Currently, vascular diseases have become a real problem for humanity. Research by microbiologists has proven that the vascular system has changed little during evolution. But the lifestyle of modern man has changed dramatically: environmental pollution, the predominance of refined foods in the diet, information load, physical inactivity - this negatively affects the condition of blood vessels and the entire human body.
However, the medical industry does not stand still, but is developing at a rapid pace - its arsenal contains an impressive collection of effective methods for diagnosing and treating pathological processes in blood vessels. Doppler studies of blood flow are considered the most informative and safe - ultrasound Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) and DS (duplex scanning) of the MAG (main arteries of the head).
Many patients, having received a referral for examination and seeing a mysterious abbreviation, ask the question: “What is this?” In our article, we want to talk about the advantages of these methods, when the examination is carried out and what changes in the vessels can be detected during the examination.
What is Doppler?
This diagnostic method got its name based on the discovery of a physical phenomenon made by the Austrian scientist K. Doppler. Its essence is to reflect changes in the frequency of the ultrasonic beam signal from blood cells moving in the vessels. This gives you the opportunity to evaluate:
- speed and direction of circulating blood;
- minute blood flow volume;
- the presence of atherosclerotic stenosis (narrowing) and blockage of the vessel;
- collateral (side) circulation;
- pulsation of blood vessels.
Indications for Doppler sonography
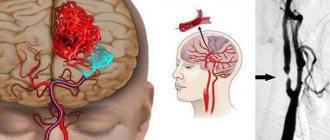
The delivery of blood and oxygen to the brain tissue occurs through the carotid (located on both sides of the lateral surface of the neck) and vertebral (which run on the sides of the spine) arteries. The slightest disruption of the blood supply to brain cells leads to serious deviations in its functional activity.
With the help of modern medical technologies, it is possible to painlessly study the condition of the veins and arteries of the head and neck in patients with high cholesterol levels, concussions, spinal injuries, and long-term smokers.
The procedure is fairly quick, but requires highly qualified specialists.
Practitioners prescribe MAG ultrasound if they suspect that a patient has cerebral circulatory disorders, which manifests itself:
- bursting headache;
- numbness and weakness of the limbs;
- hearing, attention and memory impairment;
- frequent dizziness;
- absent-mindedness;
- noise in the head;
- loss of consciousness.
Also, a study of the condition of the vessels of the head is carried out to diagnose and monitor the effectiveness of treatment measures for diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- stroke;
- hypertension;
- vasculitis;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
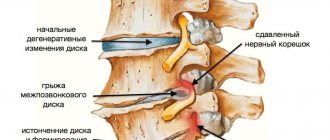
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- obesity;
- coronary disease and heart defects.
However, in some cases, dysfunction of the vascular system may occur without visible clinical symptoms. That is why people over 55 years of age and those who have a burdened family history (presence of hypertension, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction in close relatives) are recommended to undergo testing once a year.
Duplex scanning of the main arteries of the lower extremities
Identification and quantification of hemodynamically significant atherosclerotic lesions is a challenging but important task in patients with diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities. Before vascular reconstruction is performed, it is necessary to determine the location of the lesion, determine its severity, and attempt to predict its hemodynamic effects. All these tasks correspond to duplex scanning, which has been used to study the arteries of the lower extremities since the late seventies.
The method has 100% sensitivity and specificity . He has proven himself well in monitoring patients before and after operations on the arteries of the lower extremities.
Indications for the use of DS are:
- all diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities;
- the presence of risk factors for the development of diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities: smoking, hyperlipidemia (increased cholesterol levels), diabetes mellitus;
- pain in the lower extremities when walking (intermittent claudication);
- traumatic injuries of the main arteries of the lower extremities;
- control after surgical treatment of the main arteries of the lower extremities.
Features of the diagnostic procedure
No special preparation is required for Doppler examination. The patient can take medications as usual, but before the examination it is worth telling the doctor exactly what medications are prescribed. The only condition for the patient is to refrain from smoking and consuming foods that affect vascular tone on the eve of the procedure - energy and alcoholic drinks, coffee, strong tea. Diagnostics are carried out in a calm environment and comfortable conditions for the patient.
The doctor lubricates the areas under study with a special gel, which improves the glide and sound conductivity of the sensor, and scans the main arteries passing through the neck
Ultrasound waves penetrate the vascular system of the brain through the skull, and a qualified specialist alternately examines various areas of the head with a linear sensor - supraorbital, temporal, occipital, atlanto-occipital (the area where the spine meets the occipital bone). In addition to studying the blood vessels, the doctor conducts functional tests necessary to clarify or confirm disorders of regulation of the autonomic nervous system.
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
Like all diagnostic procedures, duplex scanning has both positive and negative sides. The advantages of the technique include:
Absolute safety . Considering that ultrasound has no side or disfiguring effects, it can be used by pregnant women and young children. Non-invasive, painless. The procedure is absolutely painless and does not create discomfort for patients.
High diagnostic accuracy. Due to the fact that the vessels under study are presented in different projections, with simultaneous registration of blood flow, the information content of such a study can only be compared with angiography.
Simplicity of the procedure . The scanning time takes about 20 minutes; it does not require bulky equipment or additional assistance from medical workers. The only thing that is required is the doctor-researcher’s deepest knowledge of the physiology and anatomy of blood vessels.
No contraindications. Such examination is prescribed for patients of all categories. Does not require special preparation - diet, administration of solutions or cleansing enemas.
The disadvantages of the technique include, firstly, the rather high cost. Duplex scanning of the vessels of the head is carried out with special ultrasound machines, often inaccessible to government agencies and small clinics.
Secondly, the area of study is minor. The vessels hidden by the skull are inaccessible to ultrasonic waves, so it is impossible to study the circulatory system in the brain. Examination of the brachiocephalic vessels provides indirect information.
What can be detected with Doppler ultrasound examination of blood vessels?
This diagnostic procedure makes it possible to detect the formation of blood clots not only in the vascular system of the cervical spine and head, but also in the upper and lower extremities. Using ultrasound, you can determine:
- causes of headaches;
- narrowing of the arteries;
- stage of diseases, the development of which was provoked by atherosclerosis or thrombosis;
- the presence of vascular aneurysms;
- the speed of blood flow in the main arteries and its disturbances;
- condition of the spinal vessels.
Changes identified during a diagnostic examination may indicate the development of:
- vasculitis – the echogenicity of the lumen of the vessel, the thickness of its walls and differentiation into layers changes;
- atherosclerosis – the thickness of the diameter of the vascular walls increases, an uneven type of change in echogenicity appears;
- cholesterol plaques in the arteries - hypo-echoic formations with a thin rim are detected.
Conditions in which there is a narrowing of the lumen of the arteries of more than 50% require immediate treatment.
MAG ultrasound can detect deformation of the vascular walls of the neck - a harbinger of coronary heart disease
Duplex scanning of the main veins of the lower extremities
Interest in the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the veins of the lower extremities has not only not faded in recent years, but, on the contrary, is constantly increasing. In this regard, the highest level of diagnosis of pathological disorders of venous outflow in the superficial and deep venous systems of the lower extremities is currently required.
This is urgently necessary for the production of individually based surgical interventions for each patient.
All these urgent tasks are fully met by duplex scanning, which allows patients with diseases of the veins of the lower extremities to objectively and accurately diagnose:
- diseases of the main veins;
- their localization and nature;
- severity of hemodynamic disorders in the extremities;
- serves as a valuable factor in determining surgical tactics and objective assessment of the results of surgical treatment.
For varicose veins of the lower extremities, duplex scanning allows you to assess the condition of the venous valves; establish the cause of relapse of the disease. In case of varicose veins of the lower extremities, complicated by acute thrombophlebitis, it is possible to accurately determine the location of blood clots. These data have a significant impact on the tactics and scope of the operation. Duplex scanning allows you to study the structure of thrombotic masses, the degree of their fixation to the venous wall, identify “moving” blood clots, determine the source of pulmonary embolism, indications for implantation of a vena cava filter and monitor its condition. Duplex scanning in dynamics in patients with postthrombophlebitic disease allows us to identify signs of recanalization of blood clots, the path of venous outflow and ways of its compensation. The high information content and safety of the method make it possible to recognize it as the leading one in the diagnosis of recurrent varicose veins.
The use of duplex scanning makes it possible to completely eliminate the use of X-ray contrast examination - X-ray phlebography, thereby reducing the risk, cost and time of the examination. High resolution, safety, and the possibility of repeated use make duplex scanning of the main veins of the lower extremities the “gold standard” of phlebological diagnostics.
Indications for use are:
- all diseases of the veins of the lower extremities;
- pain in the lower extremities in combination with their swelling;
- the presence of symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency without clear indications of primary venous thrombosis;
- traumatic injuries of the main veins of the lower extremities;
- control after surgical treatment of the main veins of the lower extremities;
- preparation for surgical interventions (in order to exclude possible sources of pulmonary embolism during surgery and in the postoperative period).
Analysis of vascular diagnostic indicators
Doppler ultrasound is considered a “blind” technique for scanning blood vessels, this is due to the impossibility of visualizing blood flow. Nevertheless, this procedure is highly informative. The blood circulation of the main arteries is peculiar, it can be divided into:
- Parabolic flow, which is characterized by different shear rates of the middle and wall layers. The absence of their mixing is noted; at the moment of compression of the vessel, the speed of blood flow is maximum, and during relaxation it is minimum.
- Turbulent flow - is formed as a result of the chaotic movement of red blood cells (erythrocytes) on uneven areas of the vascular walls.
Angiography of cerebral arteries
Doppler ultrasound reflects such parameters of Doppler shift as: an indicator of the speed of blood flow in the middle layers of blood vessels and the density gradient of the main component of blood - red blood cell mass. When analyzing Doppler parameters, the qualitative and quantitative aspects of blood flows are studied:
- speed – systolic, diastolic and their average value;
- general peripheral vascular resistance - a set of parameters of circulating blood viscosity, vascular tone, intracranial pressure;
- spectral characteristics – a reflection of the number of single-speed shaped cells;
- vascular reactivity, which is determined by the ratio of the duration of blood supply at rest and with load;
- mobility - relative loss of speed.
In some cases, data obtained at rest is not enough to diagnose the pathological process. Under such circumstances, medical specialists use stress tests - inhalation tests, breath holding, nitroglycerin, and compression of the carotid artery. These methods help to identify diagnostically significant disorders of blood flow through the vessels, characteristic of damage to the main arteries.
The vascular walls are affected by a number of pathological processes that can be detected by Doppler sonography. Let's take a closer look at each disease that causes dysfunction of the vascular system.
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis provokes an increase in the thickness of the intima-media complex of the carotid artery, pathological uneven thickening of the vascular walls and a uniform change in their echogenicity. With this pathology, the narrowing of the lumen of the blood vessel reaches 20%. Thickening of the carotid arteries is allowed up to 0.7 mm, brachiocephalic arteries - up to 1.2 mm.
Stenosing atherosclerosis is caused by the formation of “plaques”, which increase the narrowing of the vascular lumen by more than 25%. Each accumulation of cholesterol cells in the endothelium is assessed as a potential culprit in the development of acute blockage of a vessel - embolism. That is why their echo density, extent, the presence of accumulation of salts (calcifications) and ulcerations in the vascular surface are carefully studied.
To assess the likelihood of stopping blood flow, the structure of “plaques” accumulating in the inner lining of the blood vessel is carefully studied
Horton's disease (giant cell arteritis) causes hardening of the wall of the temporal artery and a decrease in its echogenicity. This phenomenon leads to the formation of small calcifications and damage to the process of differentiation of vascular walls into layers. Diabetes mellitus is characterized by the development of calcification - excessive accumulation of calcium on the walls of small arteries.
Hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries is the most common anomaly of the spinal vessels, in which there is a violation of their elasticity with a reduction in diameter and a deviation in the blood flow curve. Patients complain of excruciating attacks of headache and dizziness, which intensify when turning the head.
Congenital arteriovenous malformation is characterized by the presence of a complex anomalous interweaving of veins and arteries. As a result of this phenomenon, blood from small arteries bypasses the capillary bed and enters directly into the veins, threatening the drainage vessels with the development of hypertrophy, hyaline degeneration and calcification. Due to the thinning of the capillary walls, hemorrhages and the appearance of an arteriovenous fistula may occur, which leads to damage to the dynamics of cerebral circulation.
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta, its paired and unpaired branches
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta allows visualization of the abdominal aorta along almost its entire length; measure its diameter; identify the presence of local expansion, determine the presence of large atherosclerotic plaques. To identify the presence of thrombotic deposits on the walls of the aneurysmally dilated aorta, to assess the degree of their severity, location and duration. The method of duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta with color Doppler mapping of blood flows is intended for the diagnosis of aneurysms of the abdominal aorta, as well as for assessing blood flow in its paired and unpaired branches. Indications for the use of duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta are:
- the presence of a pulsating formation in the abdominal cavity;
- pain of unknown origin in the abdominal cavity;
- confirmed diagnosis of nonspecific aortoarteritis.
Ultrasound Doppler Magnetography in children
Pediatric doctors recommend a Doppler examination for all newborn babies - the diagnostic procedure helps to timely identify disorders of the circulatory system and take appropriate measures. In the presence of congenital anomalies, diagnosis must be made as soon as possible. Otherwise, this will lead to delayed mental and physical development of the child and serious pathologies of the central nervous system.
The study of the arterial circle (Willisian) of the child’s brain provides an opportunity to identify pathological processes in the early (preclinical) stages of development
Experienced pediatric neurologists prescribe a study of the state of the vascular bed if the baby has headaches, fatigue, memory impairment, mental retardation, and impaired coordination of movements. Diagnostics is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment for pathologies such as migraine, epilepsy, impaired functional activity of the cerebral cortex, laloneurosis (speech defects).
Duplex scanning of the main veins of the upper extremities
Thrombotic lesions of the veins of the upper extremities remain a fairly common pathology. The basis for instrumental diagnosis of pathology of the main veins of the upper extremities is duplex scanning, which is intended for diagnosing developmental anomalies of the venous system of the upper extremities; diagnosis of venous thrombosis and valvular venous insufficiency, diagnosis of arteriovenous developmental anomalies.
Duplex scanning allows you to examine the main veins of the upper extremities, determine their direction and course; identify the presence of thrombosis, its localization, duration and severity, diagnose valvular venous insufficiency along the entire length of the main veins of the upper extremities. In almost 100% of cases, the method eliminates the need for angiographic studies.
Indications for use are:
- all diseases of the veins of the upper extremities;
- pain in the upper extremities in combination with their swelling;
- the presence of symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency of the upper extremities without clear indications of a primary thrombotic lesion;
- traumatic injuries of the main veins of the upper extremities; control after surgical treatment of the main veins of the upper extremities;
- congenital anomalies of vein development;
- conditions after manipulations on the main veins of the upper extremities: intravenous injections, puncture of the subclavian veins.