The cervical spine is subject to constant high loads, and therefore is its weakest part. Nerve fibers and vessels pass through the cervical spine (CS), through which blood, oxygen and nutrients enter the brain.
Very often, with minor turns of the neck or head, injuries to this area occur with the subsequent development of clinical signs. To prescribe the correct treatment, an MRI of the cervical spine is performed, a study during which possible changes in the spine, surrounding tissues and blood vessels are determined.
What is magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and brain?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine and brain is one of the most informative diagnostic methods, allowing to identify any pathological processes in the vertebrae and nearby tissue structures, examine the blood supply to the brain, the presence of tumors and other changes. Carrying out an MRI does not take much time and is a completely safe procedure that does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient.
ON A NOTE! MRI of the spine is often used to diagnose herniated discs. Typically, an MRI of the neck is performed in conjunction with an examination of the thoracic spine and brain.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a popular and widely used method for diagnosing various diseases of internal organs and tissues due to the high accuracy of the results provided.
Further actions of the patient after diagnosis
After completion of the diagnosis, the conclusion issued to the patient should be transferred to the attending physician for further study, diagnosis and determination of appropriate treatment. As a rule, pathologies of the cervical spine require visits to the following specialists:
- neurologist (if osteochondrosis is detected, as well as multiple sclerosis);
- oncologist (if the appearance of malignant tumors is confirmed, including those with metastases that have spread throughout the body);
- neurosurgeon (if a hernia is detected);
- traumatologist (in case of injury to the spinal column).
Magnetic resonance imaging is a way to clarify a patient’s diagnosis; interpretation of the data obtained is carried out strictly by a doctor. Self-diagnosis based on the images obtained and subsequent self-medication are strictly prohibited. Lack of qualified treatment can cause irreparable harm to health and life.
What is visible during the study?
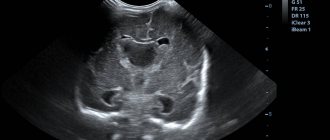
During the procedure, the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, spinal cord and tissues from the lower border of the neck to the craniovertebral junction, which is the junction of the skull, the first and second vertebrae, and the brain stem, are examined.
MRI studies the condition of blood vessels and some areas of the brain (circulatory disorders, tumors, developmental anomalies, etc. are revealed).
During the examination, a specialist diagnostician receives three-dimensional images that make it possible to identify various deviations in the normal blood circulation of the brain and the causes of this condition.
After performing a tomography, the specialist receives images that allow him to diagnose various diseases of extracranial vessels, cancerous tumors in the spine and brain.
Advantages of the method
The MRI technique of cerebral vessels allows us to determine the general condition of the organ, its arteries, assess their deep work and the deformations that occur. Foci of disease, trauma and deformation after them are clearly visible.
At the same time, the doctor assesses the condition of the blood vessels, the pituitary gland in case of hormonal imbalance or diagnoses dysfunction of various systems and organs. Advantages of the procedure over similar examinations:
- a detailed description of structural abnormalities and the development of diseases in any tissues and organs is given;
- a non-invasive tomography method that has high accuracy in determining anomalies;
- creating images in 3D;
- the results can be recorded on third-party media;
- there is no ionizing, muta-, carcinogen (unlike FLG).
The diagnostic method allows you to examine objects of millimeter dimensions; the doctor examines not only longitudinal, but also transverse sections.
What can a tomogram of the neck, head and blood vessels show?
The main indications for MRI of the cervical spine are:
- injuries to the neck area with suspected vertebral displacement and spinal cord compression;
- diseases of the spinal column accompanied by degenerative-dystrophic changes (spondylosis, osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, rupture of the fibrous ring);
- cancer formations and suspicion of metastasis of atypical cells into nearby tissues and structures;
- hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs;
- spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal, accompanied by compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots);
- Ankylosing spondylitis (an inflammatory disease of an autoimmune nature with damage to joints and surrounding tissues);
- abnormal vascular development;
- spinal tuberculosis;
- before preparing for surgery;
- in the presence of osteochondrosis to determine the severity of the disease;
- after therapy for various diseases of the musculoskeletal system in order to determine positive dynamics;
- Klippel-Fayle syndrome (short neck syndrome).
MRI is performed to identify the causes of certain pathological conditions:
- persistent headaches of unknown etiology;
- severe pain in the neck area;
- dizziness;
- a feeling of discomfort, stiffness in the neck and numbness of the upper extremities;
- frequent fainting, deterioration of visual function.
Cervical MRI results
After the procedure, the person receives images taken by a tomograph and a conclusion about the condition of the tissues (but this is not a diagnosis yet!). Usually the result is ready 1-2 hours after the MRI. This is the information that is included in the protocol describing the magnetic resonance examination of the neck:
- Is the cervical canal narrowed?
- whether physiological lordosis is preserved in this section (i.e., normal bending);
- number of vertebrae, their shape, contours, ratio;
- condition of the intervertebral discs (height, presence of exit beyond the spinal canal, etc.);
- whether the nerve roots are changed, do they all exit through the intervertebral foramina;
- appearance of soft tissue around the cervical spine;
- the condition of the articular surfaces, including the atlanto-occipital joint;
- structure, width, configuration of the spinal cord;
- whether the bone marrow MR signal is altered;
- whether the anatomy of the craniovertebral junction (the border between the upper cervical region and the skull) is disrupted.
Based on these data and, if necessary, other tests, the attending physician makes a diagnosis or assesses the dynamics of changes during treatment.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications to MRI are the presence of metal braces, crowns or dentures. All metal structures in the human body heat up when exposed to a tomograph, which leads to soft tissue burns.
The examination is not carried out in patients with a pacemaker, an insulin pump (for continuous administration of insulin for diabetes) and an ICD (device for the treatment of ventricular arrhythmia) . In this case, all implanted devices provide vital benefits to the body, preventing serious consequences of severe pathologies; in addition, all devices are expensive medical equipment. As a result of tomography, a magnetic field affects the implants and disables them.
IMPORTANT! Magnetic resonance imaging is contraindicated in patients weighing more than 120 kg and with severe heart failure.
The examination is not carried out if there is a fear of closed spaces, as well as with diseases that are accompanied by involuntary muscle spasms. In this case, any movements can affect the quality of the pictures.
What does SHOP tomography show (full list)?
MRI is used to diagnose many different diseases and pathological changes in the spine:
- protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal while maintaining the integrity of the fibrous ring (protrusion);
- compression of the spinal cord, nerve roots and blood vessels;
- tuberculosis of bones and joints;
- tumor neoplasms;
- dystrophic disorders in articular cartilage (osteochondrosis);
- fractures and displacement of the vertebrae;
- inflammatory processes in the cervical muscles with myositis;
- inflammation of the joints of the spine;
- degenerative changes in bones and their subsequent destruction;
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- carotid artery aneurysm (deformation of the weakest part of the vessel, with stretching and protrusion of the wall);
- cracks in the spine;
- atypical cells that form from bone tissue (osteosarcoma);
- osteomyelitis (a purulent process localized in the bones and bone marrow, accompanied by necrotic changes);
- multiple sclerosis (severe autoimmune disease affecting the myelin sheath of the brain and spinal cord);
- myeloma (a malignant tumor that develops in the bone marrow); congenital developmental defects;
- the presence of thrombi (blood clots) on the vascular walls;
- any pathological changes after injury;
- diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis (pathological processes of connective tissue affecting small joints);
- benign bone tumor (osteoma);
- cavity formations in the spinal cord (CNS disease);
- spinal canal stenosis;
- infectious foci;
- arthrosis of the facet joints (thinning, deformation and destruction of intervertebral discs);
- granulomatous inflammation;
- scoliotic curvature of the spine.
Features of MRI of the neck in the presence of a tumor or injury
If there is a traumatic injury to the vertebrae, the doctor will see on the images a fracture line, bone fragments, and bone deformation. In the case of a compression fracture of the vertebrae, the specialist will identify areas of osteoporosis, and possibly other pathological structures, on the resulting sections.
Tumor formations are most often detected in the area of the membranes of the spinal cord. MRI of the neck allows you to evaluate not only the structure of the tumor tissue, but also determine its connection with adjacent vascular or nervous elements, as well as with other soft tissue structures. The study allows us to accurately determine the cause of compression of the spinal cord and destruction of its tissue.
How is the procedure done?
Before starting the procedure, the patient must wear loose-fitting clothing to avoid discomfort. You also need to remove all jewelry (earrings, chain, rings) and clothing with metal elements, such as zippers or studs.
The tomograph apparatus is a tunnel with a retractable table. Next, the patient is placed on the tomograph table, the neck is fixed to immobilize and retracted. When performing an MRI with a contrast agent, the solution is injected into a vein before the procedure begins.
Next, the MRI specialist moves into a small room with computer equipment, from where he observes the patient through a window and controls the tomograph.
IMPORTANT! The main rule for a successful study is complete immobility of the patient. Even with minor movements, the quality of the image decreases, the image turns out blurry, and the results are unreliable.
Inside, the tomograph is equipped with a ventilation system and lighting; in addition, the patient can contact a specialist diagnostician at any time. In some cases, it is possible for a close relative to be present to support the patient.
How to prepare?
The preparatory stage does not require any special restrictions or measures; it is enough to exclude food a few hours before the examination; with MRI with contrast, the last meal is taken 7-8 hours before the procedure.
In patients with severe pain or strong feelings, anesthesia is administered or sedatives are used.
IMPORTANT! MRI diagnosis of the cervical spine with a contrast agent is carried out after myelography and angiography no earlier than 5-7 days later.
It is also recommended to avoid drinking liquids 1 hour before the test. Before entering the diagnostic room, you should leave all personal belongings with relatives, in particular mobile phones, bank cards, wristwatches, dentures, hearing aids, keys, etc.
Technique
Before performing an MRI of the brain, all jewelry, metal rivets, and dentures are removed. If you intend to use a contrast agent during the procedure, you must have your blood tested in advance for allergies.
After preparation, the patient is asked to lie on the retractable part of the tomograph. The medical staff secures it with bolsters and belts. Equipment is attached to the patient's head that will receive and send back radio waves. If contrast is used, the agent is administered intravenously before the start of the study. If desired, the patient can wear sound-proofing earplugs.
After turning on the equipment, a picture of the brain, its parts and structures is displayed on the monitor screen. Diagnostics allows us to detect even small neoplasms, existing disease processes and their rudiments.
How is a tomography with contrast done?
A contrast agent is used to identify pathological processes in blood vessels and when the presence of tumors is suspected.
A contrast agent is injected into a vein or into the spinal canal immediately before the start of the study.
For this purpose, medications based on gadolinium are used, substances that do not cause allergic reactions and are completely safe for the body.
The contrast method of magnetic resonance imaging is considered more informative, but at the same time more complex and expensive. However, the technique thoroughly determines the condition and patency of the vessels of the neck and head, the causes of poor blood circulation, and allows for the timely identification of tumor tumors, their degree of development, and exact location.
Decoding the results
Due to the lack of special knowledge, patients are not able to independently decipher what an MRI of the neck can show. They receive the test results and go to the attending physician. After studying images of the neck in various projections and if there are pathologies, he prescribes treatment.
What can be seen in photographs of the soft tissues of the neck
Scanning the soft tissues of the neck helps identify:
- Abscesses and cysts;
- Tumors and metastases;
- Foreign bodies and soft tissue hematomas;
- Diseases of the cervical organs (larynx, vocal cords, thyroid and salivary glands).
An MRI of the neck muscles is very informative. With its help, it is easy to diagnose sprains, atrophy and inflammation of muscle tissue.
What does an MRI of lymph nodes show?
Enlarged lymph nodes indicate resistance of the immune system to infectious, cancer or autoimmune pathologies. Therefore, MRI of the lymph nodes of the neck allows specialists to diagnose the following diseases:
- Tumor neoplasms (lymphogranulomatosis, lymphosarcoma);
- Infections (acute respiratory infections, tuberculosis, HIV and sexually transmitted diseases);
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune hepatitis).
If cancer and metastasis are suspected, MRI is done with the introduction of a contrast agent. This will make it possible to identify the smallest structural changes in the lymph nodes and diagnose cancer in the early stages.
Interpretation of MRI of neck vessels
Based on the results of MRI of the neck vessels, the doctor can diagnose the following pathologies:
- Thrombophlebitis;
- Vascular aneurysm;
- Fusion of venous vessels;
- Vasculitis (with angiography of neck vessels using MRI, not only inflammation of the vascular walls is clearly visible, but also their necrosis);
- Benign and malignant neoplasms;
- Abnormal arrangement of veins and arteries;
- Dissection of the wall and tortuosity of the carotid artery;
- Compression of blood vessels by scars after injury or surgery.
If the patient suffers from impaired blood supply to the brain, an MRI of the neck arteries will show the reasons for the deterioration of blood circulation. And MRI of the veins can detect the presence of blood clots in them.
MRI of the neck is the safest and most accurate method for diagnosing its organs, which has almost no contraindications. Most brain pathologies can also be seen precisely thanks to MRI of soft tissues and vessels of the neck, since they are closely related to each other. But in this case, the patient is recommended to have a comprehensive examination of the head and neck.