What does thrombocytosis mean?
An increase in the number of platelets in the blood leads to thrombocytosis. This is a serious disease that causes blood clots. With this disease, the platelet level reaches approximately 500,000 per mm3. The cause of the disease may be the production of platelets in the bone marrow, slowing down their breakdown, or disrupting the movement of cells in the bloodstream.
Thrombocytosis can develop into thrombosis, characterized by poor blood circulation and blockage of blood vessels. Treatment of thrombocytosis consists of preventing thrombosis and treating the underlying disease that causes an increase in platelet levels.
Why are platelets elevated?
The platelet coefficient is increased and amounts to 700*10 to the 9th degree/l in essential thrombocytosis, the main cause of which is disturbances in hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow.
The uncontrolled release of a large number of immature cellular forms into the vascular bed indicates a malignant course of the pathological process that disrupts blood viscosity.
Thrombocythemia is one of the causes of increased platelets in the blood. It is often asymptomatic and diagnosed accidentally during the examination of laboratory biomaterial.
Important information: What does an increase in ESR according to Panchenkov mean in a blood test?
The reasons for the increase in the level of cellular elements found in a blood test are due to pathological cell division and indicate the risk of developing thrombosis, which is typical for people over 60 years of age.
The development of secondary thrombocytosis is influenced by the production of thrombocytopoietin. Platelets in the blood are elevated as a result of the development of the following pathological conditions:
- infections;
- internal bleeding;
- anemia;
- inflammatory processes;
- malignant neoplasms;
- vascular changes;
- taking steroids;
There are many reasons for the increase in the number of cell plates in the bloodstream in different age groups.
Indicators will be overestimated in case of severe dehydration after surgery. Reactive thrombocytosis occurs against the background of a decrease in the liquid part of the blood. This means that the ratio of cellular elements does not change.
Among women
An increase in blood platelets in the blood during pregnancy is considered physiological if the increase in the number of platelets is not higher than 420 * 10 in 9 degrees / l. Such values indicate a restructuring taking place in the female body.
The development of iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women can increase the content of blood platelets to 500*10 to 9 degrees/l and higher. The presence of platelet indices that greatly exceed the reference range poses a risk of miscarriage.
The development of toxicosis, accompanied by frequent vomiting, leads to dehydration of the body. An increase in the level of platelets in the blood of women serves as a response to the changes occurring.
Uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives also causes an excess of platelets and serves as a risk factor for disorders of the hemostatic system.
In men
Elevated platelets in the blood of men are determined by the following factors:
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- stressful situations;
- injuries;
- heavy physical activity;
- fungal infections;
- viral infections;
- bacterial flora.
If the number of large cellular elements in the biomaterial under study is increased, this indicates the development of severe pathology and requires careful medical supervision.
Norm of platelets in the blood of women by age
The platelet rate in women varies depending on age and various physiological processes. In addition, there is a slight diurnal variation in platelet values. The maximum values were observed in the evening hours, and the minimum in the mornings.
Platelet counts in healthy females are listed in the table:
| Age | Minimum, g/l | Maximum, g/l |
| newborn babies | 150 | 420 |
| children under 12 months. | 150 | 350 |
| children from 1-1.5 years and above | 180 | 320 |
| Up to 16 years old | 160 | 390 |
| 16-25 | 180 | 380 |
| 26-35 | 180 | 400 |
| 36-60 | 180 | 340 |
| Above 61 | 180 | 320 |
| during pregnancy | 100 | 420 |
| during menstruation | 70 | 170 |
| Climax | 110 | 349 |
Causes of increased levels of thrombotic cells in the blood in women
Elevated platelets in the blood of women, the causes of which are various pathologies or physiological processes, are diagnosed when the body is poisoned or under severe stress. Thrombocytosis appears due to the rapid proliferation of platelets in the bone marrow, slow decay, and disruption of blood flow through the vessels.
An advanced disease contributes to the development of thrombosis, which often ends in death.
According to statistics, every year out of 200 people, 1 dies from thrombosis. Thrombocytosis is an independent disease, but can be a consequence of various diseases. To make a diagnosis, qualified diagnostics and comprehensive treatment aimed at preventing the disease and eliminating its causes are required.
Infectious diseases
The occurrence of a viral infection in the body is the first cause of thrombocytosis. Up to 1 million cells are observed in 1 μl of blood.
Various infectious diseases can provoke such a high rate:
- meningitis;
- pneumonia;
- hepatitis;
- fungal diseases;
- encephalitis;
- other viral diseases.
When an infection enters the body, it begins to actively produce antibodies, attracting hormones to help, which contribute to the rapid increase of platelets in the blood.
Hematological causes
Thrombocytosis is a hematological abnormality that causes disruption of the functioning of bone marrow stem cells. It leads to accelerated platelet production and limits platelet breakdown.
An increase in platelet count in the blood often occurs due to iron deficiency in the body. Chronic disease with erythremia or myeloid leukemia is a transitional stage to thrombosis. People over 60 years of age are susceptible to these pathologies, but sometimes thrombocytosis is detected in children.
Postponed surgery
Elevated platelets in the blood of women, the causes of which are previous operations, are explained by a stressful state, which acts as a catalyst for the disease. Platelets especially increase after surgery if a person is diagnosed with a malignant tumor.
Injuries
Significant blood loss also contributes to the increase in “blood platelets” - as platelets are called. The body directs its actions to maximize compensation for losses. The indicator decreases only in the first few hours after bleeding, but after a day the platelet level significantly exceeds the norm.
Inflammation
Inflammatory phenomena are a significant factor provoking the growth of platelets. This increase occurs due to an increase in the level of interleukin, which promotes the formation of a special hormone - thrombopoietin. This hormone is a regulator of the life processes of platelets, namely maturation, division and release into the blood.
Pathologies that increase blood viscosity include:
- lymphagranulomatosis;
- autoimmune inflammation of the vascular wall;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- inflammatory liver problems and others.
Splenectomy
Leukemia cells can accumulate in the liver and spleen, increasing their size. This is expressed in the appearance of fullness or swelling of the abdomen. Normally, these organs are protected by the lower ribs, but when they become enlarged, the doctor can feel them.
A third of platelets accumulate in a healthy spleen. After its removal, the volume of blood distribution is reduced with an artificial increase in platelets. A similar condition is observed in asplenia, when the spleen is absent.
Oncology
Elevated platelets in the blood of women and men are one of the most serious results of the development of tumor processes in the body.
The reason also lies in the therapy carried out against tumors, of which the most dangerous are:
- lymphoma;
- neuroblastoma;
- hepatoblastoma.
A comprehensive examination, including a chest x-ray and ultrasound of the abdominal organs, can diagnose a specific disease. An increase in “blood plates” can be life-threatening, as it leads to the formation of blood clots and clogging of blood vessels.
Thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities leads to severe swelling of the legs, which accompanies the course of the disease
There are many reasons that contribute to an increase in platelets. Finding a connection with the sources of the disease is sometimes difficult. The doctor needs to see the results of the patient’s analysis, and also study the card of his illnesses, comparing them with his current state of health.
Reasons for deviations
An increase in platelet concentration in the blood is most often explained by hematological diseases. These include pathologies of the blood and hematopoietic organs (the main one being red bone marrow). If its functioning is disrupted, the synthesis of blood cells changes. Degeneration of stem cells and myeloproliferative processes lead to such disorders.
Adults
Thrombocytosis is a complication of polycythemia vera and leukemia. The functioning of the bone marrow may be disrupted due to the growth of malignant tumors, when metastases appear in the bones (basophils and platelets often increase). The synthesis of blood cells changes with a lack of vitamins and minerals. Iron deficiency and aplastic forms of anemia can provoke thrombocytosis.
If platelet concentrations exceed normal limits, they can cause acute and chronic disturbances in the functioning of the body. The first include:
- injuries (necrosis, burns, cuts, fractures);
- poisoning (chemicals with massive damage to blood vessels by toxins);
- bleeding;
- surgical operations (persistent disorders accompany splenectomy - removal of the spleen).
Chronic provocateurs of thrombocytosis include sluggish parasitic, viral, fungal and bacterial infectious diseases (manifested by increased platelets, monocytes, ESR), autopathologies (systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, ulcerative colitis).
Certain medications can also cause deviations. Medicines that increase platelet levels include chemotherapy, corticosteroids (a shift in indicators is noted after Dexamethasone, Prednisolone), and oral contraceptives. Sometimes abnormalities in clinical blood tests occur after long-term treatment with antibiotics.
Children
Thrombocytosis in children can be provoked by both serious diseases (such as blood cancer) and any past infections. It is important to ensure that the level of corpuscles returns to normal within 2 weeks after recovery. Children in the first year of life have higher platelet counts than adolescents and adults. This is explained by the body’s increased need for corpuscles during its active growth.
Pregnant women
Mild thrombocytosis during pregnancy is considered normal. It is associated with a slowdown in metabolism and increased stress on the body, and a deficiency of certain substances. However, expectant mothers should regularly undergo blood tests in order to notice significant abnormalities in time.
Thrombocytosis in the third trimester is considered physiological. This is due to the fact that the body “stores” formed blood elements, including platelets, thus preparing for the upcoming birth and blood loss (the minimum for a natural birth of a child is about 300 ml, during a cesarean section - at least 500 ml).
Severe thrombocytosis and increased blood viscosity can adversely affect fetal development. Violation of the permeability of the placental barrier leads to hypoxia; in addition, under conditions of increased stress, the brain and kidneys of the expectant mother are at risk of ischemic processes.
Useful information: Bilirubin in urine is increased: more than 3 reasons, what does this mean, normal, treatment in adults and children. What diseases can it talk about?
Thrombocytosis in a pregnant woman can signal late gestosis, antiphospholipid syndrome, eclampsia, iron deficiency anemia (accompanied by decreased hematocrit and red blood cell counts).
To distinguish physiological changes from pathological ones, in addition to platelets, other indicators are examined - coagulogram, INR (international normalized ratio, which indicates how high the risk of thrombosis is). If necessary, medication correction is prescribed.
What does an elevated platelet level indicate during pregnancy?
Elevated platelets in the blood of women, the causes of which lie in pregnancy, are a negative factor caused by the following disorders:
- severe blood diseases;
- phlebeurysm;
- lack of fluid;
- diseases of viruses and fungi;
- inflammation;
- anemia;
- oncological diseases;
- sweating
With severe symptoms of toxicosis, thrombocytosis is observed in the early stages. A blood test will show this. When carrying a baby, an elevated level of platelets is dangerous; in this case, they even warn about the threat of miscarriage. It is important to monitor indicators in early pregnancy.
When the level reaches 400 thousand/µl, therapy with approved drugs should be urgently started. If there is a slight increase in platelet levels during pregnancy, this may be attributed to a physiological problem.
The body prepares to avoid large blood loss during childbirth. The woman is referred to an appointment with a hematologist, who can prescribe blood thinning medications. The dosage is selected taking into account all possible risks for the mother and her unborn baby.
Factors
Normally, the number of platelets in the body should be 150-320 thousand/µl . For women this meaning changes. The upper limit of normal values is 400 thousand/µl.
The indicators will depend on the woman’s age. At a young age, platelet levels are slightly reduced.
Women are characterized by fluctuations in the level of blood platelets. This is due to regular menstrual cycles. The volume of blood in the body is not constant; regular renewal occurs.
Such minor changes are considered normal. They should not arouse suspicion. But sometimes the platelet count increases due to existing pathology .
An increase in plasma platelets is called thrombocytosis.
This condition may be primary or secondary. Primary thrombocytosis involves increased cell formation in red bone marrow tissue.
This group of causes includes chronic leukemia and metastases that have spread to the bone marrow.
There may be several secondary factors that provoke an increase in platelet count.
As a rule, the blood composition changes with the development of pathologies in different organ systems.
The main reasons for a high level of platelets in a woman’s blood are:
- autoimmune conditions;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases;
- purulent processes;
- malignant tumors;
- tuberculosis;
- taking steroid-based medications;
- major blood loss;
- anemia;
- absence of spleen.
Sometimes the level of platelets in women becomes higher than normal due to a decrease in the amount of plasma.
This happens with dehydration due to intoxication, prolonged diarrhea, and regular bouts of vomiting.
Causes of elevated platelets in women over 50 years of age
Any deviation from the normal platelet count indicates a health problem. For this reason, tests are prescribed annually to detect the disease in time. In women, the indicator varies depending on her condition and age.
The increased ability of blood to form blood clots poses a danger for women over 50 years of age. Exceeding the norm of platelets is observed in essential thrombocytosis. The disease first manifests itself with small subcutaneous hemorrhages, sometimes without symptoms. Only analysis will accurately establish its presence.
With this disease, the digestive tract is affected, which is accompanied by internal bleeding. With a light blow, bruises appear that do not heal for a long time, and hemorrhages form ulcers on the skin. An increase in platelets increases the risk of thrombosis, and this is especially dangerous after 60 years of age.
Classification
An increased number of platelets is usually divided depending on the mechanism of formation. Violation happens:
- primary - when active synthesis of small platelets of blood occurs causes: damage to stem cells of the spinal cord;
- secondary - as a response to the occurrence of one or another pathological process in the internal organs;
- relative - an increase in the parameter due to a decrease in blood plasma volumes, and their true amount is within normal limits.
In the latter case, the reasons for the increase in platelets in the blood include intoxication, excessive vomiting or diarrhea, and insufficient fluid intake per day.
Causes of secondary thrombocytosis
With the pathology of secondary thrombocytosis, the number of blood platelets increases, which is most often caused by chronic diseases.
The causes of this disease are the following:
- low-quality tumors;
- operations for diseases associated with tissue necrosis;
- bone fractures;
- heavy bleeding;
- infectious diseases;
- splenectomy;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids;
- long-term inflammatory process.
A good cause of secondary thrombocytosis is meningococcal infection, which often develops in children. In the presence of anemia associated with iron deficiency, the likelihood of such thrombocytosis increases several times.
Symptoms and signs
to diagnose primary thrombocytosis by external signs. The pathology does not manifest itself with specific symptoms.
A change in blood composition can be suspected in case of secondary thrombocytosis.
The following signs are noted:
- deterioration of condition;
- exacerbation of existing diseases;
- fatigue;
- weakness.
Usually all the symptoms of the disease , which provokes an increase in the number of blood platelets in the plasma, worsen. This is a dangerous condition that requires medical attention.
Classification of thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis is classified into 3 types:
- clonal;
- primary;
- secondary.
The first two types are characterized by a similar pathogenesis - the disease develops due to a disorder in stem cells. In the clonal form, cells are affected by tumor processes, platelets begin to form uncontrollably and their interaction with other cells of the system is disrupted. There is a tendency to form blood clots.
Primary thrombosis occurs due to a disruption in the functioning of brain stem cells, in which the proliferation of hematopoietic areas is recorded. This risk group includes older people. The secondary type develops against the background of chronic pathologies that bother the patient.
Why is an increase in platelet levels dangerous?
Elevated platelets in the blood of women (the reasons for their appearance, diagnosis and treatment of the disease are assessed exclusively by a doctor) require complex therapy, which must be completed in order to avoid serious consequences. Blood clots may appear in veins, vessels and arteries. They increase in size and clog the vein, thereby causing swelling and inflammation.
An advanced state of thrombosis leads to dire consequences.
High platelet counts can cause:
- stroke;
- heart attack;
- thromboembolism of pulmonary vessels.
The latter disease is often fatal. You cannot bring yourself to such a state; a timely test will help you overcome even a serious illness.
Carrying out analysis
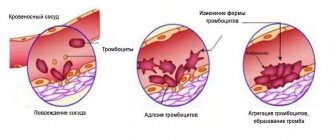
Platelets are presented in the bloodstream as small, colorless, flat-shaped cells that do not contain a nucleus. They are formed from megakaryocytes in the red bone marrow.
Blood plates are designed to ensure normal blood clotting. Platelets have phagocytic activity. The lifespan of mature forms is 7 days. Inactivation of formed elements occurs in the spleen, partially in the liver.
The number of platelet cells is determined as part of a clinical study of the taken biomaterial.
Only after a blood test for platelets can it be explained what this means and why the indicators do not correspond to the reference values.
There are basic and additional methods for assessing platelet hemostasis, depending on the symptoms of the disease.
It should be remembered that the content of platelet cells increases with smoking, drinking alcohol, eating disorders, and physical activity.
The content of cellular elements is subject to daily fluctuations. This means that the clinical analysis should be carried out in the morning, after preliminary preparation, on an empty stomach.
Important information: What does it mean to have a reduced average volume of red blood cells in the blood of an adult?
Platelet counting is carried out in 3 ways:
- in blood smears;
- in Goryaev's cell;
- electronic-automatic method.
Reference values for Plt in adults are 180-380*10 to 9 degrees/l. The reliability of the results increases if you follow the rules for preparing for the collection of biomaterial. Using flow cytometry in hematology analyzers, platelet indices are determined, which serve as markers of thrombotic complications. When the platelet level increases, the following values are determined using the hardware analysis method:
- Thrombocrit, or PCT.
- MPV - average volume.
- Cell heterogeneity (PDW).
To ensure the reliability of the results, it is recommended to repeat the blood test after a few days. In case of persistent deviation from normal values, exceeding the reference interval, it is necessary to check other indicators and conduct additional research.
Verification of the diagnosis is facilitated by the results of a biochemical blood test.
Protein fractions, iron content and other microelements are determined.
Calculated values of platelet indices help the doctor in diagnosing hemostasis disorders and functional characteristics of the platelet component of the blood flow.
Symptoms and manifestations of thrombocytosis
In the primary stage there are no symptoms, but the secondary form has pronounced manifestations, because occurs against the background of the development of chronic inflammatory processes.
The following manifestations are typical:
- fatigue;
- acute stage of a chronic disease;
- general health deteriorates;
- problems with blood vessels;
- bleeding;
- swelling;
- bruises and hematomas not associated with contusions;
- heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right;
- shortness of breath and tachycardia;
- migraine and hypertension.
Most patients learn about the manifestation of the disease from the results of a clinical blood test. It is important that the primary form of the disease can develop into a chronic stage. A patient with secondary type thrombocytosis complains of symptoms that are associated with the underlying disease. It is quickly diagnosed, treated in a timely manner, and blood clotting does not occur.
Diagnostics of deviations
The purpose of diagnosing thrombocytosis is to search for the pathology that caused the increase in platelet levels, as well as methods for its treatment.
The following list of studies will most likely help determine deviations from the norm :
- collection of information identifying episodes of thrombosis in the past;
- complete blood count with platelet level determination;
- biochemical study of inflammatory markers;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray examination of the chest organs to identify inflammatory changes, tumor lesions, etc.;
- examination of the digestive tract to exclude tumor lesions;
- study of rheumatic diseases.
The doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and identifies previous diseases. An external examination is mandatory; it includes visual observation of the skin and the presence of hematomas. The specialist probes the liver and spleen with his fingers.
Treatment of the disease is prescribed based on the combined results of a clinical examination and visual examination of the patient. If the patient needs it, he is referred to doctors of a narrower specialization: a traumatologist, gastroenterologist, nephrologist or infectious disease specialist.
Prevention
Preventive measures for increased susceptibility to thrombocytosis include:
- rational drinking regimen at the rate of 30 ml of water per 1 kg of weight;
- medical control;
- dieting.
It is necessary to give up bad habits and try to reduce the amount of salt and fat in the diet. Women who are prone to elevated platelets should stop using hormonal contraceptives.
To improve the condition of blood vessels, you need exercise, walks in the fresh air and positive emotions. It is advisable, especially for women during pregnancy, to exclude stressful situations from their lives, since the release of adrenaline into the blood during troubles at home or at work helps to increase platelet levels.
Diet for thrombocytosis
There are a number of recommendations that are useful for stabilizing the number of platelets in the blood. The effect will be positive only if all points are completed simultaneously.
- diet - eating at the same time during the day, taking into account individual characteristics, needs and distribution of proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- avoidance of foods with large amounts of carbohydrates and fats;
- inclusion in the diet of foods that reduce and normalize the level of platelets containing iodine and organic acids;
- consumption of clean drinking water daily.
With a slight increase in flat bodies, you need to adhere to a certain diet.
The menu should contain:
- vegetable oil;
- onion garlic;
- fish fat;
- green vegetables;
- persimmons, tomatoes;
- cottage cheese, cheese, kefir;
- cereals and legumes;
- liver and other offal;
- seafood and kelp.
In addition, natural herbal tea, orange, pomegranate, tomato juices, and decoctions of fresh berries are useful.
Drug therapy
Treatment of thrombocytosis with medications helps to quickly reduce the level of platelets in the blood and reduce the complications that arise.
It is necessary to begin treatment of thrombocytosis quickly using these drugs:
- based on acetylsalicylic acid, which have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- eliminating thrombosis, slowing down blood clotting - “Fraxiparin”;
- against tumors - “Hydroxyurea”;
- blood thinners - “Curantil”, “Trental”;
- immunostimulator "Interferon".
The exact dosage directly depends on the degree of development of the disease and the age of the patient. Your doctor should monitor your blood platelet count daily. If their number does not decrease, you should change the list of medications used.
For pregnant women, the list of medications used is completely different. Dipyridamole is used effectively in the amount of 1 tablet 2 times a day. This drug helps normalize blood flow in the uterus. Its use cannot harm the condition of the fetus or the well-being of the mother. During treatment you should not use hormonal and diuretic drugs.
Traditional recipes for thrombocytosis
Along with medications, traditional methods are also used to treat this disease.
An effective element in the fight against thrombocytosis is ginger, the method of preparation of which is as follows:
- Grind natural ginger into powder.
- Mix with cane sugar in equal parts.
- 2 tbsp. l. pour 250 ml of boiling water over the mixture.
- Take small sips before lunch.
In addition, traditional healers advise using the following ingredients to prepare medicinal medicines:
- a decoction of Ginko Biloba leaves, taken 2 times a day;
- cocoa without milk and sugar should be drunk before meals in the morning;
- garlic tincture (pour 2 crushed heads with 200 g of vodka and leave to infuse for 1 month). Drink it 1/2 tsp. 2 times a day;
- use of leeches;
- Make a paste from garlic, onion, honey and lemon and use 1 tsp. 3 times a day.
Reducing platelets using folk remedies is necessary in combination with diet and traditional medicine.
How to reduce platelets in the blood
To reduce the number of platelets in the blood, you need to eat right, drink enough fluids, and take medications prescribed by your doctor. In addition to the main therapy, you can add folk remedies that thin the blood, but only under medical supervision.
Medication
There are several drugs that reduce platelet concentrations. The most effective medications include the following:
- Warfarin. Reduces blood viscosity, suppressing the formation of substances that cause clotting, which regulates the active production of platelets. Cannot be used in the presence of diseases associated with the hematopoietic system and after surgical interventions.
- Aspirin. It prevents platelet cells from connecting, which reduces the risk of blood clots. Contraindicated in the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Clopidogrel. It affects the process of connecting platelets to each other, which is why most of them are excreted through the liver. Not prescribed to people who have individual intolerance to the components of the medication.
- Thrombo ACC. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that reduces the production of hormone-like substances and does not allow Bizzocero plaques to concentrate in one place.
- Trental. The drug makes the blood less viscous and facilitates its passage through the circulatory system. It is not prescribed to people who have recently suffered a stroke or heart attack.
You should not self-medicate using the medications listed above. Only a doctor can determine which drug is suitable in each individual case.
Folk remedies
It is possible to reduce platelets in the blood using folk remedies, but only in combination with drug treatment as prescribed by a doctor. At home, prepare infusions or drinks from ginkgo biloba, ginger, cinquefoil, mulberry root, peony, celery, chestnut, sweet clover, birch buds, willow bark, etc.
Important information: An effective method of increasing platelets in the blood after chemotherapy with folk remedies
The simplest recipe is to boil the grape juice by 1/3 of the original volume. You need to drink 1 glass of medicinal liquid per day.
To prepare the following tincture, 50 g of ginkgo biloba leaves are poured into 0.5 liters of vodka and left for 14 days. You need to drink 1 tsp. before meals for a month.
You can pour 50 g of mulberry root into 1 liter of cold water and leave for 60 minutes. After this, simmer over low heat for a quarter of an hour. You need to drink 1 glass 3 times a day for 5 days. After 2-3 courses with a break of 3 days, platelets will be reduced.
Another recipe: crush 2 heads of garlic, pour a glass of vodka and leave for 15 days in a dark place. Drink 1 tsp before meals.
Chestnut flower tincture helps to cope with the problem. To prepare it, you need to pour 50 g of flowers into 0.5 liters of vodka and leave for 21 days in a dark room. Use 3 times a day before meals.
Juice is also prepared from chestnut flowers. To do this, they are twisted through a meat grinder and squeezed. Can be stored in the refrigerator for no longer than 2 days. You need to drink 30 drops 2 times a day.
Before using any folk remedy, you should consult a doctor.
Most drinks are made with alcohol, which makes it impossible for them to be used by pregnant women, children and people who are contraindicated to drink alcohol even in small doses.
However, taking herbs can also have negative consequences. If you are prone to thrombocytosis, you should not often use valerian, nettle, St. John's wort, corn silk, and yarrow.
Complications and consequences
The main consequence of thrombocytosis is increased blood clotting, leading to the development of serious complications:
- thrombosis , in which blood clots form in various vessels. This can lead to tissue necrosis and gangrene of the extremities, as the organs do not receive sufficient nutrition and oxygen. This condition is especially dangerous for pregnant women and the unborn child (miscarriage, placental rejection, etc.);
- thromboembolism , as a result of the detachment of a blood clot, with the blood flow it is “carried” into organs or vital vessels. Conditions that require immediate medical attention and hospitalization may occur (heart attack, kidney and lung failure).
The article discusses in detail the reasons for the increase in platelet levels in the blood of women.
If the levels of platelets in the blood are elevated in women, you should not self-medicate. Although in women, an increase in platelet levels can have several causes, most of which are physiological, a timely routine medical examination will help to avoid serious complications of thrombocytosis and prevent its development.
Symptoms
If the deviation from the norm is insignificant, symptoms are absent or mild. It should be noted that the clinical picture of the pathological process itself will be supplemented by specific signs that are characteristic of the underlying factor.
The collective symptomatic complex will be characterized as follows:
- bleeding for no apparent reason - uterine discharge outside the menstrual cycle, nosebleeds, discharge from the gums;
- numbness of the limbs, feeling of cold;
- weakness, increasing malaise even after a long and proper rest;
- frequent headaches, dizziness;
- constant feeling of fatigue, painful appearance;
- subcutaneous hematomas that occur without any prerequisites;
- itching;
- the skin may acquire a bluish tint;
- decreased visual acuity, appearance of floaters, rainbow circles before the eyes.
Symptoms of the underlying factor will be present. The clinical picture will be mixed and nonspecific, so you cannot independently compare symptoms and treatment - such measures can cause serious complications. Determining the level of platelets in the blood is the responsibility of only a doctor.