Characteristic
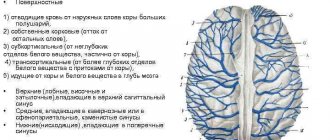
Ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck is considered a modern diagnostic method. It is characterized by the reflection of an ultrasound wave from the area under study. Through the sensor, signals are sent from the object, thereby measuring the reflective speed from the blood moving in the blood vessels. As a result of computer processing, the received information is transmitted in a two-dimensional image. It shows the area being examined and areas where blood flow is obstructed.
Ultrasound examination of the brain is an alternative to other invasive methods. They are performed using a contrast component and subsequent radiography. This diagnosis evaluates the arterial and venous circulation supplying the organs that are located inside the skull.
Kinds
Ultrasound examination of the brain, which is done to examine the circulatory system, can be of the following types:
- Doppler study. In this type of diagnosis, the sensor is installed on the arterial or venous area, without their preliminary visualization.
- Duplex examination. Dopplerography of this type is combined with conventional ultrasound. During the study, the specialist examines the thickness of the vessels using an ultrasound sensor and Doppler sonography.
- Triplex view is combined with duplex scanning and color differentiation.
- TKDG. During research using this method, the sensor is placed on areas of the skull where there is insignificant bone thickness. This method allows you to assess the condition of the circulatory system, which is located in the brain.
Any study of cerebral vessels is based on ultrasound. However, if an ultrasound examination of blood vessels is prescribed, they usually mean Doppler ultrasound combined with Doppler.
Ultrasound shows even a minor pathological focus
Contraindications
Any of the options for such ultrasound, be it duplex, three-dimensional or Doppler examination of cerebral vessels, does not pose any danger to patients. The procedure can be carried out even several times in a row. Difficulties arise only in the presence of obstacles, when the area of study is covered by bone tissue or a large amount of fat. Problems are also noted in the following cases:
- for arrhythmia and cardiac pathologies;
- in patients with slow blood flow;
- in the presence of areas with damaged skin (it is recommended to wait until it heals);
- for diseases that prevent the patient from lying down;
- serious condition of the patient.
Indications
An ultrasound of the brain in adults should be performed if there are signs that indicate vascular pathological processes:
Vascular MRI
- feeling of weakness;
- noise in ears;
- headache;
- sensation of pulsation in the temples;
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- floaters floating in front of the eyes;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- fainting;
- memory loss;
- lack of coordination;
- decreased sensitivity of the facial area;
- increased blood pressure;
- obesity;
- cardiac ischemia;
- increased blood cholesterol levels.
The study is also recommended for long-term smoking, after heart attacks and strokes, and for injuries to the cervical vertebrae. Diagnostics is indicated for men over 60 years of age. Because they are at risk of vascular diseases.
This procedure is used for both adults and children. It identifies pathologies at the stage of their development and, if necessary, allows you to take action. An examination is prescribed to monitor cerebral blood flow after surgical interventions. Due to the absence of harm to the body, the study can be carried out repeatedly.
Electrical measuring methods
Electroencephalography
Explores brain activity. The examination is carried out using a device called an “electroencephalograph”. Electrical impulses allow us to analyze brain activity.
For the procedure, electrodes are attached to the scalp. The obtained data from the device is recorded on paper. The method allows you to assess the condition of nerve fibers and blood flow in the head and neck. Used to analyze the consequences of injuries, diagnose mental disorders, epilepsy. Before undergoing the examination, the patient must let down his hair if it is long. Before the study, you should not take drugs that affect brain activity.
Electroneuromyography
The study is carried out to analyze the functioning of the peripheral nervous system and is based on muscle biocurrents.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
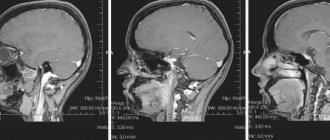
The study of the vessels of the neck and head is carried out through the action of radio waves on the body. Before the procedure, the patient is placed in a capsule in which a magnetic field is created. Diagnostics are developed on the basis of wave activity that occurs when exposed to internal organs.
High-precision research allows you to diagnose tumors, thrombotic plaques, cerebral hemorrhages, and other pathologies of various types. MRI gives a complete picture of the structure of blood vessels and their defects. Diagnosis is carried out when tumors of various types are suspected. It is necessary for correct diagnosis and therapy.
There are contraindications for the procedure. People with implanted electronic devices cannot undergo examination.
Pros and cons of the study
Ultrasound examination of blood vessels has its advantages and disadvantages. The benefits of diagnostics include:
- safety. The examination can be carried out even for infants;
- good visualization of soft tissues;
- possibility of performing the procedure frequently;
- non-invasive;
- painlessness;
- possibility of examination in different projections.
Despite a lot of positive aspects, this type of diagnosis also has its disadvantages: difficulty in visualization due to layering of projections, difficulty in visualizing bone tissue, difficulty in scanning people who are overweight. Since in this case ultrasound is absorbed by adipose tissue.
Advantages of ultrasound diagnostics of the brain
The benefits of brain ultrasound include:
- Painless.
- Non-invasiveness, that is, the absence of punctures, as, for example, with angiography.
- High degree of information content (makes it possible to identify pathological changes in blood vessels before they begin to manifest themselves clinically).
- Simplicity and accessibility of execution.
- No radiation exposure to the patient.
- Ultrasound allows you to evaluate blood flow in the vessels of not only the head, but also the neck.
- Relatively affordable price for the study (compared to angiography and MRI).
- When performing an ultrasound, there is no need for anesthesia, even if the examination is performed on a newborn (unlike an MRI or computed tomography).
What the study shows
Many people are interested in what an ultrasound of the brain shows. This diagnostic is used to detect narrowed areas of blood vessels, determine blockage of arteries and veins, detect systemic diseases, determine the sources of diseases, monitor prescribed therapy, assess the reserve capacity of blood vessels, detect vascular defects in the form of spasms and aneurysms. Most often, vascular ultrasound shows changes that are the cause of the clinical picture and vascular disorders. After the procedure, sometimes the doctor gives a referral for an MRI for a more global study of the arteries and veins in the brain.
Sometimes, to make an accurate diagnosis, several ultrasounds are necessary. This will help you monitor the prescribed treatment.
Common pathologies
The most common pathologies diagnosed on ultrasound are:
- Atherosclerosis refers to a condition characterized by cholesterol deposits on the vascular walls. As a result, blockages are formed, leading to stroke, heart attack, necrosis;
- stenosis occurs in single and multiple instances. This pathology appears to be a narrowing of blood vessels and occurs due to hypertension, atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis;
- arterial or venous compression. Pathology most often occurs due to tumors, injuries, and displacement. As a result, normal blood flow is disrupted, leading to insufficient tissue nutrition;
- impaired blood circulation, which leads to vision problems, numbness, and headaches.
Decoding
The results that the neurologist received after the procedure allow him to correctly diagnose, identify the cause of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment. The main indicator of the norm is symmetry. All measurements in the graph should be approximately the same in length, there should be no offsets of more than 2 mm.
The norm for a healthy person has the following parameters: the thickness of the vascular network is no more than 0.9 mm, arteries and veins should have lumens without obstacles to the passage of blood, there should be no turbulence in areas without vascular branches, the diameter of the vertebral arteries should not be less than 2 mm , homogeneous vascular structure, absence of compression symptoms.
Preparing for diagnosis
Preparing for an ultrasound does not require any special measures. However, for an accurate examination of the picture by doctors, it is recommended that you give up caffeine-containing products, coffee, strong tea, and any alcoholic beverages for 24 hours before diagnosis. Because they cause dilation of the head vessels. You should also avoid a diet rich in spicy foods; it is recommended to dose the use of salt.
Patient preparation will depend on the type of diagnosis
If the person being examined uses vascular medications, he must tell the doctor about it. You may need to temporarily stop taking them. It is not advisable to use medications that have an analgesic or antispasmodic effect the day before the procedure. Smoking is prohibited 6 hours before the test. This is due to the fact that nicotine can increase blood pressure, which will lead to an unreliable result.
Before starting the session, the patient needs to lie down on the couch with a small pillow under his head. Next, it is important for the person being examined to relax and restore their breathing. Before placing the sensor, the doctor feels the vessels, determining its depth and the force with which they pulsate. Usually the procedure is carried out for 20 minutes, during which the doctor studies the speed of blood flow, its tortuosity, and tone. Ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels is a painless method that can identify the cause of pathology and predict the disease.
How to do an ultrasound of the brain in a newborn
Immediately after birth, the bones of the newborn’s skull are movably connected, and there are no sutures between them. At the same time, in the areas of connection of the main bones, 6 fontanelles or non-ossified areas of the cranial vault can be distinguished, filled with dense and fairly flexible connective tissue.
All of them are overgrown during the first year of life, with the last one to close is the large fontanelle, which is of interest from a research point of view. Because of this, the brain is examined using ultrasound equipment until it ossifies.
During an ultrasound, the newborn may be dozing or awake, as any of these conditions does not interfere with obtaining reliable indicators. However, if the specialist is faced with the task of examining the vessels, then it is not recommended to feed the newborn 1-1.5 hours before the event.
The procedure for performing an ultrasound scan of the brain is no different from performing an ultrasound scan of any other organ: the specialist applies a high-viscosity gel to the area of the child’s head being examined, which is usually the large or anterior fontanel. Then he places a sensor against it - a black and white image is displayed on the equipment screen, from which the state of the brain parts is determined. Next, measurements are made of internal structures: hemispheres, ventricles, subarachnoid space, etc. If necessary, if other fontanelles are not overgrown, then the manipulations are repeated.
The data obtained in this way is carefully recorded on a special form for further decoding. If there are pathologies, the specialist can also select one frame and print it on special paper. This is done so that the attending physician can subsequently personally examine the identified pathology.
As mentioned earlier, the ultrasound procedure has no restrictions, therefore, if necessary, it is performed on all children without exception, including premature ones, which greatly facilitates the diagnosis of brain disease.