Purpose of the examination
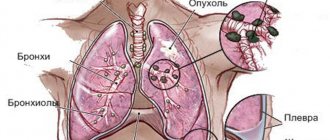
X-ray of the lungs is the most common and informative research method. This diagnostic method allows you to identify the presence of respiratory diseases:
- sarcoidosis;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
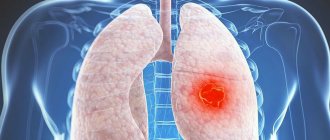
- malignant neoplasms;
- tuberculosis;
- chest injuries;
- presence of foreign objects;
- pneumothorax and other various pathological processes.
In order to prevent pulmonary diseases in citizens employed in hazardous industries (chemical industry, construction (masons), mining (miners), etc.), X-rays of the lungs are performed once a year (more often if necessary). What do research results show in such cases?
The fluoroscopy response makes it possible to promptly prevent or recognize the disease and prescribe the necessary medication or other therapy.
Indications for use
The patient can have an x-ray of the larynx without a doctor’s prescription, at his own request. If the doctor has prescribed a procedure, then there is a suspicion of the following pathological conditions:
- Traumatic injury to the neck organs.
- The presence of a foreign body in the lumen of the larynx or trachea.
- Chemical or thermal burns of the larynx, pharynx, upper esophagus and trachea.
- Chronic laryngitis.
- Paresis and paralysis of the larynx.
An X-ray diagnosis of the larynx is prescribed by a doctor if the patient suspects various injuries - external or internal. For burns, x-rays are sometimes prescribed. The most valuable method for diagnosing paresis and paralysis.
As an auxiliary study, x-rays of the larynx are used to diagnose chronic pathologies of the larynx with inflammatory processes, as well as tracheal stenosis, malignant tumors, whooping cough, and diphtheria.
X-rays also play a key role in diagnosing laryngeal cancer. The study is used in tandem with other types of diagnostics to obtain an accurate result.
The effect of radiation on the human body
Radiation exposure is considered radiation exposure, and some people refuse to undergo this procedure. However, this is in vain, medicine uses low-energy rays, the radiation dose is negligible, and the human body is exposed to them for a short period. A few years ago, scientists proved that even repeated X-rays (for medical indications) are not capable of harming health. In some cases, this procedure is also prescribed for pregnant women. Serious diseases that can be diagnosed using X-rays have more serious consequences than the minimum dose of radiation. As an alternative to conventional traditional X-rays, digital X-rays with an even lower radiation dose are now available.
What is a lung x-ray and how does it differ from fluorography?
X-ray diagnostics, as an independent technique, appeared in 1895. Wilhelm Roentgen patented the rights to the invention of a tube of the same name, which emits microparticles that can penetrate soft tissue. A feature of the described phenomenon remains the different degrees of absorption of the corresponding rays. When a special film is fixed opposite the tube, structures through which the microparticles have passed will be displayed on its surface.
Interesting! Wilhelm Roentgen worked in parallel with Ivan Pulyuy (Ukrainian physicist). Scientists communicated with each other and shared their experiences. However, Roentgen quickly patented the results of his research, which ensured his place in the history of science.
At the end of the twentieth century, the radiation diagnostic method for the first time allowed doctors to see the internal structures of the patient during his lifetime. Over the course of several years, the procedure spread throughout the world, where it was used to determine the causes of coughs, joint pain, bowel movements, and the like. The technique was improved, as were the devices.
In the twenty-first century, radiography is mainly used in traumatology (detection of fractures) and pulmonology (identification of the causes of cough and shortness of breath).
In practice, two main methods are used:
- traditional radiography;
- fluorography of the lungs.
The mechanism for obtaining the image in both cases is the same - the X-ray tube emits particles that pass through the chest organs, and the radiation with different intensities is deposited on the film located on the opposite side of the patient.
The difference between lung X-ray and fluorography lies in the purpose of the procedure and the size of the resulting image. The traditional procedure is used routinely to assess the condition of patients with cough, fever, and other symptoms of respiratory pathology.
Fluorography is a screening method used to detect tuberculosis and large tumors in the chest. The procedure is carried out regularly - once every 2 years for ordinary people. In the presence of harmful working conditions (miners, plant employees), the frequency of examinations increases.
Traditional X-rays of the lungs use films measuring 35 by 35 or 30 by 40 centimeters. In the case of fluorography - 2.4 by 2.4 or 7.0 by 7.0 centimeters.
In addition, during radiography, the patient receives a lower dose of radiation, which is due to the operating features of the devices. Fluorography only helps to detect the presence of pathology. Clarifying the causes of cough and choosing the appropriate treatment method requires the use of traditional radiation diagnostics.
Indications
Let's consider the symptoms for which the attending doctor prescribes a chest x-ray. What the image shows will determine the tactics for further management of the patient.
- Periodic pain in the sternum.
- Dyspnea.
- High body temperature that lasts for a long time.
- Blood in sputum.
- Prolonged exhausting cough.
- A large amount of sputum discharge.
- Dry cough.
For the purpose of prevention, fluorography, or x-ray, is indicated to all citizens at least once every two years or more often in accordance with the recommendations of a medical professional.
How to conduct an examination
To take a correct picture of the larynx, the patient must take a position lying on his stomach. When placed sideways, the image shows the lumen of the larynx. In some difficult cases, radiopaque agents are used, which are sprayed on.
The procedure proceeds as follows:
- The patient is placed on his side.
- A specialized film is applied to the back of the neck opposite the recording device.
- A focal distance of about 60 centimeters is maintained.
- The patient holds his breath while the image is taken. This is necessary to obtain the clearest image.
See also
Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes with chickenpox in children and adults
Read
In rare cases, a second x-ray is taken. To do this, the patient is numbed with drugs to the area being filmed, and the film is placed in the area of the larynx. The X-ray beam is directed clearly at the area of the disease focus, which makes it possible to accurately reflect the nature of the disease.
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
You have been prescribed a lung x-ray, how can you prepare for it? No preliminary preparation is required. Before carrying out the procedure, you must remove jewelry (chains, beads, necklaces) so that they do not distort the result. Immediately before the procedure, your healthcare provider will ask you to wear a special skirt that wraps around your waist to protect your genitals from radiation. Next, the doctor selects the required projection (anterior, posterior, or sometimes the picture is taken in a side-lying position).
Depending on the equipment on which the X-ray of the lungs was performed, the results will be instantaneous (digital method) or after some time after processing and developing the film.
Preparation for the procedure
No preparatory steps are required from the patient for radiography. The main condition is to remove your jewelry before the examination. The conditions for the procedure are described below.
In some cases, to improve image clarity, the organ being x-rayed is “shaded” or “illuminated” with medications. This option requires more thorough preparation (for example, refusing to eat a few hours before the procedure).
X-ray results
Did you take an X-ray of your lungs? Let's look at what the transcript shows below:
- Diaphragm defects.
- The presence of fluid in the pleural cavity. A tumor or pleurisy is excluded.
- A cavity in the lung indicates necrosis of the lung tissue. Diagnose tuberculosis, cancer or abscess.
- Small focal darkening is a sign of pneumonia and tuberculosis. Large - tumor of the bronchi, metastases to the lungs.
- Small lesions that are very common are sarcoidosis or tuberculosis.
- A large, round shadow indicates advanced tuberculosis or a malignant neoplasm.
In addition to the above, other changes in the lung tissue and lungs are also detected, which help to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Unfortunately, there are cases of false results, or in cases where the study is carried out in the early stages of the disease, it may not be seen. For an accurate conclusion, in addition to the results obtained, other diagnostic methods are used in addition to X-rays, and the necessary laboratory tests are also carried out.
What is the essence of x-rays?
The use of digital equipment increased the quality and information content of the study. The technology saves diagnostic results on any digital medium or sends them by email in DICOM, HL7 format, which eliminates the loss of the X-ray report.
Another convenience is the ability to keep a photo in perfect condition for a long time. A standard image on film loses quality over time, fades and becomes scratched, unlike its digital counterpart.
Film X-ray takes an image that cannot be duplicated. A modern diagnostic option will allow you to take any number of images.
Dark spots on an x-ray
X-ray showed spots on the lungs? The reasons for their appearance may be: incorrect position of the patient during the procedure, poor-quality equipment, or the presence of pathology. Only a doctor can accurately interpret X-ray data.
Formations in the form of white spots indicate the presence of tuberculosis, bronchitis, pneumonia, pathology in the pleura, and occupational diseases. If a person has had bronchitis or pneumonia, then spots can be detected on an x-ray. They are regarded as residual manifestations of the disease, and they will disappear after some time.
If light spots are found in the upper parts of the lung, then tuberculosis is diagnosed, the main sign at the first stage of which is a light path running from the place where there is an inflammatory process to the root system. With timely and proper treatment, inflammation decreases and tissues undergo scarring. Instead of white, a dark spot appears in the photo.
If an X-ray of the lungs shows that black spots are visible, this indicates an exacerbation and the presence of chronic pneumonia. After a course of drug treatment and complete recovery, the spots disappear. Dark formations can also cause malignant pathologies. The detection of dark spots in a practically healthy person indicates many years of smoking; in children, it indicates a foreign body.
Types of radiography
Radiography is used for a comprehensive examination of all organs and tissues of the human body; it is divided into several types that have certain differences:
- panoramic radiography;
- targeted radiography;
- radiography according to Vogt;
- microfocus radiography;
- contrast radiography;
- intraoral radiography;
- radiography of soft tissues;
- fluorography;
- digital radiography;
- contrast - radiography;
- radiography with functional tests.
You can learn how to take an x-ray from this video. Filmed by the channel: “This is Interesting.”
Panoramic radiography
Panoramic or survey radiography is successfully used in dentistry. This procedure involves photographing the maxillofacial region using a special device - an ortapontomograph, which is a type of x-ray. The result is a clear image that allows you to analyze the condition of the upper and lower jaw, as well as the adjacent soft tissues. Guided by the image taken, the dentist can perform complex operations to install dental implants.
It also helps to perform a number of other highly technical procedures:
- suggest the best way to treat gum disease;
- develop a method for eliminating defects in the development of the jaw apparatus and much more.
Sighting
The difference between general and targeted radiography is in a narrow focus. It allows you to image only a specific area or organ. But the detail of such an image will be many times greater than that of a conventional x-ray examination.
Another advantage of a targeted radiograph is that it shows the condition of an organ or area over time, at different time intervals. X-rays passing through tissue or an area of inflammation magnify its image. Therefore, in the picture the organs appear larger than their natural size.
The size of the organ or structure will appear larger in the image. The object of study is located closer to the X-ray tube, but at a greater distance from the film. This method is used to obtain an image at primary magnification. Spot radiographs are ideal for examining the thoracic region.
X-ray according to Vogt
Vogt radiography is a non-skeletal method of radiography of the eye. It is used when microscopic debris enters the eye that cannot be tracked using a regular x-ray. The image shows a clearly defined area of the eye (anterior compartment) so that the bony walls of the orbit do not obscure the damaged part.
For Vogt research in the laboratory, you need to prepare two films. Their size should be two by four, and the edges must be rounded. Before use, each film must be carefully wrapped in wax paper to prevent moisture from entering its surface during the procedure.
Films are needed to focus X-rays. Thus, any smallest foreign object will be highlighted and detected due to shading in two completely identical places in the picture.
To perform an X-ray procedure using the Vogt method, you need to take two pictures one after the other - lateral and axial. To avoid injury to the fundus, images should be taken with soft x-rays.
Microfocus radiography
Microfocus radiography is a complex definition. The research involves various methods of obtaining images of objects in X-ray photographs, the diameter of which focal spots are no more than one tenth of a millimeter. Microfocus radiography has a number of features and advantages that distinguish it from other research methods.
Microfocus radiography:
- allows you to obtain multiple magnification of objects in photographs with increased sharpness;
- based on the size of the focal spot and other features when shooting, it makes it possible to enlarge multiple times without losing the quality of the photograph;
- The information content of an x-ray image is significantly higher than in traditional radiography, with lower doses of radiation exposure.
Microfocus radiography is an innovative research method used in cases where conventional radiography is not able to determine the area of damage to an organ or structure.
Contrast radiography
Contrast radiography is a combination of radiological studies. Their characteristic feature is the principle of using radiocontrast agents to increase the diagnostic accuracy of the resulting image.
The contrast method is used to examine the cavities inside organs, to assess their structural features, functionality and localization. Special contrast solutions are injected into the area under study so that due to the difference
One of these methods is irrigoscopy. During it, radiologists examine the structure of the walls of organs while ridding them of contrast agents.
Contrast radiography is often used in studies:
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- genitourinary system;
- with fistulography;
- to determine the characteristic features of blood flow.
Intraoral radiography
With the help of an examination using contact intraoral (intraoral) radiography, all types of diseases of the upper and lower jaw and periodontal tissue can be diagnosed. Intraoral x-rays help identify the development of dental pathologies in the early stages, which cannot be achieved during a routine examination.
The procedure has a number of advantages:
- high efficiency;
- rapidity;
- painlessness;
- wide availability.
The procedure for performing intraoral radiography is not particularly difficult. The patient is seated in a comfortable chair, then asked to stand still for a few seconds, squeezing the film with his jaws for the image. During the procedure, you must hold your breath for a short time. A photo is taken within three to four seconds.
Radiography of soft tissues
Examination of soft tissues using radiography is carried out to obtain operational information about:
- muscle condition;
- articular and periarticular capsules;
- tendons;
- ligaments;
- connective tissues;
- skin;
- subcutaneous fat tissue.
Using a detailed image, a radiologist can examine the structure, density and size of connective tissues. During the examination, X-ray rays penetrate soft tissue, and the machine displays the scanned image on the screen.
Indications for examination:
- if there are suspected violations of muscle integrity;
- swelling of soft tissues, severe pain during touching;
- problems with blood vessels;
- salt deposits;
- diagnosing serious diseases (cysts, tumors);
- parasitic activity;
- at the initial stages of development of extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Radiography with functional tests
During an examination using this method, the doctor asks the person to tilt his head in different directions, up and down. In this case, the bones are fixed in a certain position, which is subsequently displayed on the pictures. This is called radiography with functional tests.
For the majority of modern children and adolescents suffering from problems associated with dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system, this type of X-ray examination is especially important.
In order to identify hidden pathologies in a timely manner, children should undergo x-rays with functional tests of the cervical spine. This examination is suitable for all children, regardless of age. In infants, examination can reveal injuries and abnormalities received immediately after birth. Pediatric radiography can promptly report problems with skeletal development (scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis).
Photo gallery
Intraoral
Contrasting
Microfocus
Radiography of soft tissues
Panoramic
X-ray according to Vogt
Sighting
Radiography with functional tests
Fluorography
Digital
Does X-ray show pneumonia?
X-ray examination for pneumonia is both a method of identifying the disease and monitoring its progress.
In order to recognize pneumonia, you need to know what the spots look like on pictures with this pathology. They may differ in size and location:
- global spotty formations on the entire surface of the lungs;
- subtotal – completely all fields (exception – upper lobes);
- segmental - spots within the boundaries of a segment;
- small spotted formations up to 3 mm with limited margins.
As a result of the development of the inflammatory process in the human lungs, fuzzy spots with blurred contours are formed and an x-ray shows inflammation of the lungs. The manifestation of spotty formations depends on the stage of the disease. The spots are more pronounced in advanced cases.
X-rays of teeth
X-ray examination has become widespread in dentistry. The image not only makes it possible to track pathologies, but also reveals deviations in the structure of the jaws. X-ray diagnostics is important when choosing optimal treatment options.
There are several types of x-rays in dentistry:
- Panoramic. This image allows the doctor to evaluate the entire panorama of the location of the teeth, determine their number, and see unerupted teeth and rudiments. The anatomical structure of the jaw and nasal sinuses is also visible. A panoramic photograph is important for dental implantation, bite correction, and wisdom teeth removal.
- Biteful. Otherwise, such a picture is called interproximal radiography. A common type of photo. It is used to detect periodontitis and caries. Sometimes a bitewing photograph is taken after the crown is placed to verify the correctness of the procedure.
- Sighting. With the help of a targeted image, you can see exactly what the diseased tooth looks like and establish the correct treatment regimen. A targeted photo allows you to see no more than four teeth.
- Digital. Safe modern diagnostics. 3D X-ray makes it possible to get a clear picture of the entire dentition and individual teeth. The three-dimensional image is displayed on the screen, after studying it the doctor determines treatment methods.
X-ray for bronchitis
The symptoms of the disease are similar to pneumonia. To confirm the diagnosis during a protracted course of the disease, certain types of examinations are prescribed, including x-rays, which will assess the condition of the respiratory system and clarify the diagnosis.
Symptoms in the patient for which fluorography is indicated (x-ray of the lungs shows bronchitis in this case):
- changes in the blood, according to laboratory tests;
- severe constant shortness of breath;
- prolonged increase in body temperature;
- suspicion of inflammation in the lungs;
- signs of obstruction.
Based on the results of the study, X-ray photographs pay attention to the following points in the lungs:
- fuzzy outlines;
- presence of root deformation;
- changes in the drawing;
- presence of lamellar lesions;
- areas of fluid accumulation.
The opinions of specialists about the information content of X-rays in identifying the disease bronchitis are divided. However, this type of research is widely used in practical medicine.
Medical X-ray Reading Algorithm
Only a radiologist can decipher
Reading x-rays is a complex process. It takes some time because there are many parameters that need to be described.
When decoding, the quality of the image and the shadow picture must be taken into account. If the picture is unclear, the patient will be asked to take an x-ray again after some time.
An approximate algorithm for reading a radiograph includes the following points:
- Projection of the photo. It is necessary to take into account the projection in which the picture was taken (lateral, posterior, anterior). The doctor must take into account the errors that are allowed in one or another projection.
- Chest shape. The patient's chest may be barrel-shaped, funnel-shaped, or cylindrical.
- Lung volume. The total lung volume is assessed. It can be low, normal or high.
- The presence of focal or infiltrative shadows. On the image, bones appear in white, lung tissue or masses appear in gray, and voids appear in black. If there are dark spots on the gray field, this may indicate inflammation or neoplasm. If such a spot is present, the doctor describes in detail its size and location.
- Deformation of the pulmonary pattern. Normally, the pattern is not deformed, it has clear edges, which indicates normal blood circulation in the lung tissues.
- Root structure. This phrase refers to the description of the pulmonary arteries. In a healthy person they have a clear structure. If the arteries are dilated and there are shadows in the area of the roots in the image, the doctor may suspect a tumor.
- Structure of bone tissue. The doctor evaluates whether the ribs are deformed, whether there are cracks or fractures.
- Diaphragm. The structure of the diaphragm and the presence of changes are described.
If there are no deviations, after completing the reading, the doctor writes in the conclusion “lungs without visible pathology.”
Deciphering a photo is a complex procedure. Even an experienced doctor admits that a mistake can be made when deciphering, so if a serious illness is suspected (tuberculosis, oncology), it is often recommended to conduct an additional examination and clarify the diagnosis.
Description of pathologies in the image
Signs of pneumonia in the picture
The doctor describes any pathologies found on the x-ray in great detail. If there are suspicions, an MRI is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis.
In a healthy person, the pattern of the lungs is clear without unnecessary shadows. The following pathologies can be detected using x-rays:
- Pleurisy. With pleurisy, the serous membrane that surrounds the lungs becomes inflamed. It is accompanied by characteristic symptoms: chest enlargement, pain, fever, cough. Pleurisy is often accompanied by an accumulation of fluid, so on an x-ray it looks like the trachea is being pulled forward.
- Oncology. A malignant tumor appears on the image as a darkening of the lung tissue. Usually this darkening has clear contours. In some cases, these may be enlarged lymph nodes, so additional examination (ultrasound or MRI) is recommended.
- Tuberculosis. With tuberculosis, a strong inflammatory process of the lung tissue is observed. On the radiograph it appears as several rounded focal shadows. As a rule, these are enlarged lymph nodes. Also, with tuberculosis, the pulmonary pattern in the upper part is strengthened.
- Pneumonia. Inflammation of the lungs on an x-ray is revealed as infiltrative darkening and a decrease in the transparency of the pulmonary fields. As a rule, the doctor diagnoses pneumonia accurately.
- Congestive failure. With congestion, the pulmonary pattern will be unclear, and on the x-ray you will notice that the size of the heart is increased. This is a heart disease, but it also affects the functioning of the lungs, coughing, shortness of breath, suffocation when lying down, weight gain and the appearance of edema.
- Sarcoidosis. This is a disease that affects many organs. Granulomas appear in tissues, which disrupt their functioning. With sarcoidosis, deformation of the roots is observed in the image, as well as round, clear darkening.
It is worth remembering that small cysts or tumors may not be visible on x-rays or may be covered by the ribs or heart. If alarming symptoms continue to bother you, after some time you need to repeat the procedure or undergo an MRI.
X-ray for tuberculosis
If you suspect this serious disease, this type of lung examination will allow you to exclude or confirm pathology.
The advantages of fluoroscopy for pulmonary tuberculosis are the ability to:
- carry out various diagnostics of the disease;
- exclude other pathologies of the respiratory system, such as pneumonia, cancer, abscess and others;
- determine the nature of damage to lung tissue;
- see the extent of the lesion;
- see the location of pathological foci.
Therefore, the question of whether an x-ray will show pulmonary tuberculosis can be answered in the affirmative. However, this does not exclude additional manipulations to accurately confirm the diagnosis. X-rays reveal different types of tuberculosis:
- intrathoracic lymph nodes;
- disseminated;
- focal;
- infiltration;
- caseous pneumonia;
- fibrous-cavernous;
- cirrhotic.
X-ray of the spine
In what cases does the doctor recommend taking an X-ray of the spine?
- For pain in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar region.
- For lumbar muscular pain of unknown origin.
- With limited mobility of the limbs.
- For injuries, falls and bruises.
- If you suspect degenerative changes in the bones.
- When diagnosing curvatures, osteochondrosis, scoliosis.
X-rays are recommended to be taken in two projections: lateral and direct. Descriptions of X-ray images are made by a radiologist; he evaluates the contours of the vertebrae, the spaces between them, the intensity of color, and the presence of growths. After this, an experienced specialist is able to immediately make a diagnosis, determine the likely prognosis and the need for surgical treatment.
Does X-ray show lung cancer?
This disease is one of the most serious human ailments in recent decades. Chest X-ray is considered a diagnostic method for identifying this pathology at the earliest stages of its development. Signs or symptoms of the disease may include:
- lethargy, constant drowsiness and weakness;
- performance at zero;
- regular fevers with apparent well-being;
- dyspnea;
- whistling breathing;
- lingering cough that does not respond to therapy;
- secretion of sputum with blood;
- lack of appetite;
- during coughing attacks, the presence of pain.
To exclude the disease, the doctor prescribes an examination. An X-ray will definitely show lung cancer, since this method is highly informative.
Depending on the type of tumor and its location, the appearance on X-ray images will be different. To make an accurate diagnosis, the attending doctor will conduct additional examinations and, after assessing the general condition of the patient, prescribe adequate therapy.
Popular methods of radiation diagnostics
Today, the most common and popular method of radiation examination in outpatient practice is intraoral radiography of teeth, or intraoral photograph of the tooth. Sometimes intraoral photographs of teeth are called targeted, which is incorrect. A targeted photograph is a photograph taken outside the standard positioning, and standardized studies are named according to the positioning method.
At a therapeutic appointment during endodontic treatment, at least three intraoral photographs of each tooth under examination must be taken:
- A diagnostic image is necessary to assess the condition of periodontal tissues at the time of examination, make a diagnosis, determine the number and shape of roots, the direction of canals, and choose treatment tactics.
- measuring photograph - a photograph of a tooth at the treatment stage with endodontic instruments inserted into the canals with a fixed stopper length of the working part or verifiers after instrumental treatment of the canals. If the orthogonal projection is performed correctly, provided that the visiograph program is accurately calibrated and there is no projection distortion for incisors and premolars, some measurements can be taken from the diagnostic radiogram. For multi-rooted teeth, it is preferable to measure the length of the canals using endodontic instruments (Fig. 1), an apex locator or from a three-dimensional photograph.
- a control photograph is taken immediately after the end of endodontic treatment in order to determine how well the root canals are filled, as well as after a certain specified time, in order to verify the absence or detect the presence of complications (Fig. 2). When examining multi-rooted teeth and in cases where there is an additional canal, in an image taken with the orthoradial direction of the beam (direct projection), the root canals often overlap each other, which significantly complicates diagnosis and can lead to errors in the treatment process. To obtain a separate image of the root canals, radiography with an oblique (eccentric) direction of the central beam is used (Fig. 1). For each specific case, the mesial or distal inclination (angulation) of the tube in the horizontal plane is selected (for more details, see: Rogatskin D.V., Ginali N.V. The Art of Dental Radiography, 2007).
Ideally, maximum information about the topography of the roots and the condition of periodontal tissues can be obtained by performing polypositional radiography. In this case, for diagnostic purposes, three photographs are taken - one in a straight line, with an orthoradial direction of the beam, and two in an oblique projection - with a distal-eccentric (Fig. 1) and mesial-eccentric direction of the beam (respectively, straight, posterior oblique and anterior oblique projections).
The most important aspects of successful intraoral radiography are standardization and consistent manipulation. Standardization of manipulations means the ability of a specialist conducting a radiation examination to choose the optimal method for each case and take a series of identical images, regardless of the position, condition of the patient and the time separating one examination from another. That is, if a diagnostic or measurement image is considered to be of high quality, each subsequent clarifying and control image must be made with the same spatial and technical settings, and each subsequent image must be identical to the previous one (Fig. 1, 2).
Rice. 1. Diagnostic and measuring images of tooth 36, taken in direct (a) and distal-eccentric projection (b). 36 - chronic apical periodontitis (K04.5) with characteristic changes on the mesial root.
Rice. 2. A control image immediately after treatment of teeth 21, 22 (chronic periapical abscess in a state of suppuration) (a) and a delayed control image 5 months after filling the canal (b), the state of repair at the treatment stage.
X-ray of the lungs in children
If your child is prescribed an x-ray, you should familiarize yourself with the following points:
- is there an alternative type of examination;
- Is there a vital need for this procedure?
If in doubt, seek advice from another specialist.
In exceptional cases, the younger generation is prescribed radiography. Basically, when this is the only manipulation with which it is possible to exclude or confirm the diagnosis.
One of the parents also comes into the office with the child. In order to reduce the negative effects of radiation, all areas of the body of the baby and his representative are protected with lead shields. The procedure lasts a few minutes, and your baby will not get tired. If an X-ray of the lungs shows that there is a focus of pathology, the doctor will prescribe treatment and the child will recover quickly.
Fluoroscopy is an effective method for diagnosing various diseases and, in experienced hands, provides invaluable assistance to the medical community.
Features of x-ray of the larynx
Radiology is a science that helps doctors make correct diagnoses. With the advent of X-ray machines, the number of diagnostic errors has decreased by an order of magnitude. And modern devices make it possible to obtain the most accurate images and thereby ensure a speedy recovery for the patient.
An X-ray image helps medical personnel in establishing an accurate diagnosis and, accordingly, prescribing the correct treatment. X-ray of the throat allows you to more accurately and more closely assess the condition of the soft tissues of the cervical spine, as well as bones. The X-ray also shows the entire structure of the cartilage. Reflects bone calcifications and tissue changes that occur with age.
X-ray is a procedure for obtaining a diagnosis, which today has no alternative (it is understood that no other procedure can surpass the quality and accuracy).
In medicine, there are ways to conduct x-rays of the larynx - direct or lateral projection (used to obtain information and detect pathologies on both sides).
Similar diagnostic methods
Since x-rays of the larynx classify the functionality of the organ, there are a number of methods aimed at the same:
- Valsalva maneuver. The procedure is performed when the patient exhales with the glottis closed and the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall tense after a deep inhalation.
- Carrying out the study while taking a long breath or pronouncing the vowel sounds “i”, “o”, “u”, “e”.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
Despite the number of alternative diagnostics, x-rays of the larynx remain an effective and affordable diagnostic method. Even when several diagnostic methods are used, X-ray readings remain decisive in making a diagnosis.