A modern x-ray method with a high degree of information content - computed tomography - has taken a leading position in the diagnosis of most diseases. Contrast enhances the capabilities of CT and, if necessary, allows you to study the area under study in more detail. Using this procedure, not only the pathological focus in the body is revealed, but also its location, outline, structure, structure of blood and lymphatic vessels. The result of CT with contrast is high-quality and informative images.
CT is based on the effect of X-rays on organs and tissues. As a result, after multi-layer scanning, a special computer converts the received data into high-quality images. Contrast agents enhance the image of the area under study.
CT scan with and without contrast, differences
Conventional CT scans provide natural X-ray transmission images of various organs and tissues. Contrasting in some cases is necessary for a more detailed study of a certain area. The contrast agent enhances the image of the necessary structures due to its properties to absorb X-rays. This increases the information content of the image, and hence the accuracy of the diagnosis. This effect is especially important for studying blood vessels and identifying cancer formations.
Where to do in Moscow
The Yusupov Hospital provides its clients with the opportunity to perform the highest quality research using innovative equipment.
Multislice computed tomography allows you to safely scan any part of the patient’s body. Such a device minimizes X-ray radiation for humans.
The Yusupov Hospital employs true professionals in their field who collaborate with the best European colleagues.
The hospital has polite medical staff who will be happy to answer your questions and also provide a comfortable atmosphere in the institution.
Author
Dmitry Yuryevich Frantsev
Doctor for X-ray endovascular diagnostics and treatment, Ph.D.
CT in oncology
Contrast-enhanced CT is widely used in oncology to identify malignant and benign neoplasms and differentiate them from each other. Computed tomography reveals:
- Abdominal cavity formations (intestines, liver, gallbladder)
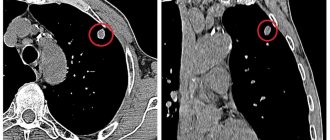
- Tumors of the chest cavity (heart, mediastinum, lungs)
- Neoplasms of the retroperitoneal space (adrenal glands, kidneys, ureters)
- Formations of the osteoarticular system (bones, ligaments, spine, joints)
CT with contrast allows you to determine the degree of malignancy, i.e. spread of the tumor process. It is also prescribed for suspected malignancy of a benign formation. It is also effective for detecting cancer metastases.
Application
How long does an MRI take?
Multislice computed tomography is most often used when an oncological process is suspected, to separate benign from malignant formations. MRI, CT scan with dye guidance recommend:
- with tumor processes of the abdominal cavity. This method is prescribed for oncology of the liver, spleen, pancreas;
- oncology of the intestine, gall bladder;
- malignant formation of the lungs, heart;
- brain cancer;
- articular, ligamentous, bone oncologies.
Contrast enhancement makes it possible to distinguish lymphadenitis from cancer and establishes the degree of oncology. In addition, it allows you to determine the extent of the process, the presence of lesions of the lymph nodes, and metastases. This procedure shows the informative value of studying an intraluminal thrombus, aneurysm, or area of narrowing of the aorta by blood clots.
Contrast agent allows for clearer images
The contrast component studies vascular changes in detail. Often used before surgery. This study provides complete information about the presence of thinning of the venous walls, varicose veins, atherosclerosis of the arteries, and thrombophlebitis.
Contrast scanning also shows the condition:
- bronchi;
- stomach;
- larynx;
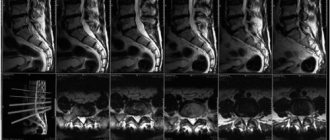
- spinal cord;
- cranium;
- jaws;
- sinuses.
Preparing for a CT scan with contrast agent
- Limit food intake 4-8 hours before the test.
- Clothing should be comfortable and not restrict movement.
- When examining the digestive tract, avoid taking gas-forming products the day before the procedure. The day before, take a drug that reduces gas formation.
- Immediately before the examination, remove all jewelry and any devices on the body.
The procedure lasts about 45 minutes. During this procedure, the patient must lie still. If necessary, at the doctor's command, you need to hold your breath.
The subject lies down on the table. If required, he is given a contrast agent intravenously. After a certain time, the procedure begins - the patient is placed in a tomograph and the necessary areas are scanned.
Results in electronic and printed form are prepared within an hour after the study.
Preparation
If a patient is indicated for a study with the introduction of a contrast component, then he needs to undergo some preparatory measures. First of all, 2-3 days before the proposed examination, you should come for a consultation with the doctor who will conduct the diagnosis. He will collect a detailed medical history of the patient.
Important! If diagnostics with contrast were performed within 24 hours, then enhanced tomography is prohibited.
If no contraindications are identified, then on the day of the procedure you must arrive 30 minutes earlier than the appointed time for the hypersensitivity test. You are prohibited from eating 5 hours before the examination. These measures will help avoid the risk of nausea and vomiting. If tomography of the pelvic tissue is performed, then to obtain a more accurate result, you need to drink 1 liter of water an hour before the procedure. Tomography with a contrast agent allows you to most accurately determine the presence of a pathological focus at the very beginning of its development.
Contrast agents
There are different classifications of contrast media. In each specific case, it is selected by the doctor individually, depending on the method of administration and the area being examined. The most commonly used contrast agents are iodine-containing contrast agents, which enhance the image as clearly as possible. However, this remedy is contraindicated for people who are allergic to iodine and seafood.
Its disadvantage is quite common side effects, such as a feeling of warmth in the body, discomfort in the projection of the injection. Such effects do not require treatment and go away on their own within a few minutes. In some cases, swelling of the larynx and difficulty breathing, urticaria, occurs. Then drug therapy is necessary to avoid the development of anaphylactic shock.
Modern nonionic contrast agents also contain iodine, but of a special structure, which reduces the risk of allergic reactions.
Contrasts are distinguished by solubility in certain media: fat-, water-, alcohol-soluble and insoluble.
For example, barium sulfate is insoluble and is used to study the gastrointestinal tract.
Urografin, Omnipaque are water-soluble drugs used to study the urinary system, blood and lymphatic vessels.
To study the structure of the spine, spinal cord, bronchi, as well as to contrast pathological structures (fistulas, diverticula), fat-soluble agents, such as iodolipol, are used.
Alcohol-soluble substances are used to examine the gallbladder and bile ducts. It is worth noting that CT scans also use gases as contrast that do not transmit X-rays well. Their properties are used to create a transparent background when examining tumor-like formations.
Methods of administering contrast agent:
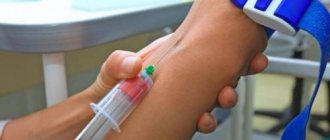
- Intravenous - the required amount of contrast is injected into a vein using a syringe.
- Bolus - a pre-installed intravenous syringe injector injects contrast as a bolus, i.e. at a given speed and dose, to maintain a constant concentration of contrast in the blood during the study.
- Oral - through the mouth. The method is effective for a detailed study of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Rectal - administration of contrast through the rectum. Used to scan the pelvic organs (uterus, bladder), colon.
- Also, the drug can be injected into the cavity of any organ or pathological formation to obtain accurate data about their structure and the presence of additional formations.
- Sometimes combined methods of drug administration are used, for example, oral and intravenous.
In any case, before performing a CT scan with contrast, the specialist always clarifies any possible allergic reactions to drugs and food. The dose of the administered medication is selected based on body weight. Concomitant pathologies of the subject and the degree of influence of contrast and radiation dose on them are also taken into account. If the risk is high, if possible, computed tomography is performed using a non-contrast method.
Indications and contraindications
The abdominal cavity examination method is recommended in the following cases:
- there is a suspicion that jaundice is developing, occurring without visible symptoms;
- dramatic weight loss without changing your usual diet;
- chronic digestive problems;
- penetrating wounds of the peritoneum;
- acute abdominal injuries;
- dysfunction of the stomach, intestines and other organs responsible for digestion.
In addition, this procedure is recommended for people preparing for surgery. If a person is undergoing treatment and it is necessary to constantly monitor changes in his well-being, multislice tomography is also prescribed.
The list of contraindications for MSCT is as follows:
- pregnancy, breastfeeding – the radiation dose, although small, can harm the fetus or a fragile body;
- intolerance to barium, Trazograph (a drug administered as a contrast), as well as its analogues;
- up to 14 years of age, research is carried out only when strictly necessary;
- renal failure - examination with contrast is risky due to the fact that the substance is primarily excreted by the kidneys, and this can aggravate the condition;
- Contrast is also not used if the patient has severe diabetes;
- the presence of metal elements (for example, implants) in the body;
- weight more than 130 kg - tomographs will not support an overweight patient, in which case referral to specialized institutions is necessary.
If the liver or gall bladder, and other organs of the peritoneal cavity cannot be examined using this technique, then the patient is prescribed an MRI or ultrasound.
CT with contrast indications
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography has found wide application for identifying heart pathologies, vascular diseases and neoplasms.
It also effectively diagnoses:
- Diseases of hollow organs (stomach, intestines, esophagus). Contrasting allows you to obtain a clearer structure of the walls of hollow organs, provides a detailed structure of the mucous membrane and reveals additional formations (polyps, diverticula, tumors).
- Vascular pathology (aorta, large arteries and veins, neck vessels). The injected contrast shows a complete vascular picture of the examined area. The condition of the vascular wall itself and the intraluminal space is determined, blood flow parameters are assessed, blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques, and aneurysms are identified.
- Examination of the liver to identify vascular pathology, inflammatory diseases, space-occupying formations, cysts, abscesses, and anomalies of organ development.
- Pathology of the mediastinal organs. Computed tomography with contrast visualizes the structure and location of the bronchi, lungs, and blood vessels, and identifies neoplasms, inflammation, abscesses, and cysts.
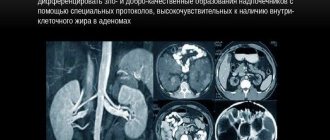
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands. Using contrast-enhanced CT, an accurate diagnosis is established and tumor-like formations are identified.
What substances are used in contrast?
As a rule, various iodine-containing preparations are used for contrast CT to increase the contrast of the resulting images. Such substances are divided into two groups:
- Fat soluble;
- Water soluble.
Drugs of the first group are quite viscous, so their use is limited. Such substances are administered only locally, for example, into the abdominal cavity to identify fistulas, etc. If the patient needs a computed tomography scan with bolus contrast (intravenous administration of a substance using a special injector) or oral administration of a contrast agent, a water-soluble drug is used. The toxicity of such substances is very low, and these drugs penetrate the blood vessels very quickly.
Is CT harmful?
During the procedure itself, the subject receives a certain dose of radiation. For a one-time study, it is quite acceptable and does not harm the body. However, you cannot get too carried away with this procedure unless absolutely necessary. Without indications, you should not perform it more than once a year. But if the potential risks of the disease exceed the unsafety of radiation exposure, then the study is performed more often. It is important to know that X-rays have a more negative effect on dividing cells. Therefore, for a child’s growing body, computed tomography is used only in complex diagnostic cases.
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI
- CT lungs
- Abdominal MRI
- CT and MRI - what's the difference?
- MRI with contrast. When there is a need for…
How often are MSCT and CT scans prescribed?
Multislice tomographs perform layer-by-layer diagnostics of the area under study, followed by reconstruction of the image into a 3D model.
The use of highly sensitive receivers and the latest developments in technology for modulating ionizing radiation on an X-ray tube makes it possible to reduce the level of patient exposure to 4-8 millisieverts.
This is advisable in the following cases:
- with low information content, doubtfulness of the main research methods, the information obtained from which does not allow making a reliable diagnosis: radiography, ultrasound;
- in emergency situations when it is necessary to obtain diagnostic information about the patient’s condition in a short time;
- if there are contraindications to MRI: the presence in the patient’s body of metal-containing foreign bodies, electronic devices that monitor vital functions;
- when the pathological process is localized in bone tissue, vascular structures of the brain.
To further reduce the radiation dose, the scanning duration, tomography phases, current strength in the tube are reduced, and the rotation of the emitter is accelerated. Bismuth screens are used to protect vulnerable organs.
The recommended frequency of MSCT for diagnosing diseases in compliance with safety measures is 1-2 times every 12 months.
If life-threatening conditions occur earlier after the study, a repeat procedure is performed at the discretion of the doctor.
A low-dose alternative and promising replacement for CT and MSCT, which has not yet received widespread use, is tomosynthesis.
What is intravenous bolus contrast?
MRI diagnostician
Prokhorov Alexander Andreevich
Head of the department, Doctor of Medical Sciences.
The method of bolus administration of intravenous contrast agent is now completely automated and is performed directly during the process of spiral computed tomography. An introducer (i.e., an intravenous catheter equipped with a valve) is first installed in the patient's cubital vein. During this type of CT, a sterile solution of a contrast agent is fed into a vein using a special injector-dispenser.
The period of time for recording X-ray radiation depends on the distance of the organ/vessel being examined from the heart. The doctor who conducts computer diagnostics must focus on the timing of the spread of contrast through a particular vessel and carry out such a study strictly on time.
For example, a contrast agent from the ulnar vein enters the ascending aorta and the vessels of the heart in approximately 15-18 seconds, into the abdominal region of the aorta - after 25 seconds, into the thoracic aorta - after 20 seconds. Taking this into account, the examination time should correspond to the spread of contrast into the examined organ or part of it.