patient to take a scraping for enterobiasis (feces). We'll talk about this analysis further.
- Scraping for enterobiasis: what is it
- What do the tests give? Indications for taking a scraping
- Submission procedure
- Patient preparation
This is a test that allows you to detect pinworm eggs. Their presence is manifested by a very unpleasant phenomenon for a person - itching near the anus. Often this disease is accompanied by intestinal disorders.
What does enterobiasis have to do with it, you ask? Despite the fact that pinworms are the causative agents of this disease. The length of these small parasites does not exceed one centimeter. Their inherent way of life is nocturnal. It is during a person’s sleep that female pinworms make their way into the rectum, onto the skin near the anus, lay eggs, then die and are excreted in feces.
Most often, a test for enterobiasis is prescribed when there is some suspicion. It allows you to either confirm or deny the presence of eggs of these parasites. This allows the doctor to plan further treatment for the patient.
The doctor sends the patient to donate a scraping (stool) when:
- suspects that a person is infected;
- it is necessary to conduct an analysis for the purpose of prevention (most often, it is prescribed during hospitalization, or if a person needs a medical book or a certificate to a public place, such as a swimming pool).
Many people are already interested in the question of how to get tested for enterobiasis? The procedure is completely simple and completely painless. There are different ways to get tested:
- Firstly, this is the so-called perinatal fold smear. Simply put, a swab is taken from the folds of skin around the anus. You need to take it with a special stick in the morning, before the first bowel movement and urination. The patient’s actions in this procedure are as follows: put on gloves, run a stick over the skin around the anus, place it in a special container.
- Secondly, scraping for enterobiasis is done using adhesive tape. The procedure is as follows: put on gloves, apply a special tape to the desired area, then attach it to clean glass.
- Thirdly, the doctor may advise you to test your stool for parasites. To detect enterobiasis, you need very little of it.
It is important to submit all materials to the laboratory no later than 2 hours after collecting the material (remember, it is valid for only two hours). All this time it can only be stored at a temperature of no more than 8 degrees.
Doctors recommend doing three tests so that the study shows an accurate result.
If the test certificate shows that the patient has enterobiasis, then there is no need to doubt it. If the scraping does not reveal pinworm eggs, then it is recommended to do a repeat analysis. How much time should pass between the first and second tests? The optimal period is a week or two.
How long will it take laboratory technicians to conduct your analysis? The most common period is a working day. That is, if the laboratory assistants are not busy, then your analysis will be ready in a minimum period of time - one day. This means that the very next day, after you submit your scraping, you may be issued a certificate.
If you receive a certificate with the results and it says that the scraping (feces) does not contain pinworm eggs, then everything is normal. And if the stool (scraping) contains parasite eggs, then we are forced to inform you of the unpleasant news - you have enterobiasis. There is no need to be upset, it can be treated!
Enterobiasis is a disease caused by worms called pinworms. Another name for this worm is eggworm. The main manifestations of the disease are periodic itching around the anus, especially at night, abdominal pain, decreased or lack of appetite and intestinal disorders. To make a diagnosis, a special test is performed - a scraping for enterobiasis. Invitro laboratory specialists recommend taking this test at least once every six months, even if there are no obvious manifestations and symptoms of the disease.
The cause of the disease is infection with pinworms, a worm the female of which has a pointed end, hence the name. During the day, a sexually mature female lives in the lower part of the small intestine of children and adults, where she feeds at the expense of the owner. At night, she crawls out through the anus and lays eggs in the folds of skin in the area of the genitals and anal canal. A special substance that worms secrete to attach eggs to the skin causes irritation and severe itching. A person infected with helminths has an unbearable desire to scratch the anus. Eggs with helminth embryos fall under the nails, and from there they spread either through the mouth into the body of the same host, causing a new wave of infection, or into a new host.
Most often, infection occurs in children between three and fourteen years of age. Gardens and schools, places with large crowds of people (shops, public transport, etc.) increase the risk of infection with various types of helminths, including pinworms. Hand washing and personal hygiene are the best means of preventing infection in children.
Our readers successfully use Intoxic to get rid of parasites. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Main symptoms of invasion:
- unbearable itching in the anus in the morning;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- Nausea and vomiting are possible;
- bowel dysfunction;
- in rare cases, the formation of granulomas with live and dead worms, as well as their eggs in the anus.
If your child begins to complain that his tummy hurts, and his hands are constantly scratching his butt or genital area, it’s time to go get tested for worm eggs. You should not be afraid of the analysis itself, it is done in vitro (in vitro), i.e. outside the body and is absolutely harmless.
It is prescribed to take scrapings for enterobiasis in two cases:
Testing for worm eggs is carried out free of charge, as prescribed by a doctor, in public clinics or on a paid basis, for example at Invitro. The offices of this laboratory are located in many cities throughout the Russian Federation. It is recommended to scrape the child early in the morning, before he goes to the toilet. Before taking the test, it is also not recommended to take a bath, shower, wash yourself or do other water procedures, as you can wash off the eggs from the folds and the test result will be unreliable.
There are three ways to collect tests for enterobiasis, and all of them are absolutely painless:
- using a cotton swab dipped in glycerin or saline;
- using a glass rod;
- using transparent adhesive tape (scotch tape).
If you take a scraping using adhesive tape, then it is simply glued to the surface of the skin around the anus and the tape with the contents is attached to a glass slide. It is important to ensure that no air bubbles get under the tape. If an adult worm accidentally attaches itself to the tape, it must also be sent to the Invitro laboratory for analysis, having first been placed in an alcohol solution in a test tube.
You can scrape the eggworm yourself and at home. To do this, you should purchase the necessary items at the pharmacy. The material collected for research must be submitted to the laboratory within two hours. The photo on the right shows the analysis procedure.
Often in public clinics they test the stool of children for an eggworm test. But the results obtained from this type of research rarely detect pinworm eggs, but other types of parasites can be detected precisely with the help of this analysis.
Normally, on the test sheet it is written that no worm was detected. If pinworm eggs are found in the scraping, the doctor will diagnose enterobiasis and prescribe treatment.
To ensure the reliability of the result, it is better to conduct the study several times. The first examination gives a fifty percent probability of disease, the second or third - 90%. It is better to conduct research every other day.
The test result for enterobiasis is valid for 10 days. If these deadlines have passed, then the material for research should be taken again.
- Bactefort
- Roundworms
- Other parasites
- Other parasites (bacteria)
- Giardia
- Opisthorchiasis
- Pinworms
- Parasites in animals
- Preparations for parasites
- Miscellaneous
- Trichomoniasis
- Chlamydia
- Tapeworm
How long does it take to analyze a disgroup?
In case of chronic constipation or diarrhea, in case of bloating, flatulence and the presence of impurities of pus (blood) in watery stool, it is recommended to urgently perform a stool test for disgroup in order to exclude the presence of a dangerous infectious agent in the biological material. Adults and children should be tested, especially if there are alarming signals from their own body.
In the latter case, parents should pay special attention if the baby develops a food allergy, sour smell of feces, or other obvious signs of dysbiosis. To determine intestinal infections, you cannot do without stool analysis for disgroup and culture. In addition, a specific laboratory test is required when applying for a job or registering a child for kindergarten. In such a situation, the smear is prepared for several days, after which its interpretation can be announced to the patient.
If antigens are detected and alarming symptoms are present, it is necessary to promptly begin treatment for an intestinal infection, especially if the patient complains of systematic attacks of nausea and fever.
Tank culture of feces decoding. When and by whom is a test for intestinal dysbiosis prescribed?
Usually, stool culture for microflora (stool microscopic analysis) is recommended by a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist or therapist, and less often by other highly specialized specialists. Bacteriological examination of stool is prescribed to diagnose dysbiosis, differentiate other diagnoses in a comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract, and general assess the state of intestinal microecology.
In case of ineffective treatment for dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis or antibacterial therapy, as well as for antibiotic-associated diarrhea, it is recommended to test stool for dysbacteriosis with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages. Because during routine research, they do not always focus on sensitivity to antibiotics.
When is it recommended to submit stool for culture:
- in the presence of an intestinal infection of unknown origin,
- for skin rashes and various allergic reactions of unknown etiology,
- for prolonged constipation, diarrhea and other functional disorders of the stool,
- in the case of long-term drug therapy with antibiotics, hormones, immunomodulators, as well as chemical and radiation therapy.
The following factors may influence the information content of a stool analysis for dysbacteriosis:
- Obligate anaerobes (for example, clostridia, which belong to the class of opportunistic flora) can only live in an oxygen-free environment. When stool is collected due to dysbacteriosis, a significant part of the anaerobes die when they come into contact with air. Therefore, the results of the analysis may show the presence of these organisms in much smaller quantities than they actually are.
- The correct algorithm for performing an analysis for dysbacteriosis has been violated (errors made in the laboratory).
- The technique of taking an analysis is violated (collecting stool in a non-sterile container, freezing stool, using laxatives for bowel movements, improper storage, etc.).
- Taking antibiotics, probiotics and other medications.
- Time of delivery of stool for analysis (the longer the time passes from the collection of stool to the start of the study, the less accurate the results of the analysis will be).
Therefore, deciphering the study of stool analysis for dysbacteriosis (stool bacterial analysis or biochemistry) is carried out only by a specialist, taking into account other tests and a general examination of the body’s condition.
In addition, the norms for lactobacilli and other microorganisms are conditional, and what may be an individual characteristic and norm for one person may be a pathology for another. The intestinal microflora is not a constant value; changes regularly occur in it, including those associated with age. In addition, the number of certain bacteria may vary depending on dietary habits, the presence of stress, and many others. other factors.
Assessment of the degree of dysbiosis (dysbiosis)
Dysbacteriosis is divided into different stages:
- With 1 degree of dysbiosis in the intestines, the level of bacteria beneficial to the body decreases. Most often, for the first few days, no obvious signs of the disease are noticeable.
- The second degree of dysbacteriosis is due to the rapid development of pathogenic microorganisms.
At this time, a disturbance in the functioning of the intestines occurs. The child feels pain in the abdomen, flatulence and upset stool appear.
- With the third degree of dysbiosis, damage to the intestinal walls occurs. The change in stool becomes chronic. Often, undigested food particles can be seen in stool.
- The final stage of the disease is the fourth, which is caused by the appearance of an acute infection. The child's body becomes very depleted, and sometimes anemia may occur. The patient feels nausea, heartburn, headache and unpleasant odor in the mouth. Similar symptoms can occur regardless of the degree of dysbiosis.
Regardless of the stage of dysbiosis, it is necessary to urgently undergo examination so that the doctor can prescribe therapy. Otherwise, the pathology in the child can lead to diseases such as gastritis and ulcers.
Tank culture of feces is done in how many days. Bacteriological examination of stool
Anyone who has stomach problems should undergo a stool test to investigate and identify the cause of the disease. How to do this correctly will be discussed in this article below.
Stool culture for analysis
Bacteriological examination of stool is an important procedure, especially for those patients who suffer from stomach diseases, including children. With the help of bacteriological analysis of stool, including that of a child, it is possible to identify information that will tell about the state of health of the child or adult, the characteristics of their digestive system and other points. It is known that fecal matter is undigested food debris that contains many elements and various microorganisms. Also, stool with stomach disease may contain other components, for example, blood, mucus or parasites. Bacteria in a child’s stool will help determine the condition of his body and begin treatment in time if necessary.
Stool culture analysis and main research methods:
The study of bacteriological analysis of feces makes it possible to identify pathologies in the body. With the help of such testing, a specialist will identify the chemical components in the collection and also determine the properties of feces.
Criteria that should be taken into account when performing bacteriological analysis of stool:
- The collection should contain no more than 80% water. This is the passing rate.
- The quantitative indicator of collection is 100-200 milligrams.
- If a specific odor appears, certain diseases of the body can be identified after testing.
- The color of the material will depend on what food the patient took. It may be different.
- Normal acidity is 6.5-7.0.
Such transcripts should be made only in the clinic with the participation of a specialist. This will help ensure an accurate result of the bacteriological examination of the stool analysis.
Also, bacteriological analysis of stool can be carried out to diagnose possible internal bleeding. There can be blood in the masses for a variety of reasons.
These are:
- Colitis.
- Cirrhosis.
- Typhus.
- Haemorrhoids.
- Tuberculosis and other issues.
In most cases, bacteriological examination of stool tests for hidden bleeding is carried out when it is necessary to obtain a result for hemoglobin, to identify helminth eggs or to identify another infection in the body. This will help to quickly diagnose the disease and begin to treat it on time.
Preparing for a tank stool test
To determine the correct results of testing the collection in a child and an adult, a bacteriological analysis must be performed correctly. To harvest crops, there are certain rules that must be followed. Doctors give the following recommendations:
- 3 days before the culture is collected, a child or adult should refrain from taking medications. This will help avoid the introduction of foreign substances into the collection and may give a more accurate culture test result.
- Also, before taking the crop, you should adhere to a certain diet. You should avoid eating foods that can change the color of stool, such as smoked meats. Such a diet should be prescribed by the attending physician during a preliminary examination. This will also help to more accurately determine the results of culture testing.
- The crops should be handed over in a clean container, which can be purchased at a pharmacy. You should defecate only in clean dishes. It is also worth trying to prevent urine from getting into the feces. Next, the seed should be placed in a container using a special spoon and sent to the laboratory.
- Before handing over the crop, the child should wash his butt. Then wipe the perineum dry with a clean towel.
During this procedure, the child should collect 6-10 milligrams of material. For an adult, this norm will be higher. The intestines should be emptied on an empty stomach in the morning of the day the doctor prescribed the procedure. Also, before taking the collection, you should refrain from cleaning your mouth with a toothbrush, so as not to cause gum bleeding. For oral hygiene, you can use special solutions to rinse the cavity.
Feces should be sent to the laboratory for culture no later than eight hours after collection. It can be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of minus 4-5 degrees.
Place the container away from the freezer so that the material does not freeze. In order to test the material as accurately as possible, you should strictly adhere to all the recommendations of your doctor for a certain period.
Decoding the results
Disgroup analysis. If the number of any pathogenic or opportunistic bacterial microorganisms exceeds the norm, they can be identified as the causative agents of intestinal disorders. Sometimes a re-analysis is required. If the results reveal that the concentration of the bacteria found has increased, this confirms the correctness of the initial diagnosis.
Harmful microflora can be detected in feces even in the absence of symptoms of intestinal infection. In such cases, the patient is only a carrier of bacteria. When the growth of microflora in nutrient media is insignificant or absent altogether, the specialist concludes that bacteria are not the cause of the pathological condition and refers the patient to other diagnostic procedures.
If the test results reveal any abnormalities, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations. Be sure to go through all the necessary diagnostic procedures, carefully following the rules of preparation for them - this is the only way to obtain reliable information about the state of your health.
Decoding
The purpose of stool analysis for disgroup is to identify not only pathogenic microorganisms. The number of beneficial bacteria that should always be present in the human intestine is also determined. Why is this necessary? Their active growth disrupts healthy microflora and can cause the development of dysbacteriosis.
Such microorganisms include:
- lactobacilli;
- bifidobacteria;
- coli;
- bacteroides;
- amoeba;
- staphylococci (only a few species);
- eubacteria;
- enterococci;
- fusobacteria;
- clostridia;
- Klebsiella;
- peptostreptococci;
- Hartmann's entamoeba, etc.
Normally, the following should not be detected in stool:
- salmonella;
- dysentery amoebas;
- intestinal trichomonas;
- shigella;
- cholera vibrios;
- balantidia;
- Escherichia (some species), etc.
The activity of pathogenic microorganisms may not always be the cause of the disease. In this case, the patient is a carrier of the infection, which does not exclude the need for treatment.
If during the process of bacteriological seeding the growth of harmful microflora in a favorable environment is insignificant or completely absent, it is also not the cause of the existing pathology. In this case, the patient is referred for a more thorough diagnosis.
When deciphering a stool analysis, the number of microorganisms is decisive. If any bacterium has a value greater than 10 5 CFU/g, it is the causative agent of the disease. In this situation, the analysis must be repeated. This is due to the fact that the result is influenced by too many factors, and the microorganisms in the sample behave differently than inside the human body. For example, the more time has passed from the moment of defecation to the delivery of the biomaterial to the laboratory, the more unreliable the results will be. But if the indicator after the repeated study has changed upward, this serves as confirmation of the previously made diagnosis.
Deciphering a stool analysis is a complex process that should only be performed by a competent specialist. In addition to studying the quantitative indicators of pathogenic microflora, he evaluates the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms. It can also provide information about various violations.