Chronic headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, nausea - harmless symptoms? Alas. Serious diseases may be hidden behind them. To exclude pathology, you need to check the vessels of the brain and neck. Let's consider the most modern, informative and safe methods. Let's figure it out and decipher all these abbreviations for the names of diagnostic procedures.
When and why are these examinations prescribed?
Comprehensive studies of the intracranial vessels of the brain and neck are not indicated for all people with neurological complaints. They are prescribed by a doctor who first talks with the person, finds out the history of the disease and checks the indicators of past diagnostic procedures.
Diagnostics using instrumental methods is used in the following cases:
- the patient complains of dizziness, frequent headaches, sclerosis, migraine attacks;
- previous injuries to the cervical spine or head;
- the appearance of tinnitus, persistent hearing or vision impairment;
- frequent nosebleeds without identified causes;
- history of frequent fainting;
- clinical signs of chronic cerebrovascular accident, including after a stroke;
- parkinsonian symptoms in the form of hand tremors, gait disturbances, etc.;
- the attending physician suspects an arterial aneurysm or malignant neoplasm;
- encephalopathy of unknown cause;
- reduced performance.
In such conditions, the patient can check the blood vessels of the head free of charge, under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
The specific examination method is chosen by the attending physician, since each procedure is used to solve a specific diagnostic problem.
Commonly Used Methods
There are rare signs of health problems, the appearance of which a person does not pay attention to.
In hot weather, I lost my balance and had a severe headache - it’s okay, it will pass, it’s because of the heat. I stood up sharply, “spots” flew in front of my eyes - that’s okay too, I had to get up more slowly. The pressure has risen - of course it will rise, the weather is changing so quickly. There are explanations and justifications for everything, but any of these signs may indicate a serious pathology. If you experience the following symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- The headache is constant and getting worse.
- Vision, speech, hearing deteriorate, and there are incidents with complete loss of these functions.
- Thought processes, memory, and attention are disrupted.
- Coordination of movements changes, loss of balance and the appearance of a shaky gait are possible.
- Convulsions appear.
- The person loses consciousness or experiences a faint state.
- Intracranial and blood pressure changes.
- “Floaters” appear before the eyes.
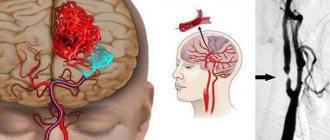
These symptoms indicate pathology of the cerebral vessels. To exclude it, a hardware medical examination may be prescribed. It includes both the basic procedure for checking vessels for patency (called angiography), as well as ultrasound, rheoencephalography, and electroencephalography.
These methods are used to clarify traumatic brain injuries, neck injuries, stroke, neoplasms, diseases accompanied by inflammation of the brain, thrombosis, and atherosclerosis. A head examination is performed before or after vascular surgery.
Depending on the pathology, either one type of study or several may be prescribed. Many methods have limitations, so they are prescribed when absolutely necessary.
Diagnosis of brain diseases using CT is based on calculating the intensity of penetration of X-rays through brain tissue. Thus, it is possible to obtain their detailed cross-sectional image. Modern devices for computer diagnostics have a low level of radiation, which does not affect the accuracy of the results.
Such a brain examination may be prescribed if the patient has a history of:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions;
- strokes;
- speech and memory disorders;
- auditory and visual impairments.
This method of diagnosing brain pathologies is contraindicated for children and pregnant women. If intravenous administration of a contrast agent is necessary, the following are added to the list of contraindications: renal and liver failure, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, asthma, thyroid pathologies, allergic reaction to iodine.
CT scan does not require special preparation of the patient. Unless before the procedure with contrast, you should not consume food or liquid for 4 hours. The examination lasts from 15 minutes to half an hour. At this time, the person is on a movable table, which moves into the tomograph. The patient is not allowed to move, and sometimes will need to hold his breath at the command of the medical staff.
It’s not for nothing that in foreign films about the work of medical institutions, doctors constantly refer patients to MRI – today it is one of the leaders among brain research methods. Visualization of the state of the organ occurs thanks to the magnetic field constantly maintained in the tomograph. Electromagnetic waves are passed through it, the energy flow from which is repelled by hydrogen atoms, which are present in all cells of the human body. Computer equipment converts the data into images of brain tissue.
MRI is effective for diagnosing a wide range of diseases: from vascular pathologies to tumors.
Examination with a tomograph is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the patient is mentally unstable, has acute pain syndrome or is in a coma;
- The patient’s body contains metal and ferromagnetic implants, pins, clips on blood vessels, and permanent crowns on teeth.
- The patient's skin has tattoos made with paint containing metal particles.
As with a CT scan, for the examination a person must lie down on a movable table, where his body will be secured with special belts, and sensors that send and read a signal are attached to his head. Afterwards the table moves into the tomograph. Depending on the number of programs used for scanning, the duration of the procedure is 15-40 minutes. All this time the person must lie motionless.
The principle of using a low-frequency electromagnetic field makes MRI completely safe for children and adults.
This technique for studying the brain is based on the same principles as MRI, but its main task is to identify pathologies of the vascular bed. Modern equipment is designed to obtain a three-dimensional image of the entire network of brain vessels, as well as to isolate thin sections of individual vessels and nerve trunks.
Using this method, you can examine the brain in order to record in a three-dimensional projection all the functional processes occurring in it. Analysis of the metabolism of brain structures occurs at the cellular level, therefore PET is the best way to distinguish benign from malignant neoplasms in the early stages.
You should not eat 4-6 hours before the procedure. It is recommended to have a protein-free dinner the night before. Part of the examination is the intravenous administration of a radiopharmaceutical. The scanning itself lasts 30-75 minutes.
Indications for examination are:
- frequently recurring headaches, migraines, dizziness;
- sharp deterioration of vision, hearing, tinnitus;
- nosebleeds in the absence of injury;
- frequent fainting with short loss of consciousness;
- tremors of the hands and head in Parkinson's disease;
- previous cerebral infarction, signs of impaired arterial blood flow (chronic ischemia);
- head and cervical spine injuries;
- symptoms indicating the presence of neoplasms, vessel aneurysm;
- encephalopathy (reduction in the volume of nervous tissue and impaired brain function against the background of another pathology);
- arterial and intracranial pressure.
Today, there are several ways to check blood vessels, but the most accurate and informative are magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. However, due to the complexity of the equipment and the lack of highly qualified doctors in small towns, the examination is carried out only in a few specialized clinics and is quite expensive. The demand for MRI and CT scans not only in the head and neck area, but also in the entire body is steadily increasing, and the cost is gradually decreasing.
In addition to magnetic resonance and computed tomography, Doppler ultrasound and rheoencephalography are most often used as accessible but informative methods. Checking the blood vessels of the brain and neck is carried out free of charge upon doctor's prescription in all clinics of large cities.
Examinations are:
- Non-invasive (without penetration into the body).
- Invasive (angiographic), when a contrast agent is injected into the patient’s artery to scrupulously examine the smallest details and structures in the affected area. Angiography is used for X-ray examination, ultrasound, MRI and CT.
Doppler ultrasound is a technique based on the Doppler effect. Its essence is that high-frequency ultrasonic waves directed at the study area are reflected from moving blood elements and converted on the device screen into a two-dimensional image that characterizes the condition of the blood vessels.
Doppler ultrasound allows you to check the main arteries (vertebral, carotid, basilar, subclavian) and veins (anterior and internal jugular, subclavian), which are located in the neck and at the base of the skull. Ultrasound ultrasound determines:
- patency (lumen diameter), degree of narrowing (stenosis), blockage, elasticity and damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- aneurysms;
- speed and state of blood flow (hemodynamics);
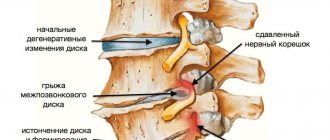
- the presence of a change in direction (tortuosity) caused by damage to the intervertebral discs and other spinal tissues.
Doppler ultrasound is widely used because it is informative, harmless and does not require patient preparation. Contraindications include severe health conditions and the patient’s inability to lie down.
A method of checking the vessels of the head, based on recording changes in the degree of resistance of blood and brain tissue when a weak high-frequency electric current flows through them, is called rheoencephalography. Metal electrodes are placed on the patient's head, secured with rubber bands, and current is passed through them.
REG informs about tension, elasticity, blood filling of blood vessels, viscosity and speed of blood movement through the arteries and veins of the brain. It is used for traumatic brain injuries, concussions, ischemia, strokes, and encephalopathies. The method is especially often used to determine the severity of atherosclerosis in older people, to control cerebral circulation after surgery, and for headaches and dizziness.
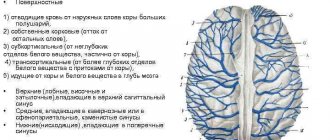
The method is based on the interaction of a magnetic field and radio frequency pulses, which results in electromagnetic oscillations. Reflecting from the internal organs of a patient placed in a closed tomograph chamber, they form an image on the monitor screen. The device scans the area under study layer by layer and forms a three-dimensional image. The method allows you to clearly and in detail consider:
- the structure of the circulatory network, all large and small vessels;
- inflammation of brain tissue, nerves;
- aneurysms, blood clots, neoplasms, areas of hemorrhage during a stroke;
- intervertebral hernias and other lesions of the spine and spinal cord.
Rheoencephalography (REG)
REG is a method that allows you to record the electrical resistance of tissues, pulse fluctuations and analyze them. The procedure can be performed using a special device in a functional diagnostics room, available in most medical institutions.
Patient photo
Rheoencephalography is indicated for people with the following conditions:
- signs of acute or chronic disturbance of cerebral blood flow;
- migraine without an established cause;
- past traumatic brain injury;
- the presence of epileptic seizures in adults and children.
The procedure does not require special preparation and has no contraindications. However, the use of REG in patients with tremor of the head and hands is not always advisable, due to the appearance of interference created by movements.
On average, rheoencephalography costs about 600 rubles, but the price can reach up to 3-4 thousand when functional tests are carried out simultaneously.
MRI
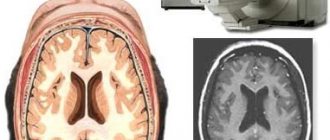
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is a procedure that provides detailed information about the structure of the brain. The detail of the resulting image of the central nervous system structures depends on the power of the devices used - the greater the power of the tomograph, the more detailed and higher the detail.
Doctors recommend performing an MRI if the patient has neurological symptoms, as well as frequent headaches.
It is important to note the contraindications: inadequate mental state of the person, lack of consciousness and the presence of metal implants in the body (vascular clips, pins, etc.). For all other patients, the procedure is safe and informative.
People suffering from claustrophobia are not very comfortable doing this examination.
The patient does not need special preparation. Checking the condition of blood vessels using MRI takes from 15 to 45 minutes. During the entire study, the patient should not make any movements or change body position. You are allowed to talk, close your eyes and swallow saliva. Upon completion of the MRI scan, the doctor joins the work - he evaluates the resulting volumetric image and layer-by-layer sections of the brain on a computer display.
How much it will cost to check blood vessels using MRI depends on the type and power of the equipment used. The average cost is about 4,500 rubles with fluctuations from 3 to 8 thousand.
How to choose a research method
How to check the brain and its blood vessels depends on the diagnosis made by the doctor. The choice also depends on the degree of equipment of the institution. Ultrasound devices have lower cost and operating requirements, so ultrasound is often the main method. MRI, PET, CT machines are expensive equipment that not every clinic can afford.
Many diseases are diagnosed using ultrasound, and often there is no need for other studies. If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, an MRI or CT scan is prescribed to obtain layer-by-layer images if the pathological focus cannot be determined using ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is the most common procedure, characterized by its affordable price and harmlessness. In cases of cancer that does not cause symptoms and is discovered by chance, a PET scan will be required to determine the stage of the disease.
The PET procedure is expensive - the average cost is about 17,000 rubles; for tumors it is combined with MRI diagnostics, which will additionally cost about 5,000 rubles. When diagnosing neurosurgical pathologies, MRI is indispensable; it is extremely difficult to determine the exact location of hematomas and other formations without this study. CT is most often performed for traumatic brain injuries, damage to large vascular trunks, and before craniotomy. Its cost is on average 4,000 rubles.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is actively used in various fields of medicine to assess the condition of internal organs, the patency of blood vessels and veins, and detect plaques in them. The following types of ultrasound are used to study cerebral vessels: Dopplerography and sonography.
Patient on ultrasound
Dopplerography (duplex scanning)
The Doppler method, based on the Doppler effect, allows you to study the speed of blood flow in the brachiocephalic arteries that supply blood to the brain, as well as identify the presence of obstacles to normal blood circulation. The procedure is prescribed if a person has dizziness, constant headache, sensation of noise and changes in sensitivity on the skin of the face and body. There are no contraindications.
Before the examination, the patient does not need to undergo special preparation. The only recommendation is to exclude foods and medications that affect blood flow in the vessels one day before the test. If Doppler sonography is performed on a child, he must remain at rest during the entire procedure.
Transcranial Doppler scanning can be done in most clinics and hospitals. The average price for one study is 1-1.5 thousand rubles. However, depending on the equipment used, the cost can be either 600 or 4000 rubles.
Sonography
Ultrasonography, unlike Dopplerography, does not allow one to know and evaluate the speed of blood supply in the cerebral vessels. This procedure is aimed at studying the general characteristics of the vascular bed: the location and direction of the arteries, shows the presence of any structural abnormalities (aneurysmal dilatation, wall dissection, etc.), and also reveals the presence of obstacles to blood flow in the form of blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques.
The method can be used in all people with symptoms of impaired cerebral circulation. There are no contraindications. No special preparation is required either. The cost of the procedure is from 500 to 1000 rubles.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
The procedure is so called because it involves studying the electrical activity of the brain.
This method is used to diagnose epileptic activity (seizures) and identify:
- inflammatory pathologies in the central nervous system;
- organic brain diseases;
- tumor neoplasms;
- complications after traumatic brain injury;
- changes in the functioning of blood vessels (spasms, low patency).
During this procedure, something like a cap consisting of sensors on suction cups is put on the patient’s head. Next, he will begin to see something like flashes, lights and stars before his eyes.
One of the features of the procedure is the ability to obtain a full encephalogram even if the patient is unconscious.
Contraindications for the study are as follows:
- open skin wounds in the area where the electrodes are supposed to be placed;
- mental illnesses in the patient that interfere with his adequate behavior.
Infants undergo a special type of screening - neurosonography (NSG).
The cost of the study in most clinics reaches 1-2 thousand rubles. But if there are indications for electroencephalography, its implementation is compensated by the financial resources of the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
Differential diagnosis
When a patient experiences ailments in the neck and head, headaches, sleep disturbances, and gait instability, he consults a neurologist who, in the absence of contraindications, prescribes a study using one of the listed methods. After scanning and taking instrument readings, the specialist who performed the procedure interprets the images and gives the result to the patient.
Based on the information received, the neurologist diagnoses brain diseases and prescribes treatment. If difficulties arise in making a diagnosis, he will refer you for a repeat examination of a higher level - contrast CT or MRI, which will allow you to see the affected area structurally and clearly.
Due to the fact that headache can have a large number of symptoms, it is imperative to carry out a differential diagnosis. For each doctor, the main task is to determine the connection between a specific headache and a specific disease. You need to understand that there will be no benefit in treating an exceptional symptom.
We present to you the sequence of all necessary examinations:
- The first step is to interview the patient. It is important for the doctor to find out the duration of pain, their sequence, nature and location of pain. It is also important to find out the patient’s body’s reaction to taking analgesics. Often, most people cannot describe such pain when they first see a doctor with such a problem;
- After the general survey is completed, doctors prescribe certain tests that need to be completed in the near future. But it is important to choose the right diagnostic measures so that the patient receives his course of treatment faster.
Angiography (CT and MR)
Angiography is an x-ray research method that allows you to visualize the blood vessels of the brain by introducing contrast agents into them. The image itself is obtained using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
In medicine, there are several types of procedures:
- general (introduction of contrast into the main blood vessels makes it possible to evaluate the entire vascular bed);
- selective (a single basin is studied, for example, the carotid arteries or vertebrobasilar);
- superselective (a specific small cerebral vessel of small diameter located in one of the pools is subject to study).
Standard angiographic examination, associated with conventional X-rays, is being actively replaced by methods using CT and MRI. This allows you to improve the quality of the resulting images, obtain a three-dimensional map of the brain vessels, and, in addition, such studies are safer for patients.
Angiography is performed in the following situations:
- suspicions of the presence of arteriovenous malformation and vascular aneurysms;
- the need to assess the degree of narrowing of the artery lumen due to its stenosis or blockage by a blood clot;
- studying the structure of the vascular bed near the tumor for planning surgical intervention.
The list of contraindications for angiography is quite extensive:
- individual intolerance or allergy to the X-ray contrast agents used;
- The CT procedure is contraindicated during pregnancy due to the presence of ionizing radiation;
- mental disorders that interfere with maintaining a still body position during angiography;
- acute infectious or inflammatory process in the body;
- disruption of the hemostasis system.
CT and MRI angiography require patient preparation for the study. The attending physician must exclude all contraindications by examining the patient and conducting laboratory blood tests. One day before the procedure, an allergy test with a radiocontrast agent is performed. During the diagnostic test, the patient must remove any metal jewelry.
The cost of angiography can reach 15-20 thousand rubles. The average price for the procedure is 7-9 thousand, taking into account the use of radiocontrast agents.
Brain Research Methods
Modern technologies make it possible to see pathologies and conduct a brain examination using several techniques that provide wide visualization capabilities:
Neurosonography
Ultrasound diagnostics is considered a reliable and harmless method that allows identifying brain pathologies, assessing disorders occurring in the cranium, the extent of their distribution and localization. With an ultrasound scan, the doctor can identify congenital diseases and defects in the development of brain structures. Ultrasound waves can only pass through soft tissue, so neurosonography is performed on children in the first year of life, until the fontanelle closes.
Children need to undergo examination:
- Premature.
- Born with underweight.
- With a skull of unusual shape and size.
- Those who have suffered oxygen deprivation in the womb or during childbirth.
- With birth trauma.
- With convulsions, delayed psychophysical development, muscle tone.
The procedure lasts no more than 15 minutes. This is enough to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment for a small patient.
Rheoencephalography
REG of cerebral vessels is a non-invasive examination that allows you to assess the condition of cerebral vessels, their tone, elasticity, and obtain information about vascular resistance and the amount of blood supply in the periphery. A neurologist may prescribe an REG to a patient if:
- Impaired coordination.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Head injury.
Such an examination is considered safe, highly informative, and painless. With its help you can find out the state of brain structures:
- Determine the level of vascular tone.
- Assess the rate of blood outflow.
- Determine blood viscosity.
- Detect cerebral circulatory disorders.
- Assess pulse blood supply.
Special electrical sensors are attached over the entire surface of the subject’s head, which are secured with a rubber band. Before the procedure, a person should not worry, drink caffeinated drinks, or smoke. Your doctor may temporarily stop you taking certain medications that affect vascular tone.
Scintigraphy
A modern diagnostic procedure based on the introduction of radioactive isotopes into the patient’s bloodstream with subsequent recording of their radiation. Such fixation, carried out by special detectors, allows one to obtain a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image of the vascular bed and the brain tissue located next to it.
This technique is used to identify the location of ischemic lesions in the brain and assess the degree of blood flow in the central nervous system in the presence of neurodegenerative diseases in elderly people. In addition, scintigraphy is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation measures for these conditions. Contraindications include childhood, pregnancy and allergic reactions to the radiopharmaceuticals used.
Preparation for the study consists of eliminating medications that affect vascular tone 3-4 days before the procedure, as well as conducting an allergy test for radiomedicine.
The average cost of scintigraphy of cerebral vessels is 6-9 thousand rubles. Depending on the specific type of procedure, its price may vary.
Procedures for examining the cerebral arteries are widely available in most medical clinics. Their correct use to check the condition of cerebral vessels is the key to prescribing effective treatment. The choice of a specific examination method and interpretation of its results is made only by the attending physician.
Author of the article: Yulia Dmitrieva (Sych) - In 2014, she graduated with honors from Saratov State Medical University named after V. I. Razumovsky. Currently working as a cardiologist at the 8th City Clinical Hospital in the 1st clinic.
Secondary prevention of stroke
Aimed at preventing recurrent stroke and speeding recovery of the body after illness. Includes primary prevention in combination with complex drug therapy. Main groups of drugs:
- Nootropic drugs - improve the activity of brain cells (Aminalon, Glycine, Piracetam, Pyritinol, Ginkgo Biloba, Pantogam).
- Beta-adrenergic blockers (Atenolol, Metoprolol).
- Calcium antagonists - restore heart rate, reduce blood pressure (Verapamil, Nifedipine).
- Antiplatelet agents – reduce the likelihood of developing blood clots (Cardiomagnyl, Aspecard)
- Sedatives - to reduce irritability and nervousness (Fitosed, Novopassit, Persen).
Drug therapy can be combined with traditional methods of treatment: taking herbal decoctions, chamomile tea, pine cones, valerian roots, mint, lemon balm, immortelle, birch buds.
The brain and blood vessels can be examined using several diagnostic methods. The choice of research method is selected by the attending physician depending on the patient’s complaints, preliminary diagnosis, and the presence of contraindications. The safest method of examination in children is neuronosography, which does not require anesthesia or sedatives. The method is allowed for babies from birth.