When is an MRI indicated?
The MRI procedure is indicated under the following circumstances:
- if necessary, assess the condition of individual organs or parts of the human body (brain, jaw rows, maxillary sinuses, heart and blood vessels, pelvic organs, etc.);
- to monitor the development of malignant neoplasms, determine the presence of metastases in other anatomical units;
- in order to exclude/confirm recurrent pathology after surgical treatment of the tumor.
What kind of diagnosis is this? How does it go and how to prepare for an MRI of the brain?
This technique is based on obtaining a result thanks to an electromagnetic field emanating from atomic nuclei at high voltage. Accurate data on the state of a particular organ or area in the human body becomes possible due to the fact that the body’s tissues are saturated with hydrogen.
Information transmitted via radio waves is displayed on the monitor screen; you can obtain a layer-by-layer image, capture it and save it on a USB flash drive, disk or paper.
The advantages of MRI over other diagnostic methods are that it is non-invasive, painless and absolutely safe.
The results can be seen immediately (there is no need to wait, as with an x-ray examination, until the image is ready). It can be performed even during pregnancy and children.
What organs are examined?
The described diagnostic method is applicable to the following organs and systems:
How MRI works
- brain;
- vascular system;
- spine;
- articular apparatus;
- pelvic organs;
- soft tissues;
- abdominal organs (gall bladder, liver, pancreas, etc.).
This diagnostic method is not always applicable. MRI scans are used in cases of low information content of alternative diagnostic methods: ultrasound, x-ray.
What pathologies does MRI reveal?
The range of diagnosed diseases in the case of MRI is wide. An abbreviated list of pathologies:
- diseases of an inflammatory nature (diseases of the genitourinary system);
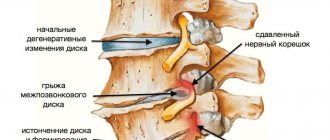
- pathological phenomena in the brain and spinal cord (diseases of the pituitary gland, spine, damage to the nervous system);
- benign and malignant tumors (in the brain, liver, respiratory organs, mammary glands, etc.);
- cardiovascular pathologies (vascular pathological processes, heart defects);
- lesions of a traumatic nature;
- infections of joints and bone tissue (osteochondrosis, etc.).
List of contraindications
Despite the fact that the described procedure is comparatively safe, there are contraindications for the examination:
- built-in pacemaker for the patient;
- implants in the ear canals;
- Ilizarov apparatus, fragments and metal plates;
- period of bearing a child (first trimester);
- mental abnormalities in the patient;
- persons in a coma or suffering from secondary serious illnesses in the stage of decompensation;
- tattoos on the patient’s body (containing metal compounds);
- body weight more than 240 kg;
- claustrophobia in the patient (if necessary, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia).
When a contrast agent is used during an examination, the list of restrictions is supplemented by an allergic reaction to the substance and severe renal failure.
Relative contraindications also include MRI for colds, runny nose, fever, cough, since such conditions can bring additional discomfort to the patient while inside the tomograph.
We should also touch upon the issue of diagnosing children. At what age can MRI be performed? There are no age restrictions for diagnosis.
If necessary, examinations are prescribed even for children under one year old, not to mention adult patients.
Types of MRI
Depending on medical purposes, there are 5 types of MRI diagnostics:
| Type of examination | Explanation |
| MRI with contrast | To clearly differentiate the tumor, the patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent. |
| MRA (angiography) | Most often, tomographic angiography is used to examine the brain, namely the blood vessels (blood flow, anatomy and functionality of the vessels are assessed). Sometimes contrast angiography is required |
| Functional magnetic resonance imaging | Using a functional magnetic resonance imaging, the areas of the brain responsible for speech, memory, and vision are assessed. During the diagnosis, changes stimulated by the functioning of neurons in the brain are recorded |
| Perfusion MRI | The technique is applicable for diagnosing the passage of blood through organ tissue. |
| MRS (spectroscopy) | The procedure is prescribed to diagnose the disease in the early stages of manifestation. During the study, biochemical changes in tissues are analyzed |
Depending on the type of study, the tomograph modes (height or brightness of the signal) also change.
Features of preparing children
Since magnetic waves are safe, the study is also performed in early childhood. Preparation rules are the same as for an adult.
The main thing is to prepare the child psychologically. The child must understand that it is important to remain calm and not move during the procedure. In rare cases, children are given sedatives or general anesthesia.
Infants are not given anesthesia, since they can be euthanized in another way, for example, by feeding them before the procedure.
If the newborn is bottle-fed, it is necessary to choose a formula that does not cause flatulence. Otherwise, the baby will move, which will lead to distorted results.
Interesting: MRI of the brain with contrast: indications and contraindications
Preparatory stage, diagnostic progress
Preparation for MRI is necessary in the case of diagnosing abdominal and pelvic organs. 3 days before visiting the doctor, the patient will have to switch to a carbohydrate-free diet; 24 hours before the procedure, the patient can eat only light foods, and should not drink coffee, tea, or alcohol.
5 hours before the MRI examination, you are prohibited from eating or drinking. Diagnosis is often carried out on an empty stomach.
If the subject has a tendency to flatulence, the patient should take a dose of activated charcoal. It is recommended to drink an antispasmodic medication 40 minutes before the event.
Examination of other parts of the body does not require special preparation. You do not need to take anything with you to the procedure (some institutions ask you to prepare only a towel).
How is the examination carried out?
The average procedure time ranges from 15 minutes to half an hour. The duration of the session depends on the volume of the body area being examined and the weight of the patient.
Once in the diagnostic room, the patient must undress (you need to undress taking into account the area being examined). They also remove jewelry and metal objects from parts of the body or remaining clothing. Then the subject is placed on a special surface and, upon a signal from a specialist, finds himself inside the tomograph tunnel.
Closed-type devices are large tunnel-shaped magnets, inside which the patient must remain motionless for the entire diagnostic period. For children, as well as people with excess body weight or claustrophobia, there is an alternative option - an “open” tomograph, the principle of operation of which remains the same, however, the device conducts the examination in an open space.
During the procedure, the specialist is in the office with the person or in an adjacent room. He manages the process: announces the beginning and end of the diagnosis, and may ask the subject to take a deep breath and hold his breath.
After the procedure is completed, the device is pulled out and the patient can get dressed and leave the office. The result of the examination, namely its transcript, is given to the patient a few hours later.
How does the procedure work?
Before the MRI, the doctor interviews the patient, looks at his outpatient card and referral. Before the procedure, you must remove all jewelry, watches, and other metal and electronic items. The patient is asked to change into clothes specially designed for the study.
An MRI scanner is a cylindrical tube surrounded by a magnet. The patient lies down on a special mobile table. Then this table slides inside the magnetic tube. There are devices that are not completely surrounded by a magnet. They will be very useful for those people who suffer from anxiety in closed spaces. For patients with excess body weight, a tomograph that is open on the sides is suitable. But all studies can be carried out in an open tomograph. All these nuances should be clarified by the doctor.
The specialist's assistant invites the patient to sit on a mobile table and secures it with bolsters and belts (you cannot move during the examination, but you can speak and hear the doctor). During magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, a cylinder containing special sensors is placed around the head.
After the patient is positioned and prepared for the procedure, the procedure begins. It lasts about forty to forty-five minutes. After the session is completed, the patient should wait a little longer while the doctor analyzes the data obtained (sometimes it is necessary to take additional images).
MRI, ultrasound, CT, radiography - what's the difference?
Let us present the distinctive characteristics of MRI from other hardware diagnostic techniques. During the MRI examination, an electromagnetic field is used.
As for CT and radiography, this method differs from the previous one because it is carried out using x-rays. However, the two methods have a common goal - to allow a specialist, after decoding the data, to evaluate a photo of an organ section with a certain step.
Magnetic resonance imaging most reliably assesses the condition of soft tissues, while CT helps detect metastases and calcifications.
During radiography, one-sided transillumination of bones, heart, respiratory organs, etc. occurs. The disadvantage of this method is the likelihood of distortion of the result due to shadows from other organs - they cover the desired area.
The ultrasound process uses ultrasound radiation, which is reflected from tissues with varying degrees of intensity. Large images of organs are visualized on the screen. The method is less informative, but the safest.
The most harmful diagnostic method
Advantages of MRI in medical practice
The diagnostic method under consideration is applicable when examining soft tissues and joints. The technique is used to identify diseases of the back and spine, and brain pathologies. The same technique is used in oncology, angiology and other medical fields.
Benefits of the procedure
The advantages of MRI are expressed in the following characteristics:
- exclusion of radiation exposure (which cannot be said about computed tomography);
- diagnosing cancer in the early stages with a high degree of accuracy;
- the ability to take high-quality images of sections without the use of a contrast agent;
- demonstration of not only structural elements, but also a number of functional indicators (blood flow speed, brain activity, temperature of internal organs, etc.);
- examination of pregnant women.
Disadvantages of the technique
Among the disadvantages of the described diagnostic method:
- duration of the procedure. For this reason, MRI diagnostics is excluded in emergency clinical cases (hemorrhages, serious injuries, violation of the integrity of great vessels, etc.);
- low information content when diagnosing bone tissue. CT is used as an alternative method in such cases;
- the need for the patient to remain motionless throughout the entire procedure. This fact complicates the process of examining children, when working with whom anesthesia is often used;
- high cost compared to other hardware diagnostic methods.
Indications for use
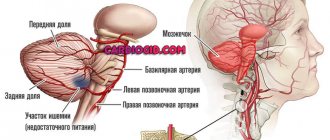
In order to conduct an effective diagnosis and identify existing abnormalities and pathologies, it is recommended to undergo tomography of the blood vessels of the brain and neck. This will give a complete picture of the condition of the patient’s veins and arteries. What does cerebral vascular tomography show?
- Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease;
- encephalopathy;
- tumors of various types;
- stroke and predisposition to it;
- atherosclerosis;
- obstruction of cerebral vessels, thrombosis;
- meningitis, abscess;
- previous heart attack;
- spasms in the arteries;
- hearing loss with speech impairment, damage to the patient’s hearing;
- deterioration of blood flow;
- suspicion of hemorrhage, etc.
To diagnose cerebral vessels, the indications (complaints) should be as follows:
- systematic headaches, dizziness;
- noise and ringing in the ears;
- frequent causeless loss of consciousness;
- nosebleeds of unknown origin;
- partial or complete memory loss;
- epilepsy;
- sudden surges in pressure (arterial hypertension);
- disturbance of consciousness;
- preoperative diagnosis – when it is planned to perform a neurosurgical operation.
Place of diagnosis, cost
You can undergo magnetic resonance imaging in a private center or in a large medical center in the city (regional hospital, specialized institutions).
The price of the procedure differs from the cost of x-rays and ultrasound and does not differ so much from the price of computed tomography. The cost of services depends on the area being examined (MRI of veins in the legs will cost more than a neck examination), as well as the pricing policy of the center. The average cost of diagnostics is 4,000 rubles (in Moscow).
How is an MRI of the spine done for children?
Since MRI does not carry radiation exposure and does not pose any threat to health, the study is performed on children from birth. For young children, tomography of the spine is performed according to strict clinical indications and, most often, under anesthesia to ensure immobility of the little patient. In this case, consultation with an anesthesiologist and his presence during diagnosis are required.
For children over three years of age who can lie motionless on their own for a long time, an MRI of the spine is done without sedation. Often the examination is carried out on an open apparatus to ensure the baby’s peace of mind - parents can hold the child’s hand and talk to him.
Patient reviews
The majority of patients undergoing diagnosis respond positively to the procedure. In some cases, patients note that they needlessly felt a sense of fear before the examination. Some patients found it difficult to stay in confined spaces for long periods of time. Others noted the unpleasant noise made by the device. No one described any fundamentally unpleasant sensations from the examination.
MRI diagnostics are relatively safe for health and informative. The technique helps to assess the condition of internal organs and monitor the functioning of anatomical structures. The advantage of the method is the elimination of radiation exposure to the patient’s body. This diagnostic method detects tumors in the early stages of their development.
Variation of MRI provides broad diagnostic capabilities, surpassing other hardware techniques in a number of indicators. Among the disadvantages of the procedure, in addition to its high cost, are its duration, difficult diagnostics in children, and low information content when examining bone structures. In any circumstances, the advisability of MRI should be judged by a specialist.