6447
0
Lymphoma is a malignant tumor of a hematological nature, one of the main symptoms of which is enlarged lymph nodes. In lymphoma, lymphocytes are found in excess quantities in internal organs. Sometimes it even penetrates into the bone marrow.
Lymph nodes are located throughout the body, the disease can be localized in any of them or in several at once. In this regard, and also taking into account the fact that the process can develop in internal organs, visual diagnosis of lymphoma is difficult - even with a thorough examination, there is a risk of simply missing a tumor located in an atypical location. Therefore, the most accurate method for determining the presence of pathology is clinical blood tests for lymphoma.
What is lymphoma
Lymphoma is an oncology that originates from lymphoid tissue, and also occurs due to the degeneration of lymphatic cells (lymphocytes). Symptoms can occur in adults and children regardless of gender or race. As the disease progresses, not only certain lymph nodes are affected, but others as well, and then organ systems and bone marrow become affected.
During illness, lymphocytes divide and accumulate, and this leads to disruption of the functioning of organs and lymph nodes, and lymphoma must be treated as quickly as possible.
Lymph nodes are distributed throughout the body, forming a system; from one affected node, oncology immediately moves on to the next.
Healthy lymph nodes perform the following functions:
- barrier (delay of harmful microorganisms and cleansing of lymph);
- transport (delivery of nutrients, intercellular fluid);
- immune (elimination of viruses and bacteria that have entered the body).
During lymphoma, the system no longer performs its functions fully and spreads cancer.
Types of lymphoma
Lymphomas are distinguished by the structure of the tumor. Determining the type of tumor also depends on the location of the affected node or organ that was affected by the lymphoma. Thus, kidney lymphoma, breast lymphoma and others are distinguished.
Oncology is also distinguished by the degree of aggressiveness:
- Sluggishly aggressive (indolent).
- Aggressive.
- Highly aggressive.
If we classify lymphoma by structure (morphological and immunological), there are 4 types:
- Diffuse lymphoma is a highly aggressive type of lymphoma that most often affects elderly and middle-aged people. The tumor usually occurs in the gastrointestinal tract. There are several options for the development of this type of disease. The first is to increase several nodes at once. Second, the tumor is located outside the lymph node. In the second option, the symptoms will be associated with the organ that was affected.
- Hodgkin's lymphoma is a malignant tumor characterized by the formation of granulomas. Because of this, the second name for this type of oncology is lymphogranulomatosis. The lymphatic tissue contains pathological cells that are the basis of this type of lymphoma. The cells are large, with several nuclei, their presence (they are detected when analyzing the contents of the puncture) indicates the presence of Hodgkin lymphoma. Pathogenic cells develop from B lymphocytes. This type is not so common and is diagnosed in patients 20-35 years old. With this lymphoma, a person may experience enlargement of the inguinal, femoral, intrathoracic, and axillary lymph nodes. The location of Hodgkin lymphoma determines the clinical picture. Enlarged nodes have a compressive effect, which can cause shortness of breath, coughing, swelling, and paralysis. Intense pain occurs. In cases of damage to the liver and gastrointestinal tract, nausea and vomiting and an unpleasant taste in the mouth occur.
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (also known as lymphosarcoma). Occurs predominantly in people over 55 years of age. Such lymphoma can be either aggressive or indolent. Aggressive tumors are characterized by metastases (spreading into other organs). A sluggish disease is difficult to treat, as it can occur unpredictably, with sudden relapses. Tumors can be located in the lymph nodes themselves in the initial stages. Treatment is treatable, but it often leads to remission.
- Burkitt's lymphoma is characterized by a very high degree of malignancy. Spreads through the lymph nodes, penetrates the blood and organs. In the case of this type of tumor, the pathogenic cells also originate from B lymphocytes. However, Burkitt's lymphoma occurs only in the United States, Central Africa and Oceania. African Burkitt's lymphoma (also endemic) is characterized by the presence of the Epstein-Barr virus. Depending on the location of the tumor, the onset of the disease may be sudden or slow. At the very first stages, lymphoma resembles a cold, then fever is added. After this, the weight begins to decrease very sharply, and the lymph nodes enlarge. It is possible that internal bleeding, renal failure, and intestinal obstruction may occur.
With timely treatment, remission can be long-term, but eventually the disease completely disappears. When a malignant tumor grows, all systems are affected, including the brain.
Indications for taking blood tests for lymphoma
As a rule, the patient experiences incomprehensible fatigue, lethargy and fatigue for a long time. Characteristic but nonspecific symptoms are a prolonged and slight increase in temperature or low-grade fever. Most patients often believe that they simply have a prolonged respiratory viral infection and they simply do not receive any treatment, enduring it “on their feet.” The most “advanced” patients, or patients who simply take care of their health more than others, begin to fear whether they have contracted tuberculosis somewhere and the first visit to the doctor often begins to unravel this whole diagnostic tangle, which, in the end, occasionally ends with the discovery lymphomas.
In this case, there is often a group of enlarged lymph nodes, where the growing tumor is concentrated. It can compress adjacent hollow organs, causing certain symptoms. If the bronchopulmonary lymph nodes compress the bronchi, a cough may occur, and if they cause compression of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, hoarseness appears.
Also, enlarged groups of lymph nodes located near the kidneys can disrupt the outflow of urine and lead to pyelonephritis. With compression of the spinal cord structures and damage to the lumbar roots, persistent pain in the lower back and reflex impairment of urination and sensitivity may occur. In some cases, a disturbance in the outflow of blood through large veins occurs with the development of various edema and a characteristic clinical picture.
Thus, the symptoms of damage to lymphoid tissue are extremely diverse and can sometimes lead even an experienced doctor in the wrong direction. In addition, the blood test for lymphoma that we described cannot yet unambiguously answer the question: whether the patient has a tumor or not. Even β - 2 microglobulin only suggests the direction of the diagnostic search. What other diagnostic methods, carried out in combination, will make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment?
Stages and degrees
Stages in oncology (including lymphoma) are the progression of malignant tumors. Each stage has its own characteristic features, such as the degree of organ damage and the nature of distribution. Depending on the stage, treatment is selected.
There are 4 stages of lymphoma development:
- The first stage is the initial stage and involves damage to 1 or several lymph nodes located in one place (axillary lymph nodes). Lymphoma, which has begun its development in an organ (without affecting the lymph node) is also the initial stage. The first stage occurs without metastases and is marked with I.
- The second stage begins after 2 or more lymph nodes located on one side of the diaphragm are affected. The marking of this stage is II.
- The third stage is damage to the lymph nodes on different sides of the diaphragm. Organs and tissues may be involved in the process. The spleen is also affected. Marking – III.
- The final, fourth stage is an almost ubiquitous tumor. Affects several organs or systems, and is located at a great distance from the original location of the tumor.
The last stage is the most dangerous, in which a person has virtually no chance of survival. The development of tumors and lifespan are influenced by the age and immunity of the cancer patient.
Increased protein
An indicator of the presence of lymphoma is an increased amount of a protein called beta-2-microglobulin. These are antibodies of protein origin that are detected in the blood in the presence of a lymphoma-type tumor, regardless of its location. The more such cells, the more advanced the oncological process. A deviation from the norm is a value above 3.5 g/l.
The number of tumor markers increases in proportion to the development of the pathological process. Their decline is observed during chemotherapy or radiation, so a blood test can be used to assess the effectiveness of treatment. With early detection of tumor markers in the blood, the patient’s chances of recovery increase.
Symptoms
Lymphoma (symptoms in adults may differ slightly from those in children) has symptoms similar to most cancers. But it also has some of its own signs that speak specifically about disease of the lymph nodes.
The problem is that at first everything can resemble a completely unrelated illness (cold, flu). Therefore, you should be more attentive to the signals that the affected organism gives.
External signs
The vast majority of patients experience enlarged lymph nodes. This can happen in one specific place (for example, on the neck) or in different places. The inflamed areas are visible to the naked eye; they are also mobile and not attached to the skin.
During growth, enlarged nodes can connect with each other, forming one large tumor. They do not cause pain when pressed.
Temperature increase
All types of lymphoma are accompanied by high fever. At the initial stages it is relatively low, not exceeding 38 degrees. Already in subsequent stages, the temperature increases - this occurs due to damage to other organs and inflammatory processes.
Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by excessive sweating. This symptom manifests itself especially strongly at night. The discharge is odorless and colorless.
Weight loss
Disturbances in metabolic processes and the occurrence of inflammatory processes lead to a sharp loss of weight in the patient. In addition, weight loss is facilitated by lack of appetite, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness (as happens when a person overeats). The human body in its final stages can reach dangerous exhaustion.
Pain
During lymphoma, a person may also experience pain, which depends on where the inflammation is located. Thus, due to compression of blood vessels, blood supply deteriorates and frequent headaches occur. As a result of damage to the chest organs, chest pain occurs. With abdominal lymphoma, corresponding pain sensations appear.
Itching
Hodgkin's lymphoma is also characterized by itching, which can be bothersome either in a specific area or throughout the body. Children especially suffer from this symptom. The unpleasant burning sensation may be mild, but in some cases the patient suffers from severe itching, scratching the irritated areas until it bleeds. Like sweating, itching is more noticeable during the day.
Weakness
Like most diseases, lymphoma is accompanied by weakness throughout the body. Some people do not pay attention to this symptom, but fatigue spreads throughout the body, even regardless of whether a person engages in physical training or not. Drowsiness and loss of interest in everything occurs for no reason.
Lymphoma has some other symptoms that depend on the location of the tumor:
- cough (dry, debilitating, followed by shortness of breath and chest pain);
- swelling of the body (decreased blood circulation in certain areas of the body);
- digestive system disorders (diarrhea or constipation, vomiting, pain, feeling of fullness).
Symptoms of oncology can be difficult for children to bear, so at these moments they need special attention.
General blood test indicators
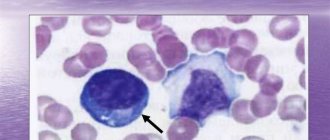
If we were talking about acute forms of lymphoblastic leukemia, then a general blood test would be the main method of diagnosis, along with bone marrow puncture. Instead of mature lymphocytes, it would be dominated by immature and completely identical lymphoblasts, which cannot be distinguished from one another.
But with lymphomas, the entire malignant process is observed in the peripheral organs of the immune system and the red bone marrow does not suffer, but produces normal cells. Therefore, it is impossible to diagnose lymphoma using a general blood test. It is possible to identify only indirect indicators that reflect the hard work of the bone marrow. Also, a blood test for lymphoma also reflects the high consumption of nutrients in the lymph nodes for the construction of tumor tissue. The main indicators that should alert any doctor to lymphoma include the following characteristics:
- The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) increases.
They carry on their membranes various molecules that weigh down their weight, which are produced and released into the general bloodstream by the tumor tissue developing in the periphery;
- with large volumes of tumor tissue, anemia syndrome occurs, with a decrease in hemoglobin levels and a decrease in the color index.
Anemia is a nonspecific laboratory syndrome and first of all the doctor must think about either searching for the oncological nature of this phenomenon, or about chronic and prolonged blood loss;
- Since it is in the peripheral lymphatic tissue that the largest amount of protein is consumed to create the tumor mass, there is not enough of it to create normal leukocytes.
Therefore, at an advanced clinical stage, blood tests for lymphoma suggest leukopenia, which can reach significant numbers. It is the decrease in the level of leukocytes that allows various infectious processes to develop unhindered, primarily this is manifested by poorly healing and often suppurating wounds and abrasions on the skin. This symptom is unfavorable, and often at this stage the primary tumor has already given numerous metastases if it is aggressive, for example, lymphosarcoma.
- The leukoformula, or the percentage of leukocytes of different types, is not an informative indicator.
The culprits of a malignant tumor in the periphery, lymphocytes, may be normal, less than normal, or more than normal. The number of neutrophils may be increased, as well as the number of basophils and eosinophils. This condition will be relative, and manifests itself if the number of lymphocytes is reduced, and this happens most often. But if there are more lymphocytes than needed, then, on the contrary, relative neutropenia and the opposite picture will occur, with a decrease in eosinophils. Therefore, you should not expect important diagnostic expectations from the leukoformula.
Perhaps these changes limit the general blood test for various types of lymphomas. In the case of an advanced process, a decrease in the number of platelets is also possible. Does the blood test norm change during a biochemical study in such patients?
Causes
Any specific reasons causing this disease have not yet been established. However, there are some factors that are present in almost all patients that trigger the appearance of lymphoma.
Reorganization of the body
Children can get lymphoma as a result of the formation and restructuring of the immune system. During these natural processes, a malfunction can occur, which causes cancer. As for adults, it is worth highlighting several factors that become causes of lymphoma.
Age and gender
These include the age and gender of the patient. Depending on the type of lymphoma, people from 25 to 60 years of age can be affected. Men are more likely to get Hodgkin's lymphoma. Most patients have the Epstein-Barr virus, which enters the body through airborne droplets and contact. This virus is also the causative agent of hepatitis, multiple sclerosis and other diseases.
Toxic substances
Constant exposure to toxic substances on the body (for example, work in laboratories, contact with pesticides) is also a factor that provokes oncology. Taking drugs that suppress the immune system can cause lymphoma. Such medications are prescribed to people who have autoimmune diseases (arthritis, lupus).
Diagnostics
Lymphoma, the symptoms of which in adults in the initial stages may not cause suspicion, is diagnosed through tests and hardware diagnostics.
| Palpation of lymph nodes | Occipital nodes, submandibular, axillary, femoral, popliteal and others. | Enlargement of nodes, location, possible pain. |
| General and biochemical blood test | ESR, bilirubin, blood protein, urea, leukocyte form and other indicators. | In general: decreased levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin, decreased lymphocytes, increased eosinophils. With biochemical: increased LDH, phosphatase and creatinine. |
| Ultrasound | Liver, spleen, intestines, spleen. | The degree of tumor growth, changes in organs. |
| CT | Internal organ systems and lymph nodes. | A more detailed study of the nature of the disease and its behavior. |
| X-ray | Anterior and lateral projections. | Widening of the mediastinal shadow. |
For all questions regarding lymphoma, contact an oncologist specializing in this type of oncology. He also performs diagnostics.
How to carry out the procedure
To conduct a general blood test for lymphoma, capillary blood is taken from the patient. Sometimes it is possible to use venous blood. If a biochemical test is prescribed, a sample is taken from a vein.
We recommend reading: Lymphoma - what it is and how long a person will live
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- The place where the collection will be performed is disinfected with alcohol.
- Below the needle, at about a distance of ten centimeters, the doctor applies a tourniquet.
- A disposable sterile needle is inserted into the vein.
- The blood sample is sent to a laboratory for testing.
To recuperate after the procedure, you can take a light snack with you.
When to see a doctor
Of course, if fatigue and some other symptoms occur separately, you should not immediately attribute this to the onset of oncology. It is necessary to undergo tests in order to understand the cause of the malaise.
Before taking the tests, you need to prepare. A day before all procedures, a person eliminates alcohol and tobacco. The stomach should be empty. The time of the last meal is at least 12 hours. It is forbidden to drink tea, juices (natural and purchased), and chew chewing gum. Only drinking water is allowed.
Another important condition is that you should not worry before the procedures. Sometimes it is difficult to prevent absolutely all factors that provoke stress. The most common cause of anxiety is waiting for a bad test result.
If a person is taking any medications, the doctor should be informed.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the next person the patient is referred to is an oncologist. After the examination, therapy, diet and prognosis for recovery are prescribed.
Prevention
Lymphoma, symptoms in adults in which can occur for various reasons, will be avoided if you follow some recommendations and exclude these causes. Prevention will help reduce the risk of damage to the body to zero.
To exclude the possibility of lymphoma, you should:
- less contact with toxic substances;
- do not neglect contraceptives during sexual intercourse with a casual partner;
- undergoes a course of vitamin therapy at least 2 times a year;
- maintain hygiene (do not use other people’s toothbrushes or towels);
- exercise regularly (moderately, at least 10-15 minutes will be enough).
Special attention is paid to hygiene and sexual relations due to the possibility of infection with the Epstein-Barr virus.
Treatment methods
Treatment of any oncology can be long, and, unfortunately, it does not yet provide complete confidence in a person’s recovery. In the final, inoperable stages, doctors give no chance.
However, timely contact with the oncology center significantly increases the likelihood of a full recovery. The state of the immune system and the age of the patient add to confidence in complete recovery from the disease. Prices for services and treatment vary depending on where the person goes.
Full treatment (immunotherapy, chemotherapy, bone marrow transplant, etc.) can cost from $1,000-$4,000 to $70,000. It all depends on the clinic and the quality of its services. Diagnostics may be paid, in which case each analysis is considered separately (for example, laboratory tests from $400).
Medicines
Lymphoma, for which symptoms in adults can be suppressed by medication, is not itself treatable with medication alone. But some biological drugs are still necessarily present. Chemical preparations in such cases are made from the cellular structures of the patient himself.
The action of these drugs is to activate anti-cancer mechanisms and direct them to fight the disease. Antibodies, interacting with pathogenic cells, destroy them.
Sometimes taking these medications is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- pain in the head;
- feverish condition.
These ailments disappear upon completion of treatment. The drugs are administered to the patient intravenously. Other necessary medications include so-called cytostatics. These medications damage tumor tissue and prevent new pathogenic cells from forming.
Lymphoma, having recognized the symptoms, it is important to immediately prescribe treatment.
Cytostatics include:
- doxorubicin;
- cyclophosphamide;
- mercaptopurine;
- prednisolone;
- chlorambucil.
Corticosteroid preparations can be applied in the form of ointments.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is completely useless in the fight against cancer, and in some cases can be dangerous.
However, some people choose to supplement their primary treatment with home remedies.
Thus, one of the most popular remedies for eliminating lymphoma is celandine. Thanks to the vitamins contained in this plant, celandine has immunostimulating properties.
However, it should be remembered that a medicinal plant in cases of oncology may turn out to be a poison, and the natural stimulant of the immune system will negatively affect the tumor. The reproduction and causes of cancer cells have not yet been fully studied, so resorting to traditional medicines is not advisable. The reaction of tumor formations can be completely unpredictable.
You should resort to traditional medicine recipes only after recovery. In such cases, you need to consult a doctor who will tell you what is best to take.
One of these means may be:
- chamomile tea;
- celandine juice and milk;
- kombucha drink;
- decoction of birch buds.
During treatment, it is best to put off all prescriptions for home remedies.
Other methods
Treatment of lymphoma can be complex and combine several methods. The most famous is chemotherapy. This method involves administering drugs that destroy cancer cells. The therapy has strong side effects, because it “kills” not only the malignant tumor, but also the healthy structures of the body.
So, after chemotherapy you may experience:
- hair loss;
- deterioration of the digestive system;
- weakening of the immune system.
The patient is also prescribed a special diet aimed at maintaining protein levels in the body and avoiding weight loss. During treatment, nausea and vomiting are common. Therefore, meals should be fractional; the menu must include porridge and soups. Food temperature is at least 50 degrees.
If vomiting occurs, food consumption stops for a while so that the person does not develop an aversion to food in the future. The diet is prescribed by the doctor, it depends on the course of therapy. The patient needs to get enough calories per day and also maintain a drinking regime.
In the case when only one tumor focus is identified in the patient, surgical intervention is performed. However, this method of treatment is not very popular and is practically not used.
Bone marrow transplantation, on the contrary, is used more often. With this method, the bone marrow begins to produce healthy blood cells. The transplant is usually performed after chemotherapy, since in this case all the malignant cells and some of the patient’s own cells die.
Bone marrow material can be transplanted from:
- identical twin;
- donor;
- the patient himself (the material is taken before chemotherapy and radiation and frozen).
Another treatment method is radiation. The high-energy effect is applied to those areas where pathogenic cells are concentrated, without affecting healthy tissue. Radiation therapy is used in combination with chemical therapy, but in the initial stages it can be used independently. The duration of such treatment is no more than 3 weeks. The procedures are carried out under the supervision of a radiologist.
Other studies
To determine the presence of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a venous blood test for cancer markers.
Being tested using general laboratory diagnostic tests is not enough to make an oncological diagnosis, oncologists say. An additional method is analysis for tumor markers of lymphoma. These are specific substances that malignant cells secrete due to active metabolism. Their detection in the blood of the subject indicates damage to the lymphatic system. This method is also used during treatment to determine tumor reactivity and sensitivity to treatment.
Instrumental techniques include ultrasound and targeted biopsy of the affected lymph nodes. With the help of such a study, cancer cells are identified, their degree of differentiation, spread and tumor growth activity are determined. Using MRI and CT, distant sites of metastasis, physical characteristics of the primary lesion, features of the blood supply to the neoplasm and the involvement of healthy tissue in the pathological process are determined.
Possible complications
Lymphoma (symptoms in adults and children may not be suspicious at first) is a fatal disease. Without timely treatment and ignoring symptoms, it progresses, and eventually death occurs. Also, self-medication with folk remedies can greatly aggravate the picture.
It is possible to cure lymphoma if you start timely treatment and pay attention to the symptoms in both adults and children. However, it all depends on the person's immune system, age and response to treatment.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky