Home » Methods » MRI or EEG of the brain – which is better and how to make a choice?
March 17, 2020 Methods
Electroencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging are most often used to diagnose brain diseases. These methods have different indications and are not interchangeable. Which is better to choose - MRI or EEG of the brain - depends on the goals and condition of the patient. The decision is always up to the doctor, but patients should know what the features of the methods are.
The main differences between EEG and MRI
Compared to EEG, MRI is a new method in examining the brain. Since the invention of the tomograph, diagnostic capabilities have expanded, each method began to be prescribed depending on the disease.
Let's look at the features of each method:
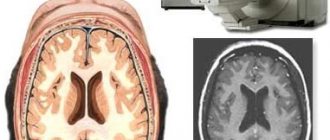
- MRI is based on the influence of a magnetic field that interacts with hydrogen atoms in the body. They change its potential, special sensors of the device capture the signal and convert it into an image. The images show brain structures and pathological formations. During the procedure, the patient is in the capsule of the device; it is prohibited to make the slightest movements, which will reduce the quality of the image.
- The EEG of the brain is different in that it is a graphical representation of its activity. These values are read by sensors in a special helmet that are sensitive to weak electrical signals from neurons. The procedure takes a few minutes, and you can make small movements during the examination. The main condition is emotional stability; if it is violated, incorrect results are obtained.
From the comparison it is clear that MRI differs in that it shows organic brain damage, while EEG shows physiological processes.
MRI
During magnetic tomography, the doctor analyzes the image and, after the encephalogram, deciphers the graph.
How does electroencephalography differ from magnetic resonance imaging of the brain?
Magnetic resonance imaging and electroencephalography are two common methods for examining the brain. These are two different diagnostic procedures. They differ not only in the principle of operation, but also in what pathologies can be detected as a result of their implementation. Let's find out which is better: EEG or MRI of the brain.
Comparison of operating principles
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the active response of hydrogen atoms to radio frequency radiation under conditions of a high or ultra-high magnetic field. The human body is mostly made up of water, with each molecule containing two hydrogen molecules. Therefore, it is clearly “visible” by the tomograph.
By registering responses from different areas, the computer converts them into a graphical form of information and assembles a single picture from them. It clearly shows all the structures of the brain and its blood vessels. Hard tissues—the skull—are less visible. This is due to the fact that bones contain fewer hydrogen atoms than soft ones.
When an ultra-precise picture is required to diagnose pathologies, the doctor - an MRI specialist - injects the patient with a contrast agent. It is based on gadolinium, which actively responds to the influence of a magnetic field.
To perform an MRI of the brain, the patient is placed on the machine table and pushed into the tunnel. If necessary, his head is first fixed and a sedative is administered: he must lie motionless inside the tomograph.
The scanning time is about 30 minutes, if with contrast - about an hour.
The procedure is painless, but not very pleasant psychologically, because the patient has to stay in a small and confined space for a long time.
The principle of operation of electroencephalography is based on the capture of electrical impulses in the brain by a special device. After all, it is with their help that the nervous system transmits signals along the nerves.
To conduct an EEG, a helmet with suction cups sensitive to electrical impulses is put on the patient's head. The examination time is only a few minutes. Diagnostics are carried out in an open space; complete immobility is not required.
But there is an important condition - the patient’s emotional calm. Otherwise, the device will give an incorrect idea of the functionality of the brain.
The way EEG and MRI obtain information about the state of the brain is different, and therefore these studies show different results from each other.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to visualize the structure of the organ, identifying pathological areas. Experts make a conclusion based on studying photographs taken from different points and in different planes. MRI helps to create a three-dimensional image and show layer-by-layer slices for a detailed examination of the area of interest of the head.
The result of electroencephalography is a graph - an electroencephalogram of electrical oscillations, displaying the activity of neurons in the brain. It is written down on paper, which is subsequently examined by the doctor. This means that EEG differs from MRI in that it allows us to detect not structural, but functional disorders of the brain.
Diagnostic value analysis
MRI and EEG reveal different, complementary information. Therefore, their indications are different. Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed in the following cases:
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Having had a stroke or heart attack;
- Suspicion of brain tumor and metastasis;
- Symptoms of demyelination and degeneration of brain tissue;
- Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis;
- Vascular examination (MR angiography);
- Postoperative control.
MRI can detect the following brain pathologies:
An encephalogram is done in cases where it is necessary to identify the functional state of the brain. EEG indications include neurological disorders:
- Insomnia and frequent awakening during sleep;
- Headaches, dizziness;
- Panic conditions and nervous system disorders;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Stuttering;
- Autism;
- Recovery period after a stroke.
An encephalogram of the brain helps to identify:
- Foci of epileptic seizures;
- Cause of hypertension and hypotension;
- Causes of disturbed sleep;
- Mental disorders;
- Psychopathic reaction.
EEG makes it possible to determine brain areas in which there are obvious disturbances. If the examination does not help make a diagnosis, then it may be the basis for prescribing an MRI, CT or MSCT.
But unlike MRI, an electroencephalogram shows whether the patient is faking his condition or whether he is really sick.
This cannot be determined during MRI, despite the fact that both research methods are accurate.
Review of contraindications
Each research method has contraindications. For EEG this is:
- Damage to the scalp (absolute contraindication);
- Violent patients. This is a relative contraindication: an EEG can be done if a sedative is administered.
For MRI this is:
- Pregnancy in the first trimester;
- The patient's body weight is above 130 kg;
- Metal structures in the study area. We are talking only about steel; titanium and other metals that are not ferromagnetic are not contraindicated;
- Gadolinium intolerance (with contrast-enhanced MRI);
- Claustrophobia and other mental disorders in which the subject cannot lie without moving (in this case, the patient can be given a sedative);
- Having a pacemaker or device installed in the middle ear (the only absolute contraindication of all).
It can be seen that in case of a traumatic brain injury, one can only undergo examination with a tomograph, while in the presence of a pacemaker, only an EEG can be done. Electroencephalography also does not cause attacks of claustrophobia. Another advantage of the method is the absence of weight restrictions, since the patient will not be on a table, but on a regular chair or couch.
Both methods do not require preparation for the study, but with the caveat that the patient must come to the EEG in a good mood and well-rested. Otherwise, the diagnosis may give incorrect results.
Pregnancy is not a contraindication for MRI and EEG, since human organs do not receive radiation during diagnostic procedures. Both methods are safe for both mother and baby.
Diagnostic cost comparison
EEG and MRI are paid diagnostic procedures, as they are carried out using innovative, expensive equipment. Let's look at the prices offered by clinics for brain research:
- EEG – from 1600 to 5700 rubles, depending on the newness of the equipment and the reputation of the clinic.
- An MRI costs an average of 5,000 rubles, and when examining the blood vessels of a person’s brain or detecting tumors, MR diagnostics can cost 7,000-8,000 rubles, depending on the amount of contrast agent administered.
- An EEG and MRI with the administration of a sedative will cost 2000-6000 rubles more.
- The cost of the procedures will increase by another 500-1000 rubles if the results of the study are recorded on electronic media (disk, flash drive).
The legislation provides for some cases for free EEG and MRI under the compulsory medical insurance policy. In other situations, the patient pays for the procedures.
There are many methods for diagnosing brain diseases, so the question is which is more effective: MRI and EEG. This is a case where there is no clear answer, because these studies are designed to study the organ from two different “sides”.
Electroencephalography will accurately identify functional capabilities and only suggest the presence of pathologies in different brain structures. And magnetic tomography accurately diagnoses the localization of brain tissue damage: the presence of a tumor, necrosis, inflammation. But tomography only suggests the presence of mental and cognitive disorders.
Thus, these are two procedures that do not replace, but complement each other.
Source: https://diagme.ru/mrt/golova-i-sheya/eeg-ili-mrt
Information content of methods
When neurological symptoms appear, the doctor chooses between two methods depending on the disease.
Each diagnostic option is informative for some pathologies and irrelevant for others.
MRI helps identify:
- injuries;
- hemorrhages;
- circulatory disorders;
- sclerosis of nervous tissue;
- vascular damage and abnormalities;
- local inflammation;
- brain tumor.
Signs of the listed conditions are visible in the images; to increase the information content, a contrast study is carried out.
The diagnosis of the disease is made on the basis of the destruction of nervous tissue or blood vessels, its thickening or hypoplasia.
EEG is prescribed for long-term physiological disorders; emergency research is rarely performed. Based on the resulting graph, disorders of brain activity in certain areas are calculated.
An encephalogram will help in diagnosing:
- epilepsy;
- hypertension;
- mental disorders;
- sleep disorders.
Oncology and stroke are determined by indirect signs of EEG. In this case, an MRI is more informative, but if it is impossible, an encephalogram is taken.
Review of contraindications
Despite the fact that in some cases only the types of research described will be able to identify the cause of the disease, there are a number of reasons why they are strictly prohibited. Before prescribing, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient to clarify possible contraindications.
Magnetic resistance tomography cannot be performed if the patient has:
- electronic middle ear implants;
- pacemaker;
- hemostatic clips in cerebral vessels;
- metal implants in any part of the body;
- Ilizarov apparatus;
- tattoos that were applied using metal-containing dyes;
- excess body weight. There are restrictions on the weight that the tomograph table can support.
If there are foreign bodies in the patient’s body, then before performing a tomography it is required to provide a certificate for the material from which they are made.
There are conditions when the procedure is undesirable, but, if absolutely necessary, it is still possible. Such conditions include claustrophobia, the first trimester of pregnancy, the patient’s inadequate psycho-emotional state (alcohol, drug intoxication, panic attack), and the patient’s serious condition.
EEG has no absolute contraindications, but the procedure can be difficult due to the presence of open wounds on the head, mental disorders that provoke an imbalance in the emotional state.
Advantages and disadvantages of methods
Both methods are safe and are carried out repeatedly to make an accurate diagnosis.
But each option has positive aspects and disadvantages - let's talk about them in more detail.
MRI
We list the advantages and disadvantages of magnetic tomography:
- Advantages - a powerful device provides a detailed image of the scanned area. This helps to identify the pathological area and assess the condition of surrounding tissues and blood vessels.
- Disadvantage - the study is carried out only in the diagnostic room, time is limited. The tomograph does not show foci of excitation, procedures are prohibited for pregnant women, the presence of braces, metal crowns, a pacemaker, and an insulin pump.
EEG
Pros and cons of EEG:
- Advantages include bedside testing. The procedures can be carried out over a long period of time and a sluggish pathology can be recognized. The device shows neural activity.
- Disadvantages - the doctor does not see tissue structures, there is an error in determining the lesion. Minor pathological changes go unnoticed.
Limitations to the study
First, we note general contraindications for EEG or MRI of the brain:
- Severe head injury - if soft tissues are damaged and there is bleeding.
- Mental disorders and intoxication - in this case there is a risk of inappropriate behavior of the patient, interruption of the procedure or damage to equipment.
EEG no longer has any contraindications, the method is safe and is carried out according to the protocol.
MRI has a wider list of restrictions - the study is prohibited in the following conditions:
- first and third trimesters of pregnancy, lactation;
- braces, metal crowns;
- a pacemaker in the body or an insulin pump;
- contrast intolerance;
- severe obesity;
- claustrophobia.
The last contraindication is considered relative; with minor claustrophobia, the study is carried out if the patient is able to overcome fear.
Which is safer for pregnant women?
Pregnancy is not a contraindication for MRI and EEG. They are harmless to women and their unborn children. The only caveat is that MRI is not recommended in the first trimester, unless there is a real threat to life. This is due to the fact that fetal organs are being formed at this time, so there is a risk that the examination will adversely affect this process.
In early pregnancy, it is potentially dangerous that the amniotic fluid heats up during the distribution of impulses. So electroencephalography is preferable.
MRI and EEG are effective types of examination for diagnosing brain diseases. They are complementary, therefore they allow us to draw up a comprehensive clinical picture, study the anatomy of the central nervous system and the mental state of a person.
Tags: EEG
Diagnostic prices
The cost depends on the year of manufacture of the device on which the examination is carried out, the price list of the medical center and prices in the region.
An encephalogram costs on average 2000-5000 rubles. The price for an MRI is 5,500-11,000 rubles. The cost will increase by 1000-2000 rubles when using a sedative.
Magnetic resonance imaging images can examine organic pathology in detail, but physiological disorders cannot be detected.
EEG shows neural activity and is indispensable for diagnosing psychosomatics. Both methods are safe and complement each other in complex clinical cases.