Everyone who goes to a clinic or laboratory must understand what exactly is being tested when determining HIV status. The most common test is ELISA, and it looks for antibodies that the body's immune cells produce in response to the presence of the virus.
Antibodies to HIV have been detected, what does this mean? It is important to understand this issue carefully so as not to misinterpret the research results.
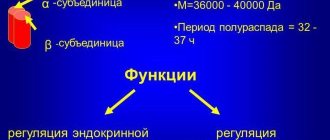
Antibodies are protein substances classified as immunoglobulins. Type M immunoglobulins are responsible for fighting viruses that enter the blood, but when testing for HIV, other structures are examined, type G immunoglobulins, which are designated as IgG. Detection of elevated levels of these antibodies indicates a high likelihood of contracting HIV. But the primary data is not unambiguous, and it is impossible to draw a conclusion so easily.
Antibodies to HIV were not detected, what does that mean ? This result can be considered great news, but additional verification of reliability is required. At short stages of the disease, there may be few antibodies, and the sensitivity of the test will not be sufficient for high accuracy of the study. Antibodies to HIV are produced immediately after the virus is recognized by the immune system, but the amount increases with the concentration of the virus.
Antibodies to HIV negative, what does this mean ? This means that you can calm down, but continue the examination if there are reasons to doubt the veracity of the result obtained.
What do HIV antibodies in the blood indicate?
What antibodies to HIV are has already been described above. This is a substance that is produced in response to an antigen produced by viruses. Antibodies are always present in the blood at a certain concentration; these indicators are known and are used to evaluate the results of the analysis. It is the concentration of antibodies that indicates a particular result.
If antibodies to HIV are elevated, it means that something stimulated their active production. The most obvious option is the presence of HIV in the blood. But sometimes the test gives false positive results. This can be caused by another viral disease that has activated all the immunoglobulins in the body.
To make everything clear, let’s clarify what is HIV? AT - those same antibodies, immunoglobulins, do not be alarmed when unfamiliar designations are found in the next article. Labels may vary in test results, but most likely the antibodies will be labeled IgG.
How is the research conducted?
How is ELISA analysis performed? Positive/negative immunoblot confirms or refutes the results of the enzyme immunoassay. The research procedure is quite simple. The specialist takes venous blood, which takes no more than five minutes. After taking samples, the injection site should be disinfected and covered with a band-aid. The sampling is carried out on an empty stomach, so after the procedure it will not hurt to eat a bar of dark chocolate or drink a sweet hot drink.
In order to receive a referral for a free test at a public medical institution, you must visit a general practitioner. In general, immunoblotting does not differ from other blood tests in terms of the sampling method. The research methodology is simple. If there is a virus in a person’s blood, the body begins to produce antibodies to destroy it. Each virus has its own set of antigen proteins. The detection of these antibodies is the basis of the immunoblotting technique.
How long does it take for antibodies to HIV to appear?
How long does it take for HIV antibodies to appear ? — A question that torments those who do not yet know their diagnosis. Let’s be clear right away that these are different times for different people. Depends on the number of viral particles that have entered the blood, as well as on the person’s immune status. But there are approximate deadlines that you can focus on.
When do antibodies to HIV appear?:
- Within 1 week after infection - if the number of viral particles is extremely high;
- Within 3-4 weeks is a common period for the appearance of antibodies;
- Within 3 months – by this point, 98% of infected people have formed antibodies;
- Within six months - if only a few cells enter the blood during infection, as well as if there are specific features of the immune system.
The production of antibodies is stimulated by HIV antigens, viral molecules that are recognized by the immune cells of the human body.
What is HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a contagious infection caused by several types of retroviruses that integrate into formed blood cells, gradually destroy the immune system and kill the body. HIV is transmitted through blood, sexually, vertically - during childbirth from a woman in labor to a baby and during breastfeeding.
AIDS is the last stage of HIV, the abbreviation is human acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. It develops as a complication of the immunodeficiency virus; if left untreated, it begins to progress 3 to 5 years after the onset of infection; With adequate drug regression, retroviruses may not appear at all or only after 30 - 40 years.
The first cases of HIV infection were reported in medical journals in 1981, when American doctors presented the results of studies of SARS and Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men. These two diseases had different risk groups - malignant formations of the dermis of the oral cavity and nasopharynx were noted in older people, and pneumonia of weakened immunity in people who had undergone radiation or chemotherapy. This strange combination of two dissimilar diseases prompted doctors to think about weakened immunity in the control group. Further research has enriched the data on drug addicts, people who practice anal sex, and antisocial layers of citizens. A random sample showed that many people from these groups have a number of similar symptoms and abnormalities in homeostasis. Further, they discovered virions with cone-shaped cores in their bodies - the human immunodeficiency virus.
How are antibodies to HIV detected?
An HIV load test is not a complicated procedure. The technique was developed quite a long time ago, even at the initial stages of studying this problem. The drugs today are stable, their use does not cause difficulties for personnel of any skill level. The study is carried out on a venous blood sample. The blood is separated into its components, releasing the serum. The resulting liquid is placed on a solid base and viral cells are placed there. Then they are treated with specific enzymes. After this, they look at the result: if antibodies to HIV are detected, what does it mean? This means that viral material was already present in the serum being tested.
During the analysis, it does not hurt to pay attention to what is specifically indicated in the “antibody” form. There are different forms of the virus, and antibodies to HIV 1 HIV 2 will be different. One form is common in Europe and America, the other in African countries. The African form is rarely found in Russia, but analysis is carried out for this rare form too.
Indications for ELISA
It never hurts to check your health. It is not necessary to wait for the doctor to prescribe the test, or for some authorities to require you to undergo an examination. You can get tested for HIV on a voluntary basis. By the way, there is no need to have any reason to worry about this. Every year, the virus is discovered in people who would not have expected such an outcome due to complete caution. Of course, this is rare.
get tested for HIV 1 2 antigen antibodies inexpensively or free of charge; this research method is not at all burdensome.
But it happens that it is simply impossible to avoid the examination. A number of people are required to undergo an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, checking the level of HIV antigen 1 HIV antigen 1 2. The following groups of people must be examined:
- Have recently come into contact with someone infected with HIV;
- Future parents (pregnant woman or planning pregnancy and father of the child);
- Persons who have expressed a desire to accept Russian citizenship (legislation varies in different countries);
- Medical personnel working with biomaterial;
- People working in the service and catering sectors;
- Blood and organ donors;
- People with a sharp deterioration in health.
HIV test results can be requested in some special cases, when applying for a job in specific structures, as well as when receiving a bank loan for large sums.
HIV – routes of infection and symptoms
The immunodeficiency virus is transmitted mainly through sexual contact with an infected person. Other routes of infection are known as through:
- during blood transfusion in laboratory conditions (donor blood is always checked for infections, but small concentrations of the virus can be missed);
- during contact between mother and child (during pregnancy, feeding or childbirth);
- there may be infection from injections (needles), non-sterile devices and instruments (manicure accessories), and so on.
Symptoms of the primary manifestation of HIV infection appear as follows after just 6 weeks:
- sore throat (aching, when swallowing, even outside meals);
- state of chills;
- muscle pain (not to be confused with physical activity);
- if mouth ulcers do not heal for a long time;
- maybe increased sweating during sleep;
- partial memory loss;
- a constant state of fatigue, but not as a result of overwork;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes throughout the body;
- pneumonia.
Decoding the indicators of the analysis of the presence of antibodies for HIV
HIV antibody testing can be done in any laboratory. Not only a doctor, but also a laboratory worker can decipher the result. Of course, you still need to consult your doctor. But if you want to independently understand the values that appear on the results form, then this is possible.
Normal immunoglobulin levels differ for adults and children. The reference values are 7.4-13.6 g/l for children, 7.8-18.5 g/l for adults. If the indicators are higher than the reference values, then there is a probability of the presence of HIV in the body. In this case, additional analysis will be prescribed, possibly using a different technology. It is important to know that the analysis in children under one and a half years old, born from HIV-positive mothers, is not considered reliable. There is a high probability of both false positive and false negative results.
Antibodies for HIV may not be detected correctly. The result can be affected by the inflammatory process, rheumatoid factor, autoimmune diseases, and an undeveloped immune system in infants.
In other words, you should not immediately sound the alarm when you see the “+” sign opposite the “antibodies” column. HIV p24 antigen 1, what is it and how will it help get rid of doubts? This antigen is a viral protein, in response to which antibodies are produced. This substance can be detected using a special analysis even before the production of antibodies, approximately 10 days after infection. The possibility of conducting such an analysis can be discussed.
The norm of HIV antibodies in a healthy person
HIV antibodies do not normally circulate in the blood. These specific compounds are produced by immune cells (B lymphocytes) in response to recognition of the virion capsule. Therefore, the normal value for a healthy person can be considered 0. But the diagnosis cannot be made only on the basis of measuring antibodies. Other indicators are also taken into account:
- Leukocyte level;
- Lymphocyte level;
- Platelet count;
- ESR;
- Hemoglobin level.
By itself, a general clinical analysis is not indicative of diagnosing a viral disease, but in combination with other studies it can tell a lot about the state of the body and help predict the course of the disease or recognize the absence of infection.
Antibodies to HIV type 1 and type 2 are different, however, the principle is the same. When conducting an analysis, laboratories immediately examine the presence of two forms of antibodies.
Antibodies to HIV have been detected - is it worth sounding the alarm?
Only on the basis of the analysis can a treatment plan be built. Depending on whether antibodies to HIV are detected or antibodies to HIV are not detected, the doctor makes his verdict. You should never self-diagnose. One test never serves as the basis for any definite conclusions. Cases of false positive test results are common.
The diagnosis is made based on a combination of facts. The doctor evaluates the following parameters:
- General condition of the potential carrier of the virus;
- History, that is, the circumstances that prompted you to seek help;
- Analysis results;
- Clinical picture of the disease, improvement or worsening.
It is always worth remembering the possibility of error or error. No test is 100% accurate. Repeated examinations provide a more complete picture of what is happening and the result, repeated several times, can be considered reliable.
It would be most accurate to focus on a final diagnosis within six months. By this point, the disease has already been determined by almost all research methods. It is difficult to make a diagnosis in the early stages. But in case of multiple positive results, HIV therapy with antiretroviral drugs should be immediately administered so as not to waste precious time.
What does “treatment as prevention” mean?
Treatment with antiretroviral drugs reduces the concentration of the virus in the blood. The goal of therapy is to reduce the “viral load” to such a low level that “the virus cannot be detected in the blood.” Large studies have been conducted involving homosexual and heterosexual discordant couples in which only one partner was HIV-positive. The results show that when an HIV-positive partner's viral load drops below detectable levels, the risk of transmitting the virus does not exceed 5 percent (even without using condoms). As your health improves, your chance of passing HIV to someone else decreases. If everyone living with HIV got the treatment they need, we could prevent most new infections.
Common mistakes when diagnosing HIV
The main mistake is taking tests too early (during the “serological window” when there are no antibodies in the blood yet).
Attention. Errors also include self-prescription and examination in a private laboratory. Without an immunologist, it is difficult to calculate the possible period of the “serological window” and correctly interpret the examination results.
It is also necessary to take into account the possibility of obtaining false-positive ELISA results in pregnant women and patients with the Epstein-Barr virus.
To eliminate errors, it is recommended to undergo the examination at an AIDS center under the supervision of an immunologist.