Every minute, many metabolic processes occur in the human body, as a result of which various enzymes appear. Some of them are useful, some are not at all, and some must be processed and removed, otherwise they can harm a person. The latter includes bilirubin.
Any deviation in the level of this substance from the average statistical indicators (both “plus” and “minus”) indicates that something is going wrong in the body.
What is the norm for bilirubin, and what is the reason for the increase in the concentration of this substance in the human body?
Bilirubin, what is it?
Bilirubin - what is it?
As noted above, various processes continuously occur in the human body. One of these processes is the regular death of old, expired red blood cells. As experts say, about one percent of red blood cells die every day in the human body. When a portion of blood cells that have completed their life cycle disintegrates, hemoglobin is released. After several more stages, so-called indirect bilirubin is produced.
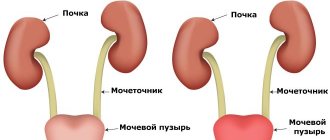
After this, the pigment is excreted into the liver. As a result of a series of reactions, direct bilirubin appears in the largest gland . From there it is excreted into the intestines. Here, too, metabolic processes occur, and the substance breaks down into its components. Some of them leave the body in feces. Part of it enters the blood again, then into the kidneys, after which it is excreted in the urine.
What is the role of the liver in pigment metabolism?
The gland, processing indirect bilirubin (it is this form of bilirubin that is extremely toxic and harmful to humans), neutralizes it.
What does a change in the level of bile pigment in the patient’s blood indicate?
The fact that some kind of malfunction has occurred in the body, and it is urgent to find out the reason for the increase in pigment concentration.
What are the reasons for strong changes in the norm?
The indicators are directly related to the high degree of bilirubin formation in the newborn’s body due to the destruction of fetal red blood cells.
In the first week, its value changes repeatedly due to the construction of new red blood cells and the destruction of those reserves that ensured the transport of oxygen during the baby’s intrauterine development. During pregnancy, the child's hemoglobin has a different structure than the iron-containing protein in a newborn child and in adults. Since fetal reserves of red blood cells after childbirth cannot cope with their immediate task, they disintegrate, which explains the jumps in bilirubin levels in the first days of a baby’s life.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-XWIaMSSbIE
The level of pigment in the blood of babies born on time and premature babies varies, and reaches its maximum on the fifth or sixth day after birth.
Kinds
What are the types of bilirubin? There are three types of substance: general, direct and indirect (free). When the pigment level increases for some reason and remains at a high level for a long time, there is a risk of a special type of stones. They are called bilirubin gallstones.
General
General - an indicator of pigment, consisting of two components, direct and indirect. These two enzymes differ from each other in the amount of the total indicator - the share of indirect pigment is about three quarters, the share of direct pigment is one quarter.
Straight
Direct (or bound) bilirubin is a non-hazardous substance for the human body, due to the fact that it has already passed through the purification of the body’s natural filter (liver).
When a hemolytic (indirect, formed almost immediately after the destruction of red blood cells) pigment, in contrast to a conjugated one, is very, very toxic before it reaches the liver.
If everything is in order in the body, then the conjugated substance is almost absent in the human blood. And then they say that the test for direct bilirubin is negative.
What does it mean to increase the concentration of this enzyme in the patient’s body (directly increased)? Deviation of indicators from the average statistical norm indicates that a metabolic pathology has occurred as a result of liver dysfunction. As a rule, this happens during the development of hepatitis, cirrhosis and other gland pathologies.
Indirect
Indirect (or unconjugated) bilirubin is, so to speak, a primary pigment. It appears in the blood after several processes that complete the decomposition of red blood cells.
Knowing the level of total and indirect substances in the body, it is possible to calculate at what level direct bilirubin is located (for this there is a special formula that doctors work with).
Pathologies that cause increased levels of amylase and lipase
Amylase is an enzyme produced by the pancreas and affects the breakdown of carbohydrates into glucose. Amylase is actively involved in the digestive process, so it is found in large quantities in the gland itself.
There are 3 types of enzyme - alpha, beta and gamma amylase. More often, the activity of alpha-amylase, which is divided into S and P types, is studied in the laboratory. About 55% of S-type amylase is found in the bloodstream. If its amount increases, then this process is called hyperamylasemia.
Diseases in which blood amylase increases:
- Mumps caused by a viral infection;
- Pancreatitis in the acute stage (the maximum level increases 4 hours after the first attack, and decreases to normal levels 4-5 days after the onset of the disease);
- Acute and chronic pancreatitis (usually enzyme activity increases many times);
- Alcohol abuse;
- Malignant or benign neoplasm in the pancreas;
- Ectopic pregnancy.
Lipase is a digestive enzyme whose main function is considered to be the process of breaking down fats. Lipase works through the action of bile acids and colipase (a coenzyme). Lipase, which is formed in the pancreas, is important for diagnosis; therefore, the activity of the enzyme is determined to identify disturbances in the functioning of this organ.
An increase in lipase activity in the bloodstream occurs when:
- Cholestasis;
- Acute pancreatitis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Pancreatic tumors;
- Ulcers;
- Gout or excessive weight gain;
- Drug abuse, especially painkillers and narcotic drugs;
- Bruises, fractures and other injuries;
- Kidney failure.
When diagnosing pancreatic diseases, lipase is considered a more different test than amylase activity. Increased lipase levels remain normal in mumps, tubal pregnancy, acute appendicitis, and liver disease.
If there is a suspicion of pancreatitis, doctors advise determining the activity of amylase and lipase at the same time. The increase in blood lipase activity in acute pancreatitis can be from 3 to 40 times higher relative to the physiological state.
To determine the acute form of alcoholic pancreatitis, the ratio of the amount of amylase and lipase is used. When this proportion is greater than 3, the cause of pancreatitis is alcohol intoxication.
When acute pancreatitis occurs, serum lipase activity increases earlier and more strongly than amylase activity. The increase in amylase levels in the bloodstream begins only 6 hours after the first attack of pancreatitis and reaches its peak after 13-25 hours. Enzyme activity remains elevated for 7-11 days.
Bilirubin test
When they say that it is necessary to take a test for bilirubin, it means that the patient will have to take a regular biochemical blood test. During the study, laboratory technicians look for blood enzymes - common and incoherent bile pigment. And then, if there is a need to know the concentration of a direct substance, it is calculated using a special formula.
Why is such a study carried out?
As a rule, it is prescribed for suspected liver pathologies, diseases of the gallbladder and the pathways through which bile circulates, problems with red blood cells. In addition, the patient is sent for “biochemistry” with an emphasis on bile enzyme during various types of preventive examinations. Indeed, sometimes some severe (and contagious) liver diseases can be detected only with the help of such a study.
How to prepare
How should a patient prepare if he has to undergo a blood test for bilirubin? Preparation for such a study does not differ from the preparation required before taking a biochemical analysis for other indicators.
Blood sampling is done in the morning, always on an empty stomach. The last meal should be 12 hours before the test. Three days before blood sampling, you should not drink alcohol, eat too fatty foods, or a lot of sweet, salty or smoked foods - this can seriously distort the result.
But it is also not recommended to specifically fast for several days, and this factor can also significantly affect the initial blood test data. The day before the test, doctors advise you to abstain from coffee.
Also, in consultation with the doctor, the patient may be advised to temporarily stop taking medications that thin the blood and disperse bile. Of course, this will only be done if the person’s health or life does not depend on these medications.
If the patient is taking any medications, if the woman is expecting a baby, if there are any already diagnosed diseases, especially if they are related to the liver, gallbladder, biliary tract, the attending doctor, who is sending for analysis, and the laboratory assistant must be warned about this. collecting blood.
How to get tested
You can get tested for bilirubin at any clinic or laboratory that collects samples. Such research is carried out both in public and private treatment and preventive institutions. The only caveat: to donate blood in a regular clinic under the compulsory medical insurance policy, you will need a referral from the treating doctor. Such a slider can be taken, say, from a local therapist or from the doctor on duty.
How to get tested?
It has already been noted above: blood sampling takes place in the morning; be sure to come for the test on an empty stomach. For examination, blood is taken from a vein (if we are not talking about a newborn child).
How are newborns donated?
A test for bilirubin in newborns is mandatory. Conclusions about the baby’s health condition largely depend on these indicators. If a blood test for bilirubin in newborns gives a result higher than the average, the baby is prescribed an additional examination. But in newborns, as a rule, increased bilirubin means the manifestation of the so-called jaundice.
How do they test for bile pigment in children who have just been born? The collection is done immediately after birth. If necessary, the analysis is repeated after some time. This is done in order to track data over time.
Where is blood taken from babies?
This question is very often asked by young mothers. Since it is quite difficult to take blood from a vein on the arm of a newborn baby, the collection is carried out from the heel or from a vein on the head.
Rules for preparing for biochemical analysis
To obtain an accurate result, you must follow the algorithm for collecting blood for biochemical testing:
- The collection is carried out on an empty stomach, the last meal no earlier than 12 hours ago. You can drink water, but only still water. The use of chewing gum, sweets and lollipops is excluded.
- 2 days before the test you should not drink alcoholic beverages.
- The day before, exclude fatty, spicy, fried foods from your diet.
- 3 days before the test, avoid excessive physical activity.
- On the day of the study, you should not be exposed to any emotional stress or even minimal physical activity.
- It is customary to take the test in the morning, from 7 to 11 am.
- It is recommended to stop taking any medications 2 days before the test. They may interfere with obtaining correct analysis results.
- You should not smoke 1 hour before the test.
- Before the analysis, it is recommended to rest for 10-15 minutes. Arriving at the laboratory, you need to sit and relax for some time.
This sequence includes:
- Preparing the patient for analysis;
- Blood sampling technique.
Bilirubin in stool
When everything is in order in the human body, bilirubin is not present in the stool, and a positive result is impossible when analyzing this indicator.
If the bile pigment index is positive in the feces of an adult, then something is wrong with the internal systems. As already mentioned in previous blocks, bilirubin is involved in various metabolic processes, the last of which occurs in the intestines. There the enzyme breaks down into its components, and it does not enter the feces in its pure form.
Is the fecal bilirubin result positive?
This indicates pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Crystals of the substance enter the body unprocessed in case of liver dysfunction, in case of acute poisoning. This scenario is also possible with dyspepsia and dysbacteriosis.
If bile pigment is detected in the stool, doctors prescribe further examination and treatment corresponding to the diagnosis, which is carried out until bilirubin in the stool gives a negative reading.
But the content of bilirubin in a baby’s stool is common. This is due to the fact that the baby’s digestive system has not yet fully matured and is not able to cope with the processing of certain substances. Therefore, the reaction to bilirubin in the child’s stool will be positive.
And when the baby grows a little, and his digestive system stabilizes, when analyzing stool, the child will have a negative reaction to the pigment.
Interpretation of analyzes
What pathologies and abnormalities occurring in the patient’s body will the transcript of the examination for bile pigment tell us about?
Usually doctors prescribe not just a test for this substance, but a general blood test for biochemical indications. If it is the bile enzyme that is of interest, attention will be paid to its level first of all.
However, for any deviation of this indicator from the norm, the doctor will look at the full summary of the study, study deviations from the norm in the level of other substances in order to understand what went wrong.
For the first time in a person’s life, blood is taken for biochemistry, in general, and for bilirubin, in particular, while still in the maternity hospital. When, on the very first day after the baby is born, the level of bilirubin exceeds the maximum permissible values (for the first day of life in full-term babies, the norm is up to 34 µmol/l - these units indicate the bile enzyme in tests), doctors talk about the development of pathological jaundice.
If nothing is done about this condition, bilirubin intoxication may develop, and then bilirubin encephalopathy in newborns. And this, in turn, leads to serious and even irreversible damage to the baby’s central nervous system.
What does increased bile pigment mean in a biochemical analysis in an adult?
This substance can increase in the human body for several reasons:
- Rapid decomposition and death of red blood cells - this condition shows in the analysis an increased content of a primary (toxic) substance, which may be associated with blood diseases,
- Poor movement of bile, which occurs as a result of cholelithiasis, when calcium stones are formed, cholecystitis, inflammation in the gallbladder, developing under the influence of infections, and other reasons. The designation of these pathologies in the analysis can be understood by the increased level of direct bile pigment,
- Hepatic metabolism is impaired. This condition is a consequence of serious pathologies of the gland - hepatitis of various etiologies, cancer, cirrhosis of the liver. These diseases will also be indicated by an increased level of non-toxic bilirubin.
As noted above, along with the level of bile pigment, doctors also look at other biochemical indicators. So, usually the blood in the “bundle” is examined for bilirubin and cholesterol. If both indicators deviate “plus” from the average statistical values, this indicates clear dysfunction of the liver, gastrointestinal tract and bile ducts, developing simultaneously.
Also, if an elevated bile enzyme is suspected during a blood examination, emphasis is placed not only on it, but also on the AST and ALT indicators. An increase in ALT AST with increased bilirubin once again confirms the presence of pathologies in the liver. If ALT and AST are elevated, and bilirubin is normal, then it is worth urgently examining the heart; necrosis of the heart muscle or a certain area of it may develop.
After gallbladder removal
Bilirubin after removal of the gallbladder, as a rule, deviates from the normal value to “plus”. Doctors consider this clinical picture to be normal, since after amputation of the gallbladder, the flow of bile in the body is temporarily disrupted.
If the organ is removed efficiently and without disturbances, after a short time the functions of the amputated bladder will be redistributed to the existing internal organs and systems, and the bile enzyme levels will stabilize.
During the patient’s recovery period after organ amputation surgery, doctors will monitor the levels of all components of the biochemical analysis. If bilirubin and other indicators do not return to normal after healing, the doctor will prescribe an additional examination to identify the cause of what is happening.
Indicators for hepatitis
Hepatitis is a disease that is difficult to diagnose in the early stages due to the absence of obvious symptoms. Not only a special test for the presence of pathogens in the body, but also biochemistry will help to establish the disease.
Bilirubin levels will be elevated in hepatitis. The level of bile pigment will show how seriously the liver has been damaged during the development of the pathology. And the type of bilirubin changed to “plus” will give information about what form of hepatitis dominates in the body. Is indirect bilirubin increased in hepatitis? This means that the pathology is most likely caused by excessive medication, serious poisoning (including alcohol) or is bacterial in nature. A deviation from the norm in the “plus” direction of the direct enzyme indicates a viral etiology of the disease.
Decoding the main indicators of the study
Biochemical research includes many indicators.
Often the doctor prescribes only a few indicators for testing that can confirm the expected diagnosis.
A standard study consists of the following points:
- Glucose. The indicator is the main one for identifying the presence of diabetes mellitus (an increase in the parameter indicates this). A decrease in the parameter includes diseases of the liver and endocrine system.
- Total protein. The indicator is prescribed for studies on the presence of infections in the body, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system, oncology (the indicator is reduced). Its increase may indicate injuries, burns, overheating of a person, or rheumatism.
- Total bilirubin. An increase in its level includes the development of cirrhosis, anemia, hepatitis, and cholelithiasis. Total bilirubin consists of direct and indirect. The direct one is associated with the outflow of bile, and the indirect one is associated with liver diseases.
- CRP or C-reactive protein. The main indicator of the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Urea. An increase in urea levels indicates poor kidney function, gastrointestinal diseases, heart failure, and neoplasms.
- Creatinine. An increase in creatinine indicates pathologies of the kidneys or thyroid gland. Often this indicator is prescribed together with a urea test.
- Total cholesterol. An increase in the indicator indicates suspicion of atherosclerosis of the liver or thyroid gland.
- Amylase. The analysis is studied for diseases of the pancreas, gall bladder and kidneys. The rate is usually higher than normal in people with diabetes, pancreatitis or cholecystitis.
- ALT (Alanine aminotransferase). An increase in this indicator may indicate hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer, blood diseases.
- AST (Aspartate aminotransferase). An indicator for checking the condition of the heart, liver, muscle disorders.
- Lipase. An increase in lipase indicates the presence of pancreatic diseases.
Bilirubin norms
The level of bilirubin in a person’s blood changes throughout life. If for a five-day-old baby the total bilirubin norm is less than 205 µmol/l, then for an adult these are catastrophically high values (the norms for all types of bile pigment in adults are in the table, which can be easily found on the Internet). Total bilirubin levels, albeit slightly, change with age in both men and women. Alcohol and fatty foods can greatly affect the increase in levels of the substance in the body.
Norms for children and adolescents
The level of bile pigment in a child's blood changes most rapidly in the first days of life. Total bilirubin in premature babies at birth can increase to 68 µmol/l. And this is the norm. If this indicator is exceeded (in the first day of life), doctors begin to monitor the dynamics of the level of the substance. If it grows, they begin to take measures against the development of pathological jaundice.
On the third day, in babies born prematurely, the amount of enzyme can exceed two hundred units. If the excess is insignificant, then this is the norm for children considered premature. If bilirubin during this period shows units of 270 in infants, then doctors also talk about pathological jaundice, since the child’s body was not yet ready for birth, such children develop only this form of pathology.
For full-term babies, the norm on the first day after birth is less than 34 units; on the second day it can rise to 149 units, and doctors will consider this to be the average statistical value. Further, from the second to the fifth day, as a rule, there is a sharp jump in the amount of the substance in the baby’s body. Therefore, the norm during this period reaches 255 µmol/l. Despite such high average statistical indicators, the level of the substance is also carefully monitored, and if it is exceeded (for example, up to 300 or even 320 units), the necessary measures begin to be taken.
Further, if everything is fine with the baby, the excess bile pigment is independently eliminated from the body, and reaches a value of 23 units. At 2 years of age (and up to the age of ten), the norm for bilirubin is even less - 12-18 µmol/l. When teenagers from 10 to 16 years old donate blood for biochemistry, their level of bile pigment is considered normal at around 11 to 17 units.
Normal for pregnant women
The level of bilirubin in pregnant women is carefully monitored by an obstetrician-gynecologist who monitors the expectant mother. A deviation from the norm of this substance in the blood of pregnant women may indicate the development of a condition that threatens both the woman who is expecting a baby and the unborn child.
During pregnancy, the normal level of total bilirubin does not differ much (only four units) from the usual average indicators of this substance in the body of a woman who is not expecting a baby. And ideally, these numbers should not change during all three trimesters. But the norms of direct and indirect bilirubin in the first, second and third trimester are slightly different from each other.
Norms of direct and indirect bilirubin for a woman expecting a child:
- 1st trimester: direct – up to 8.9 units, indirect – up to 21,
- 2nd trimester: direct – up to 10.1, indirect – up to 22.8,
- 3rd trimester: direct – up to 11.2, indirect – up to 23.9 µmol/l.
Norms for women by age
It is worth noting that the norm of bilirubin in women, if everything is in order with the body, and especially with the liver and gallbladder, does not change very much.
So, what indicator is considered normal for the fair half of humanity, depending on its age category:
- 18 – 19 years old. The lower threshold is about 3.5 units, the upper one is 17 µmol/l,
- At the age of 20 to 29 years, the norms shift slightly to “plus” - 4 – 18,
- At 30–39 years old, the norm for total substance is considered to be from 3.8 to almost 18 units,
- 40 – 49 years old. In this age category, the average indicators of bile pigment have a “range” of 3.9 – 17.6 µmol/l,
- In women after 50 years and up to 59, the norm decreases slightly (3.7 - 17.4 units),
- At the age of 60 to 69 years, among representatives of the weaker half of humanity, bile pigment in the blood can range from 3.4 to 17 with a small µmol/l,
- In elderly patients who have crossed the seventy-year mark, the normal level decreases further and ranges from 3.1 to 16.9 units.
Norms for men by age
The level of bilirubin in the blood of men is not very different from the normal level of this substance in the female body.
What is the normal amount of bile pigment in a man’s body in each age group:
- Senior adolescence (from seventeen to nineteen years) – up to 18 µmol/l,
- Young people from 20 to 29 years old, when donating blood for bile pigment, can see the following results in the analysis report - from 3.8 to 19 units. And this will indicate that there are no abnormalities in their body,
- After 30 and up to 39 years, the lower threshold of the substance level remains the same, but the upper one becomes slightly lower - 18.9,
- The next age group is 40 – 49 years old. During this period, the average statistical indicators range from 3.9 to 18.6 units,
- For men aged 50 to 59 years, the norm of the substance in the body ranges from 3.8 to 18.5 µmol/l,
- After a man retires and until the age of 69, the normal levels for the substance in the blood will be considered to be 3.7 – 18.4,
- After 70, if a man is in relatively good health, a biochemistry test will show the level of bile pigment in the region of 3.5 - 18.2 units.
Any deviation of the level of a substance in the blood from the above figures (and not only “plus”, but also “minus”) indicates the development of some kind of pathology in the body, possibly very serious. Therefore, when the conclusion on a biochemical examination of blood indicates bilirubin 160, you urgently need to undergo further examination to find out the reasons for the increase in the level of the substance.
What kind of examination is necessary, of course, will be decided by the observing doctor. Before this, he will examine the patient and also evaluate the results of other indicators in a biochemical analysis. The content of which substances doctors primarily pay attention to when assessing bilirubin levels was discussed in one of the previous blocks.
Forecasts in the event of an increase in the content of the substance in the body can be very favorable. It all depends on what kind of disease develops in the patient’s body, how long ago it began or was infected with it, and how much damage the disease managed to cause to organs and systems.
In many cases, if the diagnosis is made on time and correct, and adequate therapy is prescribed, it is possible to achieve not only relief, but also a complete cure of the disease. As a result, the level of bile pigment will normalize to normal average values.
The mechanism of increased bilirubin in a newborn
As mentioned above, the main part of the yellow pigment is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin. The latter is presented in the body in three physiological forms - adult, embryonic and fetal, as well as in several pathological ones (mutant species, methemoglobin, etc.). Fetal hemoglobin begins to form from 1 to 7 weeks of fetal development, and then is gradually replaced by the fetal form.
Main characteristics and chemical formula of bilirubin
The latter, or, as it is also called, fruit hemoglobin, is a special type of protein. It is capable of binding oxygen several times better than that contained in the body of an adult, because its purpose is to provide the baby’s body with a small volume of blood.
Moreover, the fetal form is an extremely unstable substance under unfavorable conditions. After all, with a good pregnancy, the fetus develops in warmth, darkness and does not experience any discomfort. But after birth, the baby immediately finds himself in the cold (after 36–37º of the mother’s body, even 28 degrees seems low to him).
What about the birth process itself? This is incredibly stressful for babies! Therefore, by the end of the 3rd trimester and within 1 month of the baby’s life, fetal hemoglobin is replaced by adult hemoglobin. When a large number of red blood cells containing the fetal form are destroyed, hemoglobin is released, and then a yellow pigment.
It is because of this that the level of bilirubin in the blood of an infant is higher than that of an adult, which is considered normal. However, this is not the only reason for the increase in the rate in children of this age - there are at least three more factors. But they are usually caused by pathologies.
Thus, increased bilirubin in the blood of a newborn can be observed in the following cases:
- with excessively intense breakdown of red blood cells;
- dysfunction of the liver parenchyma;
- mechanical blockage of the bile ducts.
Reasons for the increase
Elevated levels of pigment can indicate the development of many different diseases.
First of all, with an increase in the content of the indirect type of substance, doctors will suspect the presence of blood diseases, in particular hemolytic anemia.
This disease usually develops for two reasons - it can be inherited from relatives or acquired during life. In the second case, the diagnosis can be triggered by various exposures, a serious toxic attack on the body, or previous malaria.
An excessive concentration of the enzyme in the body will indicate problems with the liver. Moreover, often an increased level of pigment in the blood can become one of the few (if not the only) signs of a serious disease that is asymptomatic.
Bilirubin will “jump” in case of severe liver damage caused by poisoning (including low-quality alcohol), prolonged consumption of alcohol (especially counterfeit alcohol) and other toxic effects. Also, a similar picture in biochemical analysis is characteristic of the development of cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer.
In addition, a high content of bile pigment indicates that there are problems with bile waste and its circulation. This is caused by inflammation of the bile ducts or their blockage as a result of gallbladder diseases.
The price of biochemical analysis, and where is the best place to do it?
The listed biochemical parameters are determined in any private or public clinical diagnostic laboratory. Most laboratory sites use high-precision methods and equipment. Often, the reference values for each analysis are indicated on the study form in accordance with the age and gender of the patient.
Any laboratory, public or private, has a set of reagents and personal computers. Norms for biochemical parameters can vary greatly. If there is a need to be examined again, the examination should be carried out at the same time of day and in the same laboratory department.
The price of a biochemical analysis depends on what blood parameters need to be determined. The price of one indicator is from 100 to 700 rubles.
source