Doctors use different methods to examine the brain and blood vessels. MRI or ultrasound helps to quickly and accurately diagnose the disease. They differ in the principle of operation, but help to find the cause of the pain that worries the patient. Which method is better is decided by the doctor after preliminary tests, assessment of the patient’s risks and contraindications.
In what cases are ultrasound and MRI used?
Ultrasound is a non-invasive method of examination, that is, without penetration into the body. Ultrasound examination has proven effective in examining soft tissues. Organs located as if on the surface, that is, immediately under the skin, such as muscles, testicles, chest and the brain of an infant with an open fontanelle, are examined at a wave frequency of 7-18 Hz. High frequencies propagate axial and transverse ultrasonic waves more efficiently.
Organs with a deep location are studied at frequencies (1-6 MHz). The axial and transverse emission of radio waves is less at low frequencies than at high frequencies. But at the same time, the depth of penetration of ultrasound into tissue is ensured.
Ultrasound has found wide application in gynecology and obstetrics. It allows you to see how it develops without harming the fetus.
Magnetic resonance imaging provides images from all areas of the body. If it is necessary to detect the presence of tumors and determine their nature, then MRI in this area is considered the best. It provides a three-dimensional image of the organ being examined, identifies disorders in the central nervous system, and shows diseases of the musculoskeletal system. For example, during just one head scan, data is collected from 20 levels of the skull and brain, and a slice thickness of 4-5 mm. The thickness of the sections and diagnostic accuracy depend on the magnetic field strength.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain images of tissues in different planes
General description of tomography
MRI has recently appeared on the medical services market. This is a modern examination method based on the interaction of magnetic fields. When the scanner operates, they penetrate into the abdominal cavity, causing resonance of water molecules contained in soft tissues, blood, and vessels. When moving, they transmit information about the condition and structure of the area under study. Special sensors record the received data in thin layers, which the computer converts into a three-dimensional image.
How does an abdominal MRI differ from an ultrasound? Modern scanners diagnose not only the outer shell. They penetrate a vessel or organ, showing the structure from the inside. Step-by-step sections can be easily rotated in any projection, so there is no “invisible” zone for the doctor. This makes it possible to achieve high diagnostic accuracy - if the result is correctly deciphered, it reaches 98%.
When both procedures are contraindicated
Ultrasound is contraindicated for skin inflammation, pyoderma, and infectious diseases such as viral hepatitis or HIV. An ultrasound cannot be performed if there are open wounds in the area to be examined.
Contraindications for MRI are:
- the presence inside the body of a pacemaker or other devices that regulate the vital functions of organs;
- the presence of implants containing metals;
- heart failure;
- patient weight exceeding 120 kg;
- claustrophobia
The differences between MRI and ultrasound in contraindications make it possible in some cases to replace one diagnostic method with another.
But if, for example, a patient suffers from heart failure and at the same time viral hepatitis, both diagnostic methods will be contraindicated for him. If, with implants in the body, the patient suffers from pyoderma or other skin lesions, then both procedures will also be contraindicated for him.
The presence of metal implants is a contraindication for MRI
When is an abdominal MRI prescribed?
MRI allows you to get a detailed picture of the condition of internal organs, blood vessels and lymph nodes, and diagnose any pathological changes at an early stage. Before prescribing an MRI of the abdominal cavity, a consultation with a doctor is required, during which a specialist assesses the patient’s condition, collects medical history data, and identifies possible contraindications.
The abdominal cavity is examined using MRI to diagnose the following pathological conditions:
- abdominal trauma, hepatomegaly, enlarged spleen;
- tumor-like and cystic formations, hematomas, abscesses;
- the presence of signs of obstructive jaundice, symptoms characteristic of pancreatitis, liver cirrhosis, cholelithiasis;
- circulatory disorders in parenchymal organs;
- portal hypertension;
- metastatic lesions of the lymphatic system.
MRI is indispensable for assessing the results of surgery on the abdominal organs or monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
However, MRI has a number of contraindications, including:
- the presence of pacemakers, metal prostheses and ferromagnetic fragments in the patient’s body;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- tattoos made using metal-containing dyes;
- the patient’s inability to remain motionless due to neurological disorders;
- fear of enclosed or cramped spaces (claustrophobia);
- epilepsy, schizophrenia.
Before ordering a contrast-enhanced MRI, the doctor must make sure that the person does not have a contrast allergy, hematopoietic anemia, or renal failure. During pregnancy, the administration of contrast is contraindicated, since its effect on the fetus has not yet been sufficiently studied.
What are the features of preparing for ultrasound and MRI?
Ultrasound examination and magnetic resonance imaging are best performed in the morning, on an empty stomach. When preparing for an MRI, three days before the procedure, it is recommended to avoid foods that cause gas and constipation. The list of such products includes:
- legumes,
- fresh and sauerkraut,
- bread and yeast flour products,
- alcohol.
When examining the liver and pancreas, a two-day low-carbohydrate diet is required, excluding bread, flour products, cereals, and sweets from the diet. All food and drinks should be stopped 6 hours before the procedure. To perform a pelvic ultrasound, you must have a full bladder.
You should not drink before an MRI or ultrasound.
What does an ultrasound show?
Ultrasound is in demand in almost all areas of medicine:
- Anesthesiologists use ultrasound when they need to inject a drug near a specific nerve.
- Echocardiography is a section of ultrasound examination that diagnoses the functioning of the heart muscle.
- Ultrasound helps emergency medical professionals examine the body after severe injuries. For example, the presence of intra-abdominal bleeding or when fluid accumulates between the layers of the pericardium is determined.
- In gastroenterology, ultrasound examines large blood arteries, the pancreas, the liver with the gallbladder and duct, the spleen and kidneys. Sometimes appendicitis is detected using ultrasound. Ultrasound is not used in the diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract.
- In neurology, ultrasound monitors blood flow and determines the location of narrowings in the arteries.
- In obstetrics, ultrasound monitors fetal development and identifies possible pathologies. Through the fontanelles in the skull of a newborn, you can examine his brain and detect developmental abnormalities.
- In ophthalmology, images of the eye are performed.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs gives an idea of the health of the uterus and its appendages in a woman; prostate, testicles in men.
Ultrasound can be used to examine various organs
Differences between MRI and ultrasound
The fundamental difference between MRI and ultrasound lies in the diagnostic tools. MRI uses powerful magnets that excite hydrogen atomic nuclei. Ultrasound is based on sending ultrasound waves into the organ and receiving a sound signal that is returned to the sensor. From the sensor, the ultrasonic signal is sent to the computer, where it is converted into a picture.
MRI is a closed type device, and contact with a doctor occurs through a special connection. An ultrasound is performed in an open room where the patient can see the doctor and contact him. Also, the difference between ultrasound and MRI lies in the contraindications, as discussed above.
MRI can examine bone tissue and the substances contained in bones; bone tissue is closed for ultrasound.
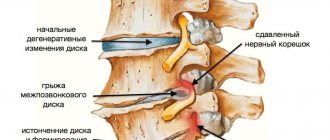
Ultrasound is not performed on the gastrointestinal tract. MRI of the stomach and intestines is performed after appropriate preparation and 2-3 days of intestinal cleansing. When studying blood vessels and the nervous system in motion, Dopplerography, or duplex scanning, is used when it is necessary to study the movement of blood or lymph through the vessels. This method allows you to identify blood circulation disorders, detect arteriovenous malformation and other diseases of the blood vessels and nervous system. Which diagnostic method will be chosen: Doppler sonography or MRI will depend on the location of the vessels in the body. To study the vessels of the brain or spine, MRI is preferable. In the area of the heart and other soft tissues, the choice may be in favor of Doppler ultrasound.
What everyone should know about CT, ultrasound and MRI - you will find all this in this video:
Features of ultrasound examination
Ultrasound examination is a method of exposing special waves to tissue and vessel walls. They create vibrations that are detected by a sensitive sensor. When the ultrasound is reflected, the computer reads the size, volume and density of the organ based on the speed of the echo signal. This helps create a picture in real time, calculating the volume of blood flow or the amount of contraction of the arteries.
If it is necessary to examine blood vessels, a more modern type of ultrasound is used - Dopplerography. It better deciphers information about the state of the riverbed and identifies areas susceptible to stenosis. Depending on the expected diagnosis, the scanning method is selected:
- Standard ultrasound in two dimensions. Better identifies problem areas, areas of fluid accumulation, cysts and other neoplasms.
- Duplex examination. When scanning the brain, it better identifies the vascular network and helps assess the consequences of a stroke or surgery. Thanks to the color image, it is easier for the diagnostician to make the correct diagnosis of arterial stenosis or aneurysm.
- Three-dimensional ultrasound. The latest development qualitatively and clearly shows the structure of the blood vessels of the brain. It highlights pathological areas, allowing you to examine them from different angles. Better suited for examining the kidneys, hepatic ducts, and spleen.
In emergency situations, doctors do not choose which is better: ultrasound or modern MRI. An ultrasound examination is carried out at the initial stage of diagnosis, making it possible to determine the cause of the patient’s complaints and ailments.
How to choose the right method
The diagnostic method is chosen by the attending physician after collecting an anamnesis and examining the patient. It is better for him to know which diagnostic method to choose: MRI or ultrasound. But it will be useful for the patient to know a few points.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics is more expensive than ultrasound diagnostics, but in a number of diseases it turns out to be more informative. MRI has more contraindications. Ultrasound is indicated even for pregnant women and infants. An ultrasound examination does not hinder the patient’s movement and is carried out in more comfortable conditions than an MRI. Not everyone will be able to lie on a hard table for 20-30 minutes.
Ultrasound Dopplerography (USDG)
Doppler ultrasound is one of the modern and accessible research methods. The principle of ultrasound scanning is based on the reaction of ultrasound to moving red blood cells in the blood, which makes it possible to determine the patency of blood vessels and even diagnose a number of vascular diseases based on indirect signs. Ultrasound ultrasound has no contraindications; it can be done even for pregnant women and children from the first days of life. Doppler ultrasound is often prescribed to infants with unsatisfactory results of ultrasound neurosonography.
How is the ultrasound procedure performed?
Ultrasound scanning
takes up to half an hour and is performed with the patient lying or sitting. During the procedure, the sonologist applies a sensor to the patient’s temples, back of the head and neck; if necessary, the eye area can be examined. During the ultrasound procedure, the patency of blood vessels is examined at points of the body that are usually scanned. However, since the outline of the vessels is not visible, the study is carried out blindly, and the results are interpreted based on indirect signs of pathologies.
#!MRTseredina!#