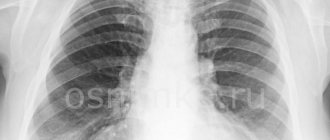
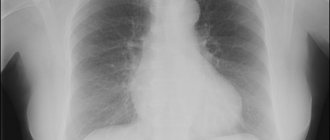
The task of every person who cares about their own health is to undergo an annual preventive examination, thanks to which it is possible to detect diseases of various organs even at the asymptomatic stage of their development. The list of mandatory diagnostic procedures includes fluorographic examination of the chest organs. Interpretation of fluorography results allows one to assess the current condition of the patient’s lungs, heart, and bone tissue of the thoracic spine.
How long to wait for the result and is it necessary to collect it in person?
The results of fluorography are not considered to be the direct image that the radiologist receives a few seconds or minutes after the procedure, but its interpretation. It is done within several tens of minutes or even hours. The final period during which the image is deciphered depends on the experience of the specialist and the quality of the image, as well as on the results of fluorography. As a rule, when pathological or potentially pathological foci are detected on images, the radiologist is faced with the task of finding the correct answer to the question - what it could be and how to classify the deviation.
It is quite problematic to receive a fluorography report on the day of the examination. The problem is that deciphering a fluorogram takes a certain amount of time: the doctor needs to look at the image, check its indicators with the norms, determine the presence of deviations and describe them in detail in a special form. Therefore, results in most clinics are issued no earlier than 2-3 hours after fluorography.
The timing of when the results are ready depends on the equipment of the fluorography room. For example, clinics that have digital equipment installed can immediately receive results and issue documents with transcripts to the patient within an hour. This is exactly what happens in private medical centers that conduct appointments strictly by appointment: in them, the radiologist can deal with the description of the image in a measured manner. You have to wait a little longer for decryption at municipal clinics. Sometimes the time frame for receiving the result can be up to 5 working days.
Good to know! In order not to waste time on an unsuccessful request for a transcript of OGK fluorography, it is worth finding out the deadlines for preparing documents in advance. In many clinics it is possible to call the receptionist and find out if the transcripts are ready.
In many clinics, radiologists are advised to appear in person for the results of fluorography, since third parties are not allowed to view the patient’s medical information. However, in reality, at the reception desk of the radiology department, the results can be given to the husband or wife, and parents can take a transcript of the examination of their children. To do this, it is enough to have with you documents confirming your relationship: a passport, marriage or birth certificate.
Preparation for fluorography and the mechanism of its implementation
Digital scanning fluorograph (the safest and most modern diagnostic method)
Fluorographic examination does not require special preparation from the patient. However, before carrying out it is necessary to take into account some features. The result is not affected by:
- medications the patient is taking;
- smoking before the study;
- products that lead to gas formation in the stomach;
- physical exercise.
Before taking a picture, it is necessary to remove objects that can appear on the film and lead to difficulties in diagnosis. Doctors warn:
- women need to remove their bra or lower it at the waist so that the fasteners are not visible;
- patients need to remove body jewelry - chains, pendants, crosses;
- Patients with long hair are advised to pin it up so that it does not fall on the shoulders and create interference in the picture.
If fluorography is necessary, it must be taken into account that it does not affect the operation of pacemakers. Therefore, patients should not worry or refuse examination if they have such a device installed.
The x-ray is monitored by a medical professional who instructs the patient and helps him find the right position. The following key points are highlighted:
- after preparation, the person is asked to stand in the booth in front of the CCD matrix and press his chest as tightly as possible; he needs to stand slightly hunched over so that his shoulders are pressed against the surface of the screen;
- at the time of the procedure, the doors of the booth are closed, and the patient is given the command to inhale and not breathe - the breath is held for several seconds, after which the command to breathe is given and the doors open. The moment of photographing is carried out while holding your breath;
- After opening the doors, you can leave the booth and get dressed.
Fluorography codes
If it is necessary to shoot in several projections, the patient will be given appropriate recommendations from the medical staff. This concludes the research.
The transcript of the fluorography is sent to the doctor who gave the referral or is pasted into the patient’s card. If the study is preventive, the patient is given a receipt indicating personal data, the time of the study, and the result of fluorography.
What do the numbers on the fluorography result mean?
The names of the diseases are not indicated in the transcript of the results. According to official standards, as a result of the examination, only the code of the identified deviation can be written. It is believed that only doctors can read the result of fluorography, which does not indicate a diagnosis, but a specific code. In fact, this is not so: if you know the principles of arranging numbers in a document, the patient himself will be able to decipher fluorography by numbers. Before you try to understand the essence of the decoding yourself, it is worth understanding that the numbers on the fluorography result mean not only diseases, but also phenomena such as diagnostic errors.
To independently decipher lung fluorography, in the conclusion of which only digital and alphabetic codes are written, it is worth studying all the codes in the table below:
| Code | What does the code mean? What deviations are visible in the image? |
| 01 | Ring shadow |
| 02 | Uniform darkening in the lung tissue |
| 03 | Focal shadows |
| 04 | Expansion of the mediastinum, increase in the size of the roots of the lungs |
| 05 | Presence of effusion in the pleura |
| 06 | Pronounced fibrous changes in tissue |
| 07 | Limited fibrous changes in tissue |
| 08 | Increased radiographic permeability (transparency) of the lungs |
| 09 | Pronounced modifications of the pleura |
| 10 | Limited modifications of the pleura |
| 11 | Numerous and large calcifications in the lungs |
| 12 | Numerous and large calcifications in the roots of the lungs |
| 11 | Numerous and large calcifications in the lungs |
| 12 | Numerous and large calcifications in the roots of the lungs |
| 13 | Numerous small calcifications in the lungs |
| 14 | Numerous small calcifications in the roots of the lungs |
| 15 | Single large calcifications in lung tissue |
| 16 | Single large calcifications in the roots of the lungs |
| 17 | Single small calcifications in lung tissue |
| 18 | Single small calcifications in the roots of the lungs |
| 19 | Anomalies in the structure of the diaphragm without changes in the pleural cavity |
| 20 | Condition after lung surgery |
| 21 | Anomalies in the structure of bone structures in the sternum area |
| 22 | Presence of a foreign body in the field of study |
| 23 | Cardiovascular abnormalities |
| 24 | Other deviations |
| 25 | OGK condition without deviations (normal) |
| 26 | Marriage |
In addition, the interpretation of the results in numbers contains information about where exactly the pathological zones are visible. So that the doctor can find out the location, the radiologist indicates the number of the lung field in the form of a simple decimal fraction, in which the numerator shows the pathology of the right lung, and the denominator shows the pathology of the left. Up to the third pulmonary field, the digital codes coincide with their numbers. For example, the first pulmonary field is designated by the code “1”, the second by the code “2”, and so on. If there are anomalies, code “4” is indicated in the first and second fields, code “5” in the first and third, “6” in the second and third, code “7” is entered in all three fields.
The next (third) column indicates the personal number of the radiologist. It usually consists of 4 or more digits. Sometimes patients try to understand them too and apply the codes described above to them. To correctly decipher the results of fluorography, this is not necessary.
The last fourth column, which indicates the decoding of the numbers, may remain empty if the patient does not require additional examination. If a bad fluorography image is received, it will contain a code “1”, indicating a call for a follow-up examination.
Good to know! An example of a numeric code would be “15. 1/4. 2087.1". It means that the patient has single large calcifications in the first pulmonary field on the right, and in the first and second fields on the left. The patient is recommended for further examination.
Another common question regarding the use of result codes is the use of the "R" code. As a rule, it contains fluorography of normal lungs and an image with pathology. The bottom line is that r in fluorography means the positivity or negativity of the results in general. For example, the code "R+" will indicate that the image is X-ray positive, that is, the appearance of abnormalities, while "R-" means that the image looks good and there are no visible changes.
Features of decoding fluorography of a smoker
Modern science has proven that even the first cigarette smoked causes certain pathological changes in a person’s respiratory organs. That is why all active and passive (persons who constantly inhale air containing tobacco smoke) smokers need to undergo a lung examination once a year.
Very often, people who abuse tobacco smoking are skeptical about fluorography. However, timely detection of a disease such as pneumonia will avoid the occurrence of many serious complications. Smokers experience thickening of the lung tissue structure, accumulation of fluid in their cavities, or the formation of tumor-like formations.
In this case, an urgent course of treatment measures is carried out, which are aimed at removing the patient from the risk zone. We hope that the above information will help our readers understand why fluorography is needed and how to interpret its results. And also that it is impossible to overestimate the importance of carrying out preventive examinations!
What could be causing poor results?
The generalized concept of bad fluorography can mean a variety of pathologies that can affect not only the lungs, but also other organs of the chest, bone structures, diaphragm, etc. Usually, in the transcript of fluorography results it is not written what kind of diagnosis this might be. The final conclusions are made by a specialized specialist:
- if the radiologist suspects scoliosis or anomalies of the ribs and sternum, the diagnosis is made by a surgeon, traumatologist or orthopedist;
- if cardiovascular pathology is detected, the diagnosis is made by a cardiologist or vascular surgeon;
- when abnormal changes in lung tissue are detected, the diagnosis is carried out by a pulmonologist, therapist, phthisiatrician, and an infectious disease specialist and oncologist may also be involved;
- changes in the diaphragm are diagnosed by a therapist, surgeon, gastroenterologist or oncologist;
- the presence of focal spots in the upper part of the mediastinum requires the participation of an endocrinologist, surgeon and oncologist in the diagnosis.
In a word, to make a correct diagnosis when receiving fluorography images with pathology, a double reading is required - the radiologist describes the pathology, notes it on the image, and a specialized specialist decides what could be the true cause of the deviation.
What signs will help the doctor see abnormalities in the OGK in the image, and what they could mean, are shown below in the table:
| Sign/deviation | What does this mean |
| The roots of the lungs are compacted and expanded | When the roots of the lungs expand, we can talk about diseases such as acute bronchitis or pneumonia. Also, expansion and thickening are observed in smokers with a long “experience”. |
| Heavy roots | In the absence of additional signs, it indicates chronic inflammation, including COPD of a smoker. If there are accompanying changes, suspicion falls on occupational pathologies, bronchiectasis or oncology. |
| Anomalies of the vascular pattern - a pronounced vascular pattern | An increase in the vascular pattern indicates acute inflammatory processes or pneumonitis (stage of lung cancer). In addition, this sign indicates diseases of the cardiovascular system - congenital heart defects, mitral stenosis, heart failure. You should not be afraid of such a result if there are symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections. They mean that the organs are supplied with blood more than usual. Alarm should arise in the absence of significant clinical manifestations. |
| Fibrous tissue in the image field | Fibrosis or accumulation of connective tissue indicates loss of lung tissue due to previous diseases or surgical interventions. Formed fibrous cords from the edge of the lungs to the pleura are adhesions, and thickened walls of the bronchi are considered a natural consequence of pneumonia or bronchitis. Extensive lesions indicate pulmonary pneumosclerosis or pneumocardiosclerosis. |
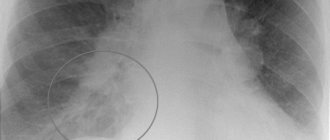
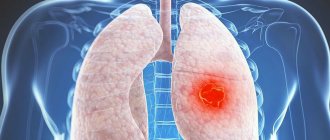
| Focal opacities | When located in the upper part of the lungs, pulmonary tuberculosis is diagnosed, in the lower part - an acute or chronic inflammatory process. |
| Round light spot | Whitish lesions in the image mean that there are large or small calcifications in the lungs. These neoplasms with clear contours indicate a previous infection (tuberculosis, helminthic infestation), which did not develop into a disease. Round, light lesions with an indistinct edge indicate a suspicion of a focus - a benign or malignant tumor. |
| Sinus sealed or free | Both a patent and sealed sinus may be normal, especially if the patient has a history of pleurisy or sternal trauma. Normally, the sinus should be open. |
| Abnormal diaphragm shape/position | A diaphragm with a curvature of the dome on fluorography is a sign of obesity, liver or gastrointestinal diseases, or previous pleurisy (in the presence of adhesions). |
| Mediastinal anomalies | The causes of poor fluorography of the mediastinum can be pathologies of the thymus gland, anomalies of the esophagus, aorta, lymph nodes and the heart itself. The expansion of the area can occur against the background of hypertension, heart failure, myocardial infarction. A significant displacement of the mediastinal shadow may indicate the presence of a tumor that puts pressure on the heart, displacing it. |
Almost all of the above diseases do not become a reason for repeated fluorography. To clarify the diagnosis and more accurately determine the localization of tumors, radiography in several projections or tomography is required. The main reasons for repeated fluorography are obtaining a low-quality (unreadable) image.
Petrification in the lungs: description, causes, treatment
Calcification (also called petrification) in the lung is an area of affected tissue or intrathoracic lymph node, surrounded by a capsule of calcium salts, a kind of scar or scar on the affected area of the organ.
Every year, every person who cares about the state of their health should visit a radiologist’s office for routine fluorography. Sometimes in conclusion you can read unfamiliar words that the patient has petrification in the lungs.
A person who is not privy to medical terminology immediately wants to know what it is, and also begins to worry whether such a diagnosis is life-threatening. Meanwhile, in most such situations there is no need to worry at all.
Description
The lungs are not the only organ of the human body in which these elements can be found.
They can appear in any parenchymal tissue, for example, in the kidney, in the structure of the thyroid gland or prostate gland. Petrification in the lungs is the result of the fight of the immune system against the source of inflammation.
They also occur after the body fights the focus of accumulation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Morphologically, petrification is an area of modified lung tissue surrounded by a dense membrane that is saturated with Ca salts.
The main goal of the calcification process is to stop the pathological process within the parenchyma of a given organ by replacing dead foci and delimiting the place of development of mycobacteria.
What are the main factors influencing the occurrence of single petrification in the lungs?
Reasons for appearance
There are many reasons for petrification:
- Presence of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Development of microabscess.
- The appearance of a foreign body in the respiratory tract.
- The occurrence of helminthic infestation.
- Consequence of pneumonia.
- Failure in calcium metabolism.
- The presence of an oncological process in the lung tissue.
- Presence of injury.
- The influence of an aggressive physical or chemical agent.
- A factor of congenital pathology, which, however, is very rare.
- Inflammatory change in the tissue of neighboring organs.
Next, we move on to consider the mechanism of development of this phenomenon.
Development mechanism
In the pathogenesis of the formation of petrification in the lungs, the following points are distinguished:
- Penetrating into the body, Mycobacterium tuberculosis multiplies in the lung tissue, forming a granuloma.
- The body's immune system begins to fight them.
- In order for the pathological focus to be isolated, a dense capsule is formed around it, which includes immune cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, and epithelioid elements.
- Over time, the outer shell of the capsule begins to become saturated with calcium salts.
Diagnostics
After a fluorogram shows calcified areas of lung tissue, a number of additional studies are usually required to monitor the activity of the pathology, for example:
- Submission of a clinical blood test.
- Carrying out biochemical analysis.
- Performing enzyme immunoassay for parasitic antigens.
- Carrying out computed tomography.
- Performing diaskintest, bronchoscopy and sputum analysis for microflora.
- X-ray examination of the lungs in special projections.
- Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics.
- Performing electrocardiography.
If after the examination there is no active focus of tuberculosis and the patient does not make a complaint, there will be no need to treat small petrification in the lungs.
In order to control the situation, you need to do fluorography annually, visiting a pulmonologist.
In order for the attending doctor to be able to monitor the dynamics of changes in tissue areas, you must have all previous images with you.
How to treat petrification in the lungs? Let's look further.
Treatment
If, during the course of research, the presence of a structural change in the lung parenchyma was diagnosed, then appropriate treatment will be required. Its type directly depends on the etiological cause of the pathological change.
If a focus of active tuberculosis is detected, the patient will require intensive therapy with anti-tuberculosis drugs (Rifampicin, Isoniazid).
The presence of helminthic infestations requires treatment with antiparasitic drugs (“Vermox”, “Dekaris”, “Pyrantel”).
When oncological diseases develop in the lung tissues, it is necessary to prescribe antitumor therapy to the person as soon as possible.
Large and at the same time multiple petrification in the lungs, which significantly impair the quality of life of patients, are very rare. They can be eliminated promptly. To restore normal respiratory functions, therapeutic exercises may be prescribed in combination with a special massage. Such patients are recommended sanatorium and resort treatment.
Prevention
In order to avoid the occurrence of such a phenomenon as petrification in the lung parenchyma, preventive measures are required:
- Maximum elimination of the hypothermia factor.
- Timely seeking medical help in case of the first manifestations of respiratory tract pathology.
- Quitting bad habits in the form of smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Leading an exceptionally active lifestyle, that is, we are talking about daily long walks in the fresh air and doing exercises.
- Maintaining proper nutrition. You need to consume a large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, include honey, walnuts, dried apricots, raisins, and prunes in your diet.
- Managing chronic concomitant diseases.
- Maintaining a rest and sleep schedule.
- Use of personal hygiene products and separate utensils.
Petrification in the lungs is not a serious pathology and in most situations will not require treatment. They very rarely become the direct cause of complaints from patients. If you see such a term in your medical record, you should not be nervous at all.
Usually, the presence of petrificates indicates a good state of the immune system, which has independently coped with the problem that has arisen, that is, it indicates that the pathological area has been delimited from healthy tissues.
In order to sleep peacefully, it will be enough to regularly visit a pulmonologist and monitor your general condition using x-rays.
Petrifications in the lungs in breast cancer
Breast cancer with such elements in the lungs is found quite often. This can be explained by the fact that, despite the fact that an oncological formation can metastasize to any organ, areas that are located close to the primary focus are more at risk.
Metastases can form from a detached cell of the primary neoplasm. Against this background, it is worth considering that they will be able to manifest themselves even after many years. There is no scientific explanation for this phenomenon yet.
But it is known that under the negative influence of certain factors, such cells can begin to divide, forming an entire system of blood vessels.
Why do they send for x-rays after fluorography?
Many patients are perplexed why they were sent for an x-ray after fluorography. As a rule, if the result is bad, they are not sent for additional research in all cases, but only if there is a suspicion of severe OGK disease. The list of diseases (even if the diagnosis is in question) for which it is recommended to undergo an x-ray after fluorography includes:
- tumors of the lungs and mediastinum;
- foreign objects found in the sternum;
- the presence of focal darkening or lightened spots in the images;
- pronounced vascular abnormalities.
The need for X-rays after fluorography is explained by the fact that this method allows you to look at pathological lesions from different angles. As a result, the doctor can more accurately determine the location, size and nature of anomalies, as well as add clarification to the interpretation of fluorography results.
Important! If the examination result is “bad” due to a defective film or a blurred picture, the patient is sent again for fluorography, and not for x-rays.
The impact of petrification on quality of life
As a rule, petrification in the lungs is an incidental finding. The patient may not feel any discomfort at all for a long time.
In cases where areas of calcification reach large sizes or are formed in large numbers, the patient’s quality of life may be impaired to some extent:
- due to an insufficient amount of normally functioning alveolar tissue, respiratory dysfunction develops: tachypnea, shortness of breath that occurs with little physical exertion or at rest;
- tachycardia;
- the skin becomes cyanotic;
- fingers take the shape of “drumsticks”, and nails - “watch glasses”;
- loss of appetite, weakness, decreased performance;
- sleep disorders;
- pain in the ribs;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes (typical in the presence of structural changes in the lung parenchyma);
- with multiple foci of petrification, vomiting may occur;
- the appearance of a headache.
It should be noted that the presence of petrificates is a risk factor for the development of cancer or tuberculosis.
What other additional examination may be required and why?
If the results of fluorography clearly indicate the presence of pathologies, the patient is sent for further examination. In this case, the fluorography transcript contains the code “R+” and the number 1 in the last (fourth) column. The main reasons for further examination are the need to establish a more accurate clinical and pathological picture, obtaining comprehensive information about the causes of anomalies and selecting adequate therapeutic measures.
The list of additional procedures that include additional examination after fluorography depends on the detected deviations:
- in case of deviations in the mediastinum, indicating heart pathologies, hypertension, a complex of cardiological studies is prescribed - blood biochemistry, blood for hormones, cardiogram, echocardiogram, consultation with a cardiologist;
- in case of deformation of bone structures, radiography of the spine and chest is required; if necessary, an MRI or CT scan of these parts of the musculoskeletal system is performed;
- if the diaphragm is deformed, the patient is sent for consultation to a gastroenterologist and surgeon, who will recommend undergoing an abdominal ultrasound, gastroscopy or colonoscopy, if radiologists have not directed these studies immediately after receiving the results.
If the patient was not sent for further examination when calcifications or signs of adhesions or localized fibrosis appeared on the fluorography image, there is no cause for concern. These conditions are not considered dangerous to health and require only systematic monitoring. If progress appears (increase in size, spread to neighboring tissues), the doctor will definitely write out a referral for further examination. He will not do this without visible reasons.
Development mechanism
In the pathogenesis of the formation of petrification in the lungs, the following points are distinguished:
- Penetrating into the body, Mycobacterium tuberculosis multiplies in the lung tissue, forming a granuloma.
- The body's immune system begins to fight them.
- In order for the pathological focus to be isolated, a dense capsule is formed around it, which includes immune cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, and epithelioid elements.
- Over time, the outer shell of the capsule begins to become saturated with calcium salts.
What shows pneumonia, pneumonia, chest tightness: x-ray or fluorography?
Thanks to fluorography, a number of diseases can be identified, for example:
- Presence of fluid in the lungs
- Tumors and neoplasms at the first stage (more than 4 mm)
- Pathological changes (cyst, cavity)
- Fibrosis
- Last stages of inflammation
In order to study the situation in more detail, it is necessary, of course, to take a chest x-ray. If after undergoing fluorography the doctor stamped it and released you, then there is no reason to worry. But if the specialist has any suspicion, he will write a referral for an additional X-ray examination, or send him for preventive procedures to an anti-tuberculosis dispensary.
Pneumonia on x-ray
X-rays are prescribed in the following cases:
- Manifestation of severe shortness of breath
- Severe pain in the chest area
- Long, severe cough
The doctor may also prescribe an x-ray for diseases such as pleurisy, pneumonia, malignant neoplasms and seals, bronchitis or tuberculosis. It is imperative for people who have had tuberculosis to be examined in order to detect it in time if a relapse occurs.
Advantages
Digital fluorography is one of the safest and most effective methods for studying many diseases. In addition, it is quite economical. Since there is no need to spend additional money on purchasing film and solutions for developing it. This method allows you to view the finished result on the device monitor. Moreover, the resulting image can be transmitted both over a local network and, if necessary, printed on a printer.
Using digital equipment, you can examine the result in more detail.
Digital fluorography has the following features compared to traditional:
Fluorography for children
- reduced x-ray load on the patient compared to film radiography by half. Irradiation compared to standard fluorography is 10 times;
- the ability to immediately obtain results, which allows, if necessary, additional diagnostics in other projections;
- computer processing allows you to improve the image, as a result of which even minor changes are detected and the structure of pathologies is assessed;
- as a result of obtaining high-quality images, there is no need for radiography;
- a digital device eliminates defects associated with erroneous exposure or photo processing;
- it is possible to study not only lung tissue, but also dense structures of organs located in the chest area;
- the ability to save the result on a digital medium;
- the time required to search for data from the archive is reduced;
- the ability to store the result for a long time, send it over long distances by e-mail. Film cannot provide such opportunities;
- efficiency.
However, this method is not yet very popular compared to the traditional one. This is due to the fact that the general population is concerned about its novelty and does not know what this research is or how it is carried out.
What are the methods based on?
The method is based on the ability of an X-ray beam to pass through opaque tissues while maintaining its activity. This also applies to fluorography of the chest organs, x-rays, and fluoroscopy. The methods differ only in the radiation dose and the method of obtaining the image.
The x-ray is a negative, so the shadows on it are white and vice versa. The human body is made up of different tissues and they all have different degrees of x-ray absorption.
In a photograph of the lungs during pneumonia, it turns out that the negative colors the densest parts white, including the bones, makes the empty parts black, and the organs give gray colors of different shades.
The final result of the picture is heterogeneous. In healthy lungs, the structure is homogeneous. If pneumonia is present, darkened areas of compaction on x-rays indicate foci of inflammation. Highlighted areas are airy fabrics. The diagnosis of pneumonia based on the image is made when there are:
- single or multiple spots;
- segmental seals;
- light and dark specific areas;
- altered roots of the lungs.