MRI of the coccyx and sacrum is an extremely informative hardware examination of the lower spine. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the “gold standard” for diagnosing coccyx pathologies. It allows you to identify both congenital deformities and inflammatory processes, circulatory disorders, cancer and other diseases.
In Moscow, an MRI of the coccyx can be done in many institutions, but in the Stolitsa network of clinics, this service will be provided to you by experienced specialists using the most modern equipment.
What is MRI of the coccyx
During the examination, the tomograph creates a magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses around the patient. Under this influence, hydrogen protons line up in tissue cells for some time parallel to the field, and then return to their original position. During this change, a small amount of energy is released. It is captured by the device’s computer, digitized and recorded as a three-dimensional image on the monitor screen.
The advantages of MRI are:
- Obtaining data not only about the coccyx, but also about neighboring tissues;
- Determination of damage, neoplasms, inflammatory processes;
- The high quality of the images makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis in one examination;
- During surgery, tomography data can reduce injury to neighboring areas;
- The absence of harmful radiation and safety allow the frequent use of MRI.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let us briefly outline the main advantages of this method of examining the coccyx:
- Shows the whole picture of the pathology (inflammation, neoplasms, condition of blood vessels, tissues, nerves);
- The high quality of the resulting images guarantees diagnostic accuracy;
- Safety and fairly simple preparation for the event.
Among the disadvantages are the following:
- Large list of contraindications;
- High cost of the procedure. In the capital, the average price is about 5 thousand rubles.
Thus, despite the shortcomings, MRI is the most popular method for studying pathologies in the coccyx area.
Indications
A patient may receive a referral for examination of the coccyx using a tomograph in the following cases:
- Anomalies in the coccygeal region;
- Possible displacement, fracture;
- Suspected tumor, metastases;
- Suspicion of cauda equina syndrome;
- Pain syndrome;
- To confirm previous studies;
- To identify the dynamics of treatment.
Previous Next
Methodology of the procedure
To conduct an MRI of the tailbone, the patient removes all metal jewelry, leaves his mobile phone and lies down on a mobile table, which will move inside the diagnostic unit. You will be in the office without medical professionals, but if necessary, you will be able to contact them using a two-way communication system (if your health worsens or there is severe discomfort).
During diagnosis, a special ring will move near the lower back and scan the desired area. You must remain completely still, otherwise the results will be inaccurate. In some cases, tomography is performed using contrast solutions that are administered intravenously. The procedure takes approximately half an hour, after which you can return to your normal lifestyle.
What will a tomography of the coccyx show?
During an MRI examination, you can obtain accurate information on the condition of the coccygeal region and:
- Identify congenital or acquired anomalies;
- Detect tissue destruction in the coccygeal region;
- Identify possible post-traumatic changes;
- Find out the condition of the coccyx. When healthy, it represents an inverted pyramid;
- Find out the number of vertebrae that form the coccygeal bone;
- Determine the position of the coccyx, the presence of injuries, fractures, displacements;
- Consider the condition of the vessels that are located in the pericoccygeal region;
- Determine the presence of fistulas, abscesses, as well as tumors and cysts;
- Examine the articulation of the patient’s coccygeal bone and the sacrum;
- Note changes in connective tissue or bones;
- See the presence of degenerative changes.
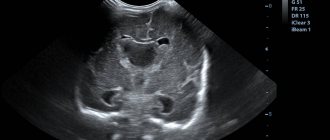
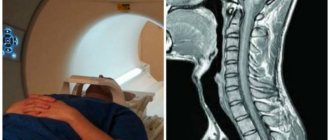
Coccyx on MRI image
| MRI of the coccyx | MRI of the coccyx with coccydynia |
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1100 rubles!
(more about prices below)
Contraindications for MRI
- first trimester pregnancy;
- last stage of heart failure;
- implanted artificial heart valves, as well as a pacemaker;
- installed apparatus of A. G. Ilizarov;
- implants made of metal;
- installed intracranial hemostatic clips (made of metal).
MRI images of the lumbosacral spine
How to prepare for a tomography of the coccyx and sacrum
No special preparation is required to study the coccygeal region. A person may not change his eating habits and lifestyle. Special instructions can be set by the doctor only if contrast is administered to the patient. As a rule, restrictions include refusing food 2 hours before the procedure.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
Preparing for the examination
Usually, even during the registration for the examination, the patient is immediately informed about what needs to be known and done before visiting the MRI. Preparatory measures vary depending on the area being scanned. Before an MRI of the coccyx and spine, it is advisable not to eat food for 4-5 hours.
Immediately before the scan, the patient needs to remove all metal items, jewelry, and piercings. No need to undress. You cannot take electronic devices or magnetic cards into the office. Some tattoos can be done with metallic ink. In such cases, irritation often occurs on the skin.
If you are having an MRI with contrast, it is recommended to do an allergy test first, since urticaria, dizziness, itching, and shortness of breath are possible.
How is an MRI examination of the coccygeal area performed?
When a doctor recommends undergoing an MRI examination, a person immediately has thoughts about how the procedure will go and whether it will be painful. You can immediately calm down - this method is absolutely painless and safe.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the coccygeal area takes place in several stages:
The first step is to remove all metal objects from the body. All chains, rings, belts will need to be removed during the procedure, and all electronic devices - phones, tablets, watches - should be left in the preparation room.
Next, the patient takes a comfortable position on a special table, which slides into the MRI machine. You will have to lie on your back or stomach.
The tomographic scanner will begin its work. It is worth noting that the device sometimes makes specific noises. While the scanner is taking pictures, the patient will hear noises and tapping sounds. To rid yourself of these sounds, you can use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones.
The entire diagnosis usually lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. When the table with the subject leaves the MRI machine, the diagnostic procedure is considered complete.
You can find out the results of the study in about 1 hour. Occasionally this time can be increased to 2 days.
Questions about diagnostics
Dress code
You can enter the MRI room in any clothing that does not contain metal. When going to the clinic, it is best to wear loose, non-restrictive clothing without metal elements (zippers, rivets, hooks), in which you can lie comfortably. For women, we recommend bringing a T-shirt or not wearing a bra with metal wires or hooks.
Preparation
This tomography does not require any preparatory steps from the patient.
Is MRI harmful to health?
MRI is a completely harmless diagnostic method for the human body. This method of examination can be carried out at any age and for any disease an unlimited number of times, unless you have contraindications.
Contraindications
Some pacemakers and foreign objects in the body may pose serious limitations to tomography. In particular, cochlear implants, vascular clips, stents, heart valves and insulin pumps, pacemakers, neurostimulators, steel screws, staples, pins, plates, joint endoprostheses may be a contraindication to diagnosis. The patient must notify the radiologist about all implanted objects in the body. The diagnostician will be able, based on information about the composition and model of the implant, to assess the possibility of conducting diagnostics.
If you are having an MRI with contrast, be sure to report any allergies to medications or kidney problems. It is also necessary to inform the radiologist about a possible pregnancy.
Is it possible to do an MRI with braces and dental implants?
Dental implants and crowns are not a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic field does not have any negative effect on them. Fixed brace systems can produce artifacts on tomograms during MRI of the head. If the light effect is too strong, the doctor will stop the study and offer the patient alternative diagnostic methods.
Is the device noisy?
Any MRI machine in working condition makes noises reminiscent of tapping. The open tomograph is one of the quietest installations. The noise from its operation is significantly lower compared to closed tomographs. If the sounds of the operating unit cause you anxiety, you will definitely be offered special noise-canceling headphones.
What should I do if I have claustrophobia?
An open tomograph is the optimal solution for patients suffering from panic attacks in a closed space. It is open on the sides on three sides and does not create a claustrophobic feeling.
Can I take sedatives before an MRI?
If you are a little nervous, before the tomography you can take mild sedatives, for example, valerian, motherwort infusion or afobazole. Taking sedatives does not have a negative impact on the quality of MRI.
Why is it important not to move during the test?
Any movement during the examination reduces the quality of the resulting images. Multiple motion artifacts may appear on the images, and the MRI results will be uninformative.
Can I do the research with an accompanying person?
Absolutely yes. You can invite any accompanying person from among your family and friends to the MRI room. It is important that your companion does not have metal implants or artificial pacemakers in his body.
MRI technique
Before the scanning procedure, the patient removes metal jewelry and clothing containing similar elements.
This is a prerequisite for obtaining high-quality images - steel and its alloys are magnetized and create interference. Then proceed to the procedure:
- the patient lies down on the machine table;
- the subject receives an emergency call button, listens to instructions on the conditions for its use, and puts on soundproof headphones;
- the instrument table moves into the tunnel, the scanning procedure begins;
- After 30-40 minutes, the study ends and the device platform moves out.
During operation, the device makes sounds according to the scanning mode. The patient is prohibited from moving, as this creates interference in the image.
A disk with a doctor’s conclusion is handed out 1-1.5 hours after the procedure.
Applying Contrast
Sometimes it is necessary to administer a contrast agent to increase the information content of the study. Indication is suspicion of oncology:
- Tumors are characterized by an abundant blood supply, as a result of which blood vessels grow in the tissues;
- the contrast stains the vessels, accumulates in the parenchyma of neoplasms and improves their visualization.
Allergic reactions to contrast are rare. If intolerance is suspected, the active substance is administered in a minimal amount a few minutes before the procedure. If there are no complications, scanning begins.
Interpretation of MRI results of the coccyx
An example of MRI decoding of the coccyx
Area of study: MRI of the coccygeal spine In a series of MR images weighted by T1 and T2 in the sagittal and axial planes, the structure of the coccygeal vertebral bodies is quite homogeneous, the intensity of the MR signal from the bone marrow of the coccygeal vertebral bodies is moderately increased on T2 and T1-weighted account of fatty degeneration.
Location of the coccygeal vertebrae according to type 1. There were no signs of bone marrow edema of the vertebral bodies. Direct MRI signs of post-traumatic changes are not determined. Presacral fatty tissue is not changed. Conclusion: Initial degenerative-dystrophic changes in the coccygeal spine. It is difficult for an ordinary person to independently understand and interpret the results that, after an MRI, will be given to him on a digital medium. Therefore, with the conclusion of the radiologist and the photographs, he should go for a consultation with the attending physician, who will make a final diagnosis based on the summary data of the examination, medical history and tomography data. In our clinic , after an MRI, you can have a free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist . Doctor
- will answer all questions based on the results of the research and the conclusion received
- Helps explain tomography results without using complex radiological terminology
- will conduct an examination and, if necessary, offer treatment.
“Second independent opinion” service Medicine is an area where we want to be 100% sure . Therefore, at your request, we will be happy to offer you the service of a second independent opinion from the leading consultant of our clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences , a doctor of the highest category with 18 years of experience in the field of tomography and radiology N.V. Marchenko.
What pathologies can be detected during examination?
Like all other parts of the spine, the coccyx is also susceptible to various pathological processes: traumatic, inflammatory, destructive and oncological. Due to the inconvenient location of this organ, it is not always possible to use the X-ray method, so in most cases magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
Traumatic lesions
Unfortunately, coccygeal injuries are very insidious. When a person is bruised or falls, they often do not go to a medical facility for examination and receive appropriate assistance; the pain gradually goes away and life continues as usual. But in some cases, with such injuries, fractures, cracks or dislocations occur, which will become a sad reminder after a certain time in the form of diseases that arise as a result of them. Most often this happens after many years, when no one remembers the trauma that occurred.
What is better MRI or CT scan of the spine?
They begin to restore past events only when inflammatory and destructive diseases affecting bone and cartilage tissue have already developed and continue to develop. Also, such injuries can lead to pinching of nerve fibers located in the coccygeal or sacral regions.
The X-ray method cannot always show fractures and cracks that occurred many years ago due to the nature of the injuries themselves, while MRI can detect almost all defects of this nature. By performing layer-by-layer scanning, it will be easy for the doctor to detect old destruction and foci of inflammation.
Also, it has long been confirmed in practice that MRI of the lumbar region, sacrum and coccyx has significant advantages in terms of the information provided. Whereas computed tomography may not be able to detect certain pathologies in fresh injuries in all cases. MRI allows you to detect inflammatory processes not only in bone formations, but also in the surrounding soft tissues.
The use of this technique is effective for fresh fractures with the formation of large hematomas, as well as for dislocations accompanied by ligament ruptures.
Indirect symptoms
It is not always possible to diagnose pathological changes in the coccyx based on signs related directly to its diseases. Often, injuries or dislocations of the coccygeal region lead to a change in its position - if bent inward, it can lead to pain and disruption of the rectum, and also become a significant obstacle to natural childbirth.
Timely detection of such pathologies will allow you to avoid serious health problems in the future.
When conducting diagnostics, the doctor should pay attention not only to the organs that caused the patient’s visit, but also to the coccygeal region in order to exclude its influence on the manifestations. It is possible that painful sensations in the pelvis, caused by the coccygeal region, can be mistaken for diseases of the genitourinary system. To avoid errors when making a diagnosis, MRI of the coccyx is included in the list of recommended examinations.
Destructive and inflammatory processes
Using MRI of the coccyx, inflammatory and destructive processes are successfully detected even at the initial stages of their occurrence, such as:
- osteochondrosis;
- hernias and protrusions;
- bone tuberculosis;
- coccygeal cyst;
- vascular pathologies;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- septic destruction.
The ability to recreate the coccygeal region in three dimensions with excellent visualization of nerve endings, muscle tissue, blood vessels and spinal cord structure allows a clear understanding of the disease.
Also, MRI of the coccygeal region provides high accuracy in determining the location and size of tumors, as well as deviations to which vertebrae are subject to in normal condition. Using electromagnetic fields, clear visualization of intervertebral joints is possible. Based on reliable information, it will be easier for the doctor to prescribe the most appropriate therapy for the stage of the disease.
Oncological neoplasms
For several decades, MRI has been recognized as the most effective method for detecting tumor processes both at the onset stages and in the late stages with the spread of metastatic foci. Also, this technique allows you to examine in detail the tissues involved in the process, lymph nodes, blood vessels, assess the degree of their damage and make a prognosis for the development of pathology. Contrast enhancement is used to obtain the most accurate results.
What determines the price of tomography of the coccyx?
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2400 rub. | 2900 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) / MR angiography of cerebral vessels | 3300 rub. | 2400 rub. | 2900 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 4800 rub. | 5800 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2400 rub. | 2900 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 6500 rub. | not implemented | from 5900 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland and brain | 6800 rub. | 4800 rub. | 5800 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 8900 rub. | 11600 rub. |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 3000 to 5000 rub. | from 3000 to 5000 rub. |
What determines the cost of tomography?
Tomograph power
Applying Contrast
Personnel qualifications
Promotions and discounts
Medical centers engaged in diagnostics set their own prices for procedures. The cost depends on various factors. The most important of them is the tomograph model. The higher its inductive power, the more expensive the service. In diagnostic centers of St. Petersburg, MRI of the coccyx can be done most cheaply using open-type devices, and the best quality is possible using ultra-high-field tomographs of the latest generation 3 Tesla.
In addition, the price increases when a contrast agent is used. If, according to the doctor’s recommendation, the diagnosis should be carried out with contrast, and the patient underwent tomography without it, then the diagnosis may be made incorrectly.
| OPEN TYPE MRI | SEMI-OPEN MRI | CLOSED MRI |
The coccyx as an important component of the sacral spine
The coccyx is a small part of the spine, a kind of completion, consisting of several fused vertebrae - normally there are from three to five, with each subsequent one being smaller in size than the previous one. Because of this, the tailbone has the shape of a cone, inverted with the base up and slightly facing forward.
The muscle bundles of the anus and pelvic floor, as well as some fibers that make up the gluteus maximus muscles, are attached to it, and thus the coccyx is directly involved in the functioning of the pelvic organs and hip joints. And also when bending backwards, part of the load from the upper vertebrae is distributed onto it.
Classification of tomographs
Magnetic resonance examinations are carried out using special equipment – a tomograph. There is a wide variety of installation variations, differing in appearance and technical characteristics. Which MRI machine is most optimal for examining the sacrococcygeal spine? The choice is individual and depends on the capabilities that the tomograph provides.
The speed of research and the detail of the sections depend on the device design. Based on design parameters, there are three types of tomographs suitable for diagnosing any part of the spine:
1. open 2. closed (tunnel type) 3. vertical (multi-position).
Open tomograph
is a magnetic resonance device that does not have closed circuits. The scanning device is divided into two modules - upper and lower, and between them there is a table for placing the patient.
The demand for such devices is due to their advantages:
- Comfortable diagnosis of pathologies of the sacrococcygeal spine in patients with anxiety disorders, claustrophobia, and epilepsy.
- Examination of children in the presence of parents.
- Examination of traumatology patients who have had their limbs fixed at an angle.
- Patients with large dimensions and body weight above 120 kg.
Weaknesses of open type installations:
- An open tomograph is able to generate a magnetic field of low and medium intensity.
- The images have low and medium resolution, which makes it difficult to diagnose the early stages of pathological processes.
- Not suitable for studying cancer tumors.
Closed tomograph
– a cylindrical capsule-coil with sensors for reading and converting body impulses. A retractable table delivers the patient to the scanning chamber.
The main advantages of closed-type equipment:
- Regeneration of high voltage magnetic field.
- Detailed, high resolution and accurate projections.
- Capable of visualizing microscopic defects and significant abnormalities.
- Suitable for monitoring oncological processes.
Disadvantages of closed-type MR machines:
- The limited diameter of the tunnel and the load capacity of the retractable couch limit the ability to diagnose obese patients.
- A closed space leads to a panic attack in patients prone to claustrophobia.
- The noise of working magnets, the absence of a parent and tight spaces frighten small children.
Vertical multiposition tomograph
- a type of open type device. The tilt angle of the scanner and stage can be changed from vertical to horizontal position. Some tomographs have special devices for studying the sacrococcygeal region in a sitting position.
Advantages of diagnostics using a vertical tomograph:
- Ability to conduct functional motor tests.
- Assessment of the processes occurring during flexion and extension of the sacral part of the spine.
- Scanning for severe pain that does not allow you to remain motionless in a lying position for a long time.
- Diagnosis of early stages of osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement.
- Examination of the spine in the position where pain is greatest.
Disadvantages include the high cost of equipment and the limited number of devices in our country and neighboring countries.
| Open tomograph | Closed tomograph | Multiposition tomograph |
According to the generated magnetic field strength, tomographs are divided into:
- ultra-high-field – 3 Tesla
- high-flow – 1.5 Tesla
- mid-field – 0.5 –1 Tesla
- low-floor – 0.3 – 0.5 Tesla.
The higher the magnetic field voltage, the better the quality of the sections, but the cost of the study is higher. The ideal price/quality balance for diagnostics can be obtained by examining a closed tomograph with a voltage of 1.5 Tesla.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
Progress and stages of the examination
For those undergoing the procedure for the first time, it will be useful to know how an MRI of the tailbone is performed.
A special device - an MRI scanner - looks like a cylinder, in the center of which there is a tunnel with a built-in retractable table. The table automatically moves out of the cylinder, the patient is placed on it, the arms and legs are secured with belts, and bolsters are placed under the legs and head. Then the table slides back into the tunnel, the doctor goes into the next room and performs a scan.
The subject is warned about possible noise and knocking during the procedure. If the patient suffers from claustrophobia, an open type of tomograph is used. To communicate between the patient and the doctor, the device has a built-in microphone. Closed-type tomographs have a remote control with a button, which sends a signal in case of problems with the patient.
Diagnostic time, on average, is 30 minutes. During scanning, maintain a motionless body position.
Features of the MRI procedure in children
The problem when examining young children using MRI is to keep them still for 20-30 minutes. If such difficulties arise, sedation and the use of open tomographs are indicated. Parents stand next to the child and monitor the body position and well-being of the little patient.
An MRI scan without contrast does not have any harmful effects on a child. Medical centers perform MRI scans for children over 5 years of age. The younger age category is examined in specialized children's medical centers.
What can be seen during this diagnosis?
The coccyx is a process consisting of fused vertebrae. It is considered a vestige of a tail. The main purpose of the coccyx is to attach ligaments and muscles that ensure the full functioning of the intestines and reproductive system. This section distributes the load and promotes flexion and extension of the hip.
Many people are interested in the safety of MRI of the coccyx.
, as the study shows. Magnetic resonance imaging shows the general condition and shape of the coccyx, allows you to identify the number of fused vertebrae, study the condition of the sacrococcygeal joint, and evaluate the location and absence of displacement. Using the method, the necessary information is obtained and the following problems are identified in this area:
- consequences of injuries;
- congenital and acquired anomalies;
- development of degenerative and destructive anomalies;
- cysts, tumors, abscesses and fistulas;
- osteochondrosis, hernias, protrusions, arthrosis and spondylosis;
- vascular diseases;
- Bekhterev's disease.
#!MRTseredina!#
Computed tomogram of the coccygeal-sacral region
The bones are visualized quite well on a CT scan, but sometimes the patient is recommended to undergo a contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan. The administration of an iodine-containing drug makes it possible to better examine the architecture of blood vessels, confirm or exclude the oncological process and metastases.
The radiopharmaceutical accumulates in pathological areas, which helps to carry out differential diagnosis, identify the disease in the early stages and prescribe appropriate treatment.
There are situations when, during diagnosis, tomograms reveal areas suspicious of a tumor or its secondary manifestations. Their nature can be clarified using a series of photographs after the introduction of contrast. Considering the systematic nature of the process, in these cases, not only a CT scan of the coccyx is performed, but also a study of all the bones of the skeleton (scintigraphy).
The administration of contrast is unacceptable if the functional capacity of the kidneys is impaired (increased blood creatinine levels), allergies to iodine, overproduction of thyroid hormones, or while taking Metformin. If the endocrinologist allows you to stop the drug for several days, diagnosis is possible.
The appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth, fever, nausea are common reactions to the administration of contrast; after a short period of time, these sensations pass.
Patient position during diagnosis
The progress of the procedure must be monitored: sometimes side effects develop during contrast. The doctor carefully monitors the patient's condition, if there is a suspicion of an allergy: shortness of breath, redness, palpitations, rash, swelling, drop in pressure - appropriate medications are immediately administered.
During the procedure, you can report all alarming symptoms to the doctor: there is a special button for communication.
Computed tomography is performed only for vital indications of the following categories of persons:
- nursing women;
- children under 5 years of age (CT with contrast is not performed until 12 years of age).
In these situations, functional diagnostic specialists recommend using other methods that do not involve radiation exposure.
The study involves keeping the patient in a motionless horizontal state for up to 20 minutes. Some people may experience autonomic reactions: dizziness, weakness, sweating, etc. A light meal will help minimize the likelihood of these effects developing.
Before the examination, you need to choose loose clothing without metal parts, remove jewelry, and empty your pockets.
The radiologist should be warned about existing implants and allergies to iodine.
The doctor will give the patient a conclusion and a disk 2 hours after completion of the diagnosis. If desired, and for an additional fee, you can order the study to be printed on film. This can be done as needed; the results are stored in the database of the Magnit diagnostic center.
The patient must take into account that in most cases the final diagnosis is established based on the results of all studies. Thus, a CT scan of the coccyx will show a metastatic lesion, but will not be able to answer the questions: where is the primary tumor located, what is it like.
To verify the diagnosis, MRI of the pelvic organs, ultrasound, biopsy, etc. are additionally prescribed.
If you already have conclusions from previous studies, take them with you.
It is better to come to the Magnit diagnostic center with a referral from a doctor, which indicates a preliminary diagnosis and a specific method of examination suitable for your case.
If contrast is to be administered, the result of a blood test for creatinine is required; express diagnostics can be carried out in our center. The test will take about 10-15 minutes, so you must come for a CT scan of the tailbone with contrast with plenty of time.
Contraindications for the study
It is strictly forbidden to be even near a working tomograph for people who have:
- there are any metal objects in the body: staples, pins, dentures, plates, bullets, fragments, piercings, etc.;
- implanted electronic devices (pacemaker, electronic pump, etc.).
The examination is not recommended for women in the first trimester of pregnancy. At this time, all the vital organs of the fetus are formed, and the influence of the magnetic field on this process has not been fully studied.
A separate group includes contraindications for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- chronic renal failure;
- intolerance to drugs used for contrast.
It should be noted that there are iodine-based and gadolinium-based contrast agents for intravenous administration. If adverse effects from the administration of an iodine-based drug were previously noted, then there are no contraindications for the use of a gadolinium-containing drug.