X-ray of the lungs is a summation image of the soft tissues of the chest. Along the path of X-rays, some structures absorb and others reflect radiation. Such a game is displayed on x-ray film or digital media.
A radiologist reads an x-ray consisting of a complex of white and gray shadows. Their combination forms an image, which a specialist deciphers and makes a description.
Our specialists are ready to interpret readers’ X-ray images for free. We also suggest that you carefully understand on your own the complex of X-ray darkening and clearing.
X-rays of the lungs are normal
X-ray images of the lungs (chest organs) are analyzed according to the “PoChiFora and InRiCoS” scheme. How to decipher these terms:
- Po – position;
- Chi – number;
- Fo – form;
- Ra – dimensions;
- In – intensity;
- Ri – drawing;
- Ko—contours;
- C – displacement.
This algorithm is taught to medical university students preparing to become radiologists.
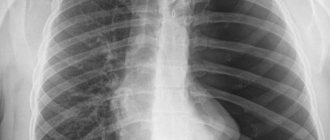
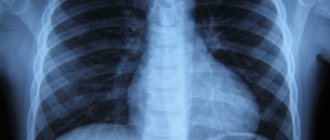
Consider, for example, an x-ray of a normal lung:
It visualizes a lot of darkening and lightening (white and black), which can intimidate readers. In fact, this radiograph is easy to decipher (see next image)
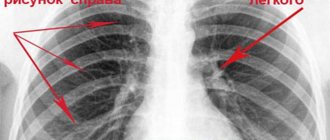
All anatomical structures are labeled on the radiograph to make it easy for readers to understand. We suggest you remember the intensity of the lung fields. The norm does not imply the presence of pathological darkening (white) and lightening (dark), which are not in the image.
If you get your eye on it, you will learn to clearly distinguish normal from pathology.
Features of lung radiography
Content:
- Features of lung radiography
- Indications and contraindications for examination
- About the dangers of radiography and fluorography
- X-ray of the lungs
- Results of the study
X-ray of the lungs is the most popular method of studying this organ, which is used in medicine much more often than magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
An X-ray image is obtained by passing through the human body and projecting the resulting beam of rays through the tube of an X-ray machine.
This diagnosis is similar to an ordinary photograph, with the only difference being that the tissues of the human body can transmit rays through themselves in different ways and reflect this in the photograph by coloring areas in different shades of gray - the denser the tissue, the lighter the area of the photograph.
Thus, bones appear white on X-rays, while cavities and soft tissues appear gray to black, depending on their light transmittance.
X-ray of the lungs is of two types - overview or targeted. With a survey radiography, the entire lungs are examined, and with a targeted version, the part of them necessary for a medical report is examined. When performing a computed tomography scan of the lungs, X-rays are also used, passing through the body from several angles at once and giving a complete three-dimensional picture of the organ.
The information content of computed tomography of the lung is higher, but this study is much more expensive, and the radiation dose to a person is several times higher, so it is used only when it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
When performing magnetic resonance imaging, the harm to the body is zero, since its essence comes down to the effect on the human body using magnetic fields. However, this diagnosis is quite expensive, and it cannot be used by people who have any metal implants in their bodies - artificial joints, heart valves, pacemakers, and even pins for dental prosthetics.
When choosing a research method, doctors are based on specific indications, however, when determining the general condition of organs, it is not advisable to use anything other than radiography. Many patients do not know the difference between X-rays and fluorography, but there is such a difference, and it consists in the fact that a fluorograph allows an X-ray image to be transferred to film, as a result of which doctors receive a rather blurred and inaccurate picture of the affected areas, which rarely gives a true idea of the situation cases in the area under study.
However, this method is very accessible, and therefore it continues to be used in public medical institutions. Ideally, fluorography should be completely replaced with radiography over time.
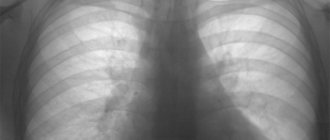
X-ray of healthy lungs, how to read
X-rays of healthy lungs should be described according to the classical standard. First, entries are made about pathological X-ray syndromes, then the pulmonary fields, roots, domes of the diaphragm, costophrenic sinuses, cardiac shadow and soft tissues.
Classic algorithm for describing healthy lungs:
- In the pulmonary fields without visible focal and infiltrative shadows;
- The roots are not expanded, structural;
- The contours of the diaphragm and costophrenic sinuses are without features;
- Heart shadow of normal configuration;
- Soft tissues without any features.
The above radiograph fits this description.
We hope that we have answered readers how to read x-rays of the lungs normally, so we move on to the next point about x-ray syndromes in pathology.
Which result is more accurate?
The diagnostic capabilities of tomography are much wider. It is CT that makes it possible to identify benign and malignant tumors of bones and soft tissues at the earliest stages. CT cannot replace conventional x-rays. It will not give the doctor some very important and necessary diagnostic information.
CT makes it possible to conduct angiography of blood vessels with high accuracy, to identify the direction, speed and characteristics of blood flow, as well as a number of pathological cases associated with changes in the properties of blood. CT can reveal the condition of blood vessels and structural changes in lung tissue. The pictures are accurate and clear.
When ordering an x-ray or tomography, you need to inform the doctor about any medical procedures being performed, especially if they are performed privately. In a situation where contrast is administered, it is necessary to mention the possible occurrence of allergies if there is a predisposition to it.
X-ray of the chest organs with pneumonia - pathology
An x-ray of the lungs with pneumonia is a classic manifestation of pathology. We give an example of an image of inflammatory changes in lung tissue (pneumonia), so that readers understand how normal differs from pathology.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the pictures below for pneumonia and normal conditions. Answer the question: which x-ray is normal and which is pathological? Determine which x-ray shows pneumonia.
Digital chest x-ray No. 1
Digital X-ray No. 2
Let us tell you that the darkening is small and localized above the diaphragm.
X-ray of healthy lungs is a classic of radiology, since radiology is focused on detecting tuberculosis, cancer and pneumonia.
What is the purpose of x-rays?
What does a lung x-ray show a doctor? Why is it needed?
Projection research makes it possible to identify pathological processes affecting the respiratory organs. The specialist analyzes shadow intensity, coverage and outline.
X-ray of the lungs is normal.
Among the probable diagnoses made on the basis of the information received:
- inflammation of the bronchi, pleura, lung tissue;
- emphysema;
- tuberculosis;
- malignant formation;
- swelling of the respiratory system;
- rib fracture;
- pneumothorax, etc.
In addition to helping in making a diagnosis, x-rays of the lungs provide control over the treatment of all pathological processes of the respiratory system.
Reading the X-ray
On the presented radiograph of the lungs, an infiltrative shadow is visualized in the supradiaphragmatic zone on the left. The roots are heavy. The costophrenic sinuses are not veiled. Heart shadow of a classic configuration. No pathology in soft tissues can be traced.
Conclusion : X-ray signs of left-sided segmental pneumonia. An X-ray of the chest organs in the left lateral projection is recommended to establish the localization of the darkening.
Digital X-ray No. 4
Indications
Compaction syndrome.
Low to medium density lesion. Tuberculosis. Possible patient complaints include:
- persistent cough;
- progressive shortness of breath;
- increased body temperature;
- active production of sweat;
- chest pain;
- wheezing;
- cough producing blood or sputum;
- prostration.
In addition, patients with suspected tuberculosis, pleurisy, pneumonia, heart disease, injuries of paired organs and bone tissue are examined.
For preventive purposes, lung images are taken for people working in hazardous conditions. For example, miners, masons, staff of tuberculosis dispensaries, etc.
Digital X-ray – what is it and how to read it
Digital radiography is a product of modern developments in radiology. In the era of the birth of X-ray diagnostics, in order to obtain an image after X-rays passed through the anatomical structures of the body, it was necessary to use fixatives and developers to create a photo negative. The process is similar to how photographers develop film.
Modern technologies have made it possible to get rid of this labor-intensive procedure. Digital research has replaced film. They involve the use of special sensors that record the intensity of the rays at the exit from the object of study and transmit information to the software. It analyzes the signals and displays a digital image on the screen. It is analyzed by a radiologist. When reading the image, the specialist has the ability to enlarge or reduce the image, convert a negative into a positive, and many other functions.
A normal x-ray of the lungs does not differ in a digital image from its film counterpart. However, the novice radiographer will need to get used to the technology, as the X-ray shadows it produces are somewhat different from those produced by film.
Contraindications and complications after radiography
X-ray has its limitations:
- severe stage of diabetes mellitus;
- kidney and liver pathologies;
- internal bleeding;
- pregnancy.
After an x-ray, complications develop in extreme isolated cases. During the session, the radiologist takes into account the required dose of radiation exposure and does not allow it to exceed the norm. What is better - chest X-ray, CT or MSCT - is determined by the attending physician.
The dose of X-ray radiation per person per year should not exceed 1 m3v. X-rays of the lungs are allowed 1-2 times a year. Before starting the procedure, the condition of the person being examined is taken into account. Scanning of severely frail patients is not performed.
Pathologies
On a chest x-ray of a healthy person you cannot see :
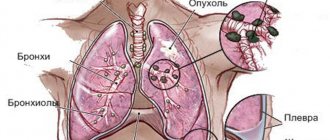
- Airways . At the level of the VI vertebra, the larynx passes into the trachea, which continues to the IV or V thoracic vertebrae. Here it is divided into the main bronchi: right and left.
- Trachea and bronchi . In a healthy person, they are not visible on an x-ray because their walls are too thin to reflect radiation. They are visible only when the tracheobronchial tree is displaced to the affected side (with atelectasis - collapse of the lung), pleural effusion, pneumothorax (presence of air in the pleural cavity).
- The lymph nodes. They can be detected during inflammation in the main bronchi and during cancer metastasis in the form of enlarged round spots with smooth contours.
- Articulations of ribs and sternum . Calcification of the first rib occurs at 30-36 years of age . Ossification of the cartilaginous part of the remaining ribs appears after 50 years with various pathologies of the endocrine system.
White spots
White spots (focal opacities) in the lungs may be a sign of:
- pneumonia (indistinct, blurry contours, varying intensity);
- tumors;
- atelectasis (triangular in shape; the end is directed towards the root, coincides with the size of the segment);
- tuberculosis (various).
Photo 1. An example of how an X-ray of a healthy person’s lungs should not look like: an image with a tumor.
Cavity
The cavity indicates:
- tumor decomposition;
- abscess ;
- focus of tuberculosis .
Small lesions
Small scattered foci can be detected when:
- silicosis;
- tuberculosis;
- sarcoidosis.
A high position of the diaphragm cone is possible with postthromboembolic syndrome.
With emphysema, the diaphragm becomes flattened .
Deformation of the cardiac shadow indicates diseases of the cardiovascular system or pathology of the mediastinal organs.
CT scan
Tomography can be called an improved x-ray. The operating principle of CT is based on the effect of X-rays, but when examined on a spiral/multispiral type tomograph, it is possible to obtain layer-by-layer images with a slice size of 1 mm.
What is better - X-ray or tomography of the lungs ? It should be understood that CT is a clarifying diagnostic method and is often used in situations where fluorography or x-rays have already raised doubts among the doctor about the presence of lung disease. On CT images, tumor compactions are clearly visible, the size of which is equal to the scanning step. When using contrast, it is possible to examine in detail the foci of pathology and existing metastases, regardless of the depth of their occurrence.
CT examination is indispensable in diagnosing lung cancer, sarcoidosis, aortic aneurysm, and tuberculosis. Despite the fact that when testing on a tomograph, the patient receives a considerable radiation dose, its harm is significantly less than the opportunity to detect a serious disease at an early stage.
Advantages and disadvantages of both methods
In order to choose an examination method - radiography (including fluoroscopy) or CT - it is necessary to consider the pros and cons of diagnostic methods.
Among the advantages of classical x-rays are:
- availability. This examination can be completed at any clinic;
- low cost. The price, as a rule, does not exceed 1,500 rubles;
- safety. The radiation dose is low;
- the opportunity to repeat the procedure in a few days.
The tissues are clearly visible on the x-ray, but the structure is not easy to see.
Thanks to CT you can:
- see the organ separately, from different points;
- determine the size and depth of the disease focus with high accuracy;
- reduce the effect of overlapping images of other organs. To do this, it is enough to reduce the time of CT scanning.
The resulting images clearly show the structures of organs and tissues.
Despite higher quality images, CT has disadvantages compared to X-rays:
- high price. The price of the examination is from 3 to 6 thousand rubles;
- harmful radiation at a higher dose.
Dangers of CT and X-rays
When carrying out both procedures, low-energy radiation is used, they try to reduce the diagnostic time, and follow all instructions and precautions. However, sometimes unforeseen situations arise. Ionizing radiation can:
- temporarily change the composition of the blood;
- interfere with the functioning of cells;
- change tissue molecules;
- cause cataracts or the development of tumors;
- change the protein structure.
Where is there more radiation - CT or X-ray
The radiation dose on X-ray is lower than on CT and is 0.2-0.9 m3v, while on a tomograph it is 3-10 m3v. But in this case there were some exceptions. 3D devices used in dentistry are characterized by a minimal radiation dose.
Preparatory stage and examination
Digital scanning fluorograph (the safest and most modern diagnostic method)
No special preparation is required before taking an x-ray. The patient's actions during the examination are as follows:
- Undresses from the waist up and removes metal objects (watches, glasses, jewelry, etc.).
- Removes hair from the area being examined.
- Leans against the equipment.
- Takes a deep breath and holds it, listening to the doctor's command.
- Restores breathing after completion of the procedure.
During the examination, the patient is required to remain motionless. For these purposes, during the diagnosis of children, fixing products and supports are used.
The duration of the procedure is a few seconds. Usually they resort to plain radiography of the lungs, taking a picture in a direct projection. The patient is directed with the anterior part of the chest towards the matrix. Sometimes the patient needs to stand sideways, in which case the x-ray is taken in two projections.