Research result
Microbiologists write out the results of the study on a special form. To decipher the result of a throat smear, indicator values are required. The name of the microorganism consists of two Latin words denoting the genus and type of microbe. Next to the name, indicate the number of bacterial cells, expressed in special colony-forming units. After determining the concentration of the microorganism, they move on to designating its pathogenicity - “opportunistic flora”.
In healthy people, bacteria live on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and perform a protective function. They do not cause discomfort and do not cause inflammation. Under the influence of unfavorable endogenous and exogenous factors, the number of these microorganisms increases sharply, which leads to the development of pathology.
Normally, the content of saprophytic and opportunistic microbes in the nasopharynx should not exceed 10 3 - 10 4 CFU/ml, and pathogenic bacteria should be absent. Only a doctor with special skills and knowledge can determine the pathogenicity of a microbe and decipher the analysis. The doctor will determine the feasibility and necessity of prescribing anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs to the patient.
After identifying the causative agent of the pathology and identifying it to genus and species, they proceed to determining its sensitivity to phages, antibiotics and antimicrobials. It is necessary to treat a disease of the throat or nose with the antibiotic to which the identified microbe is most sensitive.
Options for the results of a throat smear examination:
- A negative culture result for microflora means there are no causative agents of bacterial or fungal infection. In this case, the cause of the pathology is viruses, not bacteria or fungi.
- A positive culture result for microflora indicates a growth of pathogenic or opportunistic bacteria that can cause acute pharyngitis, diphtheria, whooping cough and other bacterial infections. With the growth of fungal flora, oral candidiasis develops, the causative agent of which is biological agents of the 3rd pathogenicity group - yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
Microbiological examination of the throat and nose flora makes it possible to determine the type of microbes and their quantitative ratio. All pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms are subject to complete identification. The result of laboratory diagnostics allows the doctor to correctly prescribe treatment.
Inoculation of the test material
Each microorganism grows in its “native” environment, taking into account pH and humidity. Media can be differential diagnostic, selective, universal. Their main purpose is to provide nutrition, respiration, growth and reproduction of bacterial cells.
Inoculation of the test material must be carried out in a sterile box or laminar flow hood. The healthcare worker must wear sterile clothing, gloves, a mask and shoe covers. This is necessary to maintain sterility in the work area. In the box, you should work silently, carefully, ensuring personal safety, since any biological material is considered suspicious and obviously infectious.
A nasopharyngeal swab is inoculated onto nutrient media and incubated in a thermostat. After a few days, colonies of different shapes, sizes and colors grow on the media.
There are special nutrient media that are selective for a specific microorganism.
- The main medium for germs of the throat and nose is blood agar. This is a highly sensitive medium containing nutrients for saprophytic and pathogenic bacteria. Pneumococci and Staphylococcus aureus produce hemolysins and cause hemolysis of red blood cells. The hemolytic activity of microbes is the main pathogenicity factor that most pathogenic bacteria possess. The growth pattern, color and zone of hemolysis differ among microbes of different genera and species.
- Sabouraud's medium or thioglycollate medium is universal and suitable for a wide range of microbes.
- Yolk-salt agar is an selective medium for growing staphylococci.
- Warmed Blood Agar – Chocolate Agar. This is a non-selective, enriched nutrient medium used for growing pathogenic bacteria. On this medium, gonococci, Haemophilus influenzae and pathogens of purulent bacterial meningitis grow.
- Endo medium is a differential diagnostic medium for the cultivation of enterobacteria.
- Enterococcus is a nutrient medium for the isolation of enterococci.
The material is rubbed into the medium with a swab on a small area measuring 2 square meters. cm, and then using a bacteriological loop, streaks are scattered over the entire surface of the Petri dish. The crops are incubated in a thermostat at a certain temperature. The next day, the crops are examined, the number of colonies grown is taken into account and their nature is described. Individual colonies are reseeded on selective nutrient media to isolate and accumulate a pure culture. Microscopic examination of a pure culture makes it possible to determine the size and shape of the bacterium, the presence of a capsule, flagella, spores, and the relationship of the microbe to staining. The isolated microorganisms are identified to genus and species, and if necessary, phage typing and serotyping are carried out.
Treatment to eliminate pathogens from the nose and throat
Nasal infections and throat diseases are recommended to be treated under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. Only he can prescribe adequate treatment.
Often, discomfort in the nasopharynx is relieved with the help of bacteriophages produced in the form of a spray or solution, for example, Chlorophyllipt.
Chlorophyllipt also exists on an oil and alcohol basis. The oil version of the drug is intended to lubricate the sinuses and tonsils. It is good because it can be used by small children and women in an interesting position. The alcohol composition is used to wash the throat and nose. Often, anaerobic bacteria in the nasopharynx are removed using traditional methods. For example, a collection that contains herbs such as:
- Mint;
- Hawthorn;
- Coltsfoot;
- Rose hip.
Herbal medicine is considered an effective way to eliminate discomfort in the nose and throat. This technique is allowed during pregnancy as it is a natural and safe treatment. The first results are usually felt a few days after starting to take the herbal mixture. Since anaerobic infections in the nasopharynx are persistent, treatment with herbal medicine should last at least three weeks.
In order to correctly collect samples from the upper respiratory tract, you need to follow the preparation rules, then there will be no difficulties in treating the identified disease. Any discomfort in the nasopharynx cannot be ignored, since even a banal runny nose can turn into a serious pathological process, the consequences of which can be sad.
It is not recommended to prescribe medications for yourself and your children, for example, for a runny nose, because not all medications for clearing the nasal mucosa are suitable for every person.
How to prepare
In order for the results to be as reliable as possible, it is very important to adhere to certain recommendations. Before taking the analysis you must:
Avoid using mouth rinses that contain antiseptic ingredients 2-3 days before the procedure. Avoid the use of sprays and ointments that contain antibacterial and antimicrobial substances several days before the procedure. Avoid consuming food or drinks 2-3 hours before the test. It is best to take the test on an empty stomach. On the day of the procedure, it is advisable not to brush your teeth or at least several hours before the examination not to chew gum.
Solutions for
gargles for throat
and nose eliminate most of the microorganisms that are on the mucous membranes. As a result, the analysis will give unreliable results.
After eating or using toothpaste, some of the bacterial microorganisms are washed off, which also negatively affects the result.
Analysis transcript
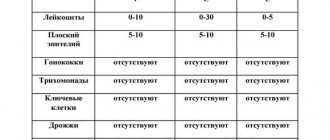
So, what does a swab taken from the throat show? Normally, the pharynx of each person contains many different microorganisms, some of which are considered absolutely normal residents.
Others are quite dangerous, but their small numbers do not threaten human health, which is why such flora is called opportunistic.
The following are considered acceptable in a throat smear: epidermal staphylococcus, fungi of the genus Candida in small quantities, herpes simplex virus, pneumococci.
What pathogenic flora can a throat swab reveal?
- Staphylococcus aureus is the cause of many inflammatory processes and not only in the pharynx, it may well be the culprit of systemic lesions. When immunity decreases, it becomes activated and can cause diseases such as tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis, diseases of the urinary system, inflammation of the digestive tract, purulent skin diseases, and damage to bone tissue.
- Hemolytic streptococcus causes tonsillitis, severe pharyngitis with large amounts of purulent discharge, and scarlet fever, which is a dangerous childhood infection.
- A throat swab can reveal the causative agent of diphtheria - Loeffler's bacillus, and also show how toxic this bacterium is to the body.
- The number of fungal microorganisms exceeding the maximum permissible norm is of concern, as it indicates a sharp decrease in immunity.
- In some cases, a throat swab may reveal the presence of eosinophils, cells released during an allergic reaction, which may indicate a non-infectious nature of the inflammation.
The doctor who prescribed the procedure deciphers the throat smear. The algorithm for determining the pathogenicity of identified microorganisms is indicated in specially compiled tables, based on which the doctor prescribes adequate treatment.
Microflora of the nasopharynx
On the surface of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and oropharynx there are a large number of different microorganisms. Among them there are not only beneficial, but also opportunistic microbes. In a healthy person, they all make up the general microflora, without causing various diseases. But a lot depends on their quantitative composition.
If some favorable conditions for bacteria are created, for example, a decrease in immunity against the background of hypothermia, influenza, etc., then lightning activation of microbes occurs with their intensive reproduction. In addition, diseases can develop during primary infection of the body, in which microbes settle on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
In a normal smear, in the absence of severe symptoms, there are Escherichia coli, streptococcus and staphylococcus, Neisseria, Klebsiella, fungi and many others. It is interesting that almost 25% of the world's population has Staphylococcus aureus in a smear, but infection with it and further development of the disease is never observed.
Staphylococcus aureus grown on a nutrient medium
Among all the bacteria, it is worth noting those that can cause serious diseases: pneumococcus, streptococcus, meningococcus, Loeffler's bacillus, fungi, Haemophilus influenzae bacillus, Branchhamella and many others.
Types of smears on flora
A vaginal flora smear is taken from three main areas - the vaginal mucosa, the cervix and the urinary canal. The gynecologist sends the woman for analysis:
- for pain in the lower abdomen;
- cystitis;
- burning or itching of the genitals;
- thrush;
- long-term use of medications.
The study is conducted for those women who are planning to conceive a child.
To conduct a bacterioscopy for flora in men, you will need prostate secretion, scraping from the urethra and sperm. performs this manipulation during a routine examination of a man. Indications for the procedure include: discharge from the urinary canal, suspicion of infertility, pain when emptying the bladder.
Indications
This study is performed in the following situations:
Preventive examination before hiring. Usually a smear is needed if a person plans to work with food, children, the sick, etc. Examination of pregnant women. This helps prevent the development and activity of bacteria that pose a danger to the baby. Examination of children who are going to enter preschool institutions. This helps prevent outbreaks of the disease in children's groups. Diagnosis before hospitalization or in preparation for surgery. In such a situation, the doctor must make sure that there are no microorganisms that could aggravate the course of the postoperative period. Examination of people who have had contact with infectious patients. This will help prevent the subsequent spread of the disease. A study to accurately determine the causative agent of ENT pathologies. The procedure also helps to establish the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to drugs. Detection of tonsillitis, diphtheria, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media and other pathologies.
Summarizing the information, we can conclude that a smear for flora examination is required in 2 cases - to determine the carriage of pathogenic microorganisms and to detect the causative agent of a certain disease.
Why do they take a smear for flora, says the doctor:
Methods for studying biomaterial
During microscopic examination, the resulting biomaterial is Gram stained and examined after treatment with immersion oils. The method allows you to identify gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, coccal flora, and coccobacilli.
Bacteriological culture is one of the main diagnostic methods, since each microorganism can multiply only in a certain environment, at a comfortable level of pH and humidity; during the study it is important to maintain complete sterility. .
Bacteriological culture is the main type of diagnostics for identifying pathogenic microorganisms
If an increase in microflora is detected, antibiotic sensitivity tests must be carried out; many microbes are able to quickly develop immunity to drugs - in the presence of ineffective therapy, severe complications develop.
A fingerprint smear is a specific analysis for studying the composition of cells in the nasal mucosa. The sample is applied to a glass slide, and the number of eosinophils and other particles is counted. The study is prescribed if you are predisposed to allergies.
If antibacterial therapy is ineffective, phage sensitivity tests are performed. The result allows us to select bacteriophages to eliminate the manifestations of infectious pathologies - these are modern antimicrobial drugs that cause the death of only certain types of bacteria.
The most accurate research method is PCR diagnostics, which allows you to identify the DNA of the causative agent of the infectious process, the reliability is more than 95%.
Rules for collecting material for analysis
A smear on the microflora does not cause pain in the patient, but it is unpleasant because when the cotton swab comes into contact with the mucous membrane, vomiting develops. When a test is taken from a child, it must be prepared by explaining what will happen. Without this, the baby may become very frightened and experience shock.
The material is collected in a special room by a medical professional with proper qualifications. During the smear, the patient is seated on a chair and asked to open his mouth wide and tilt his head back slightly. As a result, the back wall of the pharynx becomes accessible. Sometimes possible diphtheria is detected during preparation for a smear.
The patient sticks out his tongue, and the doctor, pressing it with a special spatula, takes the discharged contents of the pharynx using a special sterile cotton swab. The pharynx is not injured. Afterwards, the swab is placed in a sterile sealed tube and delivered to the laboratory for testing no later than 2 hours later. In this case, the resulting microflora is not disturbed.
With increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane, the patient experiences a particularly strong urge to vomit, which, due to the lack of contents in the stomach, turns out to be unproductive. How long it goes through is determined by individual characteristics.
If the material taken was not delivered for examination in a timely manner, or its sterility was compromised, a second smear is performed, since the previous one turns out to be unreliable. Repeated analysis can be carried out even when therapy does not bring results. In this case, there can only be 2 options:
- error in identifying the causative agent of the disease;
- error in determining bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
The need to retake the test is determined by the attending physician.
A smear from the throat, nose, throat of a child: norm, interpretation, preparation
Smears are not prescribed to all categories of children, but only to some who have certain diseases or are suspected of having them, or who are undergoing preventive examinations or are in quarantine.
Smear collection will be indicated when:
- Suspicion of acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis), which can be caused by hemolytic streptococcus. It must be identified due to the danger of complications such as rheumatism, kidney damage and heart valves.
- the presence of boils or other staphylococcal skin lesions, if carriage of staphylococcus is suspected in the nasopharynx.
- exclusion of diphtheria of the pharynx when the tonsils and posterior wall of the pharynx are affected with the formation of extensive plaques.
- to exclude pertussis or meningococcal infection.
- in the diagnosis of laryngitis, mononucleosis of the pharynx, if retropharyngeal abscesses are suspected.
Smears are also taken from children who have been in contact with other children suffering from dangerous infections (diphtheria, meningococcal infection, whooping cough). It is necessary to carry out similar smears on those children who are enrolled in kindergartens or schools in order to exclude the carriage of dangerous microbes (bacterial carriage and bacterial excretion).
What analysis options are possible?
Most often, swabs from the nose and throat are carried out in order to determine the composition of the microbial flora of the nasopharynx and identify dangerous pathogenic strains among them.
For this purpose, the material collected with sterile instruments is sent to bacteriological laboratories for the purpose of inoculating them on nutrient media, growing colonies and determining their nature, as well as, if dangerous microbes are detected, conducting tests for sensitivity to antibiotics.
note
In some cases, a targeted analysis is done to identify a specific pathogen, which is indicated in the accompanying referral from the doctor (BL smear, determination of whooping cough, staphylococcus).
A special variant of the study would be to take fingerprint smears to determine the composition of the cells of the nasal mucosa.
The materials obtained from the mucous membrane are placed on a glass slide so that they can then be closely examined by a laboratory assistant. Eosinophils and other cells within the microscope's field of view are usually counted.
This is necessary to identify allergic predisposition and respiratory allergies
Microbial communities in normal and pathological conditions
From the birth of a child, the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx is actively populated by saprophytic (harmless) and opportunistic flora. During infections, pathogenic species of microbes can also be detected.
When studying smears, both a qualitative determination of the composition of microbes is carried out, and the number of certain groups living both in the nose and throat is counted.
There is a whole group of microbes that can be found in the nose and throat, and do not harm the child in any way; doctors know them very well.
In pathologies, completely different types of bacteria can be detected - pneumo-, staphylo- and streptococci, diphthyretic bacteria, fungi and many other pathogens.
The form with the results indicates their presence, the type of microbe and its quantitative characteristics.
If these are pathogenic, dangerous microbes and a decision on treatment is necessary, the sensitivity of the pathogens to antibiotics is determined, indicating the groups of drugs.
How to prepare a child for smear collection?
Taking smears is not particularly difficult or painful, although the procedure may be a little unpleasant for the baby. In order for the results to show maximum reliability, it is important to correctly collect materials for the study.
At least two weeks before, oral antibiotics are stopped, and a week before smears, all local medications in the form of rinses, solutions and sprays, ointments and other forms are stopped.
The test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach; you cannot brush your teeth, chew gum or drink liquids before taking smears, otherwise the results may be significantly distorted.
If we are talking about nasal swabs to determine eosinophils (allergies), they are also taken on an empty stomach, or two hours after eating. Before their collection, nasal sprays, antihistamines and saline rinsing are not used.
Methods of collecting smears from children: help from parents
To properly collect a sufficient amount of material, it is important to hold the child correctly during the procedure. If it is a baby, he is placed on the couch, and the parents fix the body and head. If these are older children, they are placed on their knees, clasping their legs with their legs, holding their chest with one hand, and holding their head pressed to their chest with the other in the forehead area.
A nurse or doctor uses a spatula to press the tongue and use a special sterile stick to remove material for examination from the pharynx. This is the most unpleasant part of the procedure.
Then the stick with cotton wool at the end is placed into a test tube with a sterile nutrient solution.
It is important to hold the child tightly so that he does not twitch, and staff do not touch the root of the tongue, this provokes the urge to vomit.
A nasal swab is taken with a similar stick with sterile cotton wool at the tip by inserting it into the nasal passages, and turning it in the nasal passages, pressing firmly against the mucous membranes.
Then the stick is also placed in a test tube with a sterile solution and taken to the laboratory for testing. Before collecting smears, she recommends blowing the child’s nose.
Conducting microscopic analysis
After the material is delivered to the laboratory, it is pipetted onto a glass slide, the necessary stages of processing the preparations are carried out, and then placed under a microscope, where a laboratory assistant examines them. Detection, identification and counting of microbial bodies found in the preparation are carried out.
In this way, it is possible to determine coccal flora, bacillary flora, gram-negative rods or positive ones. Based on certain characteristics of microbes in smears, it is already possible to draw preliminary conclusions about the nature of the infection. But it can only be supplemented and clarified based on the results of crops.
Source: https://zdorovo.live/obsledovaniya/mazok-iz-zeva-nosa-gorla-u-rebenka-norma-rasshifrovka-podgotovka-2.html
Types of analyzes
Biological material collected by taking a smear from the throat and nose area is sent for further laboratory testing. For these purposes, modern medical specialists use the following informative techniques:
- Inoculation - during this study, particles of mucous membranes are applied to a special nutrient medium that promotes the active reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. This type of analysis makes it possible to identify the presence of specific microbes and bacteria in the patient’s oropharynx and determine the degree of their sensitivity to certain antibiotic drugs, which is necessary for prescribing adequate and effective treatment;
- PCR diagnostics - this analysis is a laboratory study of the DNA structures of the patient’s mucous membranes. PCR research gives a specialist the opportunity to determine the types of pathogenic microorganisms that populate the patient’s nasal mucous membranes;
- Antigestagen tests are an informative procedure that involves the use of special systems characterized by increased sensitivity to particles of certain pathogens. In most cases, this technique is used when the presence of streptococci is suspected. Antigestagen tests are highly accurate, and the test itself takes no more than half an hour. A positive test result indicates the presence of infection with certain types of microbes, while a negative result indicates the absence of infection.
Preparatory stage
In order for the analysis to provide the most accurate results, you must follow some recommendations. Preparation includes:
5 days before the examination, it is prohibited to take antibacterial drugs, which will allow the proliferation of pathogenic microbes to resume; 3 days before the diagnosis, the use of rinsing solutions, as well as sprays with an antiseptic effect, will be discontinued. They reduce the number of pathogenic microbes, which makes diagnosis difficult; a throat swab is performed on an empty stomach; Before the study, chewing gum and drinks are prohibited, and brushing your teeth is undesirable.
Research algorithm
When collecting material for research, increased sterility measures are also observed. The whole procedure takes place in several stages. They have the following sequence:
- The patient assumes a body position (sitting, lying) in which he can tilt his head back without difficulty.
- Pressing the wing of the nose, the specialist inserts a sterile cotton swab into the cavity to collect material.
- Similarly, microflora is collected from the second nostril.
- The swab is lowered into a test tube pre-filled with transport medium. It eliminates the possibility of microbes dying during transportation.
- The exact time the material was taken is marked on the tube.
Biological nasal discharge must be delivered for examination within 2 hours from the moment the smear is taken. Before the procedure, the nasal cavity is pre-treated: it is cleared of mucus and lubricated with a 70% alcohol solution.
If children have an allergic rhinitis, how can one understand the nature of the course based on the symptoms?
Often, even before diagnosing mucus from a child’s nose, parents can already guess what exactly is causing the long-term runny nose. In childhood, persistent rhinitis occurs quite often. Moreover, if children are allergic to various irritating particles, then parents have to constantly fight with the provocateurs of catarrhal discharge.
Allergic rhinitis can be seasonal or year-round. The first option is caused by seasonal allergens, such as pollen or insect bites. A year-round runny nose is observed with allergies to household dust, paper mites, food products, etc.
Using the table, parents can see the difference between the symptoms of the two types of allergic rhinitis.
| Signs | Seasonal type | Year-round type |
| Swelling of the nasal passages | Transient | Constant |
| Nasal discharge | Watery | Mucous, drains into the pharynx, periodic |
| Sneezing | Permanent | Impermanent |
| Smell disorders | In rare cases | Often |
| Symptoms of eye reactions | Almost always | Very rarely |
| Chronic sinus inflammation | Occasionally | Often |
If a child has such symptoms of a prolonged runny nose as in one of the groups described, it means that he is worried about an allergic reaction. Treatment of such a problem is quite complex and requires a lot of effort on the part of both children and parents in order to eliminate contact with the allergen and maintain health at a normal level. The sooner you start therapy, the easier it is to get rid of the ailment and prevent the development of complications.
Decoding the results
As a rule, the mixed microflora presented in a smear from the throat of a healthy person contains a small amount of pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms - some types of streptococci, corynebacteria, neisseria, veillonella and even E. coli.
This state of affairs is considered the norm if there are few harmful microbes, and the consequences of their vital activity do not pose a threat to health. Moreover, it will not be possible to completely eliminate every single pathogenic microorganism: a short time after the end of the course of antibiotic treatment, they will again settle on the mucous membrane.
What indicators are the most dangerous?
Harmful microorganisms that can be identified by performing a throat swab include the following:
beta-hemolytic streptococcus, part of group A; causative agent of diphtheria; fungi; causative agent of whooping cough.
Most pathologies of the ENT organs are caused by increased activity of streptococci. It is these microorganisms that are identified when tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or pneumonia are suspected. In order to exclude
allergic factor
, during the study, the level of leukocytes and eosinophils is determined.
How to distinguish the herpes virus from a streptococcal infection, says Dr. Komarovsky:
Purpose of analysis
Indications for the study of throat flora
This analysis may be prescribed in the following cases:
- As one of the preventive examination procedures when hiring, if a person is applying for a job related to food products, children, sick patients and the like. The results of the analysis will show whether the person is healthy and whether he can work in this field.
- When examining pregnant women, in order to prevent the development and action of bacteria that can cause diseases that complicate the course of pregnancy and threaten the life of the baby.
- When examining children entering preschool institutions to prevent the occurrence of infectious outbreaks in children's groups.
- Before hospitalization of the patient in the hospital and in preparation for surgery, to ensure the absence of microorganisms that can cause complications during the postoperative period.
- Screening people who have had close contact with patients with highly contagious microbial diseases to prevent further spread of the disease.
- To accurately identify the pathogen that provoked a particular disease of the ENT organs, as well as to determine the sensitivity of this pathogen to the medications used.
- For detection and treatment of sore throat, diphtheria, sinusitis, sinusitis, external otitis, etc.
If we summarize all of the above, we can say that a smear on the flora is prescribed in two cases: to find out whether a person is a carrier of pathogenic microbes and to identify the causative agent of any disease.
Preparation
Proper preparation for a smear test
In order to obtain the most reliable results, you need to follow certain rules, because this analysis requires some, albeit simple, but extremely important preparation. . So, before taking a smear you need to:
So, before taking a smear you need to:
- refuse any rinses and mouth rinses containing antiseptics 2-3 days before the procedure
- Avoid throat sprays and ointments containing antibiotics and antimicrobial substances 2-3 days before the procedure
- do not eat or drink any drinks 2-3 hours before the test (best on an empty stomach)
- It is advisable not to brush your teeth on the day of the test or at least 2-3 hours before it
- don't chew gum
It is necessary to refuse mouthwash solutions and throat sprays because they kill most of the microbes found in the mucous membrane of the pharynx and reduce their numbers to a minimum. As a result, the analysis, of course, will not show the true number of microbes in the mucous membrane and the bacteria that can cause or have already caused the disease will not be detected in the smear.
The food or drinks a person takes, as well as toothpaste, can simply wash away some of the bacteria, and this will also affect the result, which will not show what microorganisms are actually on the mucous membrane.
It is advisable not to eat or drink at all on the day of the test, and if possible, it is better to refuse even a glass of water or a mug of coffee in the morning after waking up.
Thus, bacteria need to be given free rein and allowed to multiply freely in the mucous membrane for 2-3 days without exposing them to various antibacterial agents, and only then can the real picture be seen.
Research procedure
During the procedure, the patient throws his head back and opens his mouth wide. Pressing the patient's tongue with a medical metal or wooden spatula, the doctor runs a sterile cotton swab placed on a metal loop along the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
The procedure does not cause any pain and virtually no discomfort in the patient, with the exception of perhaps the gag reflex, which can appear from touching the back wall of the throat.
The stick with the material collected on it is placed in a sterile container, where all conditions are created for the comfortable life of microbes so that they do not die before arriving at the laboratory.
In the laboratory, the collected material is placed in various nutrient media depending on the purpose for which it was carried out. Depending on the reaction and behavior of microbes, the results of the analysis are formed.
Preparing for the test
The study of nasopharyngeal microorganisms will show a reliable result only if biological material is submitted correctly and the patient is prepared for the collection of biological material:
- 1 week before taking a bacteriological culture, the use of antibacterial solutions, which will destroy pathogenic microflora and have a negative effect on beneficial microorganisms, is discontinued.
- It is prohibited to use any solutions for rinsing the mouth, nasal sprays, or topical drugs.
- A swab is taken for analysis strictly on an empty stomach. In order for the analysis to show a reliable result, in the morning it is strictly forbidden to eat or drink anything, brush your teeth, and chew gum. The use of plain water is also excluded.
- If there is mucus in the nose, it must be removed before taking a sample of biological material. Crusts on the nasal mucosa are removed by softening them with a special solution. The presence of mucus can negatively affect the veracity and information content of the analysis.