Atypical cellular elements that are detected during a cytological examination of a smear from the surface of the cervix and cervical canal, as well as a positive result for HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis, may indicate the occurrence of a pathological process. When visually assessing the cervix, many changes accompanied by atypia and activation of HPV are invisible. In this case, colposcopy comes to the rescue.
All women with pathological changes detected as a result of cervical cytology should undergo a more detailed examination in the form of colposcopy. The same diagnostic method awaits patients with a positive PCR result for human papillomavirus. The main purpose of colposcopy is the timely detection of precancerous changes that are not visible to the naked eye.
Before performing a colposcopy, for a more accurate interpretation and choice of treatment tactics, the gynecologist collects an anamnesis. Menstrual function, contraception, number of pregnancies and births, smoking, previous pathological changes in cytology results and measures taken, and patient complaints are taken into account. If a woman is taking oral contraceptives, then there is no need to stop taking them before colposcopy - this will not affect the transcript.
A colposcope is a microscopic optical equipment equipped with illumination and magnifying devices. The doctor gets the opportunity to examine the surface of the cervix at multiple magnification (6-40 times). For initial assessment and interpretation, a low magnification is selected; to clarify the vascular pattern, a magnification of 20 times or more is performed.
The optimal time period for colposcopy of the cervix is 10-14 days of the cycle. During the ovulatory period, cervical mucus is not so viscous, which will give a more accurate result. If oncology is suspected, the study is carried out on any day.
How is the colposcopy procedure performed?
The patient does not feel pain. Perhaps the unpleasant sensations due to the gynecological speculum being in the vagina throughout the entire process. Moreover, it does not last long, only 10-20 minutes.
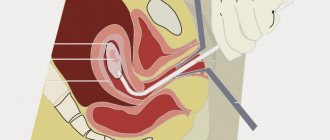
How does all this happen? The patient is located on a gynecological chair, next to which there is a colposcope. After a speculum is installed in the vagina, the study of the epithelium and blood vessels begins. This is done using diagnostic tests. The doctor lubricates the cervix with iodine solution (Lugol) and vinegar solution. At this moment, a short-term burning sensation is possible. Lugol is neutral. This is done in order to get a good look at the desired area, since the solution provokes “swelling” of the cells for a short time. After this, a detailed inspection is carried out.
Unpleasant pain occurs when tissue samples are taken for analysis. Afterwards there is mucous or bloody discharge. Don't be afraid of them; they will disappear over time.
Colposcopy is safe and available even to nulliparous women. However, it is contraindicated if:
- less than 8 weeks have passed since birth;
- less than 4 weeks have passed since the abortion;
- the woman is bleeding or menstruating;
- there is a pronounced inflammatory process.
If necessary, vaginoscopy and colposcopy are performed on virgin girls, without breaking the hymen or causing pain. For this purpose, special children's gynecological speculums are used. Sometimes only with the help of such an examination can a foreign object be detected in a girl’s vagina and removed.
The cost of colposcopy depends on the type and purpose of the examination. In addition, the price of tissue analysis (histology) is taken separately. On average, the examination will cost from 1000 rubles. Plus about 2000 rubles for a histological report. Remember, an ultrasound of the cervix performed vaginally cannot replace colposcopy.
Back to contents
Treatment of gynecological pathologies
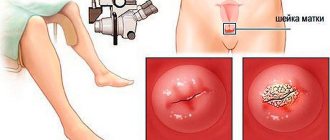
Colposcopy should be performed regularly for women. This will make it possible to identify abnormalities (iodine-negative zones, atypical vascular pattern, acetowhite epithelium) at an early stage and prescribe the correct treatment. Otherwise, advanced cervical dysplasia tends to turn into cancer.
There are several methods for treating dysplasia depending on the depth of tissue damage. In mild cases, medications are prescribed that stimulate the growth of new cells. In addition, prescribed medications may include vitamin complexes, immunostimulants, fatty acids (omega-3), and probiotics. In some cases, with a mild form of dysplasia, chemotherapy or cryodestruction is prescribed. In this case, I influence the damaged cells with drugs or cold directly in the vagina using a colposcope.
For more severe forms of dysplasia, surgical intervention is prescribed:
- Coagulation of affected areas. This method is common in medicine and is effective when performing abdominal surgeries. To carry out the necessary manipulations, electrodes are used that cauterize damaged tissue areas to the required depth. Coagulation shows high results in small areas. If the affected area is too large, this method can lead to the formation of rough scars, which, in turn, can negatively affect the woman's reproductive function.
- Laser surgery. To treat cervical dysplasia, a laser can be used to vaporize damaged cells. During this procedure, local anesthesia is used. The disadvantage of this method is the complexity of the radiation dosage, which can lead to burns of mucous tissues. At the same time, the accuracy of laser surgery is maximum, which is why it is prescribed to girls who have never given birth.
- Conization of the cervix. This method has been used in medicine for a long time and is the most dangerous and traumatic. During the operation, the patient is under general anesthesia, and the surgeon uses a scalpel to excise the damaged tissue. The method is fraught with bleeding and a long recovery period.
- Amputation of the cervix. The cause of this manipulation may be cancer. The operation is also performed under general anesthesia using a scalpel.
Main types of colposcopy
There are three types of colposcopy: simple, extended and video colposcopy . In case of downtime, a routine examination is carried out, which lasts no more than 10 minutes. During this type of examination, a speculum is placed in the vagina and discharge from the vagina is removed using a special tampon. There is no need to insert the colposcope into the vagina. He, being at a distance, increases the desired area several times. The doctor conducts an examination without using any medications.
The second type is extended colposcopy, which differs from simple colposcopy in that tests are performed with this research method. They use 3% acetic acid, which spasms intact blood vessels. Using an aqueous solution of iodine, a Schiller test, a vascular test (adrenaline test), as well as tests that help detect signs of cancer and its advanced stages and tests with dyes are made. This type of colposcopy should be performed if changes in tissues are visible, condylomas are present in the vagina, surgery is needed, oncocytological smear results are poor, and a routine examination after treatment is necessary. Extended colposcopy gives more accurate results, the ability to easily save images, which are compared during subsequent examinations, that is, specialists track the dynamics - whether it is positive or negative.
Using video colposcopy, you can save not only photos with abnormal areas, but also videos. The device is inserted into the vagina and an image enlarged 30 times in real time is displayed on a computer monitor. By doing this, the doctor can explain and show everything to the patient in detail, with a clear example. With the help of video monitoring, it is possible not only to accurately diagnose, but also to carry out treatment with millimeter accuracy.
Back to contents
Norm
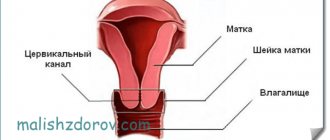
The length of the cervix in a healthy adult woman varies within 3 cm. The external os - the opening of the cervical canal - has a different shape. If the patient had a history of natural childbirth, the pharynx will be slit-like and may have scar changes due to ruptures. A nulliparous woman is characterized by a pinpoint external os. These data are indicated in the colposcopy transcript.
Flat epithelium
The stratified squamous epithelium that forms the surface of the outer part of the cervical region can be either normal or altered. The healthy normal appearance of such tissue is described as a result of colposcopy by a pale pink color and a smooth surface.
Normal squamous epithelium does not turn white when tested with acetic acid, but becomes dark brown when smeared with iodine. If the covering epithelium of the outer part of the cervix is changed, then during colposcopic tests the boundaries and nature of the pathologies will be marked, which is indicated in the transcript.
In menopausal women, the results of colposcopy may describe the so-called atrophic epithelium. This happens as a result of a sharp decrease in estrogen production.
Columnar epithelium
The type of tissue that lines the inside of the cervical canal is designed to produce mucus to form a protective plug that protects the uterine cavity from infection. Normally, the cylindrical epithelium should be located only in the endocervix - inside the cervical canal. During colposcopy, the location of this type of epithelium must be noted in the transcript. If it is localized abnormally - on the surface of the cervix, in the vagina, then upon external examination it is determined as an area of redness. The glandular tissue is velvety, as it consists of villi; in the center of each, a blood vessel is visible. During colposcopy, the doctor sees a finely lumpy red surface if the cylindrical tissue is located on the cervix. In addition, a faint white color is noted when treated with vinegar, which will definitely be indicated in the transcript. When touched with an instrument, such a lesion bleeds.
Transition zone and metaplasia
The boundary between two types of epithelium is one of the most important characteristics of the colposcopic picture of the cervix. Gynecologists call this area the transformation zone, since it is in this area that two types of anatomical tissue structures that are susceptible to pathological influences meet.
Experts distinguish 3 types of transformation zone in deciphering colposcopy of the cervix.
- When type 1 is detected, the analyzed area is completely located on the cervix. Normally it is registered in pregnant women and girls.
- The second type is described in the transcript as an area located in the cervical canal, but barely visible upon examination. It is observed normally in an adult woman.
- The third type - the transformation zone is not visible during colposcopy. Typical for women in menopause.
One of the characteristics of the transformation zone that can be described as a result of colposcopy is metaplasia. Most often this term is encountered:
- young women or girls;
- pregnant women;
- patients taking oral contraceptives.
Metaplasia of the squamous cell variety is considered to be the result of the replacement of columnar tissue with squamous epithelium. It is important for the doctor to distinguish metaplasia from other cervical pathologies. In the transcript of colposcopy, if a metaplastic process is suspected, the following is noted:
- the surface of the cervix is smooth, even, but with translucent thin blood vessels in the area of the external pharynx;
- a moderately pronounced white color is noted when treated with vinegar;
- partially positive (iodine-negative areas) Schiller test.
Differentiating metaplasia can be difficult. Only a biopsy of the suspicious area will help determine the final result.
Metaplasia is the result of the excessive influence of increased estrogen production. Female sex hormones are synthesized in excess both during physiological conditions, for example, during puberty, but also during pathologies, in particular, endometrial hyperplasia.
Preparing to examine the cervix using a colposcope
To have a colposcopy, you do not need to go to the hospital; it is carried out in the antenatal clinic. Before this procedure, you must adhere to these rules.
- Abstain from sex for one to two days.
- A couple of days before the procedure, you should not use vaginal suppositories, douche or insert tampons, so as not to accidentally injure the cervix.
- There should be no menstruation; it is advisable to carry out colposcopy from the 9th to the 20th day of the cycle.
- If there was unusual vaginal discharge, itching, or signs of thrush, you need to inform your doctor about this, since during an inflammatory process, examination of the cervix under optical magnification will be uninformative.
There is no need to take any tests. A cytological smear (Pap test) should be taken a few days before the procedure. After all, when you take it, the brush slightly injures the delicate mucous membrane, but this can change the colposcopic picture.
As already mentioned, if any problems are identified, a biopsy of the cervical tissue is done, in other words, a sample of abnormal tissue is taken for analysis. There are no nerve endings there, so it is painless for the patient. However, gynecological intervention provokes discomfort in the lower abdomen. If you need to do a biopsy of the vulva, it is better to use a local anesthetic. Styptics are used when scraping or pinching is done to stop bleeding. Sometimes a tampon is inserted into the woman's vagina to stop bleeding after a biopsy. But in general, problems rarely arise.
General (intravenous) anesthesia is not used for biopsy. However, sometimes two procedures are combined - curettage of the uterine cavity and a biopsy, and since the second is performed under total intravenous anesthesia, she does not feel the biopsy.
Back to contents
What is an iodine negative region?
The method for identifying affected cells on the epithelium lining the cervix is called the Schiller test. The doctor applies a solution of iodine and glycerin, then looking to see if all the cells of the inner layer are colored. The area of epithelium affected by the inflammatory process will not turn brown if the woman develops the disease. The affected area remains light - this is the iodine-negative zone.
If during diagnosis a light area of the cervical mucosa was discovered, what is it? These are changes in the stratified squamous epithelium that are visible after Lugol's diagnosis.
Why and is colposcopy of the cervical mucosa necessary during pregnancy?
Colposcopy is a safe procedure, but it is undesirable for a pregnant woman , since the cervix may subsequently bleed. Hypertonicity appears. However, if malignant tumors are suspected, the expectant mother is allowed to do this procedure. Preferably at 20-26 weeks, when the risk of miscarriage and premature birth is low, and the expectant mother feels relatively well. If there is no urgent need for examination, then it is best to do this after childbirth.
It will be problematic for a doctor to perform this study during the patient’s pregnancy. The neck cannot be completely exposed in the mirrors. And even if it works, the information content of the study will be low, since almost all expectant mothers have an abnormal colposcopic picture, which goes away on its own after childbirth.
Back to contents
Indications
In these cases, the doctor may decide to prescribe colposcopy:
- When the result of cytology of a smear from the cervix is suspicious for oncopathology (the presence of atypical cells in the smear is confirmed by several studies).
- With a positive test for human papillomavirus.
- If the patient experiences vaginal bleeding outside of menstruation, bleeding after sexual intercourse.
- For diseases affecting the cervix and under certain conditions that can cause cancer (for example, polyposis, cervical erosion).
- If there are other changes, perhaps identified during the history or examination, forcing the doctor to exclude malignant changes in the cervix.
Colposcopy serves as a reliable method for the prevention and early detection of cervical cancer, as well as the control of benign diseases.
Answers on questions
– What is the localization of the cervix? – The concept of localization of the cervix does not exist in gynecological practice. There is a term that determines the location of the lesion - localization of ectopia (tumor, endometriosis, tumor).
– What is cervix with GRC? – GRC – cystic dilated glands on the surface of the cervix. They are formed due to hormonal imbalances in the patient and are amenable to conservative and surgical treatment.
– What is a completed transformation zone? – The incomplete transformation zone is an active area of transformation with immature squamous metaplasia and proliferation of germ cells.
– Is an iodine-negative zone during colposcopy cancer or not? - No. Lack of staining may not be associated with cancer. This reaction indicates cell atypia.
– Why is the cervix stained with iodine? – A special Lugol’s solution containing iodine and glycerin is applied to the cervix. With cervical lesions, staining occurs. This method allows you to diagnose various diseases in the early stages, when changes are not visible to the naked eye. This technique is called extended colposcopy.
– How is the cervix stained with iodine? – Simply lubricate the surface of the ball with the reagent and observe the reaction. If there are no violations, the surface will be uniformly colored brown.
– What is the transition zone of the cervix? – The transition zone or transformation zone is the replacement of columnar epithelium with squamous epithelium. In histology, this condition is called metaplasia. To determine it, after applying iodine, repeat the application of acetic acid.
– What is cervical mottling? – Mottling appears after treatment of CMM with iodine and indicates the development of an inflammatory process.
Similar article - Colds in intimate places - symptoms in women
– What is the original squamous epithelium of the cervix? – This is normal squamous epithelium. It is thin, colorless, and lines the vagina and the vaginal part of the uterus.
Colposcopic examination is an important test to assess women's health. Not all pathologies occurring on the cervix can be detected by a gynecologist with the naked eye, so this procedure should be performed at least once a year. The procedure is unpleasant, but painless; the main value of the technique is that it allows you to identify various diseases of the reproductive system at an early stage of development.
Girls. no more strength((((I was at an appointment with a gynecologist. I just came to get checked. They did a colposcopy, found many cysts on the cervix. Also, several areas were not stained with Lugol’s solution (suspicions of oncology((((sent for a biopsy, and before that another two and a half weeks. I’m going crazy(((((Perhaps this is just the doctor’s guess? I want children. I have one son. I want two more. Oh God, I’ll go crazy before the result of this test. Now they have prescribed Hexicon suppositories
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Andrey Burdak (Gnatenko)
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Egorova Anastasia Vladislavovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Anastasia Sergeevna Shikhaleeva
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Svetlana Chernyshova
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Vyacheslav Potapov
Psychologist, consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Antakova Lyubov Nikolaevna
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Nekrasova Natalia
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Veronica Viktorovna Dobroselskaya
Psychologist, Weight correction. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Boldova Olga Ivanovna
Psychologist, Supervisor, Medical psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Transformation zone
Transformation zone, or ZZ. It is a section of tissue in which one type of epithelium (squamous) passes into another (glandular). That is, the transformation zone is the junction of types of epithelial cells. The transformation zone is not always determined during a colposcopic examination. Based on this factor, it is divided into three types:
- the transformation zone of the first type (ZT type 1) can be completely visualized during colposcopy;
- transformation zone type 2 (ZT type 2) includes endocervical elements and is not fully visualized;
- the transformation zone of type 3 (ZT of type 3) is not completely visualized.