CT scan of the thoracic spine - what is it?
The vertebral column plays a rather significant role. The trunk is the best basis and functional defense of the internal organs. It is a reliable frame for the body. The spinal cord flows through the small foramen magnum in the skull, distributed throughout the thoracic region and then into the neck.
Once upon a time, standard computed tomography was significantly inferior to ordinary MRI - a method of research in terms of quality and visualization of organs. The procedure is used today to scan bone tissue to detect various pathologies in the desired area. Modern tomographic devices help competently study soft tissue.
When using CT of the thoracic spine, the question arises - what will this study show? Its use helps to detect:
- tumor process;
- cyst;
- anatomical abnormalities;
- birth defects;
- spinal cord rupture;
- diseases;
- destructive and atrophic changes in bones and muscles.
A computed tomography scan performed on the thoracic portion of the spinal trunk can detect all sorts of neoplasms in the bones, severe bruises and cracks, developmental deficiencies, and also enlargement of the spinal canal.
Nerve endings are located in the sections of the sacrum, lower back, and chest. They branch from the column to various internal organs located in the pelvis and legs. The CT machine scans the soft tissues of internal organs, an extensive network of blood vessels and the bones of the chest.
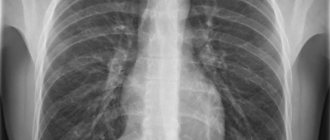
The results show a three-dimensional pattern of the desired thoracic area and help directly examine the vertebral trunk and lymph nodes with vascular branching. The scan results are viewed in various planes and sections.
If a tumor is suspected, a contrast agent is used when scanning organic tissues. The substance is necessary to obtain a more accurate visualization picture. Typically, a solution based on iodine compounds is used, which is introduced into the vein cavity before the procedure.
Indications
Computed tomography of the spine can act as an initial screening and as an expert form of diagnosis. The doctor will immediately order a CT scan of the spine if necessary:
- assessment of post-traumatic changes - detailing trauma-related injuries, identifying fractures, dislocations, the presence of bone fragments in the spinal canal, spinal cord compression;
- assessing the likelihood of spinal fractures in patients with osteoporosis.
As a method of further examination, a CT scan may be sent if necessary:
- differential diagnosis of bone tumors and metastatic lesions of spinal bone tissue;
- assessment of the results of surgical intervention;
- clarification of X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging data of the spine;
- diagnosis of congenital anomalies and assessment of the anatomical features of the structure of the vertebrae.
In what cases is the study indicated?
The main indications for performing the CT procedure:
- spondylitis or inflammation of the chest bones;
- discitis - an inflammatory process of the spinal discs;
- osteochondrosis;
- upcoming surgery;
- chest injury;
- spinal column injury;
- syphilis degenerative changes;
- tuberculosis;
- bacterial attack.
CT scan of the thoracic vertebrae and the entire spine is needed for the most informative diagnosis of developing pathology.
A vertebra destroyed by the disease can severely impinge on the spinal cord, which causes disturbances in the functionality of the limbs and human organs. Detection of the disease at the initial stage guarantees positive medical prognosis.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Osteochondrosis is a disease in which intervertebral discs lose their shock-absorbing properties. They begin to deteriorate greatly, their functions weaken. The disease contributes to the destruction of the spine, the formation of protrusion and the development of hernias. Diagnosing osteochondrosis is quite complex and difficult. Tomography of the thoracic region eliminates any error and doubt about the correct diagnosis.
Presence of spinal injuries in this area
Injuries to the sternum do not occur often, and serious damage must be sustained to impair the functions of the column. However, often a person begins to think about injury only when obvious clinical signs appear. Pain is felt when moving, bending, breathing. CT differentiates the condition of bones and vertebrae, and differentiates the characteristics of damage.
Pain of unknown cause in the thoracic region
The patient sometimes complains of chest pain of unknown etiology. CT allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image, which clearly shows the entire pathological focus. The majority of spinal diseases do not contain precise clinical signs, as a result of which the thoracic region is difficult to diagnose without x-rays or tomography.
Suspicions of vertebral displacement, intervertebral hernia, protrusion
Protrusion appears with any type of osteochondrosis; sometimes the disc protrudes strongly from the intervertebral space towards the main canal of the trunk. Intervertebral deformity occurs when the annular section ruptures and the center of the disc itself shifts. With subluxation, the vertebrae are positioned anatomically incorrectly. Pathology often negatively affects not only the position of the musculoskeletal system, but also the functioning of organs. It is possible to differentiate the disease only with the support of hardware study.
Inflammatory diseases of the thoracic region not diagnosed by other methods
Spondylitis, which appears due to degenerative changes in the spinal column, causes a purulent process in the bone. There are other diseases that provoke inflammation. It is possible to identify them with the support of CT at any stage, which greatly increases the chance of healing.
What does the cost depend on?
The cost of computed tomography of the spine largely depends on three fundamental pricing factors:
- cutting power of CT device;
- the need to use contrast enhancement;
- qualifications of doctors.
The more cuts the unit can make per revolution of the Gantry ring, the more detailed and expensive the examination will be. For high-quality diagnostics of vertebral structures, you should choose medical centers equipped with multislice computed tomographs with a minimum number of slices of 32 or more. Some spinal cord pathologies and complex spinal injuries, when the spinal canal is affected, will require examination using more powerful 64-128 slice devices. The decision about the type of CT scanner should be made by the attending physician. He usually specifies the minimum equipment requirements in his CT referral. There he also indicates the scanning procedure - with or without contrast.
What diseases can tomography help identify?
What does a CT scan of the thoracic spine actually show? Progressive and modern equipment allows you to see all sorts of:
- tumor configuration;
- characteristics of the injury;
- tissue destruction;
- inflammation.
CT makes it possible not just to see, but to clearly discern the extent of the disease.
Spinal injuries
Injuries to the spine and thoracic area are quite dangerous for the spinal cord. They provoke a rupture of the spinal cord. This condition is very dangerous, it severely disrupts the functions of internal organs and contributes to the appearance of tissue disorders and necrosis. A correctly performed CT scan of the thoracic region accurately differentiates an acquired fracture, a rupture of the ligamentous-muscular apparatus and damage to the spinal cord.
The essence of any injury, the level of damage to bones and muscles can be found out in great detail based on the results of tomography. Sometimes a person lives for years with a spinal injury and is unaware of the presence of the pathology. And only with the help of hardware diagnostics can you find out about injury.
Structural changes in the vertebrae, that is, various types of deformities
The result of a sedentary life, difficult strength work and other initiating moments are all kinds of destruction of the spinal column. CT helps the doctor understand what happened in a certain situation and differentiate the causes of the disease. Hardware examination shows destruction. Sometimes vertebral prolapse, hernia and displacement provoke a feeling of pain in neighboring areas. In this case, a general CT scan of the thoracic spine is performed.
Development of arthritis and osteoporosis
Arthritis is a well-known disease of the musculoskeletal system that affects the joint system and connective tissue. The disease becomes a cause of disability. Osteoporosis is a metabolic mineral imbalance in which bones lose strength due to calcium leaching. Osteoporosis is also a debilitating consequence of arthritis. Injuries and inflammatory processes can be detected at the primary stage only by CT scanning. The performed studies of the spine show the exact clinical picture and changes in the injury.
Congenital spinal defects
There are certain groups of spinal column defects:
- Morphological changes. The deviation occurs due to incorrect development of the spine. This provokes their fusion or increased mobility of the discs.
- Quantitative. The deviation is manifested by a discrepancy between the number of vertebrae and the norm.
- Anomalies. Bone matter remains dystrophic. The defect is detected using a CT scan procedure. Diagnostics reveals bone density and other pathologies.
CT scan helps to find out the pain treatment center, congenital pathologies of the spine, and features of bone changes. The CT imaging method allows you to see all degenerative processes in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. After diagnosis, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition. This research method helps to prescribe an accurate treatment regimen.
Contraindications and risks
A CT scan of the lumbosacral vertebrae is absolutely painless, but in some cases it can be harmful to health. Thus, the contrast agent can negatively affect the condition of the kidneys. This side effect is especially likely to occur in patients with renal failure.
It is also not recommended to do this procedure during lactation, since the contrast agent passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding women who still need a CT scan should not breastfeed their baby for two days after the procedure.
In addition, CT has a number of other contraindications. Shouldn't do it:
- Pregnant women (there is a risk of tomography having a negative impact on the fetus).
- People who are allergic to iodine.
- Persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Patients with elevated levels of keratin in the blood.
- The patients are in serious condition.
- Patients whose body weight exceeds 120 kg. Depending on the equipment, some clinics allow examination of patients weighing up to 200 kg.
- Children under 12 years old.
It should be noted that children can have a CT scan of the lumbar spine. If it is necessary to conduct research on a child under 12 years of age, then this is done with sedatives or even under anesthesia. Sedatives are necessary to keep the baby still during the examination.
The same applies to patients with severe pain and hyperkinesis (involuntary movements). CT is contraindicated for such patients, however, if they have severe back pain, the doctor may prescribe a research procedure using a sedative or anesthesia.
Preparing for a CT scan of the thoracic spine
If you use any medications, you must inform your doctor. Iodine-containing preparations may cause reactions and be incompatible with medications used. In this case, you must refrain from taking medications.
Preparation for the study includes giving up alcohol and smoking. An examination is carried out if the patient is not intoxicated.
The X-ray emitter is highly sensitive. It may react to pacemakers and dentures. The doctor should be notified about the presence of implants and devices; the diagnostician does not study the medical record page. To accurately diagnose diseases, it is necessary to remove removable dentures and hearing aids.
You must bring with you the results of all previous studies: MRI, ultrasound, radiography. You will need to follow some standards during the procedure.
- Remove iron objects and jewelry.
- Notify the doctor about foreign objects in your body: implants, ligature structures, or a pacemaker.
- Be in a stationary body position during the examination to obtain an accurate image of the spinal cord.
During the contrast procedure, an iodine-containing medicinal product is administered intravenously. A preliminary test is performed on the coloring substance. Only after a reaction to the drug has been ruled out can contrast be completely injected into the vein.
How does the procedure work?
No special preparation is required for the procedure and examination of the thoracic region. The exception is the procedure using special contrast. In this situation, the necessary tinting agent is administered intravenously to the sick person using catheterization. The medicinal solution accumulates in the tissues of the spinal canal and intensely stains the site of inflammation.
If contrast is administered, you need to come to the hospital on an empty stomach. They stop eating food seven hours before the start of the scan. Before entering the examination room, metal objects are removed from the body. The tomograph is sensitive to its particles and may give incorrect diagnostic results.
If a person has an installed pacemaker, the examination procedure using CT is not carried out. During the procedure, the patient lies motionless. In order to limit movement, the body can be secured with belts.
The study time ranges from 20 to 40 minutes. The received data is processed by special computer programs. They create several multi-slice images of the desired area. Afterwards, the radiologist carefully examines the obtained images and makes a diagnosis.
Contraindications for CT scanning
There are certain limitations to scanning the spinal column. Contraindications to tomography:
- bearing a fetus;
- hyperkinesia;
- fear of closed spaces.
Contraindications when using contrast:
- allergy to iodide compound;
- lactation;
- weight above 120 kg;
- insufficient kidney function.
High-quality computed tomography is contraindicated in children, at any stage of gestation and during breastfeeding. In exceptional cases, a CT scan may be performed on the child to identify an accurate diagnosis.
How is diagnostics carried out?
The patient's chest is scanned in the supine position. It is placed on a special table. It is pushed into the apparatus tunnel, where the whole process takes place.
A contrast agent is administered before the procedure. Sometimes the use of contrast causes discomfort, but it goes away after a few minutes. In some cases, bolus contrast is used. This means that contrast will continue to flow through the catheter throughout the examination.
The procedure does not last long - in standard situations it takes only 10-15 minutes. With contrast, the examination time increases to 30-40 minutes. An important condition for diagnosis is the immobility of the patient. It is not always possible to provide this, especially if the scan is performed on a child. In this case, resort to sedatives.