A small amount of red blood cells in a flora smear indicates the normal state of the female body. Exceeding the normal levels of red blood cells contained in vaginal discharge is considered a sign of some hormonal disorders in the female body and inflammatory processes, which can be externally expressed in the form of unpleasant and, in some cases, dangerous diseases. In this article, you can learn why red blood cells are determined in a smear for flora, what the normal values are, and what deviations from the permissible values will indicate.
Why do doctors take a smear?
Flora smears are a diagnostic method - studying under a microscope biomaterial collected from the surfaces of the woman’s vaginal mucosa. However, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the analysis of red blood cells in a smear for flora is done for everyone: both women and men. For representatives of the stronger sex, a smear is done to identify any urological disease. Materials for research in men are taken directly from the urethra. In women, a smear can be taken from the urethra, as well as the vagina.
The study of microflora, as well as the cytological composition of the collected biomaterial obtained by scraping or an imprint of the mucous membrane, makes it possible to diagnose various infectious diseases, including sexually transmitted and hormonal diseases. These same tests help detect cancer, background and precancerous conditions. A smear is taken for both therapeutic and preventive purposes. During a course of treatment for any disease of the genitourinary system, a smear is usually taken before and after treatment.
Taking a smear is a completely painless procedure that helps to correctly assess the state of the reproductive system in a woman’s body. Biomaterials are applied to a glass slide, after which a thin smear is made, which is a microslide suitable for subsequent study under a microscope.
Materials for research are selected using a glass pipette or a sharp spoon, and then applied to the edge of a special glass slide and smeared with the edge of a coverslip. The smears are slightly dried in air or on a burner flame, and then painted.
There are only two methods for staining vaginal smears. Monochrome is used in cytological analysis, as for polychrome, it is used for cytological and hormonal studies. After all the manipulations performed, the microspecimen will be ready for study under a microscope.
Violation of the smear preparation technique can lead to an unreliable result, but this situation is extremely rare in practice, since vaginal smears are a standard test that does not require any special advanced qualifications from a health worker.
Squamous epithelial cells
Squamous epithelial cells are dead cells of the vaginal mucosa that have been desquamated from the surface. On the mucous membranes of various organs, including the vagina, constant renewal of surface cells occurs, during which dead and old structures simply slough off, and new, young elements remain in their place.
Therefore, normally 5–10 epithelial cells may be present in a vaginal smear. If there are more epithelial cells in the smear than normal, then this is indirect evidence of the inflammatory process occurring in the vagina. The causes of inflammation are exactly the same as those caused by a large number of leukocytes in the smear.
If there are no epithelial cells in the smear, then this indicates either atrophy of the vaginal mucosa or a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body with a deficiency of estrogen and an excess of androgens (male sex hormones).
Key cells are normally absent in the smear. The appearance of key cells is an undoubted and typical sign
The “microflora” column usually indicates the predominant type of bacteria, for example, rods, cocci, yeasts, etc. If approximately the same amount of several types of bacteria is determined in the smear, then all types are indicated in the “microflora” column, for example, “cocci rods”.
Normally, the vaginal microflora should be represented by Doderlein bacilli, which are usually indicated simply as “bacillus” or “bacillus” in the analysis results form. If rods or bacilli are indicated in the “microflora” column, then the woman has a normal vaginal flora.
Preparation for collecting biomaterial
Women should come prepared for their smear test. In order for the analysis to be most reliable, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse for two days, not to douche, and not to carry out therapy with vaginal suppositories, creams and ointments. It is also recommended to urinate no earlier than three hours before going to the gynecological office. It is advisable to take this test on the 5th day of the cycle, when the woman’s period ends.
To determine red blood cells in a smear for flora, a man must also prepare before submitting the material: do not have sex a couple of days before visiting the doctor, do not smoke or drink alcoholic beverages several hours before the test.
Possible complications
Ignoring painful symptoms associated with changes in the microflora inside the urethra, vagina and cervical canal, and the appearance of excess mucus, can lead to the development of the following complications and negative consequences:
- infertility in men and women;
- uterine cancer;
- ovarian cystosis;
- benign prostatic hyperplasia in men;
- reduction or complete cessation of spermatogenesis;
- opening of vaginal bleeding;
- miscarriage if a child is conceived;
- penetration of infection into the kidneys, bladder, rectum;
- prostate cancer.
Mucus in a smear for microflora in women is one of the most effective methods for diagnosing the general condition of the vagina, cervical canal and urethra. To obtain the most accurate and reliable results, biological material is collected from all 3 places at once.
A flora smear makes it possible to find out about the level of leukocytes, red blood cells, epithelial cells, and the possible presence of infectious microorganisms. This type of analysis allows you to detect signs of hidden inflammation when a woman does not yet feel all the symptoms of the disease.
Taking a smear to determine the purity of mucus requires minimal preparation, is completely painless, and is completed in 10-15 minutes.
Red blood cell norm
How many of these bodies should be present in the biomaterial? Normally, there should be no red blood cells in the flora smear. However, a small amount of them is not harmful to the body and health.
We found out what number of red blood cells in a smear for flora in women is considered normal. It is also considered normal to have several bodies in the field of view of the laboratory doctor who is looking through the eyepiece of the microscope. An increased number of red blood cells in women in a smear for flora indicates an inflammatory process in the cervix. This sign is not direct, but indirect.
A woman's cervical smear should be taken with a special brush with silicone bristles. With a strong inflammatory process, the cervical tissue becomes so vulnerable that the elastic bristles of the brush scratch it until it bleeds, and a huge amount of red blood cells penetrate into the smear.
What are red blood cells?
Normally, there should be no red blood cells in the flora smear, or there should be no more than 3 of them in the field of view. But what is it? The red blood cell is a non-epithelial element of the vaginal smear. The norm for red blood cells in a smear for flora is not to be located in the mucus, but directly in the blood, where these bodies carry oxygen from the lungs to the body tissue, and also transport carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. Red blood cells are the most numerous cells in the human body. Statistics show that every 4th cell in our body is an erythrocyte.
Every second, more than two million red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, which are found in the blood and perform their important functions. Red blood cells in human blood are extremely small cells, shaped like discs, slightly concave on both sides.
This shape and size allow these red blood cells to move freely through the smallest capillary and have a fairly large surface area, thus allowing gas exchange.
Indications for the study
Mucus in a smear for flora, as well as the content of pathogenic microorganisms in it, can only be determined in a biochemical laboratory. Indications for this analysis are pathological conditions of the genitourinary system in women, men and children of all age groups.
Smear sampling with determination of mucus indicators is prescribed in the following cases:
- suspicion of infection of the reproductive system with sexually transmitted infections;
- atypical foamy vaginal discharge, which is white, greenish, gray, yellow in color, and also has an unpleasant putrid or yeasty odor;
- a feeling of severe cutting pain and burning that appears at the time of urination (this indication for the study applies to adult men and women, as well as children of all age groups);
- inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, which is caused by a bacterial, viral or fungal infection;
- chronic or acute prostatitis in men (a smear for mucus and biological agents is taken to determine the infectious pathogen that causes inflammation of the prostate gland);
- the period of rehabilitation of the organs of the reproductive system, the tissues of which have undergone surgical intervention (the schedule for taking a smear for mucus and pathogenic microorganisms is drawn up by a gynecologist on an individual basis as the diseased organ heals);
- benign and cancerous tumors of the uterus, cervical canal, ovaries;
- chronic cystitis of bacterial etiology, which is in the acute stage;
- previous injuries to the genitourinary system, which require long-term rehabilitation and regular monitoring by a gynecologist or urologist;
- acute and chronic kidney diseases associated with an inflammatory process of infectious origin;
- bladder oncology;
- bacterial urethritis, accompanied by acute symptoms, purulent discharge and erosion of the walls of the urethra;
- control testing after completing a course of treatment for sexually transmitted infections;
- infertility of unknown etiology, when a woman has no obvious signs of a painful condition of the organs of the reproductive system, but pregnancy does not occur within 12 months;
- sexual and erectile disorders in men (a mucus smear is taken to determine hidden infections that lead an intracellular parasitic lifestyle, causing low-grade inflammation of the prostate, testicles, testes, disrupting the functions of the genital organs).
Mucus in a smear for flora is indicated for determination in women who are pregnant. The primary analysis is carried out on the day of the first visit to the gynecologist, when the expectant mother only learns that a child is being formed in her womb. If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, then the next smear sampling for mucus and microflora is performed at 30 weeks of fetal development.
Control diagnostics are carried out at 35-36 weeks of gestation, when the baby is expected to be born. Determination of mucus in a smear and the qualitative composition of microflora is a mandatory analysis of a preventive medical examination by a gynecologist, which is carried out at least once every 12 months.
Entry of cells into the smear
Red blood cells can reach the mucous membrane of the cervix or vagina only together with blood. These cells do not leave the bloodstream on their own. Most often, an increase in the number of these cells occurs when biomaterial is taken to determine red blood cells in a smear for flora. The large number is explained by the fact that the analysis is taken with a shaggy brush, which may accidentally slightly scratch the cervix.
This way, some blood will get into the material. In these cases, a large number of red blood cells in a smear for flora is not a pathology, but an absolute norm.
Blood can also enter directly into the vagina not only due to injury. Increased red blood cells in a flora smear can occur for natural reasons, for example, during menstruation. These bodies found in a smear at a given time are a natural phenomenon, even if they are there in large numbers. Single red blood cells in a smear may appear on certain days of a woman’s menstrual cycle:
- during ovulation (usually the 13th–15th day of the menstrual cycle);
- on the 28th day (just before the start of menstruation).
As mentioned earlier, red blood cells are normally absent in a flora smear, but a large number of them in material taken directly from the cervical canal indicates the development of cervical erosion or an inflammatory process in this area of the vagina. The reason for the appearance of red blood cells may be intrauterine contraceptives and hormonal disorders accompanied by bleeding.
Red blood cells in biomaterial for cytology
In some cases, red blood cells in a smear in women can be detected in the biomaterial for cytology. This happens due to the fact that the specialist took the material for the smear roughly and accidentally destroyed the vessels that pass through the delicate tissue of the cervix.
In this case, after taking a smear, a woman may experience a slight discharge with a small admixture of blood for several hours. Of course, under these circumstances there will be a large number of red blood cells in the smear.
In this situation, the presence of blood cells will not be a pathology. The doctor who took the material for the study noted on the form accompanying the microslide the real reason for the presence of red elements - red blood cells in the smear, which normally should be absent. The reasons for the appearance of these bodies can be different, ranging from the area where biomaterials were taken and ending with circumstances independent of the patient’s health status.
Corpuscles in a smear from the urethra
Red blood cells that were found in a smear from the urethra may be symptoms of a tumor or stones in the urinary tract. Blood in urine will never be normal. This condition indicates acute inflammation, including inflammation of a bacterial nature. The most common reason for the appearance of bodies in a smear from the urethra is traumatic urethritis. The cause of this pathology is often a certain medical procedure associated with mechanical entry of blood into the urethra.
When to treat if there is mucus in smears
We already know that the presence of a large amount of mucus in smears indicates an inflammatory reaction.
After identifying the infectious pathogen that caused it, treatment must be started immediately.
This will allow you to more successfully fight the infectious agent and avoid many complications.
If the inflammation is caused not by an infection, but by a traumatic factor, then it is also necessary to treat and prevent the addition of a secondary infection to the organs of the genitourinary system weakened by inflammation.
Among women
A smear from the urethra in women is usually taken in combination with biomaterial from the cervix, as well as from the vagina. This analysis is needed to diagnose infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract, discomfort in the urethra and frequent urination. In addition, smears from the urethra in the fair sex can be prescribed as an additional examination to cultures. To take such a smear, the doctor inserts a special applicator 2–4 centimeters into the urethra, and then carefully rotates it to collect more epithelium.
The disease infectious urethritis is caused by various pathogenic microorganisms. The main symptom will be the appearance of bloody discharge from the urethra. The volume of these secretions increases significantly in the morning.
All of the listed diseases will necessarily be accompanied by the formation of red blood cells in the smear.
About the flora smear
The normal microflora of the female vagina is quite diverse; it contains a large number of different bacteria. In representatives of the weaker half of humanity of reproductive age, the main microorganisms are lactobacilli, but in addition to them, ureaplasma (in 80% of patients), gardnerella (in 45% of patients), candida (in 30% of patients) and mycoplasma (in 15% of patients) are also found - this opportunistic microorganisms, with a decrease in the immune system, which can rapidly multiply and also lead to the occurrence of an inflammatory process. They require adequate treatment. In the absence of any clinical manifestation, for example, pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor or itching in the perineal area, the definition of these microorganisms as a pathology should not be interpreted.
Chlamydia, as well as viruses, can be present in patients who do not show any complaints, but these agents are not considered part of the natural microflora, and their presence indicates a hidden infection.
The microflora in the vagina is dynamic, it can change on different days of the cycle. There are periods when the lactobacillary flora dominates and those days when gardnerella predominates. A significant disturbance in the balance of microorganisms in the microflora, which is accompanied by clinical symptoms, is the basis of such conditions, for example, bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis. Such conditions can often recur, including even the slightest change in the patient's health status or while taking antibiotics. Women who have a family predisposition especially suffer from this.
A flora smear (also called a “general smear”) is the first and important step in assessing an infectious and inflammatory process localized in the urogenital area. This smear allows you to quickly identify one of the following conditions:
- Norm.
- Vaginal microflora disorders, which include bacterial vaginosis.
- An infection caused by Candida fungi, such as thrush.
- Infections that are sexually transmitted, in particular gonorrhea and trichomoniasis.
- Nonspecific, or bacterial, vulvovaginitis. In this case, leukocytes are present in large numbers in the smear. If a huge number of leukocytes are detected and there is a clinical picture of the inflammatory process, it is possible to prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics that destroy up to 90% of bacteria. If there is no therapeutic effect, it is necessary to carry out bacteriological culture, since microscopically it is impossible to determine the specific type of microorganism that caused the inflammation. Bacterial culture is usually accompanied by identification of sensitivity to antibiotics, thanks to which you can choose the optimal drug, as well as achieve the desired effect of therapy.
A flora smear is not able to determine:
- Intracellular and hidden infections (chlamydia, mycoplasma, herpes, HPV, ureaplasma, HIV). To determine them, the DNA of the agent must be determined by PCR.
- A woman is pregnant.
- Pretumor and tumor pathology. A smear is made for cytology, the essence of which is to determine the qualitative change in the epithelium using special stains.
Smear
Taking a smear is a study that involves collecting biological material and analyzing it under a light or electron microscope. There are two types of analysis: native (the sample is not subjected to any processing) and with staining.
Depending on the suspected disease, the doctor may take a smear: from the epithelium, from the nose, mouth, from the vagina or urethra (urethral smear).
Indications for taking a smear in men
In what cases is a urethral smear prescribed? The procedure may be prescribed by a urologist during examination, if urogenital infections are suspected, or if a slow-acting inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system is detected.
An examination is also prescribed in cases where an infectious disease is detected in a partner.
A smear is prescribed if the patient complains of:
- discharge from the urethra;
- pain during and after urination;
- swelling and redness of the genitals;
- rashes;
- frequent urination;
- infertility.
Indications for the test are also any diseases of the genitourinary system, suspected infections.
For women
Women are advised to have pap smears regularly. Minimum - once a year, even in the absence of any health complaints or symptoms of disease. The fact is that a large number of infections do not manifest themselves once they enter the body. The latent period varies depending on the virus and the immune system of the individual.
A study is required when:
- complaints of itching and burning in the groin area;
- the presence of unusual discharge from the genitals;
- sudden pain in the lower abdomen.
- pregnancy planning;
- preparation for IVF;
- pregnancy - regularly throughout the entire period.
It is recommended to take a smear after unprotected contact with an unknown partner (there is a risk of contracting an infectious disease).
Speaking about the smear, we note that it is effective not only for diagnosing diseases of the urogenital area, but also in identifying cancer.
We strongly recommend that women undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist!
Important! Preparing for the study
Both women and men need to prepare for the procedure of taking a smear from the genitourinary system.
When performing a smear from the urethra, men are advised to avoid sexual intercourse 1-2 days before the test. In the evening, you need to take a shower the day before. 2-3 hours before the test, do not urinate (during a smear, the doctor collects microflora from the urethra, and urine can wash it away).
Women need to consider their menstrual cycle. It is recommended to take the test before the start of menstruation, or after (after a certain number of days). For example, when taking a smear on the fifth day, there is practically no chance of blood getting into the sample. This period is considered optimal.
Despite the simplicity of the procedure, women are recommended to take a number of preparatory measures: exclude vaginal suppositories and tampons. Do not use ointments or douching. Sexual intercourse should be avoided for 1-2 days.
If a patient has an inflammatory disease accompanied by secretion, doctors advise first carrying out a course of treatment and then taking a test.
On the day of delivery of the biomaterial, do not use intimate hygiene products or urinate for 1-2 hours.
Analysis indicators, disease diagnosis
The analysis result is usually ready within 3 days from the date of delivery.
The results that the patient receives contain: the number of epithelial cells, leukocytes, mucus, cocci. Other identified cells are also included in the results.
Normal cell counts in a smear in a man:
If an increased number of leukocytes or epithelium is observed in the smear, red blood cells, eosinophils appear, or an increase in the amount of mucus is observed, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
The presence of gonococci, trichomonas, as well as yeast cells and other foreign bacteria indicates the presence of a disease.
Please note that only a doctor can correctly determine the diagnosis and interpret the results!
A smear test for hidden infections can be ready in a shorter period of time (1-2 days). If the result is positive, he may be detained for additional tests. The norm does not imply the presence of hidden infections.
List of tests for hidden infections:
- chlamydia;
- gonococcus;
- Trichomonas;
- ureaplasma;
- mycoplasma;
- herpes virus;
- cytomegalovirus.
The list can be narrowed or expanded during an examination by a urologist.
The result that women receive depends on what type of study was prescribed by the doctor.
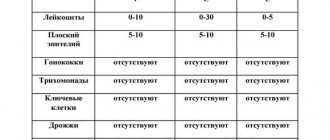
When analyzing flora, normal indicators are:
- The squamous epithelium indicator should be within fifteen cells in the field of view. If the squamous epithelium exceeds this norm, this indicates an inflammatory process in the body. Lower values indicate the presence of a hormonal disorder.
- The value of leukocytes should not exceed ten (30 in the cervix).
- Dederlein's bacilli, which provide healthy microflora of the genital organs, should be present in the smear in large quantities. Their lack indicates problems with the vaginal microflora.
- The “Mucus” indicator in the smear should ideally be “moderate amount”. If there is a lot of mucus, this indicates inflammation or an infectious disease.
- Fungi such as candida, gonococcus, trichomonas should not be present in the smear. Their presence indicates a disease.
In addition to the presented indicators, the smear may contain one of 4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness. Only the first and second values are valid.
Women can receive their results 1–2 days after the test itself.
A test for latent infections can identify the following diseases:
- herpes of the first and second types;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- human papillomavirus;
- gardnerella;
- treponema pallidum;
- mobiluncus;
- ureaplasma;
- bacteroides;
- gonococcus;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma
The need for women to undergo regular testing is due to the fact that some infections can occur covertly over very long periods of time - up to several years. Moreover, the complications caused by such diseases are very serious, including serious problems during pregnancy or infertility. The most effective way to detect hidden infections in a smear is PCR (a general smear is powerless here). During the test, the doctor takes secretions from the cervix or vagina. Sometimes samples are taken from the urethra. The result of such an analysis is the identification of all pathogenic bacteria and their ability to cause diseases. PCR is prescribed by doctors if there is a suspicion of sexually transmitted diseases. It is they who are practically asymptomatic at the first stage;
The last type of smear that women are prescribed is an oncocytology smear (Pap test). Its task is to detect cervical cancer at an early stage. In this case, the doctor can start therapy on time. The Pap test detects most inflammation and malignant tumors. This analysis is recommended for women over 21 years of age every year. The test is required when:
- menstrual irregularities;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the cervical canal;
- infertility;
- diabetes or obesity 2–3 degrees;
- pregnancy.
We are waiting for you at the REAL MED clinic
The smear test is an unpleasant but important part of diagnosing infections for both men and women. Infections and viruses recorded in the smear will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis, and therefore choose effective treatment.
Choosing a modern laboratory and an experienced doctor will help make the analysis procedure as painless as possible. Waiting for you!