Who is tested for staphylococcus?
Anyone can become infected with staphylococcus; the infection is very dangerous.
- If there is an inflammatory process in the body, especially purulent, you cannot hesitate and wait for complications.
- You should immediately consult a doctor, who will refer you for a test to detect a staphylococcal infection.
- Dangerous types of staphylococcus cause enormous harm to the body.
Most often, patients with symptoms of an inflammatory process are referred for this analysis:
- women with mastitis;
- with skin diseases - folliculitis, carbuncles, impetigo;
- in the presence of a diagnosis such as cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis.
- With diseases of the ENT organs - laryngotracheitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media, pharyngitis;
- for pneumonia and pulmonary diseases;
- with inflammation of the osteoarticular system - osteomyelitis, arthritis;
- during pregnancy, etc.
Staphylococcus test during pregnancy
Collection of material from the throat and nose
Now you know what needs to be done before submitting your biomaterial for analysis for staphylococcus. How the sample is taken (blood, smear) should not concern you. After all, this responsibility falls entirely on the shoulders of specialists. It should only be noted that such a fence is carried out very quickly and painlessly.
Most often, a swab from the throat and nose is used to identify dangerous types of staphylococcus. This is due to the fact that if a bacterium is found in such biomaterials, then it will certainly be found in others.
Before taking this test, the patient is advised to prepare. To do this, he needs to stop eating and drinking 8 hours before the test.
Biomaterial is collected only in the early morning. Before visiting the clinic, the patient is prohibited from brushing his teeth, rinsing his mouth, throat, or blowing his nose. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in inaccurate test results.
Types of tests for staphylococcus
Staphylococcus bacteria
The test for staphylococcus is called microbiological. During the research process, the type of bacterium and its sensitivity to various antibiotics are revealed. The following types of analyzes exist:
- blood test for staphylococcus;
- bacteriological analysis of urine and feces;
- urogenital smears;
- collection and examination of breast milk;
- examination of purulent masses;
- smears from the oral cavity, mucous membranes, and nasal membranes.
When is it prescribed?
It is recommended to submit biomaterial for analysis for staphylococcus if you suspect an infection that can be caused by this microorganism. In addition, such a study is used in the diagnosis of nosocomial diseases.
If a person is not sick and has no complaints, then such an analysis can be prescribed during a regular and scheduled professional examination of medical personnel and catering workers, as well as in the presence of pregnancy.
Often such a study is carried out to treat diseases caused by staphylococcus. This method allows you to diagnose the existing deviation and evaluate the effectiveness of antibacterial treatment. It is also used to identify bacteria carriers and select the correct medications.
Breast milk research
If staphylococcus bacteria are found in the stool or blood of infants or there are risks of infection, then the nursing mother is prescribed a breast milk test.
- Examination of breast milk for staphylococcus allows one to exclude infection of the mother and child, and if an infection is detected, prescribe appropriate treatment for her and the baby.
- You need to donate milk in two sterile containers - a separate container for each breast.
- First, you need to thoroughly treat your breasts and nipples (with an bactericidal solution), then dry them and start pumping.
- The first milk is expressed, but not into containers.
- The rest can be safely used to collect analysis.
- When expressing milk, avoid touching your nipples with your hands - this will prevent the introduction of foreign bacteria.
- Breast milk should be stored in the refrigerator, but not more than 24 hours.
What is staphylococcus?
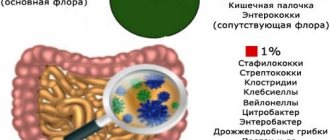
Staphylococcus is a bacterium that has a regular spherical shape and belongs to the group of gram-positive non-motile cocci. For humans, staphylococcus in some cases is part of the opportunistic microflora, that is, it always lives on the body. But pathogenic staphylococcus is also isolated, which, once inside the body, will definitely cause disease. In addition, the pathogen is widespread in nature.
In the presence of certain conditions conducive to this, the bacterium can exhibit pathological activity and cause an inflammatory process in any organ or group of organs. This could be the skin, nervous tissue, brain, heart, digestive system, etc.
Staphylococcus has a large number of strains (27), the most common and pathogenic of which are Staphylococcus aureus, epidermal, saprophytic and hemolytic staphylococci. Each of them has a varying degree of aggressiveness and pathogenetic activity.
The danger of these microorganisms is that they produce toxins and enzymes that are pathogenic for cells and disrupt their vital functions. Bacteria have a destructive effect on connective tissue, skin and subcutaneous tissue. They cause a number of dangerous diseases, including sepsis, toxic shock, disorders of the central nervous system, pneumonia, purulent skin lesions, and general intoxication of the body. Complications after inflammatory diseases and surgical operations are often associated with staphylococcal infection.
Staphylococci are stable in the environment and have a fairly high resistance to antibiotics.
Types of staphylococcus
There are three types of staphylococcus, which are the most common and harmful to the human body:
- Saprophytic staphylococcus most often affects women, causing them inflammatory diseases of the bladder (cystitis) and kidneys. Saprophytic staphylococcus bacteria are localized in the layers of the skin of the genitals and the mucous membrane of the urethra. Of all the types of staphylococcus, it causes the least damage;
- Staphylococcus epidermidis can live on all mucous membranes and any part of human skin. With normal immunity, the body copes with this bacterium, and it does not cause any diseases. But if somehow epidermal staphylococcus gets from the skin into the blood of a person with weak immunity (after surgery), inflammation of the endocardium (the inner lining of the heart) may develop as a result of blood poisoning;
- Staphylococcus aureus is the most common and dangerous species. Adults and children, men and women are equally susceptible to infection. The bacterium can infect any organ, causing inflammatory diseases, the number of which exceeds a hundred. This is an extremely persistent and tenacious microorganism that can withstand very high temperatures, exposure to direct sunlight, 100% ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide and a number of antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus causes purulent skin lesions (boils, boils, styes, etc.). It also causes a large number of dangerous systemic and general infections: staphylococcal sepsis, pneumonia, toxic shock, the formation of abscesses in the brain, heart, liver and kidneys, osteomyelitis, food poisoning, etc.
Smears and sputum from mucous membranes
To find the cause of frequent ENT diseases (sinusitis, otitis, tonsillitis), specialists take smears from the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
- It is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible the day before the test.
- This can be plain water, low-fat soups, fruit drinks, teas, fruit juices, compotes.
- A large amount of liquid will thin the mucus and make it easy to take the required amount of sputum and smears.
- The test is taken eight hours after the last meal, on an empty stomach and only in the morning.
- Before taking the test, you should not brush your teeth, blow your nose, smoke, use chewing gum, or drink water.
Who is asked to take the test?
An ENT doctor, a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist, and other specialists can ask for a nasal swab. This is not the only type of analysis, although most often specialists take a swab from the throat or nose. Sometimes doctors ask for blood, sputum, breast milk, urine, feces, etc. tests. The doctor decides what kind of analysis is needed in this case. Who usually gets tested:
- If a person has a rash, the sebaceous and sweat glands and hair follicles become inflamed.
- The patient suffers from a constant runny nose that does not go away and cannot be treated. If your nose is constantly stuffy or there is a lot of discharge, your doctor may ask you to take a nasal swab.
- The patient complains of a sore throat and suffers from cough. It could be a common cold or an infection.
- If a person is at risk, because in this case, the doctor must be prepared for a long struggle, because Such patients quickly pick up bacteria, but have difficulty getting rid of them. The risk group includes people suffering from diabetes, cancer, and HIV.
- People who work in medical institutions undergo mandatory examinations.
- Pregnant women should be tested for staphylococcus in order to later exclude infection of a small child.
- This examination is prescribed to all those who are going to go to the hospital.
- Catering workers must be examined for preventive purposes.
How to take a throat swab
Before the procedure itself, the patient must properly prepare for it.
- In a few days, at least a day before, he needs to give up sprays, syrups, and rinses.
- The patient sits in a chair, throws his head back and opens his mouth wide.
- The doctor uses a special device to press the tongue and use a special cotton swab to rub it along the mucous membrane of the throat and tonsils.
- This stick is placed in a sterile container and submitted to the laboratory for research.
Streptococcal infection
Another type of opportunistic microorganisms, streptococci, also accompany people from birth to death. These are also spherical bacteria, but under a microscope they look like beads - that is, they are strung one on top of the other. The main method of infection is contact, from sick to healthy.
The following strains of streptococcus are distinguished.
- Hemolytic or greening, alpha group. Just like Staphylococcus aureus causes inflammatory diseases of the larynx, if it enters the bloodstream it can provoke endocarditis;
- Group beta hemolytic streptococcus is also localized in the throat, causing purulent sore throat and scarlet fever. It has a subspecies – streptococcus pyogenes;
- The safest types of these bacteria are gamma. They live in the intestines, on the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth, and do not provoke inflammatory processes.
When released into the blood, streptococci cause the same general symptoms as staphylococci, but the resistance of the bacteria is much lower and therefore treatment is easier.
Bacterial analysis of stool
- A few days before taking a stool test, the patient should stop taking laxatives (ointments, suppositories, herbal preparations, tablets, syrups).
- Spicy, too sweet and fatty foods are also excluded from the menu.
- This is done to eliminate the impact on the intestinal microflora.
- The material must be collected from a dry and clean surface (pot, oilcloth, paper).
- The feces themselves are taken in three different places using a special spatula.
- The special container should be one third full.
Treatment of staphylococcus
In order to get rid of bacteria, a competent selection of antibacterial therapy is necessary.
The most commonly used treatments are the following:
- Amoxicillin, which is able to suppress the reproduction and growth of pathogenic bacteria and promote their destruction. It has a fairly wide spectrum of action and blocks the production of peptidoglycan. Used regardless of meals, no more than 1 g three times a day;
- Vancomycin helps block a component that is part of the bacterial cell membrane, changes the degree of permeability of its wall, which leads to the death of staphylococcus. It is given intravenously, either every 6 or every 12 hours. The dosage is determined by the doctor;
- Cloxacillin. Helps block membranes that are at the stage of bacterial division. It is necessary to take the drug every 6 hours at a dosage of 500 mg;
- Cefazolin. It has a wide spectrum of action and prevents the production of bacterial cell wall components. Can be used both intravenously and intramuscularly, up to 4 times a day;
- Oxacillin. It has a detrimental effect in the later stages of bacterial development and promotes their destruction. Used intravenously, intramuscularly and orally;
- Cephalexin. The drug prevents the synthesis of components that make up the bacterial cell wall. Must be taken before meals, every 6 hours;
- Cephalothin, which disrupts the ability of bacteria to divide normally and also has a destructive effect on the membrane of staphylococci. Used both intravenously and intramuscularly;
- Cefotaxime. The drug is aimed at suppressing the growth of bacteria and preventing them from multiplying. Used both intravenously and intramuscularly. The dosage is selected individually;
- Clarithromycin, which prevents bacteria from producing their own proteins. Most often used in tablet form, although for severe infections it may be given intravenously;
- Erythromycin also interferes with protein production and must be used every 6 hours;
- Clindamycin is also aimed at eliminating the ability of bacteria to produce a certain protein, which leads to its death.
Before you start using this or that drug, it is necessary to conduct an antibiogram. This will help identify the sensitivity of staphylococcus to a specific drug. Conducting such a study is important for the patient’s health; it will guarantee that the bacteria will not develop resistance.
Any antibacterial agents can be prescribed exclusively by the attending doctor and only after a thorough diagnosis.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection requires strict adherence to the frequency of administration, time of use of the drug and its dosage. It is important to take the prescribed antibiotic not until the first symptoms disappear, but for at least 5 days. If it is necessary to extend the course, the doctor will inform you about this. In addition, treatment cannot be stopped; therapy must be continuous.
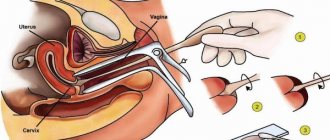
Urogenital smears
- Three hours before handing in the material, men should refrain from going to the toilet.
- Women should take a smear test 1-2 days before the start of their period.
- It is possible to take the test after your period, two days after the end of your period.
- 2-3 days before taking a smear, avoid sexual intercourse.
- Drink as much fluid as possible.
- A laboratory assistant takes biomaterial for analysis using a special spatula or cotton swab.
- The procedure is completely painless and takes a minimum of time, a few minutes.
Symptoms of the presence of bacteria in the blood
There is no single sign indicating the presence of staphylococcus in the body, and specifically in the blood. The location of the bacterium can be recognized by manifestations that characterize the presence of a particular disease. The clinical picture will directly depend on several factors: the type of pathogen, its location and the capabilities of the human immune system. The main symptoms are the following.
Pyoderma
Purulent-inflammatory lesions of the skin often spread to the sweat glands, hair follicles and sebaceous ducts. Regardless of the location of the infection, tissue swelling and purulent accumulations are observed in pyoderma. There may also be pain, but their intensity depends on the severity of the process. In addition, nausea, vomiting and fever are sometimes noted, but these symptoms are not decisive.
Rhinitis
When you have a runny nose, mucus accumulates in the nasal passages, which is the best environment for the growth and reproduction of almost all types of pathogenic flora. The main symptoms are an increase in mucous discharge from the nose of a purulent nature, difficulty breathing and a change in voice.
Sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis
Staphylococcus infection of the paranasal sinuses is accompanied by nasal congestion, purulent discharge, discomfort and headaches in the affected area. Severe forms of the disease are often combined with high fever (38-39º).
Laryngitis, pharyngitis
The main symptoms are inflammation of the mucous membrane, soreness and pain in the throat, dry cough with purulent discharge. Sometimes there may be a slight increase in temperature.
Bronchitis
It is characterized by a severe cough, accompanied by purulent discharge from the throat (sputum), pain in the chest area, shortness of breath, and fever up to 39o. Such signs are one hundred percent proof of the presence of the described pathogen in the blood.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia caused by staphylococcus is one of the most dangerous pathologies. The patient experiences shortness of breath, a painful cough with purulent sputum, and significant pain when breathing or coughing attacks. As a result of lack of oxygen, the patient often experiences a blue face.
Poisoning (intoxication), indigestion
Intense abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea are the main manifestations of the presence of staphylococcus in the gastrointestinal tract. As a rule, such a process is rapid and develops 20-30 minutes after the introduction of the pathogen. All of the above symptoms should alert the patient, and in no case should one refuse to test the blood for the presence of staphylococcus. It might just be a common cold or a virus, but it wouldn't hurt to be on the safe side.
Tests for Staphylococcus aureus
Tests for Staphylococcus aureus are prescribed:
- before hospitalization in a hospital;
- pregnant women;
- for the purpose of preventive examination of workers of certain professions,
- for the purpose of preventive inspection of public catering places and child care institutions;
- if you suspect that pharyngitis or tonsillitis was caused by this infection;
- to determine an effective antibiotic;
- to improve the results of antibacterial therapy,
- if you suspect that a person is a carrier of bacteria.
Analysis results
Today there are no problems with where and how to get tested for staphylococcus. Both employees of a regular hospital and specialists from private clinics can collect material and conduct laboratory tests.
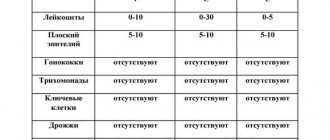
As a rule, the result of such an analysis is never in doubt. There can be only 2 options here: bacterial growth and its absence.
A positive test result indicates the presence of an acute infection caused by staphylococcus, as well as its asymptomatic carriage. As for the negative, it indicates the absence of bacteria in the body.
Carriage of staphylococcus, which does not cause any discomfort to the patient, is not subject to treatment.
Prevention of staphylococcal infection
At risk are:
- health workers,
- children, especially newborns,
- nursing mothers,
- aged people,
- patients with weakened immune systems,
- patients with serious injuries, surgical wounds, burns, etc.
In accordance with sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities, bacteriological studies of air and sterility control are constantly carried out in medical institutions, especially in children's departments.
Methods for diagnosing infection
The results of the smear will help confirm or deny the presence of bacteria
The most accurate diagnostic method is the detection of staphylococcus in the discharge from the oropharynx. For analysis, a smear from the mucous membrane or sputum secreted when coughing is taken. Then it is placed on a nutrient medium where colonies of bacteria grow.
Staphylococcus grows relatively quickly - about 3 days. The detected colonies are examined under a microscope and bacteria are found in them. This method is the most accurate, but it takes time. Typically, treatment is prescribed without waiting for the results of this analysis; they act as confirmation or refutation of the correctness of the chosen tactics.
A bacteriological study is usually combined with an antibiogram - a study showing sensitivity to certain types of antibiotics. This is important because staphylococcus quickly adapts to methods of combating it and develops resistance to antibiotics.
A faster method is ELISA.
The material for analysis is blood from a vein. The method is based on the detection of antibodies to bacteria. It confirms that the cause of the disease is staphylococcus, and not another microorganism, and also detects it within 24 hours. Additionally, other tests are carried out - blood biochemistry, urine analysis, which show the general condition of the body. It is possible that an examination for rheumatic factor will be prescribed in order to identify and begin to treat rheumatism in time.
The danger of staphylococcus in the nose
The danger of this infectious pathogen lies in its rapid movement throughout the patient’s body.
If there is no therapy for any reason, or therapeutic measures are not carried out in full, then first of all the infection spreads to the following organs:
- Lungs and oropharynx. In this case, the chance of developing pneumonia, tracheitis or inflammation in the tonsils increases.
- Penetrating into the paranasal sinuses, sinusitis, sinusitis or sinusitis occurs.
The most dangerous manifestations of staphylococcus:
- Endocarditis. Damage to the inner layer of the heart (endocardium). Most often, simultaneous damage to the lining of the heart occurs with the mitral or aortic valve.
- Meningitis. Purulent inflammation localized in the meningeal membrane of the brain. The disease is most often a consequence of the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus.
- Toxic shock. It can become a consequence of surgical therapy in the nasal cavity; cases of occurrence after childbirth are often noted. In this situation, the patient experiences an abrupt increase in body temperature to 40 degrees, which occurs against the background of a decrease in blood pressure. The inflammatory process involves lung tissue and other vital organs.
- General blood infection in the form of sepsis. The danger of this pathology lies in the ability to form foci of inflammation in the intestines, liver, lung tissue and brain. In childhood, it can cause death in a child.
How and when to get tested for staphylococci
Did you know that a cold or constant inflammation on the skin can be a consequence of the activity of Staphylococcus aureus - a dangerous and very common bacterium that can be infected anywhere? What are the risks of infection with staphylococcus and how do you understand that you need to take a test for this microorganism? In the article we will talk about the options for infection and testing, and also give some tips on choosing a clinic for research.
Types of tests for the detection of staphylococci
Staphylococcal bacteria have a spherical shape, are gram-positive, and there are about 30 species of them. Some representatives of the genus are present in the body, on human mucous membranes and skin, without causing harm. But Staphylococcus aureus, saprophytic and epidermal staphylococci can cause a serious blow to health. In some cases, bacteria cause inflammatory processes. The action of dangerous representatives of staphylococci is to damage the body with toxins that they produce in the process of life, as well as to reduce the barrier function of the immune system.
Saprophytic staphylococcus is localized mainly in the urinary and genital organs, more often in women than in men, and can cause cystitis. Staphylococcus epidermidis always lives on the surface of our skin, but if, when the integument is damaged, it enters the blood, then in case of weakened immunity it can cause infection.
The most dangerous - Staphylococcus aureus - can harm absolutely any organ. It equally easily affects women and men, the elderly and children. It mainly causes purulent processes on the skin or in internal organs (brain, heart, etc.), and can also cause food poisoning, pneumonia, meningitis and other diseases. And the worst thing is that Staphylococcus aureus is very difficult to defeat; it is not afraid of high temperatures or pure alcohol, and is resistant to many antibiotics and antiseptics. Despite the fact that the bacterium has been studied in some detail for a long time, a completely effective treatment does not yet exist.
You can become infected with Staphylococcus aureus through airborne droplets, through external contact (dust, surfaces of things, clothing), through blood, and unsterile medical instruments. The pathological activity of staphylococci can be provoked by severe hypothermia of the body, constant consumption of nicotine and alcohol, permanent stress and lack of sleep.
By the way, you can “catch” Staphylococcus aureus by eating an expired product. This is especially true for dairy and fermented milk products: cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt and even ultra-pasteurized milk. Be sure to check the expiration dates and, if they are expired, throw away the product, even if it does not emit an unpleasant odor or the taste has not changed.
Since staphylococcus can be localized in almost any part of the body, only a qualified doctor can decide what kind of biomaterial needs to be submitted to confirm or refute the presence of the bacterium. To test for staphylococcus, a swab is most often taken from the nose, throat or other mucous membranes. They also donate blood, urine or feces, and breast milk.
The appearance of pathological activity of staphylococci is not asymptomatic. There are a number of signs that may indicate the presence of an infestation. If you notice them, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When should you get tested for staphylococcal infection?
If a person notices rashes on the skin, frequent and seemingly causeless inflammation of the sebaceous or sweat glands, or hair follicles, this is a reason to consult a specialist. A constant runny nose that cannot be cured, constant nasal congestion or excessive discharge may also indicate the activity of staphylococci. Sore throat, dry or wet cough, fever - even these “familiar” symptoms can be caused by staphylococcus. The probability, of course, is not high (about 5%), but getting tested will not hurt.
There are groups of people whom the above symptoms oblige to undergo testing for staphylococcus. The fact is that they become more easily infected with these bacteria and find it more difficult to get rid of them. At risk are people suffering from cancer, diabetes or HIV, and patients on hemodialysis. Here are those who often suffer skin injuries (cuts, burns) and work in medical institutions or in agriculture. The elderly and newborns, breastfeeding mothers and people with weakened immune systems are also among those at increased risk of contracting staph.
Not only those with symptoms are tested for staphylococcus. It must be prescribed to pregnant women to exclude the possibility of intrauterine infection, to hospitalized patients for preventive purposes, to catering staff and medical personnel. A referral for analysis can be given by a general practitioner or pediatrician, ENT specialist, infectious disease specialist, urologist, mammologist, dermatologist, and even a gastroenterologist. If a person has received such a referral, then it is necessary to fulfill a number of instructions that affect the degree of reliability of the result.
How to prepare for research
Before being tested for Staphylococcus aureus, you should not take antibiotics for two months. If the patient has been treated with antibacterial drugs, be sure to inform the doctor about this. The same applies to antiviral medications if a blood test is performed. The material is collected on an empty stomach, usually in the morning. It is best to refrain from smoking for several hours before visiting the laboratory.
A patient taking sputum from the nose or throat for analysis needs to drink plenty of fluid 10–12 hours before the test. This will make the discharge less thick, and it will be easier for the doctor to take the material. Eight hours before the test you should not drink, eat or brush your teeth, so the test is usually scheduled for the morning.
Two days before donating urine, the patient needs to stop taking diuretics, and three days before donating feces, stop taking laxatives or other drugs that affect bowel function (including suppositories and ointments). If a genital smear is taken, men are advised not to visit the toilet three hours before the procedure, and women are advised to come for testing before menstruation or two days after it ends.
How to submit biomaterial for analysis correctly
If the patient collects biomaterial independently, he is responsible for the correctness of the procedure. It must be remembered that feces or urine must be collected in a sterile container, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. You should not sterilize containers at home; this does not provide a 100% guarantee of cleanliness.
The collection of material in a medical institution occurs as follows. A swab from the nasal and oropharyngeal mucosa is taken with a small cotton swab; the procedure is absolutely painless. Then the doctor places the sample in a special nutrient medium, where bacteria, if any, will rapidly multiply. But taking blood can cause somewhat unpleasant sensations, because it is taken from a vein.
Collecting discharge from a wound or any other affected area is also done using a cotton swab. Whether it will be painful depends on the nature of the damage, but, as a rule, a very small amount of biomaterial is enough for the doctor, so the pain is tolerable.
Staphylococcus test results
You can get the result of a blood or smear test after 24 hours, and a stool or urine test a little later. In the latter case, the timing depends on the specifics of the medical institution (from one and a half to three days).
If the result is negative, it means that there are no Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in the human body. If the result is positive, this means that the person is either sick or a carrier of the infection. In both cases, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment, since the bacterium will certainly show aggression and make itself felt with unpleasant manifestations.
A person who does not have medical knowledge cannot independently determine the fact of infection with a staphylococcal infection. No symptoms can clearly indicate the presence of bacteria in the body. Therefore, in case of frequent occurrence of respiratory tract diseases, inflammation, or in case of periodic poisoning, it is better to contact a specialist and get tested for Staphylococcus aureus. Prompt results and timely treatment can save the patient from many complications, some of which develop into chronic diseases and are almost untreated.
www.kp.ru
Review of medications that are prescribed for the treatment of staphylococcus in the nasal cavity
The use of medications in the development of this pathology requires an individual approach, for which the patient must go to a medical institution for an appointment with a general practitioner.
This need arises due to the rapid progression of the disease, as a result of which delay can lead to undesirable consequences (especially in childhood).
The use of drops and nasal sprays for staphylococcus in the nasal passages
The following types of antibacterial agents are used for topical use:
- Isofra. The therapeutic effectiveness is due to the presence of the main ingredient Framycetin. Has a detrimental effect on staphylococcal infections. The main advantage of the drug should be considered a wide spectrum of action (except for staphylococci, it has a depressant effect on streptococcal microflora). High efficiency allows you to get rid of the negative symptoms of staphylococcus in a 10-day course of treatment.
- Dioxidine. A successful combination of antiseptic and antibiotic in one preparation. Correctly performed therapy ensures a quick recovery without causing irritation of the nasal mucosa. The big advantage is that it can quickly neutralize purulent discharge from the nasal passages. The negative side of the drug is the impossibility of use in children under 12 years of age, and in women who are expecting the birth of a child.
- Septisol . Antibacterial effectiveness is ensured by ingredients of natural origin (Zhivitsa, Mumiyo and Stone oil). In parallel with the antibacterial and antiseptic effect, it has an analgesic effect. The main advantage is that it does not affect beneficial microflora. Due to low toxicity, it is allowed to be used by women who are in any trimester of pregnancy, and during the period when the baby is breastfeeding. Due to the presence of natural components, allergies may develop in some cases.
Isofra
Dioxidine
Septisol
Antibacterial drugs for systemic use
This infection has the peculiarity of constant mutation, which leads to the emergence of a resistant form of Staphylococcus aureus. This causes certain difficulties when choosing an antibacterial drug.
To suppress the development of this pathogenic microflora, the following types of antibacterial agents are used:
- Clarithromycin. It is a prominent representative of the Macrolide group. The therapeutic effect lies in its penetration into the infectious pathogen, after which it has a destructive effect on the intracellular nucleus. The wide coverage of action on bacterial pathogens allows it to be used in the development of laryngitis, rhinitis or when skin rashes occur. It is not advisable to take this drug in any trimester of pregnancy.
- Amoxicillin. Antibacterial agent of the Penicillin series. Used as a treatment for the consequences of staphylococcal infection. Most often with the development of sepsis. Not prescribed if the main or additional ingredients are an allergen for the patient. Do not use in any trimester of pregnancy.
- Azithromycin . Represents the pharmacological group of Azalides. Copes well with the manifestations of the disease, which is localized in the nose and oropharynx. Therapeutic effectiveness is based on the suppression of protein fractions inside pathogenic microorganisms. Use during breastfeeding is not allowed; during pregnancy, the frequency of use and duration of the course are determined by the doctor.
- Ciprofloxacin. Belongs to the pharmacological group of Fluoroquinolones. Of this series, it is considered the most commonly used drug. Can be used in case of damage to the visual organs by staphylococci. Not prescribed to persons under 18 years of age. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are a complete contraindication.
- Vancomycin. A dosage form belonging to the pharmacological group of Glycopeptides. Has a detrimental effect on staphylococcal streptococcal microflora. But due to the peculiarity of causing severe allergic manifestations, the first dose of the drug should be under the supervision of a doctor. A complete limitation to the scope of use of this drug is kidney dysfunction and liver failure. The drug is not prescribed in any trimester of pregnancy, elderly people and newborns.
Amoxicillin
Azithromycin
Ciprofloxacin
Clarithromycin
Vancomycin
What is the best way to treat the nasal cavity if staphylococcus occurs?
To create obstacles to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora, the following types of drugs are used:
- Chlorophyllipt. In addition to destroying staphylococci, it has a regenerating effect on the mucous membrane that lines the inner surface of the nose or throat. Particular effectiveness is noted if the solution is applied to a small cotton pad, which is placed in the lumen of the nasal passages, or when treating the tonsils. This manipulation is allowed for children, after diluting the solution with vegetable oil.
- Brilliant green solution (Zelenka) . Treatment should be carried out only from the outer part of the nose, this will avoid burning the mucous membrane, which may result in a burning sensation.
- Staphylococcal bacteriophage. It contains special phage viruses. They are able to destroy Staphylococcus aureus even in cases where it is resistant to antibacterial agents. Its use is not associated with the development of side effects, and it has no contraindications. For ease of use, it is recommended to use it in the form of applications (a small cotton wool is inserted into the nasal cavity). The duration of therapy is from 7 to 10 days.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Before use, dilute with clean water or Sodium chloride (ratio 1 to 11). Patients note particular effectiveness when pustular rashes occur.
Chlorophyllipt
Hydrogen peroxide
Zelenka
Staphylococcal bacteriophage
Additional therapy with immunomodulators
Immunomodulators allow you to restore the body’s natural strength and increase resistance to emerging infections.
Particularly effective:
- Drops for nasal use IRS-19.
- Immunal.
- Cycloferon is used in the form of intramuscular injections according to the scheme.
IRS 19
Cycloferon
Immunal
What situations should be avoided to prevent the development of a staph infection in the nose?
Preventing the development of staphylococcus is much easier than starting its treatment.
Therefore, both adults and children must follow the following recommendations:
- In the autumn-winter period, if possible, limit visits to places with increased crowding (public transport, supermarkets and shops).
- , wash your face and rinse your nasal passages first
- any damage associated with an open wound surface with antiseptics, and, if necessary, apply a sterile bandage.
- Dress according to the season, avoiding exposing your body to prolonged hypothermia.
- Vegetables and fruits must be washed well before eating , and meat and fish must undergo full heat treatment.
- Carry out wet cleaning in the apartment at least once every three days.