Medical services in the modern world occupy a separate and significant niche. Compared to the 2000s and 1990s, the level of medical care has almost tripled. Many examination methods make it possible to make a reliable and complete diagnosis, determine the degree of damage and the location of the injury.
The newest diagnostic techniques are CT and MR tomography. With their help, you can look inside the body and thoroughly study the existing pathology. Most people turn to these examination methods without a doctor's referral - which is why it is important to know how one procedure differs from another.
What does a CT scan of the cervical spine show?
The following types of disorders can be identified in the images obtained during the examination::
- congenital features of the development of the spine;
- cervical injuries: fractures and displacement of the vertebrae, hematomas;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- tumors;
- osteochondrosis, disc herniation;
- changes in vertebral bodies, their deformations;
- inflammatory processes localized in the vertebrae, spinal cord, soft tissues surrounding the spine;
- changes in the spine, characteristic of a number of diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis;
- consequences of injuries and surgical operations.
CT scan of the cervical spine with contrast
The examination can be performed either with or without the use of a contrast agent. Bone tissue is clearly visible in images without contrast enhancement. But vessels, benign and malignant formations, foci of inflammation can be practically indistinguishable on native images.
The decision about the need to administer a contrast agent is made by the radiology doctor who conducts the examination. The need to administer contrast may arise during an examination in cases where the doctor sees changes in the images, but cannot identify them due to the lack of details important for diagnosis.
Examination of the cervical spine is carried out using an iodine-based contrast agent intended for intravenous administration..
Most often, the drug is administered once before or during the procedure. Bolus (long-term, dosed) administration of contrast is indicated in cases where it is necessary to obtain information about the condition of the vessels of the neck and the characteristics of the blood supply to the tissues.
The following symptoms may occur in response to the administration of a contrast agent::
- sour or metallic taste in the mouth;
- pain at the injection site;
- flushes of heat in the body;
These reactions are not harmful to the patient's health.
Contrast drug intolerance is manifested by the following symptoms::
- swelling of the face, ears;
- difficulty breathing due to swelling of the larynx;
- sore throat;
- nausea and vomiting;
- itchy skin;
- hives
- bronchospasm;
- drop in blood pressure.
The appearance of these symptoms requires special treatment, so you should not wait until the end of the procedure; you must immediately report your discomfort to the medical staff using voice communication.
The risk of developing an allergic reaction is increased in individuals with intolerance to drugs containing iodine, seafood, as well as in patients suffering from bronchial asthma.
What can be revealed on a CT scan of the neck?
CT scan of the soft tissues of the neck shows:
- abnormal development of cervical organs;
- the presence of benign and malignant tumors in the bones and soft tissues of the neck, metastases;
- the presence of atherosclerotic changes in the walls of large cervical vessels, compression of the vascular system by a large neoplasm, aneurysm, etc.;
- whether there are expansions and formations of a diverticulum (protrusion of the walls) in the esophagus;
- the presence of pathological thyroid nodules;
- the presence of destructive (destroyed) foci in the cartilaginous tissue of the throat;
- the presence of stones in the salivary glands;
- whether the neck tissues are damaged due to injury, whether there are foreign bodies;
- is there a cyst in the neck;
- are the lymph nodes enlarged?
- is there inflammation in the cervical tissue (phlegmon, abscess);
- whether the cervical region of the spinal column is changed, whether the vertebrae are deformed.
This method is used to diagnose cysts in the neck area
What exactly will be examined on a CT scan of the neck - hollow organs or bone structure - depends on the goal of the diagnosis. In accordance with the appointment, the diagnostician determines the scope of the upcoming procedure and the need for contrast.
Indications for examination
Computed tomography of the cervical spine is performed in the following cases:
- acute and chronic spinal injuries;
- the presence of chronic neck pain, headaches, dizziness;
- abnormalities of the spine;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- hemorrhage in the spinal cord;
- tuberculous spondylitis (inflammation of the vertebrae);
- tumors of the spine and surrounding soft tissues, metastases of tumors to the spine from other organs;
- malformations (vascular anomalies), circulatory disorders in the spinal cord;
- osteomyelitis;
- preparation for surgery on the spine or spinal cord;
- monitoring the condition of the spine and spinal cord after surgical treatment, chemotherapy or radiation therapy during the period of remission.
Computer scan of the neck organs: indications
X-ray diagnostic methods are performed on the recommendation of a doctor. Compliance with the indications is necessary in order to avoid harm from ionizing radiation. Before prescribing the method, the specialist evaluates the benefits of tomography and the harm of the procedure for the patient.
The use of computed tomography for suspected cancer takes precedence over imaginary complications from ionizing radiation. Malignant tumors are deadly. Early detection and proper treatment help save a person’s life.
Verification involves the use of an integrated approach - CT, MRI, radiography, laboratory tests. The task is to find all malignant foci for early destruction.
Main indications for tomography:
- Clarification of the localization of the foreign body;
- Determination of the nature of blood flow, the degree of blood supply to the brain;
- Detection of purulent, destructive changes, inflammatory processes;
- Diagnosis of cervical diverticula and cysts;
- Verification of lymphatic tissue diseases;
- Detection of anomalies, aneurysms.
Scanning the neck with contrast has contraindications - allergy to iodine, renal failure, severe diabetes. The relative limit is weight more than 120 kilograms.
Contraindications for examination
CT scan of the cervical spine is not performed in the following cases::
- pregnancy at any stage;
- patient weight that exceeds the maximum permissible load on the tomograph table (about 120 kg).
A CT scan of the cervical spine is performed with caution and only if there are serious indications.:
- children under 12 years old;
- nursing women (milk becomes unsuitable for feeding the baby for some time);
- patients with renal failure;
- with multiple myeloma.
Contraindications for the administration of iodine-containing drugs:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- renal and liver failure;
- diabetes;
- intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents.
How is the examination carried out?
Chains, hairpins, and beads will need to be removed before the examination, as metal products can leave shadows on the pictures. The quality of the images will be below average, which can significantly reduce the information content of the entire examination.
The patient is placed on the extendable tomograph table in a supine position. To exclude voluntary or involuntary movements during the procedure, the patient’s head is fixed using a head holder. Complete stillness guarantees high quality images.
For bolus administration of a contrast agent, a special catheter is placed in the patient’s vein, which is connected to an injector (automatic dispenser) using a thin tube. When the drug administration system is connected, the table and the patient are moved into the tomograph and the examination begins. If a single injection of a contrast agent is expected, the injection can be performed both before and during the examination.
To prevent displacement of neck tissue during the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to hold his breath for up to 15 seconds.
If the images are taken without distortion, are sufficiently contrasting and detailed, then the examination is considered completed, and the results of the procedure are sent for interpretation.
How is a cervical CT scan performed?
It is necessary to ensure that there are no metal fasteners (zipper sliders, buttons, metal buttons, etc.) or trim elements on the clothing in the neck area. You will also have to remove jewelry such as a chain, pendant, beads, brooch, hair clips, hearing aids, and removable dentures. Metal parts leave shadows on images, which significantly reduces the information content of the examination.
The patient may be asked to change into a special robe with clasps or a shirt. Any voluntary or involuntary movements can spoil the images, so the patient may be secured on the tomograph table with straps.
The table moves into the tomograph together with the patient. The medical staff leaves the room in which the tomograph is located to avoid exposure to radiation, but continues to monitor the patient’s condition through a special window that is impenetrable to X-ray radiation. You can contact the nurse using two-way voice communication or a call button for medical staff, if this model of tomograph is equipped with one.
The examination takes about 5 minutes. If a cervical CT scan is performed with contrast, the patient will have to spend about 30 minutes in the CT scan room.
In what cases is a CT scan of the neck performed?
A CT scan of the soft tissues of the neck is performed in the presence of a herniated disc or to determine whether the ligaments in the neck are stretched. The procedure is also necessary if the doctor suspects that the patient has a vascular pathology or an abnormality of the lymph nodes. This allows you to determine the presence of atherosclerosis or aneurysm.
Doctors often prescribe MSCT of the cervical spine
The patient is referred for MSCT of the neck:
- with severe neck and head trauma;
- to determine the level of blood supply to the brain;
- to determine and confirm the formation of a tumor, its location, nature and anatomy are determined;
- in the presence of a cyst;
- to determine the presence of a foreign body;
- to confirm osteochondrosis of the spinal column;
- with purulent lesions (abscesses, phlegmon, infiltrates);
- if therapy for inflammation in the head, neck and throat does not bring results;
- in the presence of diverticula in the throat.
Read also: MSCT and its features.
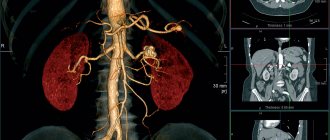
With the help of CT angiography, the condition of the cervical vessels is determined with greater accuracy. During the examination, the specialist identifies blockages, abnormal tortuosity in the carotid arteries, damage and aneurysm, scans arterial and venous blood clots, and determines the anatomy of neoplasms where the vascular system is involved.
If the doctor has doubts about the diagnosis and suspects that the patient has a stroke, MSCT of the neck vessels is mandatory.
Decoding the results obtained
A radiologist or radiation diagnostics doctor is engaged in decoding. The description of pathological changes and the formulation of the conclusion take time, so the patient can receive the document either an hour after the end of the examination, or the next day. After decoding, the patient receives photographs on digital media or printed on film, as well as a doctor’s report certified by signature and seal.
It should be understood that the conclusion of a radiology doctor is not a diagnosis. The diagnosis is made by the attending physician taking into account the clinical picture of the disease, patient complaints, data from instrumental and laboratory tests.
Preparation
Computed tomography of the spine does not require any preparatory steps with a few exceptions.
- If contrast material will be injected during diagnosis. In this case, you should refrain from eating for six hours before the procedure. Stop taking the liquid an hour before diagnosis.
- When examining the lumbosacral region, do not eat foods that lead to gas formation during the day. The evening before the day of the study, it is necessary to empty the intestines.
How is the examination done?
The patient lies with his back on the tomograph table. If necessary, the body position is secured with belts and bolsters to prevent involuntary movements.
During the procedure, the table moves inside the tomograph. A ring with an X-ray machine rotates around it. The tomograph makes a slight noise.
The duration of the study takes three minutes, with the use of contrast - twenty-five minutes. The patient receives processed diagnostic results an hour and a half after the end of the procedure.
How often can a CT scan of the cervical spine be done?
Due to the fact that some of the X-ray radiation is absorbed by tissues during the examination, restrictions have been introduced for computed tomography on the volume of one and the frequency of procedures. Small doses of radiation do not harm human health, so one procedure performed according to indications will not cause disturbances in the patient’s body. It’s another matter if examinations are carried out one after another. In this case, radiation doses accumulate, which can lead to the development of radiation sickness or the appearance of tumors.
The optimal interval between CT examinations is 12 months, regardless of whether the same area of the patient’s body will be examined or some other area. If there are serious indications, a re-examination can be performed no earlier than 6 months after the first.
How does a CT scan differ from an MRI?
Due to some similarities in the procedures, people often confuse MRI and CT diagnostics. It is worth understanding what common and opposing features both methods have.
| Comparative characteristics | CT | MRI |
| Principle of operation | Use of X-ray radiation | The source is a magnetic field |
| Use of special equipment | A CT scanner is used | An MRI scanner is used |
| Injection of contrast agent | Rarely, for the purpose of diagnosing complex multifactorial diseases | Often used to determine the pathology of the vascular bed |
| Safety | Has limitations in use for detecting diseases in children | Can be used in children's practice |
| Examination result | Taking pictures | Dynamic pictures and recording of results onto media |
| Cost of the procedure | From 3,000 to 15,000 rubles | From 5,000 to 25,000 rubles |
| Time spending | 15 minutes | 20 or more minutes |
Both instrumental diagnostic methods are quite widespread in domestic and foreign medicine. With their help, it is possible to establish primary diagnoses and monitor the dynamics of progression and cure of existing pathologies, thus preventing relapses. The main difference between them is only in the principle of operation and some safety of MRI.
Advantages and disadvantages of CT
Important and significant advantages of diagnostics traditionally include:
- Possibility of rapid detection of pathology. A few hours after receiving the described image, the doctor can begin treatment.
- No pain or penetration into the body. No incisions or other access to the organ are required.
- High definition images. Unlike X-rays, the image is dynamic and allows you to track progression.
- Speed of implementation. In cases of an urgently developing pathological condition, this property will be indispensable.
- Less sensitivity to random movements. This allows you to get a blur-free and clear picture in the shortest possible time.
- Patients with metal structures, braces and piercings can be examined. The radiation will not affect them.
- In most cases, the procedure saves the patient from surgery. Instead of an exploratory laparotomy, the surgeon will make a careful incision for the laparoscope.
Disadvantages of the method:
- X-ray radiation can cause radiation sickness and provoke some types of tumors. There is no need to go through it more than twice a year.
- Pregnant women are prohibited from making such diagnostics. It is assumed that the study has an ambiguous effect on the growth and development of the fetus in the womb.
- Young children are very sensitive to foreign influences. There is no need to subject them to examination unless urgently indicated.
- Reaction to contrast agents. Anaphylactic shock may occur directly on the treatment table.
Pros and cons of MRI
Advantages of magnetic resonance examination:
- The result of the procedure is a high-quality image. The three-dimensional structure will allow experts to make a conclusion about the exact location of the pathology.
- Soft tissues that are not visible during a computerized examination are visible under the magnetic field. This makes it possible to detect many diseases.
- The nervous system is well visualized. The same goes for muscle fibers.
- Safety. Magnetic fields do not have a negative effect on the body.
- Using this procedure, you can see the source and initial stage of the infectious-inflammatory process. This will allow treatment to begin immediately.
- In the postoperative period, when the patient is weak, such diagnostics can be used to assess the condition and healing of a wound or spinal fracture. It will not cause deterioration in your health.