The biochemical features of the human body are represented by thousands of operations and reactions. They are accelerated by special compounds known as enzymes. Insufficient synthesis leads to critical disruptions in the functioning of the body.
TPO or thyroid peroxidase acts as an accelerator of energy metabolism reactions. To make the question clearer, you need to turn to anatomical information.
The thyroid gland is a special organ that regulates all metabolic processes. Processing of nutrients, energy production, and other phenomena. This is very important because it forms the basis of biological life.
The enzyme thyroid peroxidase, which naturally accelerates positive processes in the body (is a catalyst), is responsible for the normal performance of functions. Violations of the functional state of all structures are possible.
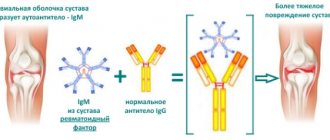
Anti-TPO antibodies are antibodies that are synthesized to destroy the catalyst. Normally, thyroid peroxidase is concentrated in the thyroid gland itself and is produced by it. As soon as something goes wrong, the organ cells are destroyed and the enzyme enters the blood.
At this point, the body begins to react negatively. Perceives the substance as a foreign agent and attacks it first. Then, after some time, the thyroid gland itself. Because there is a lot of substance concentrated here.
This is how a circular process occurs: on the one hand, in order to stop the disorder, it is necessary to eliminate the damage to the gland. On the other hand, this cannot be done, because an autoimmune attack occurs on one’s own cells.
Complex treatment is required.
What are thyroid peroxidase antibodies?
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (the norm in women is important for making a diagnosis) are produced under the influence of the immune system during the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Rarely does the immune system get confused and begin to react to its own cells.
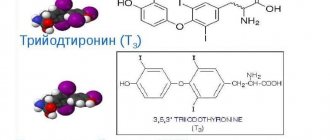
Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme produced by the thyroid gland. It produces hormones of thyroid origin, hence the name. Namely, thyroxine and triiodothyronine. The enzyme is responsible for the production of iodine and the regulation of metabolic processes.
The role of the enzyme in the body
Without going into complex biochemical explanations, the substance acts as the main accelerator of the natural reaction.
Normally, the thyroid gland is responsible for energy metabolism and the breakdown of biologically active substances. This happens under the influence of hormones. It is their catalysis (acceleration of the reaction) that the actions of thyroid peroxidase are aimed at.
There is also a not so obvious function, which is rather artificial. The fact is that the study of antibodies to TPO is used as a marker of an inflammatory, destructive process that affects, at a minimum, the thyroid gland itself. Possibly some other organs as well. In any case, we need to understand in more detail.
What significance do anti-TPO antibodies have for the body?
AT – TPO has a certain significance for the body.
Namely:
- maintaining optimal hormonal balance (T3 and T4);
- maintaining the functionality of the thyroid gland;
- ensuring optimal functioning of the endocrine system;
- fight against toxic substances.
A healthy body contains a moderate amount of AT - TPO. But with increased production, thyroid peroxidase can be destroyed, and thyroid diseases appear.
Features of the analysis
To avoid abnormalities of the thyroid gland, as well as to minimize the consequences of destructive processes in the body, blood is taken to determine the amount of TPO antibodies. In pregnant women, timely testing will allow the detection of chromosomal mutations in the fetus, such as Down and Turner syndrome.
They donate blood from a vein on an empty stomach; the last meal should be no earlier than 8 hours before the collection of biomaterial. The results of the analysis may be affected by medications that the person took the day before. That is why you should avoid taking medications three days before the test. If you have chronic diseases and you cannot just give up medications - inform your doctor about the situation, and he will decide whether it is advisable to use a particular medication.
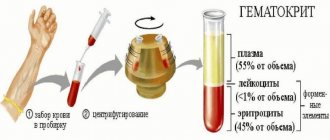
For diagnostics, a small amount of blood is removed; for a full analysis, 5 mm of biomaterial is sufficient. The procedure is virtually painless, although some may experience discomfort due to a low pain threshold. The analysis is no different from the usual blood sampling for biochemical analysis. The nurse bandages the patient’s arm with a tourniquet so that the vein is clearly visible, then wipes the skin on the arm with an antiseptic and makes a puncture. Venous blood enters the syringe through a thin needle. Next, the syringe is removed and the puncture site is sealed with a band-aid.
Like any diagnostic procedure, the blood test for TPO antibodies has a number of indications, including:
- suspicion of autoimmune thyroiditis;
- hypothyroidism;
- suspicion of thyroid cancer;
- preparation for surgery and post-surgical control;
- enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- heterogeneous structure of the thyroid gland revealed by ultrasound;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- pregnancy;
- prescription of the drug Amiodarone.
Norm of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase in women by age, during pregnancy
AT – TPO does not change much with age. A characteristic feature is that at age over 50 the rate increases slightly. This is considered normal and does not require therapy. The main thing is that the level does not go beyond the optimal values.
Normal indicators of AT - TPO in women:
| Method of analysis to obtain the result | Description | Age category (years) | Indicator value (in units/ml) |
| Immunoluminescent method | Consists in the use of luminescent serums | Less than 50 | From 0 to 34.9 |
| More than 50 | From 1 to 99.9 | ||
| Linked immunosorbent assay | An enzyme is used as a label for signal registration | Less than 50 | From 0 to 30 |
| More than 50 | Up to 50 |
Regardless of age, a change in the level of AT - TPO by 20 units/ml is allowed. This is normal and does not require therapy. But constant monitoring of the indicator and being under the supervision of a doctor is necessary. This is required to prevent values from being too high or low.
When the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase rises above 25 units/ml from the optimal values, consultation with a specialist and prescription of therapy is required. Often the AT-TPO indicator is elevated. But there may also be a reduced value. Low AT - TPO - is less than 10 units/ml. For pregnant women, the AT-TPO level is important. It is necessary to take a blood test to identify the indicator.
If the values are too high, the condition threatens the health of the mother and fetus.
The likelihood of complications after childbirth also increases. After 2 - 3 months. after the birth of the baby, the patient may have postpartum thyroiditis. This is rare, according to statistics, in 10% of women. For pregnancy to proceed normally, the level of AT - TPO should not exceed 2.6 mIU/ml or 25 units/ml.
What does it mean
Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme without which the production of the active form of iodine is impossible. An important component necessary for the iodification of thyroglobulin protein.
With an excessive level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, the activity of iodine decreases, which negatively affects the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Against the background of triiodothyronine and thyroxine deficiency, development and growth in childhood slows down, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and heat exchange deteriorate, and the heart muscle weakens. Negative processes occur in parts of the nervous system and skeleton, physical development is disrupted, and psychosomatic disorders arise.
AT to TPO is a marker indicating pathological changes, in most cases autoimmune diseases, changes in the condition of the thyroid gland and rheumatic organ damage. In women, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are elevated more often than in males. In some cases, a slight deviation is not a consequence of diseases and negative conditions: the indicators stabilize after the disappearance of the factors that provoked a slight change in AT values.
How to lower hemoglobin in the blood of men and what are the reasons for increased levels?
We have the answer! Adenoma of the left adrenal gland: what is it and how to get rid of the formation in women? Read the answer in this article.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (the norm in women is important for making a diagnosis) are tested in cases of suspected thyroid disease. Often an analysis is prescribed to exclude or confirm pathologies. Additionally, they may recommend testing TSH, T3, T4.
Indications for prescribing analysis for AT - TPO:
- hyperthyroidism – increased levels of thyroid hormones;
- hypothyroidism – reduced amount of thyroid hormones;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- toxic form of goiter (Graves' disease);
- problems with the thyroid gland after childbirth, surgery, injury;
- diabetes;
- exophthalmos – forward displacement of the eyeball;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- monitoring the effectiveness of prescribed therapy;
- increased likelihood of thyroiditis due to heredity;
- anemia.
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase should be tested if anemia is suspected.
In addition to the indicated indications, an AT-TPO test is prescribed to women regularly to check the value. It is also necessary to monitor the indicator while carrying a child.
Who should have a thyroid examination?
Approximately 70% of humanity has colloid nodules in the thyroid gland. It is believed that 40% of nodules are caused by iodine deficiency. The natural mechanism of protecting the organ is triggered - it grows in order to obtain the missing element from the blood. In this case, ultrasound is used to clarify the diagnosis.
Only if cancer is suspected, a puncture biopsy and the radiological method of contrast radiography are additionally prescribed - it is 10 times more dangerous than conventional X-rays due to the radiation of iodine radionuclides.
Blood tests are taken:
- with the growth of gland tissue;
- if you suspect hypo- or hyperthyroidism;
- the first signs of iodine deficiency;
- hereditary predisposition to thyroid gland pathology;
- women with infertility;
- women during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, venous blood is examined for concentrations in it:
- hormones T3 and T4;
- pituitary hormone (TSH);
- antibodies to thyroglobulin;
- antibodies to thyroid peroxidase.
Preparation and conduct of the study
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (the norm in women is important to decipher the result of the study) - a test for which you need to prepare. If measures are not followed, the indicator may deviate from the norm and will not be entirely correct. If the patient is taking hormonal medications or iodine-containing medications, it is recommended to consult a doctor before taking the test.
The specialist must find the best option, that is, stop the medication or continue use. It is also not recommended to conduct research in the presence of an inflammatory process in the body or immediately after surgery.
Preparatory measures before taking the test for AT - TPO:
- Limit physical activity. There is no need to overload the body 1–2 days before the test.
- Reduce stress and anxiety.
- Avoid fatty, fried and salty foods. It is also not recommended to eat smoked food. It is better to steam, boil or bake food 1 – 2 days in advance.
- Eliminate alcohol, carbonated drinks, and strong coffee from liquids for 3 days.
- Completion of physical therapy, which involves impact on the neck, 5 - 7 days before donating the biomaterial.
After waking up on the day of donating the biomaterial, it is not recommended to take food or any liquid. If a person smokes, it is recommended to abstain from cigarettes 2 to 3 hours before the test.
Blood is taken in a laboratory setting. An employee without proper qualifications cannot work in an institution. To collect biomaterial, sterile instruments are used, which are changed with each new patient. The nurse finds the right place on the arm, inserts the needle, and takes the required amount of blood. Next, the tube with the biomaterial is labeled and sent to the laboratory.
Why are high levels of antibodies to TPO dangerous?
The main risks are associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland itself. A cyclical pathological process develops. Vicious circle.
- The damaging factor affects the organ. The release of the substance into the bloodstream is observed.
- The body responds by producing antibodies. This is a protective measure that is aimed at protecting the condition of all structures.
- Since the process can no longer be stopped, it has started, and those substances that are located in the thyroid gland itself, in its cells, are also attacked.
- There is destruction of organ tissue and an even greater release of substance. Everything flows in circles.
If you do nothing, severe inflammation is guaranteed, the death of thyroid tissue and disruption of its function. Decrease in synthesis of T3, T4. The body will not be able to ensure normal energy metabolism.
The result is hypothyroidism. Insufficient production of hormones. Then a chain reaction begins. Not enough substances - the reproductive system does not work, the heart suffers, the brain is damaged. Problems appear with endocrine structures and so on.
If you do nothing in a very aggressive condition, the matter will not be limited to discomfort. There is a real possibility of death. It is necessary to find the cause in time and carry out treatment.
On the one hand, eliminate the effect of anti-TPO on the gland. On the other hand, remove the inflammatory process in the thyroid gland itself.
Only an endocrinologist can cope with both tasks. It would not be a bad idea to be hospitalized during the acute phase. Until quality treatment is selected.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase in women may not always be within normal limits. If you deviate from the optimal values, it is advisable to consult a doctor to prescribe therapy. The AT-TPO indicator can be normal, increased or decreased.
Promotion
The AT - TPO indicator can be increased.
This happens in the following cases:
- penetration of viruses;
- exposure to radiation;
- living in places with poor ecology;
- injury to the thyroid gland;
- penetration of toxic substances;
- vasculitis – inflammation of blood vessels, capillaries, arteries;
- insufficient or excessive amount of iodine;
- chronic diseases - anemia, diabetes and others;
- transmission of an indicator by heredity;
- goiter;
- neoplasm of the thyroid gland.
With a high level of AT - TPO, a woman will be bothered by various symptoms.
Namely:
- increased sweating;
- weight loss;
- increased heart rate;
- anxiety;
- fatigue with minimal physical activity;
- increased fragility of hair and nails;
- swelling of the extremities, but most often the lower ones;
- dizziness;
- sleep disturbance;
- poor memory;
- feeling of thirst;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- impossibility of conception.
Sometimes the AT-TPO value is increased in a healthy person. This often happens in women over 45 years of age. If other indicators are normal, therapy is not required. It is possible for people to have thyroid dysfunction, but this is rare.
Demotion
If the thyroid gland is working normally, then antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are in the body at a low level. But there is an option for a reduced amount of AT - TPO.
This occurs in the following cases:
- increased likelihood of developing autoimmune diseases;
- the indicator is normal for humans and is associated with a hereditary factor;
- improper preparation before taking biomaterial;
- test error.
If the condition is severe, the following symptoms appear:
- disruption of the heart;
- sleep problems;
- nervousness;
- anxiety;
- severe fatigue with minimal physical activity;
- depression;
- weight gain;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - gas formation, constipation.
Reasons for the increase
Growth factors and indicators are determined by pathological processes. Always. Which ones exactly:
Autoimmune inflammation
The so-called Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Although there are other forms of the pathological process.
The hormone (or more precisely the enzyme) TPO is synthesized in normal quantities. It also enters the bloodstream, which leads to a reaction and even greater tissue destruction. It turns out to be a double autoimmune process. This is a very dangerous condition.
The symptoms are approximately the same as with other forms of inflammatory process in the organ. Among the manifestations:
- Headaches for no apparent reason.
- Increased body weight due to insufficient metabolism.
- Temperature drop.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Heaviness in the arms and legs.
- Dyspnea.
- Blood pressure disorders.
Analysis of antibodies to TPO clarifies the situation, but does not provide accurate information about the nature of the pathology - it is necessary to study markers of the autoimmune response, for example, C-reactive protein.
The treatment is specific. The goal is to eliminate inflammation. Loading doses of glucocorticoids are prescribed. Prednisolone, Dexamethasone and more powerful analogs are options.
If they are ineffective, immunosuppressants are used, but these are very heavy drugs. They don't accept them for a long time. The patient's condition is monitored by an immunology specialist, endocrinologist. Or a tandem of doctors.
Diffuse goiter
A generalized name for conditions in which uniform growth of organ tissue occurs. It is not cancer because the process is benign.
Cells multiply in the correct sequence and under the control of the body. As a result, the amount of hormones increases, as well as the production of thyroid peroxidase.
Some of it inevitably gets into the blood, and that’s where the autoimmune reaction begins with the release of antibodies to TPO.
This condition can be prevented if treatment of the pathological process is started at the earliest stage, when there are no functional abnormalities yet.
Symptoms of diffuse goiter are:
- Headache.
- Weakness.
- Insomnia.
- Increased body temperature.
- Protruding eyes.
- Nausea.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Pathological thinness.
Metabolic processes accelerate, this is the main problem. Treatment consists of drug correction with iodine preparations. To slow down the disruption and eliminate it.
Be sure to additionally prescribe a diet low in this element.
Nodular goiter
Approximately the same process in nature. With just one change. The thyroid gland does not grow completely and evenly.
Individual parts suffer. So-called nodes develop. They are benign and do not tend to transform into cancer.
The symptoms of the pathological process, as well as the mechanism of the autoimmune reaction, are identical.
The treatment is about the same. However, there is the possibility of targeted removal of nodular formations.
Minimally invasive methods are used at an early stage. Open surgical intervention - when the nodes are large enough and require removal. Therapy is the task of the endocrinologist.
Consequence of childbirth
In some cases, changes in the thyroid gland occur after gestation has resolved. This is a complication. It is associated with hormonal instability.
It makes sense to conduct a full diagnosis to identify the cause. Treatment is not always required at all. In 70-80% of cases, the condition returns to normal on its own; you don’t need to do anything. All that remains is to observe.
Waiting tactics in this case are key.
Idiopathic forms of hypothyroidism
Simply put, when there is a violation, and what exact origin it is, is not clear. It is assumed that the reason lies in genetic predisposition.
Also in the nature of nutrition, ecological situation, environmental factors.
There are many options, but it is impossible to determine the exact reasons. It remains to fight the symptoms of the pathological process.
Diabetes
A condition in which little insulin is produced or tissues are not sensitive to it. The body is damaged due to the abundance of glucose, which is not processed.
Diabetes gives a lot of symptoms:
- Leg pain.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Shortness of breath.
- Exercise intolerance.
- Weakness.
- Visual impairment.
An even bigger problem is complications. A strong increase in AT-TPO is one of these consequences of diabetes.
Treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist. A diet is prescribed, plus insulin is used according to the situation.
Arthritis
Inflammatory process of autoimmune origin. We are talking about its rheumatoid form.
In this case, the thyroid gland, as they say, comes under attack. It is rather an accident that develops into a pathological pattern.
It is necessary to treat both arthritis and the inflammatory process of the endocrine organ. The task is not easy.
Again, drugs from the glucocorticoid group and immunosuppressants are used. Dosages, as well as treatment regimens, are determined by a specialist.
lupus erythematosus
If AT-TPO is highly elevated, this means the possible development of lupus erythematosus. Another autoimmune process. In this case - generalized. That is, all tissues and organs suffer simultaneously. Urgent medical attention is required.
Therapy includes powerful doses of hormones and immunosuppressants. To somehow eliminate pathological phenomena.
It is not possible to radically cure the disorder. But in the initial stages there is a good chance of taking the disease under control and avoiding fatal complications.
Other factors
In some cases, the increase is false. Among these possible situations:
- Features of genetics. Levels of the substance will initially be slightly higher than in other patients. Deviations from the norm within a couple of percent are quite acceptable if there is no reason to diagnose pathology.
- Use of iodine preparations. The systematic use of drugs and the natural disruption of the structure of thyroid cells have an effect. This is an insignificant point.
- Chronic diseases of the body in the acute phase.
- Postponed surgeries.
- Thyroid injuries.
These situations require an individual, special approach.
- If you have genetic conditions, no help is needed. This is fine. But it would not be superfluous to carefully examine the patient to make sure that the deviation is of natural origin. Every year you need to be checked by an endocrinologist.
- You also won’t have to do anything after taking iodine supplements. Once the therapy is over, everything will return to normal on its own. Without outside help.
- Chronic pathologies are corrected depending on the nature of the disorder and its degree. Accurate localization.
- Surgical treatment requires careful rehabilitation. This is the key to a quick recovery.
- Injuries need urgent correction. Conservative or surgical. Plus, hormones are prescribed preventively to prevent an autoimmune response.
Treatment for elevated anti-TPO antibodies
If the AT-TPO level is elevated, there is no need to immediately make a terrible diagnosis. The value may not be greatly exceeded. In any case, deviation from the norm can be treated. To make a diagnosis, other tests are prescribed - ultrasound, TSH. Based on the results of the procedures, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Popular medications for the treatment of excess AT - TPO values are listed in the table:
| Group of drugs | Name | Action | Side effects | Contraindications | Price (in rub.) |
| Antithyroid | Tyrosol, tablets | Inhibits the production of thyroid hormones |
| Hypersensitivity to components, agranulocytosis (reduced level of granulocytes in the blood), granulocytopenia (reduced level of granulocytes with a reduced number of leukocytes) | 120 – 350 |
| Beta blockers | Metoprolol tablets | Normalizes heart rate |
| Increased likelihood of an allergic reaction, bradycardia, acute myocardial infarction. The drug is also prohibited for use during breastfeeding and for children under 18 years of age. | 50 – 250 |
| Glucocorticoids | Prednisolone tablets | Anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-shock effect | Agitation, sleep disturbance, allergic reaction | Increased sensitivity to components | 90 – 110 |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Nurofen tablets, capsules | Relieves pain, inflammation, swelling |
|
| 80 – 350 |
| Adaptogens | Eleutherococca extract tablets, syrup | It is of plant origin. Improves well-being, adapts the body to external conditions | Allergic reaction, pain in the head | Increased excitability, hypertension, insomnia. It is also not recommended to take the product during pregnancy, during breastfeeding and in case of an increased likelihood of an allergic reaction. | Up to 50 |
| Vitamin complexes | Alphabet, tablets | Normalizes the level of nutrients | Allergic reaction | Increased sensitivity to components | 200 – 300 |
Treatment of elevated levels of AT-TPO in a pregnant woman should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. The doctor calculates the benefits of taking it and the harm to the fetus after use, then makes a conclusion about the prescription of medications.
Surgery may be used as therapy. This happens in rare cases. For example, if it is impossible to carry out drug therapy, the case is advanced and the thyroid gland is greatly enlarged in size.
To lower the AT-TPO level, you can use traditional methods. They have a plant composition. But it is better to use them in combination with medications, this way you can improve the effect of therapy. Thanks to folk methods, your well-being improves.
Popular recipes are listed in the table:
| Name | Description |
| Sagebrush | The method helps to get rid of unpleasant sensations. To prepare you will need 200 g of pork lard and dry wormwood. The first component needs to be melted, add the 2nd plant and mix. Apply a warm compress to the neck. To enhance the effect, you can use the recipe before bed. Course of therapy – up to 14 days |
| Sea kale, honey, lemon | The recipe relieves pain and inflammation. To prepare, take 50 g of kelp, 25 g of pine buds. And also 1 - 2 plantain leaves, 1 tsp. honey and lemon juice. To stir thoroughly. Place in a water bath for 30 minutes. Take the mixture 1 tbsp. 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The effectiveness of therapy will be noticeable after 30 days |
| Herbal collection | To prepare you will need:
The components need to be crushed and mixed. Take 0.5 tsp. mixture, dilute in 500 ml of hot water. Leave for 30 minutes. Take 100 ml in 5 – 10 minutes. before meals. Course of therapy – 2 months. |
AT-TPO is elevated: what to do?
The treatment regimen for elevated AT-TPO levels is selected by the doctor depending on the cause of the deviation.
Drug treatment
- If the production of thyroid hormones is insufficient, patients are prescribed hormone replacement therapy.
- With increased values of hormonal parameters , on the contrary, thyreostatic drugs that suppress the secretory activity of the thyroid gland.
- To reduce the activity of the autoimmune process, the patient is prescribed antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids.
- For inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used.
- Symptomatic therapy is carried out with the help of antihypertensive drugs, beta-blockers, etc.
Diet therapy
Patients with hyperthyroidism are advised to follow a diet; strong tea and coffee, spicy and fried foods should be excluded from the diet. More foods rich in vitamins and minerals (vegetables, fruits, lactic acid products) are added to the menu.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent the development of abnormalities associated with thyroid function, it is recommended:
- rejection of bad habits;
- balanced diet;
- maintaining an adequate work and rest schedule, a full night’s sleep;
- avoiding physical and mental overload;
- for people at risk - regular preventive medical examinations (at least once a year).
Treatment for low anti-TPO antibodies
Therapy for low levels of AT - TPO involves the use of medications - thyroid hormones.
Popular drugs are listed in the table:
| Name | Action | Side effects | Contraindications | Cost (in rub.) |
| L – thyroxine, tablets | Replenishes thyroid hormone deficiency | When used correctly, they occur in rare cases. The most common side effect is an allergic reaction | Hypersensitivity to components, acute myocardial infarction, adrenal insufficiency | 130 – 170 |
| Eutirox, tablets | Hypersensitivity to components, impaired functionality of the adrenal glands, pregnancy | 100 – 160 |
With a reduced level of AT-TPO, the use of traditional methods is allowed. Popular:
- Juice. To prepare, take beets, potatoes, carrots. Squeeze juice from vegetables. Take equal parts of beet, potato, and carrot juice. The total volume should be about 150 ml. Take the indicated amount per day, can be divided into several doses. Course – up to 50 days.
- A mixture of components. To prepare, take 100 g of chopped seaweed and add 100 ml of hot water. Next, add 120 g of low-fat cottage cheese, 6 walnuts, and 2 tbsp full-fat sour cream. Mix everything and eat throughout the day. You can divide the mixture into several doses. Prepare the recipe every other day for 1 month. The mixture can be stored in the refrigerator.
Description of the procedure
The material for the study is blood from the ulnar vein. Specific preparation for the diagnostic test is usually not carried out, however, the instructions require the patient to comply with the following recommendations:
- Exclusion (if possible) of medications that affect the activity of the thyroid gland - levothyroxine, some antibiotics, corticosteroids.
- Limit physical activity and stress 1-2 days before blood sampling.
- Avoid alcohol 24 hours before the examination.
- Taking the test in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach.
Note! Before taking the test, consult your doctor and make sure that this type of examination is really indicated for you. Determination of antibodies to thyrocyte thyroid peroxidase is considered an expensive examination method: the average price of the test ranges from 1000 rubles.
Blood is drawn from the ulnar vein (pictured)
Consequences and complications when indicators deviate from the norm
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (the norm in women varies slightly depending on age) is an indicator that, if it deviates from the optimal values, various complications may occur in pregnant women.
For example:
- increased or decreased amount of hormones;
- loss of a child during pregnancy;
- premature labor;
- abnormalities in the fetus after labor.
With an increased or decreased level of AT - TPO in a woman, the risk of tumor formation increases. If the indicator deviates from the norm, the patient’s general well-being suffers - the skin becomes dry, nails and hair break.
AT - TPO are produced by the immune system. A healthy body contains a small amount of them. Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase fight pathogenic substances. But when a malfunction occurs in the immune system, an indicator is produced and its effect on thyroid peroxidase occurs.
If a woman suspects that she has an elevated level of AT - TPO, it is recommended to be tested for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase. The norm depends on age. Often after passing, the result sheet indicates if the value is not within the optimal level. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to regularly take an AT-TPO test.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Decoding the results
Diagnostic search depends on test results
The results can be presented as “Negative”, which means the normal absence of antibodies to TPO in the body in concentrations significant for diagnosis. When recording “Positive”, the concentration in Units/ml or IU/ml is usually additionally indicated, depending on the laboratory test method.
Most often, the result is presented in numerical form with units of concentration. In this case, to decipher it, you need to focus on the normal range indicated in the result form. Exceeding the threshold level indicates the presence of TPO antibodies in the blood in a concentration significant for health; in this case, autoimmune pathology cannot be excluded.
Symptoms of increased performance
At the initial stage, with a slight increase in the level of immunoglobulins to thyroid peroxidase, a person may not pay attention to negative signals. The greater the increase in this indicator, the greater the negative impact on the human body.
The symptoms of an increase in this case resemble hypothyroidism, that is, a lack of T3 and T4 iodine-containing hormones:
- Severe weakness, fatigue;
- Deterioration of hair and nails. Hair falls out rapidly, nails peel, break and become thinner;
- Increased thirst;
- Intense sweating even with minimal physical activity;
- Drowsiness , as well as sleep disorders at night;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Memory impairment;
- Pale skin;
- Depressive state;
- Hypothermia (body temperature 36 degrees or below);
- Constipation;
- Increased gas formation;
- Hypotension – decreased blood pressure;
- Weight gain, in severe cases obesity;
- Menstrual irregularities in women;
- Infertility and miscarriage.
All these symptoms should alert a person. If they are present, it is necessary to donate blood to determine the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase.
Increased levels of antibodies to TPO: possible causes
Increased levels of antibodies to TPO are relatively rare and are diagnosed in only 7%-10% of the world's population. If the deviation from the norm does not exceed 20 IU/ml, then such a fluctuation can be taken as a normal condition, due to the influence of certain factors. The patient is advised to undergo a comprehensive examination and constant medical supervision to monitor the dynamics.
If the level of antibodies to TPO increases, the patient is advised to undergo a full examination and regular medical supervision to monitor the dynamics.
The level of antibodies to TPO may increase for the following reasons:
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis, which is autoimmune in nature;
- toxic diffuse goiter;
- subacute thyroiditis;
- hypothyroidism of idiopathic etiology;
- systemic autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis);
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland in the postpartum period;
- rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis;
- various neoplasms localized in the thyroid gland (carcinomas, adenomas);
- liver disease (this organ performs the function of recycling excesses of various substances synthesized by the body, including antibodies to TPO);
- pregnancy (increased production is caused by the reaction of maternal immune system proteins to fetal antibodies, especially if the antigens of the mother and the unborn child are identical).
Measures to take when hormone levels increase
If TPO AT is elevated during pregnancy, the woman should definitely be examined. The endocrinologist will perform the following actions:
- taking anamnesis;
- referral for TSH and associated T4 tests;
- prescribe an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland;
- in accordance with the results obtained, he will prescribe measures for therapeutic correction.
Before visiting an endocrinologist, a woman should stop taking iodine supplements for a month.
Normally, a woman’s AT TPO content is less than 5.6 U/ml. But sometimes it is elevated. However, the woman does not reveal any pathology that could provoke this phenomenon. Then such a condition is regarded as an individual feature of the female body and should not cause cause for concern.
As for drug therapy, everything here is strictly individual. There is simply no general treatment plan. Each drug is selected individually for each specific woman. If there is insufficient production of hormones, then drugs are prescribed as part of replacement therapy. L-thyroxine is prescribed in an individual dose. In the opposite case, when the production of hormones is increased, drugs are prescribed that inhibit their production.
To reduce the activity of autoimmune processes, glucocorticoids are prescribed. We are talking about prednisolone and its analogues. Antihistamine drugs are introduced into the treatment complex. To reduce the manifestation of inflammation in the thyroid gland, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Symptomatic treatment is carried out aimed at relieving the symptoms that arise.
Diet plays an important role in therapy. It coincides with nutrition for hypothyroidism in general and includes foods rich in vitamins and minerals. In this case, the patient should not eat fried, over-salted, smoked foods, as well as strong tea and coffee.
Traditional remedies
Indeed, there are quite a lot of folk remedies for such conditions, but it is necessary to clearly understand that they are never able to reduce the number of antibodies. You shouldn't even count on it. The remedies of traditional healers can only alleviate the condition, reducing the manifestation of certain symptoms. They, of course, can serve as a good addition to the main treatment, but in no case replace it.
Traditional medicine will be effective only in combination with treatment prescribed by an endocrinologist.
The growth of goiter causes the occurrence of pain in the area of the projection of the thyroid gland. A compress of dry wormwood will help relieve pain:
- Melt 200 g of pork lard.
- pour wormwood on it
- which also needs to be taken 200 g.
A warm compress is used on the neck area. It is done at night for two weeks.
The patient can be helped by infusion of seaweed . Kelp is mixed with plantain, honey, pine buds and lemon. The composition must be kept in a water bath for 30 minutes. A tablespoon of infusion is taken before meals. And this is done several times a day. The effect does not occur immediately, but after a certain time. The product helps eliminate pain.
Regardless of the prescribed therapy, if an increase in TPO AT is detected once, the level of blood immunoglobulins will have to be regularly monitored.
If a problem arises with the AT TPO hormone, you cannot do without medical help. There is no need to self-medicate and use only folk remedies. The sooner appropriate treatment is prescribed, the greater the chances of a successful outcome.
When is it necessary to get tested: indications
In what cases is a test to determine the level of antibodies to TPO prescribed? Firstly, if you have the symptoms listed above, especially several at once. Secondly, diagnosis is prescribed for diseases and abnormalities already existing in the anamnesis: hyper- or hypothyroidism, Hashimoto’s disease, toxic diffuse goiter, enlarged thyroid gland. The study may also be recommended during pregnancy.
In the video, a famous doctor talks about a thyroid blood test (transcript).