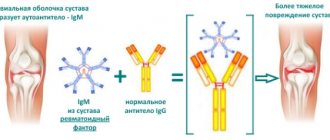
What does ACCP mean? This is a test that detects antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCCP). Laboratory assistants at the Yusupov Hospital determine anti-ccp for rheumatoid arthritis. For testing, the method of scattering a laser beam in a liquid medium is used.
For the treatment of patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, the therapy clinic has created all the necessary conditions:
- Cozy rooms with a European level of comfort;
- Modern diagnostic equipment from the world's leading manufacturers;
- The use of modern medications that are highly effective and have a minimal range of side effects;
- Individual approach to choosing treatment tactics for each patient.
Citrullinated peptide is a protein found in the human body. When the immune system is disrupted, it begins to be “attacked” by antibodies produced by the immune system. Their detection indicates the presence of autoimmune diseases in the patient - rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus.
A blood test for ACCP has the following advantages compared to rheumatoid factor, which is also used to diagnose these diseases:
- It has high specificity (there are no other factors that can lead to the appearance of ACCP in the blood);
- Appears before clinical manifestations of the disease;
- Gives a positive result even in seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (in such patients, the test result for rheumatoid factor is negative);
- The concentration of ACCP allows us to assess the severity of the disease and prognosis.
The presence of antibodies to citrullinated peptide is one of the factors in the progression of the disease. The concentration of antibodies to citrullinated peptide 17 U/ml and higher is regarded as a positive test.
The essence of the method and the role of CCP in the body
Diagnostics is based on a method of biochemical examination of a blood sample. The essence of the technique can be described as follows.
Transformations constantly occur in the body, mainly at the molecular level. These complex processes ensure normal functioning. ACCP (anti-CCP, A-CCP) stands for antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide.
Behind the complex name lies a vital substance. We are talking about an essential amino acid that ensures protein synthesis, albeit indirectly.
That is, without cyclic citrullinated peptide it is impossible to create “building material” for the body. This is a kind of fundamental structure.
The body strictly monitors that the concentration of cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) does not rise above a certain norm. Because it is dangerous for the liver, kidneys and the entire body as a whole.
The fact is that the synovial bursa, that is, the structure that covers the cartilage, is itself capable of producing this substance.
The body perceives an excess of the compound as something foreign. The immune system synthesizes antibodies that destroy the substance. Thus, the concentration of cyclic citrullinated peptide decreases, but the number of compounds (antibodies) synthesized by the body’s defense system increases significantly.
Interestingly, ACCP indirectly confirms other disorders. But not with 100% accuracy. Therefore, the technique is considered narrowly targeted and useful only in the context of rheumatoid arthritis.
The intensity of the increase in the indicator depends on the strength of the immune response and the development of the underlying disorder.
The essence of the ACDC test
An ACCP test can detect arthritis before symptoms appear.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints. The pathology progresses rapidly, can cause complications in internal organs and leads to disability due to impaired motor function of the joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis has no cure. Therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms and reducing the rate of disease progression, so timely diagnosis plays a fundamental role in the further course of the disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by two specific autoantibodies: rheumatoid factor and ACCP. These substances are found in the blood only in rheumatoid arthritis, and in no other diseases, which allows an accurate diagnosis.
Rheumatoid arthritis comes in two types: seropositive and seronegative. The seropositive form is diagnosed based on rheumatoid factor.
This analysis is included in the list of mandatory studies if arthritis of any nature is suspected.
The presence of rheumatoid factor allows an accurate diagnosis; therefore, in the case of a seropositive form, tests for ACCP in rheumatoid arthritis may not be performed.
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is a dangerous form of the disease, characterized by rapid progression and the absence of rheumatoid factor in the blood. In this case, only the rheumatoid arthritis marker ACCP can accurately establish the diagnosis.
The abbreviation ACCP stands for antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide, which is released into the blood only in rheumatoid arthritis. Moreover, these antibodies begin to be produced even before the clinical manifestations of the disease. ACCP analysis for rheumatoid arthritis makes it possible to make a prognosis approximately 1-1.5 years before the onset of the pathological process in the body.
Suspicion of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis - indication for an ACCP test
Analysis is prescribed in the following cases:
- suspicion of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis;
- family history of rheumatoid arthritis;
- risk of arthritis complications;
- progression of the disease.
If seronegative arthritis is suspected, when specific symptoms of the disease are present, but rheumatoid factor is not detected in the blood, an ACCP test is mandatory. Alarming symptoms that may lead to referral for this test:
- joint swelling;
- pain syndrome;
- stiffness of movements;
- increased discomfort in the morning.
These symptoms are characteristic of arthritis of any nature and require a detailed examination of the patient.
The ACCP analysis allows you to assess the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. An annual examination is recommended for people whose close relatives have had autoimmune joint disease.
Despite the fact that the genetic theory of the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis has not been confirmed, there is a considerable risk of developing the disease if there is a tendency to joint pathologies.
If a person has already been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, doctors recommend regular ACPP testing, even with constant drug therapy. The fact is that this test allows you to predict the further development of the disease and assess the risks of complications of arthritis.
It is also recommended to do the test if, with the help of drug therapy, it was possible to achieve stable remission and stop the progression of the disease. In this case, ACPP analysis is a marker of an incipient exacerbation, allowing timely therapeutic measures to be taken.
Preparation for analysis is quite simple. Blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach; breakfast should be abandoned. The last meal should be no later than 8-9 hours before the test.
You should not take any liquid for 24 hours before the test. The restriction applies to water, tea, coffee, broth and any other liquids. A few days before the test, you should completely avoid drinking alcohol.
You should not smoke immediately before the test. Experienced smokers who find it difficult to abstain from smoking for a long time should limit themselves to cigarettes at least 2 hours before donating blood.
Venous blood is taken for analysis
- Blood for ACCP is taken from a vein in the morning, always on an empty stomach. If the patient feels unwell, the doctor should be notified.
- The examination requires blood serum, which is obtained from the obtained sample by passing it through a centrifuge.
- The blood serum in a test tube is placed in a dark place for 7 days at an air temperature no higher than 20C.
- A week later, the blood is examined; it can first be frozen at a temperature of -2000 C. If the blood has been frozen, it is examined immediately; it cannot be thawed, frozen or stored again.
- The serum is examined using a laser, which can detect antibodies produced only by rheumatoid arthritis. The rheumatic test itself is carried out in a matter of minutes; blood preparation takes a long time.
The ACCP norm for adults and children is different
ACCP for rheumatoid arthritis, the norms of which do not depend on age, is estimated in units per milliliter of blood.
The normal level of cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies for women (ACCP) is no more than three units; higher values indicate rheumatoid arthritis. ACCP increases in rheumatoid arthritis; the norm in healthy men can reach 3.1 U/ml, but not more. In children, the normal value is 2.7 U/ml.
Quite often, the analysis results do not indicate exact values, limiting themselves to the word “negative” or “positive”. There is no negative ACCP in rheumatoid arthritis; this formulation indicates the absence of the disease.
A positive result indicates a high likelihood of rheumatoid arthritis, but more research is needed
Decoding ACCP indicators for rheumatoid arthritis allows you to understand what stage the disease is at.
Usually, when taking a rheumatic test, an ACCP-positive result indicates rheumatoid arthritis. More detailed information can be obtained by knowing the exact values of this antigen in the blood.
The interpretation of ACCP for rheumatoid arthritis is given in the table.
| Decoding the analysis results | |
| ACCP value, units/ml | Diagnosis |
| 0-3 | The test is negative, there is no rheumatoid arthritis |
| 4-20 | Initial or pre-symptomatic stage of rheumatoid arthritis |
| 20-39 | Mild arthritis |
| 40-59 | Progressive arthritis |
| Over 60 | Rapidly progressing arthritis with risk of complications |
The reliability of the analysis is 98%. However, to make a diagnosis, additional hardware methods are prescribed - radiography and MRI of the joints.
What diseases will the analysis indicate?
ACCP blood test is a study that allows you to identify five main autoimmune pathological processes:
- Arthritis of rheumatoid origin. Simply put, an autoimmune form of inflammation in the joints. The technique is so sensitive that it can detect abnormalities years before the first symptoms appear.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflammatory process of a generalized nature.
- Crohn's disease. Damage to the digestive tract. Often ACCP in this condition is within the clinical norm. Even when the disorder is aggressive.
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Inflammatory process of the thyroid gland. By itself it is quite rare.
- Sjögren's disease. Autoimmune pathology at the systemic level. Affects connective tissue. Including cartilage. Hence the intensive production of specific substances and rheumatoid factor.
This is the essence of the analysis. It allows you to diagnose autoimmune pathological processes. Fast, safe and high quality.
Decoding of the ADDC analysis
Normal values or intervals will depend on the laboratory, the equipment used and the method of testing the serum.
If an immunofluorescent technique is used, the following values may appear on the results form:
- less than 3 units/ml – “negative” result;
- less than 5 units/ml – “weakly positive” result;
- 5 units/ml or more – further research is needed.
If the assay is performed using chemiluminescence, the cutoff value will be 17 U/ml.
When using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (the “gold standard” for detecting ACCP), you can focus on the following reference indicators:
- up to 30 RU/ml – antibodies are not detected, “negative” result;
- from 30 to 90 RU/ml – the antibody concentration is low, a “weakly positive” result. In this case, it makes sense to repeat the study in a month;
- more than 90 RU/ml – significant results.
The results of the analysis cannot independently serve to make a diagnosis. You can talk about the presence/absence of a disease based on the overall picture, including symptoms, data on heredity and other studies.
General provisions are given in the table:
| Analysis results | Symptoms | Results of other studies (rheumatoid factor, spondylitis marker) | Forecast |
| Negative | Absent | Doesn't play a decisive role | The risk of developing the disease is small, but if the process begins, it will be mild |
| Positive | Present | Rheumatoid factor can be either positive or negative | The development of the disease is likely, or it occurs at an early stage |
| Positive, antibody concentration is high | Present, corresponds to the clinic of rheumatoid arthritis | Rheumatoid factor positive | The process is developing rapidly, severe symptoms may appear |
The table shows only general cases. In real life, symptoms and the presence of genetically determined diseases, including joint diseases (for example, ankylosing spondylitis, which destroys the joints of the sacrum and spine), are objectively assessed.
Indications for use
There are quite a lot of reasons to undergo testing for ACCP:
- The study of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide is indicated for long-term joint pain. Especially if there are suspicions of autoimmune disorders. The question remains with the doctor.
The technique is also used as part of diagnosis verification. That is, when there is every reason to suspect arthritis, but other methods are not enough to identify the disease and confirm guesses.
- Swelling of the joints. Changes in the volume of intercellular fluid at the local level. Develops as a result of the inflammatory process. Accompanied by other symptoms. As a rule, swelling does not appear immediately, but several hours after waking up or in the evening.
Changes are especially noticeable when the joints of the legs are affected. Because the lower limbs experience enormous loads.
- Stiffness in the morning. After the patient wakes up. Patients describe this condition as like a tight sock or a rough glove that prevents them from moving normally.
- Decreased motor activity of one or a number of joints at once. Depending on how widespread the pathological process is. As a rule, it all starts with small cartilages, for example, the fingers. Symptoms then spread to larger joint structures, such as the knees or elbows. Less often shoulders.
- Redness of tissues. Local hyperemia accompanies rheumatoid arthritis, although other options are possible. For example, gout, psoriatic forms, infections, erysipelas and others. The issue is resolved by analyzing ACCP, since it grows only during autoimmune processes.
- Increase in local temperature. Serious. Almost always indicates rheumatoid arthritis.
- Preventative examination. Early screening of the pathological process. There is no inflammation yet, no symptoms either. But, if laboratory analysis reveals changes in the type of growth of ACCP, this is a reason to “sound the alarm.”
There is almost a 100% guarantee that an autoimmune form of joint inflammation occurs. The remaining fractions of a percent are accounted for by other disorders. They are named above.
There are quite a lot of indications. We are mainly talking about symptoms of inflammatory autoimmune processes.
Rheumatoid factor
A blood test for rheumatoid factor is aimed at identifying specific IgM class antibodies to IgG class antibodies.
A laboratory test for rheumatoid factor is a screening test aimed at identifying autoimmune disorders. The main objective of the study for rheumatoid factor is to identify rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's disease and syndrome and a number of other autoimmune diseases.
A rheumatoid factor test may be needed for the following symptoms:
- pain and swelling in the joints;
- limited mobility in joints;
- feeling of dryness in the eyes and mouth;
- skin rashes like hemorrhages;
- weakness, loss of strength.
1 Rheumatoid arthritis
2 Rheumatological examination
3 Rheumatological examination
Norms of rheumatoid factor in the blood
Theoretically, rheumatoid factor should not exist in a healthy body. But still, in the blood of some, even healthy people, this factor is present in a small titer. Depending on the laboratory, the upper limit of normal for rheumatoid factor varies from 10 to 25 international units (IU) per milliliter of blood.
Rheumatoid factor is the same in women and men. In older people, the rheumatoid factor level will be slightly higher.
The normal rheumatoid factor in a child should be 12.5 IU per milliliter.
Rheumatoid factor testing is used to diagnose the following diseases:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic autoimmune diseases;
- Rioglobulinemia.
Other causes of elevated rheumatoid factor
Additional reasons for increased rheumatoid factor may be the following:
- syphilis;
- rubella;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- malaria;
- tuberculosis;
- flu;
- hepatitis;
- leukemia;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- sepsis
If the cause of increased rheumatoid factor is an infectious disease, for example, infectious mononucleosis, then the titer of rheumatoid factor is usually less than with rheumatoid arthritis.
However, rheumatoid factor testing primarily helps to recognize rheumatoid arthritis. However, it should be emphasized that it is impossible to make a diagnosis on its basis alone. Since rheumatoid factor can be elevated in many other pathological conditions of an autoimmune and non-autoimmune nature. In addition, in approximately 30% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a blood test for rheumatoid factor may be negative (seronegative rheumatoid arthritis).
A blood test for rheumatoid factor is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach (8 to 12 hours should pass since the last meal).
Preparation and delivery
To undergo the ACCP study, it is enough to give up some everyday moments in a few days.
- Smoking. One of the most dangerous habits from an analytical point of view. Causes an increased concentration of antibodies to CCP. True, the phenomenon is temporary. Therefore, you should quit smoking two to three days in advance. Otherwise, false results cannot be avoided. This means inappropriate actions on the part of the doctor.
- Drinking alcohol. Alcohol “works” in much the same way. Another condition is possible. Ethanol has the ability to reduce the concentration of a substance - therefore, the result will be false negative. This means rheumatoid arthritis will remain unattended.
Alcoholics are especially at risk in the second stage of addiction and beyond. Avoid alcohol several days before the test. It is desirable that the products of ethanol metabolism have time to leave.
- Physical exercise. Intense mechanical activity creates risks. During training, even if not at full strength, problems develop. A huge amount of cortisol, adrenaline, and catecholamines are released into the blood. They inhibit the functioning of the immune system and do not allow the clinical picture to fully manifest itself. Therefore, they give up physical activity in about 3-4 days.
- Overheating, temperature changes. For example, when visiting a bathhouse, sauna and suddenly going out into cold air. This is harmful because the immune system is again suppressed. Consequently, the concentration of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide may decrease. You should not overheat or overcool for 3 days before the analysis.
- Avoiding certain medications. Only with the permission of doctors. Since unauthorized appointment can bring complications. The results are influenced by drugs such as anti-inflammatory drugs, especially hormonal ones. Also diuretics, immunosuppressants, oral contraceptives.
The question is complex. Before the study, it is worth clarifying the effect of the drugs and informing the doctor about the treatment being carried out. To the one who will decipher the diagnostic results.
- 30-40 minutes before the procedure you need to remain calm. Otherwise, adrenal hormones will distort the results.
The analysis is quite simple:
- The patient arrives at the clinic or laboratory at the appointed time.
- The specialist takes some blood from the vein. Places the sample in a test tube.
- Labels it and sends it to the laboratory.
- Then, after 1-2 days, the patient receives the results in his hands. Or the results are sent to the doctor who is treating the patient.
Everything takes a few minutes. Then it's up to the laboratory. From a technical point of view, the patient will not notice the difference between the analysis for ACCP and simple biochemistry.
Tests for rheumatoid arthritis: list and explanation
To diagnose and differentiate arthritis, the patient needs to undergo two types of tests. Specific ones allow you to accurately determine the presence of inflammation. Nonspecific are additional and support the diagnosis. We can talk about the development of rheumatoid arthritis if there are deviations in the results of ACCP, plasma and synovium.
A person who consults a specialist with suspected RA will need to undergo several types of blood tests. In order for them to be reliable, special preparation is needed.
What does it consist of:
- On the eve of the study, you must give up alcohol and smoking.
- It is also recommended to interrupt the use of NSAIDs, contraceptives, antibiotics and glucocorticoid drugs. If this is not possible, you should notify your doctor about the therapy being carried out.
- 2–2.5 hours before the analysis you need to limit nervous and physical stress. It is better to come to the procedure in advance so that you can sit quietly and catch your breath for 15–20 minutes.
- If on the same day the patient needs to visit a physiotherapy office, x-ray or other diagnostic procedure, this should be done after the tests.
In addition to the listed factors, the reliability of the results can be affected by women’s periods. Therefore, it is advisable to choose the time for the procedure 4–5 days after the end of menstruation.
Tests for rheumatoid arthritis must be taken before 10 am, on an empty stomach. Otherwise, the test blood may clot, making screening impossible.
General blood analysis
It is the main research method for any type of arthritis, including rheumatoid. A general blood test helps to suspect the disease long before the appearance of pronounced symptoms. The patient exhibits a decrease in iron concentration, slight leukocytosis, and an increase in ESR. The dynamics of changes in plasma parameters depends on the strength of inflammation in the joints.
For clarity, here is a breakdown of a normal blood test for rheumatoid arthritis.
| ESR | 3–15 mm/h | {amp}gt;23 mm/h |
| Red blood cell count | 3.5–5.0*1012/l | {amp}lt; 3.5*1012/l |
| White blood cell level | 4.0–10.0*109/l | 15.0–20.0 *109/l |
| Hemoglobin | 120–180 g/l | 2.5 mmol/l |
| Haptoglobin | 0.44–3.05 g/l | {amp}gt; 3.1 g/l |
| Fibrinogen | 3–4 g/l | {amp}gt; 5 g/l |
A biochemical blood test allows you to assess the degree of inflammation in the tissues of the joint. The higher the blood protein level, the more active the arthritis.
Special mention should be made about acute phase C-reactive protein. In a blood test to determine rheumatoid arthritis, the value of the protein is not directly indicated, so its increase can only be detected through an increase in alpha globulin, of which it is part. The CRP marker is good because it allows you to identify the inflammatory process within 5–10 hours after its onset.
In blood tests of a healthy person, the concentration of C-reactive protein is negligible or it is not detected at all. 3–5 mg/l is considered normal. Exacerbation of arthritis can increase this figure to 100 mg/l. With multiple severe joint damage in the relapse stage, the indicator can reach a value of 200 mg/l or higher.
In addition to high sensitivity to inflammatory processes in the body, the marker quickly responds to the use of drugs, so it is often used to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
ACPP are antibodies that attack synovial membrane proteins modified as a result of inflammation. In a rheumatology clinic, A-CCP is considered the most informative test and allows you to detect the disease in advance, for example, in cases of family history. In rheumatoid arthritis, the test for ACCP is positive in 95–98% of cases.
Blood for A-CCP testing is taken from a vein. Diagnosis is carried out both at the beginning of therapy and during the treatment period. Based on the level of antibodies, a specialist can judge the effectiveness of medications and, if necessary, adjust the choice of drugs.
Normally, the data from the analysis of ACCP in rheumatoid arthritis are the same for everyone, regardless of gender and age, and range from 1.0 to 3.0 U/ml. In rare cases, there may be a slight difference in values. For example, in pregnant women, A-CCP can rise to 4.0 U/ml. The rates are also higher for older people. In their case, the norm is 3.0–3.5 U/ml.
The interpretation of ACCP for rheumatoid arthritis is shown in the table.
| 0–19, 0 | negative |
| 20,0–40,0 | onset of the disease |
| 41,0–60,0 | moderate stage |
| Above 60.0 | there is an active process of inflammation |
Some experts are ready to argue with the data presented and recommend completely excluding rheumatoid arthritis only if the ASSP indicators in the tests are zero.
One of the most reliable tests used in the diagnosis of RA is screening for antinuclear antibodies (ANAs). Analysis for rheumatoid arthritis of joints is carried out in 3 ways:
- ELISA - enzyme immunoassay method;
- RNIF - a set of immunological tests;
- Immunoblot is an additional indirect analysis of antinuclear antibodies.
Simultaneously with the identification of antinuclear factors, the amount of antibodies, especially the IgM type, is assessed. The detection of these markers in the blood indicates a high risk of arthritis.
In healthy people, antinuclear antibodies are absent in the analysis or are in minimal concentration. The ANAs norm for the ELISA method is given in the table.
If joint disorders are suspected, a complete examination of the patient is carried out. It is mandatory to check the ACCP indicator for rheumatoid arthritis - whether it is normal or not. This study has important diagnostic value, identifying a specific indicator of RA.
An analysis for antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP, or ACCP) allows you to diagnose the disease as accurately as possible. Thanks to this analysis, it is possible to determine the presence of pathology even at the very beginning of its development, when other methods are still ineffective.
Cyclic citrullinated peptide is involved in the process of maintaining the normal condition of joint tissues. When the immune system is disrupted, this substance is perceived as a pathogenic, pathological element for the body, and specific antibodies are produced against it.
The presence of the disease is determined by their presence. Antibodies can be detected as soon as they begin to be produced, even before the joints are seriously damaged by the destructive effects of rheumatoid arthritis.
Thus, it is possible to determine the presence of the disease already at the latent stage, when clinical symptoms are completely absent.
There are certain indications for the study, which the doctor relies on when prescribing the test. This study is carried out with the following objectives:
- identifying the disease at an early stage, when it develops in less than 6 months;
- detection of the disease at the first stage, which is determined from 6 months after the onset of pathology to a year;
- determination of the seronegative form of the pathology, when rheumatoid factor is not detected in the blood;
- differentiation of the disorder from other forms of arthritis and other joint pathologies;
- Determining the likelihood of developing articular deformities already at the initial stage of the disease is necessary to develop the correct therapeutic tactics.
If a patient has a predisposition to the development of rheumatoid arthritis, then he is recommended to undergo regular testing to timely determine the onset of the disease if pathology occurs. It may never appear during life, but, nevertheless, control is necessary.
Indicator norm
The norm for women and men for the ACCP indicator is the same. It varies solely depending on age.
| 3.8-4 U/ml | From 2 U/ml | 2.7 U/ml |
If the indicator is higher than normal, this indicates a disruption in the functioning of the immune system and the development of a pathological process.
| Up to 5 U/ml | From 5 to 10 U/ml | From 10 to 17 U/ml | From 17 U/ml |
Despite the fact that if the level is up to 5 U/ml, the test result is considered negative, most doctors believe that if the ACCP exceeds the generally accepted level, then the person should be included in the risk group and regularly (once a year) have their blood tested. This, if the disease develops, will allow it to be detected as early as possible.
The analysis is today recognized as the most effective and accurate means of diagnosing RA.
Advantages of the method
Blood serum is used for analysis, in which antibodies and their quantity are determined. Blood for research is taken from the veins. The advantages of this diagnostic method are:
- the ability to accurately determine pathology at the onset of the disease before the first signs of joint destruction appear in 85% of cases;
- accurate detection of the degree and rate of disease progression in 85% of cases;
- reliability of the received data – 98%;
- the ability to determine in which direction the disease will progress and, based on these data, to build treatment tactics to prevent the rapid development of disability in the patient;
- low cost of analysis compared to other diagnostic methods for detecting rheumatoid arthritis.
This study is recommended for patients in all cases where there is a risk of developing autoimmune joint disease.
To obtain reliable results, you must follow the rules of preparation for the procedure. If they are violated, the results will be distorted, and ultimately false data will be obtained about the patient’s condition.
Already 3 days before blood sampling, fatty, smoked and fried foods should be excluded from the menu. Also during this period you should not drink alcohol and sugar.
If there are no medications that are used for vital indications, then it is not advisable to take medications within 5 days before blood sampling.
The rules for preparing for the procedure are as follows:
- refusal to eat 12 hours before blood sampling (even lollipops and chewing gum are prohibited);
- one day before blood sampling, you should not drink coffee, tea, or juices;
- stopping smoking 24 hours before taking the material - as a last resort, you can use a nicotine patch, but this is also undesirable, since the blood picture will change to some extent;
- maximum reduction in physical activity 6 hours before blood donation.
- Rheumatologist of the highest category Oleg Valentinovich
- 39324
- Update date: October 2019
Reasons for the increase
As already mentioned, the concentration of ACCP in the analysis changes as a result of autoimmune processes. The main one is rheumatoid arthritis.
The disease affects young people and patients over 50 years of age. That is, there are two main peaks when the pathological process begins.
Scientists still do not know what causes the disorder to develop. It is assumed that infectious diseases and excessive sensitization of the body are to blame. When the body becomes extremely susceptible to any irritant. The immune system “plays it safe” and attacks healthy cells—this is a random failure.
The disease is accompanied by severe symptoms: pain in the limbs, impaired motor activity, and rising temperature. Both local and general.
Over a long period of time, critical changes begin. Ankyloses. That is, areas of joint fusion. Mobility becomes zero. Terrible deformations put an end to the functions of the limbs. This is why it is so important to start therapy as early as possible.
How to treat rheumatoid arthritis?
- Use hormonal medications. Prednisolone as the gold standard and primary intervention.
- If ineffective, Dexamethasone is prescribed. It is many times more powerful than the previous drug.
- If there is zero effectiveness, the most powerful of the series of glucocorticoids, Betamethasone, is indicated.
Most often, the drug is injected directly into the joint cavity. It is safer and more effective than taking oral tablets.
If a beneficial result does not occur or is weak, immunosuppressants are indicated. Like Methotrexate and similar ones. Only in short courses. so as not to destroy the body's defenses.
Attention:
Rheumatoid arthritis rarely goes away completely. Most often, the disease subsides - remission occurs. Then, under certain conditions, an exacerbation begins - a relapse. It is important to prevent this from happening and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
There are other autoimmune diseases that provoke an increase in the concentration of ACCP.
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Inflammation of the thyroid gland. It is often confused with cancer or nodular goiter. Less commonly, with diffuse changes in a small organ. The disorder is accompanied by all the symptoms of dysfunction.
- There is pain in the neck and a feeling of fullness.
- The patient complains of a lump in the throat.
- During sleep, in advanced cases, shortness of breath develops. Since the enlarged organ puts pressure on the trachea, it blocks the airways.
- The concentration of T3, T4 increases. TSH usually remains normal.
- Blood pressure jumps, heart function is disrupted.
- Body temperature also changes.
Thyroiditis manifests itself as hyperfunction, less often hypofunction of the thyroid gland.
Treatment is standard. A diet low in iodine, drugs from the glucocorticoid group with a gradual increase in dosage until it is effective. Quickly increase the number of farms. funds are not possible. Is it dangerous.
Crohn's disease
Classic pathology of the digestive system. Accompanied by autoimmune inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, starting from the oral cavity and the mucous membrane of the underlying tissues. Those that can be called initial.
The symptoms are severe. As a rule, Crohn's disease is accompanied by abdominal pain and an increase in ACCP in the blood. Intense diarrhea and vomiting are also observed.
Attention:
If the disorder is not treated, there is almost a 100% guarantee that necrosis of individual sections of the digestive tract will begin within a couple of years. That’s why it’s so important not to let the disease progress.
Therapy is carried out with large doses of immunosuppressants. For example, Methotrexate. Patients systematically receive glucocorticoids: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone. In courses, not all the time. At least in fairly mild forms of the disorder.
A mandatory measure for correcting the pathological process is a special gentle diet. Recommendations should be obtained from a gastroenterologist.
ACCP does not always increase in Crohn's disease, so other studies are needed. This is the only way to talk about pathology or its absence.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
A complex and extremely dangerous disease. Accompanied by severe damage to the connective tissue of the body.
The symptoms are quite typical:
- A red rash appears. Usually in the face area.
- Ulcerative defects of the oral mucosa also develop, and damage to the external genitalia is possible.
- Normal vision is impaired. The reason for this is a disorder of the integrity of the conjunctiva and lacrimal glands.
- Changes occur in internal organs.
The reasons are still unknown, at least not exactly. There is an assumption that the main culprit can be considered to be previous viral diseases.
The trigger (trigger mechanism) is stress.
Against the background of systemic lupus erythematosus, ACCP indicators increase significantly, but there are no changes in the joints. At an early stage - for sure. Later there may be confusion. Especially if lupus is in a relatively mild form.
Treatment is carried out using loading doses of immunosuppressants and glucocorticoids.
Sjögren's disease
It can be an independent disease, but more often it is part of the structure of other disorders - for example, systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this case, it is considered an exacerbation. Parallel treatment of Sjogren's disease and the main diagnosis is necessary.
Symptoms concern damage to organs and glands. The disruption occurs with changes in all systems.
This is a potentially fatal condition. The treatment is identical to the previous one described.
Rheumatoid arthritis: what the patient needs to know
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disease of the joints and connective tissues. The disease progresses quite quickly - from the onset of inflammation of the synovial membrane to the destruction of cartilage tissue and deformation of the joints. This can lead to immobilization and disability of the patient.
RA most often affects small joints (metatarsophalangeal, elbows, hands, wrists). But with the intensive development of pathology, the knee and hip joints are also affected. The latter is typical for seronegative RA, when rheumatoid factor is absent in rheumatoid tests.
Rheumatoid arthritis, unlike other types, also affects other organs of the patient, which can cause serious complications.
The following changes occur in tissues during RA:
- Destruction of articular fragments;
- Damage to periarticular soft tissues;
- Damage to cartilage joints;
- Loss of muscle tone and functionality;
- Hardening of the joint structure and immobilization.
As with many autoimmune disorders, success in recovery from RA depends on early diagnosis of the problem. Favorable prognoses are typical for the first years of the disease, provided that early RA is correctly diagnosed.
The primary stage is determined at 1.5-12 months from the onset of the disease. If a test for ACCP was carried out during this period, the patient will receive the maximum effect from the treatment and, with a high probability, will recover.
The speed and extent of the process of stopping joint damage and tissue restoration will depend on many factors:
- Degree of damage and duration of RA;
- The presence of other chronic diseases;
- Correctly selected treatment regimen;
- Patient's age, etc.
Additional examinations
Supportive measures are prescribed to make a correct diagnosis. The list is something like this.
- Oral interview and history taking. It is important to identify the patient’s symptoms, health complaints, and his or her condition. Also determine the diagnostic vector.
- Measurement of antibody concentration.
- Ultrasound of joints.
- Ultrasound examination of the digestive tract.
- MRI/CT of cartilage structures.
Basically, this is enough. If necessary, additional procedures are prescribed.
ACCP is a marker of autoimmune processes in the body. It is mainly used to determine rheumatoid arthritis. But not only. We are talking about a subtle, sensitive technique.
Antibodies to CCP
Immunoglobulins produced in response to proteins containing citrulline are mainly class G (IgG). They exhibit a fairly high specificity and are detected in 80–90% of patients who are not yet particularly aware of the development of RA, one might say, long before the onset of the disease , even at the preclinical stage.
As you know, rheumatoid arthritis is a very common systemic pathological process of an autoimmune nature, affecting up to 2% of the world's inhabitants. However, symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis may be evidence of other rheumatic diseases, making differential diagnosis difficult.
A-CCP is detected much more often and earlier than the common marker, which is called rheumatoid factor (RF). Its study is primarily used when RA is suspected, but it signals pathological changes only after some time (≈ 45 days) from the onset of their development. The study of ACCP shows not only the height of the disease, a blood test that reveals ACCP (titer is increased) can signal an approaching danger a year or two in advance, which is very significant in terms of identifying the disease at the initial stage and its early treatment, before irreversible damage occurs in the joints degenerative and destructive changes.