What can you see on a hip x-ray?
Hip arthroplasty
X-ray as a research method is designed to visualize bone structures. When diagnosing, the following are clearly visible:
- Pelvic bones. Anatomical defects, fractures, cracks, and asymmetry are visible.
- Joint. Dislocations, subluxations, widening of the joint space, narrowing or fusion with the formation of ankylosis are detected.
- Head of the femur. The trochanter and femoral neck are examined, cracks, fractures, developmental and structural anomalies, osteomyelitis and osteoporotic changes are identified.
Anatomical and functional features of the hip joints
The structure of the hip joint, like other joints of the human body, is entirely determined by its functioning. The organ bears a significant load, both weight and motor, which is possible only due to its morphological characteristics. Thus, the hip joint is a multiaxial joint formed by the head of the femur, the acetabulum and a strong articular capsule, to which many ligaments are attached.
The outside of the joint is covered with muscle tissue, which plays a direct part in all musculoskeletal actions. The inner surface consists of a synovial membrane that produces synovial (articular) fluid, which acts as a kind of lubricant. The edges of the acetabulum are covered with hyaline (vitreous) cartilage, which increases the depth and area of the articular surface.
The mobility of the hip joint is low compared to some joints, such as the shoulder. This is due to the depth of the acetabulum and the complex muscular-ligamentous apparatus. Due to the joint's exposure to regular loads, its main feature is strength, which is considered the norm, regardless of whether it is adults or children, men or women. Almost the entire surface of the femoral head is covered by the pelvic bone, and this is the main reason for limiting the mobility of the joint.
Nevertheless, the hip joint performs several types of motor activity, providing a person with mobility and maximum functionality in various types of activities - socially useful, sports, professional, such as:
- lead,
- casting,
- rotation,
- bending,
- extension.
The structure of the hip joint, the anatomical elements of which are assessed by x-ray diagnostics
For what symptoms is an x-ray recommended?
Fracture of the pubic bone
X-rays of the hip joints are performed both in early childhood and in adulthood.
In children, an x-ray is necessary if there is limited or asymmetrical spread of the child’s legs in the “frog” position (the baby lies on his back, the legs are bent at the knees and spread to the sides), shortening of the limbs in relation to each other, or lack of support on the baby’s legs.
Osteomyelitis
In adults, an x-ray of the hip joint may be required if there is a suspicion of a fracture or inflammation in the hip joint or osteomyelitis of the femur. In this case, the complaints common to all are: severe pain in a given anatomical area, the presence of edema, changes in the color of the skin, local temperature in the joint area, severe limitation of movement, lameness and unsteadiness when walking, changes in limb length.
If osteomyelitis and other inflammatory processes in the hip area (purulent inflammation of the bone marrow of the femur) are suspected, intoxication in the form of impaired appetite, weakness, lethargy, apathy and, without fail, fever is added to the above symptoms.
How is the procedure done?
The patient lies down on the work table of the X-ray machine, the markings of which indicate the area of exposure to ionizing rays. Parts of the body that are not subject to examination (especially the thyroid gland and genitals) are protected with lead aprons.
To perform direct projection shooting, the subject lies on his back with his legs extended forward. For the lateral projection, he must assume a position lying on his side with his body tilted back and the other leg. You must maintain this position until the end of the study. The entire diagnostic procedure lasts no more than 5-7 minutes.
What diseases and injuries does the study reveal?
Pathologies that can be examined on x-rays are:
- Hip dysplasia. It is detected in early childhood and manifests itself in the form of delayed ossification of the nuclei, subluxation of the femur (the head is not in the cavity of the glenoid cavity).
- Fractures and cracks. An x-ray can show the location of the injury, the presence of displacement and the number of fragments and splinters, and the degree of displacement of the bone structures.
- Dislocations. The exit of the greater trochanter of the femur from the articular surface of the acetabulum is visualized.
- Osteoarthritis. A degenerative disease of the cartilage tissue of the joint, which on an x-ray appears as a narrowing of the joint space, the formation of bone growths on the articular surfaces (osteophytes).
- Arthritis of the hip joint. It occurs as a result of autoimmune reactive changes in the soft tissues of the joint, accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and possible effusion in the cavity. An x-ray reveals compaction of soft tissues, widening of the joint space, if necessary, a contrast study is performed with intravenous administration of an iodine-containing substance, and an increase in the vascular pattern at the site of inflammation is observed.
- Necrotic changes. They occur when blood circulation in the joint cavity is impaired due to a fracture of the femoral neck, since the trophism of the femoral head is disrupted and it dies.
- Osteoporosis. Bone degeneration associated with age-related changes and hormonal imbalance. Characterized by leaching of calcium from bones. On an x-ray, it looks like a decrease in the density of bone structures and an increase in their transparency.
- Ankylosing spondylitis. Persistent changes in the joints, which manifest themselves in the form of ossification and lack of movement. The X-ray shows the formation of persistent ankylosis, absence of joint space, and callus at the articulation site.
- Osteomyelitis. An inflammatory disease of the bone marrow that occurs when an infection occurs through the hematogenous route or as a result of traumatic injury. In this case, lysis of bone tissue occurs, which on x-rays looks like blurred contours, clearing in the center of the bone, hypertrophy of the periosteum above the site of the lesion. It is possible to conduct a study with contrast.
- Oncological diseases of bones. Benign or malignant tumor growths inside the bones, metastatic screenings. They look like pathological foci (darkening with “plus tissue” and clearing with the appearance of cysts, sequestration, cavities) with blurred, indistinct contours, and irregular shape.
Arthritis
Indications for radiography of the femur
A hip x-ray may be prescribed in the following cases:
- Injury. In this case, there may be aching or acute pain in the thigh, visually noticeable deformation, swelling and redness, limited ability to move the leg or complete immobility.
- The need to monitor surgical treatment. After fractures, it is important to evaluate how correctly the bone fragments are juxtaposed and how quickly they heal.
- If you suspect a tumor of the femur and soft tissues, as well as metastases.
- If you suspect the presence of purulent, inflammatory diseases of bone tissue: osteomyelitis, periostitis.
- If degenerative diseases of the femoral bone are suspected (aseptic necrosis of the femoral head).
What does a hip x-ray reveal?
X-ray allows you to reliably identify the following pathological situations:
- fractures, cracks of the femur;
- the presence of bone fragments and their displacement;
- tumors in the femur and surrounding soft tissues;
- osteomyelitis;
- periostitis;
- deformation of the hip bone due to illness or injury.
Contraindications for diagnostics
Dysplasia
Since the X-ray diagnostic method is an ionizing one, its use has some limitations. This is due to the pathogenic effect of rays on cells with the formation of free radicals that damage healthy tissue.
The main contraindication is pregnancy. To protect healthy tissue during diagnostics, other areas of the body are covered with a lead apron, which is necessary to reduce the total radiation dose. Modern devices allow you to reduce the dose as much as possible without losing the quality of the image, but the developing fetus is located next to the area under study and there is a possibility of the formation of mutations and developmental anomalies.
A relative contraindication is childhood. However, if dysplasia is suspected, radiography is the main diagnostic method. To reduce the total radiation dose, carefully monitor the frequency of the procedure.
With the introduction of a contrast iodine-containing substance (Ultravist, Urografin and others), the contraindications expand significantly. The following categories of patients cannot be tested:
Ionic
Nonionic
- with an allergic reaction to contrast;
- with renal failure (since the contrast is excreted by the kidneys);
- with severe cardiovascular insufficiency;
- with tuberculosis in the active stage;
- in an extremely critical condition of the patient.
Indications and contraindications
X-rays show various diseases and changes in the hip joint : injuries, inflammation, degenerative and congenital pathologies, tumors, metastases.
Indications for the diagnosis of hip joint pathologies:
- injuries,
- severe pain, partial numbness of the limb,
- swelling and bleeding over the hip joint,
- suspicion of developing arthritis or monitoring the course of the disease,
- degenerative diseases: arthritis, coxarthrosis, arthrosis,
- tumor processes in bone tissue,
- necrotic joint changes,
- hip dysplasia.
Contraindications to the procedure:
- pregnancy in any trimester,
- children under 14 years of age, unless there are special reasons for this,
- Carrying out a procedure with the introduction of a contrast agent can cause allergies,
- severe pathology of the kidneys and liver,
- immunodeficiency,
- cardiovascular failure,
- active tuberculosis,
- oncology,
- general serious condition of the patient.
X-rays for hip dysplasia in children are an indispensable research method . Only this method gives a complete picture of changes in the joint and helps determine the method of treatment. The main rule is the dosage of radiation exposure.
Comparison with MRI and ultrasound
Sometimes ultrasound is used to diagnose joint pathology. The studies are diametrically opposed, since radiography helps to identify bone pathologies, while ultrasound helps to identify soft tissue diseases.
X-rays look at the anatomical structure, while ultrasound reveals functional deficits, such as insufficient or excessive amounts of intra-articular fluid. Often, for the most complete picture of the disease, a joint appointment of studies is required.
Tomographic examination is a relatively new method, compared to conventional x-rays, which is much more informative. The main advantage of X-rays compared to MRI is its general availability, since the machines are present in every hospital, and its low cost, since MRI is much more expensive.
MRI
Advantages and disadvantages
Radiography has a number of advantages. Among them are:
- ease of implementation;
- availability;
- low cost (compared to other types of diagnostics).
The disadvantages of x-rays include:
- exposure of the body to radiation;
- superimposition of surrounding tissues on the area under study (as a result of which it is difficult to decipher the radiograph);
- inability to assess the functional ability of the hip joint;
- it is impossible to draw a conclusion about the state of the soft tissue structure (this requires the introduction of a special contrast);
- low information content (relative to computer and magnetic resonance imaging).
Preparing for X-rays
Radiography of the hip joints does not require special preparation. When conducting diagnostics in infants, the presence of both parents is required, as they must hold the baby in the required position during the examination.
Before radiography, the patient must take off his outer clothing, metal objects (belt plaque) and lie down on the couch. Severe non-ambulatory patients are laid down by orderlies.
What does the procedure determine?
The correct interpretation of the obtained images largely depends on the professionalism of the radiologist.
Pathologies of the hip joint that a specialist pays attention to when interpreting an x-ray:
| Identified pathology | Probable diagnosis |
| Violation of the position and correspondence of the bones in the joint relative to each other or the pelvic bones | Dislocations, subluxations |
| Presence of bone fragments | Fracture |
| Changing the size of the joint space | Osteoarthritis |
| Deformation/damage/proliferation of bone tissue, cartilage and periosteum. | Arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis |
| Inferiority of the glenoid cavity or femoral head | Dysplasia |
| Additional volumetric articular inclusions | Tumor formations |
Radiation dose and permitted number of sessions for one patient
Careful monitoring of the radiation dose is carried out in young children, since X-ray examination can lead to such adverse effects as suppression of bone marrow function. Complications may include diseases: leukemia, anemia, thrombocytopenia. The study begins at three months of age. Even with modern devices, examinations for children under three years of age are carried out no more often than once every 4 months.
Adults are less susceptible to the effects of ionizing radiation, and modern digital equipment minimizes exposure.
For each patient, depending on his weight, his own dose is selected. A film device irradiates with a dose of 0.5-0.9 mSV, while a digital device irradiates with a dose of 0.1-0.3 mSV. More than 10 studies on a digital device are not recommended per month; the implementation is regulated by strict indications. Use the “Full Dosimeter” at the end of the article for information on radiation exposure.
Benefits of the study
Modern radiographic systems make it possible to obtain high-quality images scanned in different planes. The main advantage of the method is the speed of diagnosis: depending on the complexity of the injury or other pathology, the entire process takes no more than 10 minutes. Digital signal transmission speeds up the speed of image processing - this factor is especially important if you urgently need to understand the cause of the patient’s serious condition.
The procedure is carried out in comfortable conditions. Modern devices can read digital images from different planes, without uncomfortable poses for patients (people sit on a comfortable table). Thanks to the digital image, the attending physician can immediately make a diagnosis and begin urgent treatment. The radiation exposure is strictly regulated by international protocols, so the health of the patient undergoing the study is not threatened.
Interpretation of diagnostic results
Radiologists interpret the results of the study. Computer equipment displays the image on the screen and helps in analyzing the results. Using the software, you can increase the contrast and clarity of the image, zoom in and out, and also measure the density of bone tissue areas.
The results are returned to the attending physician who referred for the study. After analyzing the results and comparing them with the clinical picture, therapy is prescribed or adjusted.
Why is a hip x-ray done?
Digital X-rays are commonly used for initial evaluation of bones, joints, and lungs. The procedure itself takes only one second. Over the years, technological improvements have reduced radiation exposure. Currently, an X-ray of the lung corresponds to exposure to radiation equivalent to a flight from Zurich to New York.
With digital radiography, the image can be viewed and evaluated directly on the monitor, eliminating long wait times. Digital archiving ensures that recordings will continue to be available in their original quality for years to come. This allows you to access earlier images and discuss medical issues and diagnoses with greater certainty.
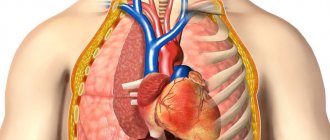
A healthy, air-filled lung passes through a lot of X-rays, causing it to appear dark on an X-ray. The heart, with its supply and discharge vessels, is denser and therefore transmits fewer x-rays. They appear bright on an x-ray. A chest x-ray may show changes in the lungs, such as pneumonia and an enlarged heart, as well as signs of decreased cardiac function.
The examination takes about 10 minutes. In the radiologist's office, you must remove your outer clothing.
During the procedure, you are required to stand directly in front of the X-ray detector. The picture is taken after a long inhalation with a short pause. This allows for a better assessment of the lungs. It is important that the patient does not breathe or move during recording. Lateral radiography is often necessary. It is usually performed with the patient lying on the left side of the detector. The arms are placed above the head to prevent interference.
Bone transmits only a few X-rays and appears bright on an X-ray. The image may show changes in bones and joints - fractures, arthrosis, arthritis.
Fluoroscopy uses weak X-rays. The radiologist sees the “live image” directly on the screen and can assess the patient’s condition.
Where is the research done and the cost?
The procedure is carried out in every X-ray room of the hospital: clinic, hospital, emergency room, and so on. It is carried out both routinely and urgently in the presence of traumatic injury.
On average, the cost of the procedure is 500-600 rubles for a machine with X-ray film and about 1000 rubles for modern digital equipment. In public hospitals, the cost is 30% lower than in private clinics and medical centers.
If you have a doctor's referral and an insurance policy, the procedure can be performed free of charge in budgetary medical institutions. If it is necessary to administer a contrast agent, the price doubles.
Preparing for an X-ray of the pelvic bones
Preparation for the procedure requires the patient to exclude from the diet foods that promote gas formation, perform a cleansing enema or take enterosorbents. Preparatory activities begin 72 hours before the diagnosis. For this period of time, dairy products, legumes, fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as black bread are excluded from the diet. Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach: at least twelve hours must pass between the last meal and the procedure. A cleansing enema is done in the evening before the day when the examination will be carried out, and, if necessary, two hours before it.
X-ray at home
If a femoral neck fracture is suspected, elderly patients are not transportable. It is possible to call a traumatologist at home. The diagnosis is made by clinical signs.
X-rays at home are carried out only in large cities by private medical centers. Specialists visit the patient within an hour from receipt of the application. The cost of the service is from 5000 rubles.
X-rays of the hip joint are performed to study the condition of the bone structures and joint. Diagnostics are often prescribed by an orthopedist, traumatologist or rheumatologist. The study is prescribed as a primary diagnosis, then other diagnostic techniques may be required to confirm the diagnosis and correct treatment tactics: ultrasound, MRI.
X-ray examination of the hip joint
When this type of diagnosis is an urgent necessary measure, then all patients undergo it, regardless of age category. After a patient receives a referral for a hip examination, it is necessary to properly prepare for it.
Modern X-ray machines provide targeted visualization of bone elements, so other areas of the body are not exposed to radiation.
Preparation rules
Before carrying out the procedure, you should pay attention to some points to obtain high-quality images. 2-3 days before the x-ray, the patient is advised not to take anti-inflammatory drugs, as they distort the overall picture.
Since the area being examined is close to the intestines, some preparation will be required. It is first necessary to clean the organ, because feces affect the image of the joint tissue, leading to an unreliable result.
To avoid such moments, it is better to do an enema in the morning. You can use another method, for example, drink any laxative on the day of the x-ray. It is important that during the procedure there is no accumulation of gases in the colon.
That is why, several days before the examination, limit the consumption of foods that increase gas formation.
To eliminate bloating, special medications like Espumisan are prescribed.
Features of the event
During the entire procedure, the patient is under the supervision of a doctor. The patient needs to remove clothing, jewelry, and metal objects located in the area of the hip joints, as they interfere with the film. You should definitely tell your radiologist if you have a pacemaker or other implants.
In adults
The patient lies down on a special table. Before the procedure, lead plates are placed on it, which are used as protection from radiation to other parts of the body. Diagnosis of joints is done in several projections: anterior, posterior and lateral. Both joints, left and right, are often examined, even when only one is problematic. This is necessary to obtain a clearer picture by comparing the condition of the healthy and affected area.
X-rays are targeted, that is, the device is aimed only at the area under study and sends there a beam of rays passing through the bone tissue. The procedure is absolutely painless and does not cause discomfort. The hip joint is shown on a special film. The white color in the picture shows dense tissues, the dark shade shows soft tissues - muscles and tendons.
X-ray diagnostics are carried out for about 10 minutes. The radiation dose is approximately 1.5 mSv. The result is deciphered by a specialist within an hour.
If the patient has metal objects in the hip joint, for example, connecting pins, fragments, then this type of examination is not performed.
In children
There is no point in X-raying infants under three months, since they have not yet completed the ossification process. In addition, radio radiation is harmful to the developing organism. As a rule, infants at this age are prescribed an ultrasound examination of bone structures.
In addition, radio radiation is harmful to the developing organism. As a rule, infants at this age are prescribed an ultrasound examination of bone structures. Children can only undergo X-rays according to strict indications with a minimum dose of radiation.
X-rays are considered harmful to a child's health. In the future, he may develop hematological disorders, change his oncological profile, or develop mutations at the gene level. It is important to ensure that during the x-ray the baby’s limbs do not bend and he lies calmly, without moving.
In some cases, when it is impossible to put the child down and make him not move, he is given a sleeping pill.
X-ray at home
To perform such a complex procedure, special equipment is required. Thanks to advanced developments, a mobile X-ray machine has appeared. It is lightweight, small-sized and easy to use. With its help, you can diagnose the hip joint at home. Their names are different, but the principle of operation is the same.
Of course, you can buy a device for a lot of money, about 4,000 rubles, but with its help you can take pictures of patients who:
- lie with injuries to the lower extremities and cannot move;
- keep to bed and do not get up;
- are severely weakened, and their transportation to a medical facility will only do harm;
- want to save their time.
With the resulting image, you can immediately contact your doctor for additional advice.
Description of examination results
X-rays do not always show the real condition of the hip joint, that is, there are some errors. This is due to the fact that radioactive rays disperse in a stream during the examination.
The accuracy of the diagnosis largely depends on the qualifications of the doctor. At the same time, disorders in the bone structure can be interpreted differently by several doctors.
In such a situation, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s medical history, study the anamnesis and take into account previous examinations, because each pathology has its own characteristic signs.
In adults
With proper preparation, all pathological processes of the hip joint will be clearly visible on the film. The radiologist makes only a preliminary diagnosis; the final verdict is made by the attending physician, based on the patient’s complaints, symptoms, results of laboratory tests and instrumental examination methods.
The doctor measures the width of the joint space and the angle between the acetabulum and the head of the femur, evaluates the structure of the cartilage and the degree of deformation, if any.
In difficult cases, the patient is referred for additional diagnostics: MRI, ultrasound, densitometry (determining quantitative indicators of the content of essential minerals in bone tissue).
In children
The peculiarity of interpreting x-rays of hip joints in children is that the cartilaginous structure of the head of the joint is poorly visible on film at this age. There is a high probability of incorrect interpretation of diagnostic results, which will not allow timely detection of hip dysplasia (HJD).
To identify disorders and determine the stage of development of the disease, the doctor uses the Hilgenreiner technique.
The essence of this method is to assess the inclination of the roof of the acetabulum, since each age has its own angle. For babies the figure is 85-90°. If it is greater, then we are talking about articular dysplasia; if it is less, then the toddler’s condition is satisfactory. The degree of bone coverage for children over 5 years of age is ¾-1.
Deviations from the norm in a child are visible not only on x-ray film, they can also be detected at home. This is an uneven arrangement of folds, different lengths of the lower limbs, insufficient extension of the bent legs to the sides. If such obvious signs are detected, you should urgently contact a pediatric orthopedist.
Normally, there are no pathological shadows in the resulting images; on the film, the outlines of the bones will look clear and even.
Indications for the procedure
There are many reasons why you might want to know what a hip x-ray shows. The popularity of such research lies in its high information content.
For injuries to this area or polytrauma
Dislocations, subluxations, disruption of bone integrity due to fractures or cracks - each type of pathology requires timely diagnosis and treatment. An X-ray will allow you to visualize all the structures of the joint, examine the bone and cartilage tissue, and then prescribe treatment. Insufficient information about the condition of the joint can cause improper fusion of bones and aggravate the patient’s condition. Based on the results of the diagnosis, it will be known whether the results of the x-ray of the hip joint are normal.
For hip dysplasia
This condition is often congenital. In order to diagnose congenital dislocation or subluxation of the head of the hip joint, it is necessary to carefully examine it.
Pain and swelling in the joint area
An X-ray of the pelvis is necessary for pain of any degree, especially if symptoms persist for a long time. Pain may indicate inflammation, infectious and even necrotic processes. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the higher the chance of treatment success.
With a decrease in range of motion
The reasons may be the development of inflammation of the joint capsule, arthritis or arthrosis, as well as many other types of diseases. No doctor can tell offhand what the cause is, so detailed imaging of the hip joint will be required. If your joints have become less mobile, better learn how to prepare for a hip x-ray and get examined at your nearest clinic.
Crunching and clicking noises when moving
Such symptoms appear when disturbances occur in the structure of cartilage tissue. When the cartilage becomes thinner and becomes less elastic than before, it cannot fully perform the functions of a shock absorber. In this case, not only a crunching sound may appear, but also a creaking sound, and the condition is accompanied by painful sensations.
In the presence of malignant neoplasms
You will have to find out what an x-ray of the hip joint is, what this research method shows and how to prepare for it if doctors suspect a tumor process. An x-ray is prescribed only if the formation consists of bone tissue, since soft structures cannot be seen in the images due to the specifics of the study.