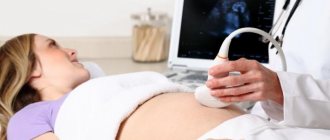
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes a number of research procedures, including ultrasound examinations.
They are prescribed to monitor the condition of the fetus, diagnose the condition of the mother and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment. Ultrasound of the cervix is considered an indispensable procedure for identifying pathologies.
Why is an ultrasound of the cervix performed during pregnancy?
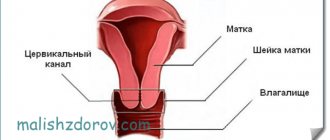
The cervix (cervix) is an organ located at the bottom of the uterus. During pregnancy, it holds the fetus in the uterine cavity and prevents infections from entering the uterus.
During this period, the uterus, depending on the duration of pregnancy, undergoes certain changes that are signs of maturation of the organ. At the beginning of fruiting, the neck is hard, which allows it not to stretch and release the fetus, but by birth, on the contrary, it becomes soft and elastic.
The main purpose of cervical ultrasound is to prevent pathologies that may interfere with normal pregnancy and birth of a child. The condition of the organ is checked and diagnosed based on the length of the cervix.
An ultrasound test that measures length is called cervicometry.
What are they watching?
The most favorable time for an ultrasound is the first week after menstruation. Using ultrasound, the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder, and intestines are examined. Obviously, the uterus can be examined with a transabdominal ultrasound, but cervical erosion can only be approximately seen transvaginally.
Ultrasound can detect the following diseases - fibroids, endometriosis, polyps, uterine and cervical cancer, ovarian cysts and inflammation of the ovaries, abnormal development of the genital organs. At a short stage of pregnancy, the transvaginal method makes it possible to eliminate the possibility of developing an ectopic pregnancy in a timely manner.
The length of the cervix is measured transvaginally - this parameter must be known if a pregnant woman is suspected of shortening the length of the cervix. The bladder is examined in the same way.
A woman should come for an ultrasound if she experiences pain during intimate relationships, has no menstruation, or has a problem conceiving a child. As a rule, a woman will be referred for an ultrasound by a gynecologist after an examination on a “chair”, but, as mentioned above, cervical erosion is easily detected on this chair. For this reason, the gynecologist will refer a patient with erosion for additional studies, but not for an ultrasound.
In what case does the doctor prescribe the procedure?
The length of the cervix is necessarily measured during screening ultrasound procedures. If the pregnancy proceeds without deviations, then cervicometry is not prescribed separately. But there are women who are at risk for certain reasons.
For those who are included in these groups, cervical ultrasound is prescribed unscheduled:
- Suspicion of ICI (isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a condition in which the organ cannot cope with the increasing load).
- Indications for screening ultrasound.
- There were threats of termination of pregnancy, miscarriages or premature births.
- Pregnancy with twins or more.
- Previous abortions, operations and the presence of stitches in the pelvic organs.
- Inflammation and infection.
Also, the small size of the uterine organs may be due to the individual characteristics of the female body.
Data decryption
Endometrial cancer of the uterus can be diagnosed by ultrasound if there are deviations from the norm. In order to understand whether there are deviations or not, you need to know the normal indicators.
- The shape of the organ should be cylindrical and oval in cross section.
- The contours are smooth, without bumps, breaks or features.
- The size of the uterus varies from person to person. It should be taken into account that the length of the body of the uterus in relation to the length of its cervix is 3:1.
- The structure of the muscle layer of a healthy organ is necessarily homogeneous.
Timing of an ultrasound scan of the cervix
During the entire period of bearing a child, a woman with a normal pregnancy is prescribed an ultrasound scan three times, every trimester.
The procedure dates are scheduled for:
- 11-16 weeks;
- 17-24;
- 32-34.
Each screening is aimed at identifying certain features of a woman’s condition, determining the length of the cervix and the degree of its maturation.
Length indicators for different trimesters:
- up to 24 weeks – 35 – 45 mm;
- at 25-28 weeks - at least 35 mm;
- at 32-36 weeks – at least 30 mm;
- in the prenatal period - at least 10 mm.
What pathologies does the examination show?
Cervical status is the most important source of information about the progress of pregnancy. If the process of gestation proceeds normally, the cervix has a dense consistency, the cervical canal is less than a finger in diameter.
The gynecologist detects these indicators by touch during examination. If the canal opens easily, and the cervix itself is short and soft, the question is about diagnosing the threat of spontaneous abortion. If the canal expands in the last stages, there is a risk of premature labor.
Ultrasound of the cervical cavity during pathology reveals the following pathologies:
- A possible pathology during fruiting is immaturity of the cervix, leading to the fact that the organ loses its elasticity and cannot stretch. The cervix usually reaches a mature state by 37 weeks. If this does not happen, complications may arise during childbirth and the only optimal solution to save the fetus will be a caesarean section.
- ICI – isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This pathology is the inability of the pelvic muscles to contract. Thus, the uterus cannot withstand the load of the fetus, and it descends to the internal os earlier than expected. In the early stages this leads to miscarriage, in the later stages it leads to premature birth. The main symptom of ICI is stabbing pain in the genital area, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. But most women who have encountered this diagnosis claim that the disease has no symptoms and is detected during a gynecological examination.
- Endocervitis is an inflammatory process occurring in the cervical canal. Inflammations are caused by infections that have entered the canal cavity through sexual contact. Characteristic scarlet inflammations help diagnose pathology. Symptoms of endocervitis are copious discharge in the form of liquid with an unpleasant specific odor.
Possible diagnostic errors
Do ultrasound data always allow an accurate diagnosis? Of course not. Errors cannot be ruled out, especially in the early stages of the disease. Their cause may be deficiencies in the equipment, lack of training on the part of the patient or insufficient qualifications of the sonologist, as well as other factors.
What can be confused with an oncological lesion of the uterine body?
A qualified doctor is able to distinguish oncology from submucosal fibroids, hyperplastic processes in the endometrium and polyps, but this is where mistakes are possible . Therefore, a comprehensive examination of the patient for each of the above diagnoses is recommended in order to collect as complete an anamnesis as possible and give an accurate and reliable conclusion.
Preparing for diagnosis
The ultrasound procedure is performed transabdominally and transvaginally. Examination with a transvaginal sensor is prescribed more often, as this is the most accurate method for diagnosing pathologies. Many women worry whether it is harmful to the fetus. BUT the procedure does not pose any danger to the child and mother.
You need to prepare for cervicometry:
- the vagina should be washed with regular soap;
- on this day you should not drink water, since a bladder filled with liquid will interfere with correctly diagnosing the condition of the cervical canal;
- the day before you should not eat food that is poorly digestible and contributes to increased gas formation.
Ultrasonography
Quite often, many specialists prescribe an ultrasound of the cervix for a more detailed diagnosis. Most often, an ultrasound examination of the cervix is necessary to diagnose pathologies of this organ. Such a study makes it possible to assess the structure of the mucous membrane and its thickness, as well as form an idea of the size and structure of the organ. In addition, the procedure allows you to diagnose changes in the blood supply.
Receiving the information
Also, using ultrasound, you can determine such pathological processes as:
- Deformation of individual areas.
- Cyst.
- Tumor.
- Structural anomalies.
When a tumor is detected during an ultrasound examination, its main parameters are determined:
At the same time, ultrasound examination in the initial stages of erosion development is ineffective.
How to diagnose
Ultrasound of the cervix can be performed in 2 forms:
The transabdominal method is characterized by filling the bladder. This is necessary to lift the intestines.
Preparing for an ultrasound examination includes drinking several glasses of water 60 minutes before the procedure. The transabdominal method is characterized by moving the sensor in the abdominal area. Before the procedure, the abdominal wall is treated with a special gel.
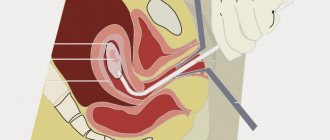
Ultrasound of the cervix, such as transvaginal, is carried out under the condition that the bladder is empty.
After the study, the woman needs to visit the toilet. The procedure is performed using a special sensor that is placed in the vaginal area.
Diagnosis of other diseases
Ultrasound is quite good at diagnosing cysts. During the procedure, both multiple formations and a single cyst can be detected. During the study, they are displayed as rounded formations.
Endometriosis is shown by ultrasound of the cervix as a small altered area, with a characteristic thickening of the wall. Also, such a study allows you to detect benign tumors, for example, fibroids.
Minor polyps are quite clearly visible during the procedure. Quite often, during an ultrasound of the cervix, not only polyps of the canal, but also endometrial polyps are diagnosed.
Diagnosing erosion using ultrasound of the cervix is almost impossible. Since it is quite difficult to determine changed cells under the influence of ultrasound.
How to do an ultrasound of the cervix
The transvaginal examination procedure takes place in a regular ultrasound room and lasts on average 2-3 minutes. The patient lies down on the couch, spreads her legs and bends them at the knees. The gynecologist inserts a sensor, previously lubricated with a special sound-conducting gel, into the vagina, looks at and reads the information on the computer monitor.
There you can see an image of the median uterine section and its lower segment. The internal and external openings and the mucous membrane of the cervical canal also become visible.
A situation may arise where the image is artificially lengthened due to excessive pressure on the sensor. To avoid incorrect readings, the sensor is removed before the image on the screen blurs and reinserted. There may be inaccurate measurements due to uterine contractions. In this case, the smallest numbers are recorded. Also, the length of the cervix depends on the location of the fetus.
Difficulties during the study arise in the case of curvature of the organ or the presence of a polyp on the wall of the cervical canal.
Survey results
Thanks to the results of cervicometry, the gynecologist finds out the condition of the pregnant woman’s organs.
Decoding of normal indicators:
- First trimester. The cervical canal is closed and does not allow a finger to pass through. The internal and external pharynx of the cervix are closed. Length approximately 3-5 centimeters. It is worth considering that for women who have given birth, the rates are slightly lower.
- Second trimester. The internal os is closed. The external pharynx is slightly open in women who have given birth, while in first-time mothers it is tightly closed. The normal length is 3 cm.
- Third trimester. The results of this procedure are assessed according to degrees of maturity. A zero degree of maturity indicates that labor will not begin in the near future. The neck has a dense consistency, length no more than 2 cm, the external pharynx is either closed tightly or slightly open to a distance that allows a finger to pass through. The uterine organ has a backward slope. Signs of the first degree of maturity: compacted consistency, length - 1-2 cm, forward slope, opening of the external pharynx increases by a finger. These signs indicate that delivery is approaching. Second degree maturity warns of imminent childbirth. The length of the cervical canal is no more than 1 centimeter, the uterus is relaxed, loose, tilted along the pelvic axis.
If the cervical length is more than 3 cm, this is normal and the risk of premature birth is very low - only 1%. A length of less than 15 mm in 30% indicates birth within a week, and in 50% about premature birth at up to 32 weeks. In case of multiple pregnancy, such risks arise at sizes of 25 millimeters.
Indicators of 30-25 mm indicate the need for consultations with the observing gynecologist and weekly cervicometry. 25 mm or less is a reason for a medical conclusion about a high risk of premature birth.
In this case, the patient is placed under full medical supervision, after which she is prescribed either progesterone or wearing an obstetric pessary - a special silicone ring. In extreme cases, cervical cerclage is performed - suturing. After surgery, transvaginal examination is no longer performed.
Cervicometry can be done free of charge upon referral from an observing gynecologist at the antenatal clinic at your place of residence or at any private institution where ultrasound is performed. The average price for the service is 2500 rubles.
A gynecologist will tell you in detail about normal length indicators in this video: