What is the cervical canal in gynecology
The cervical canal (CC) is located deep in the cervix and acts as a kind of bridge connecting the internal and external genitalia. It is formed by the ectocervix and endocervix. Its dimensions differ among representatives of the weaker half. It grows until puberty. In the photo you can see the structure of the female genital organs.
Functions of the canal in gynecology:
- Acts as a link between the internal and external genital organs.
- Protection of the genital organs from sexually transmitted infections.
- Provides the process of conceiving a child.
- Performs the function of the birth canal.
Violation of any of these functions leads to undesirable consequences. For timely diagnosis of certain diseases, a woman is prescribed a test such as a smear.
Indications for the study
After puberty, a woman should undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist at least once a year. In this case, a smear must be taken from the urethra, vagina and cervical canal (scraping of epithelial cells). In addition, scraping is prescribed in the following situations:
- Registration during pregnancy.
- When a woman complains of pathological discharge.
- During treatment of various gynecological diseases to monitor the success of therapy.
- Suspicion of a glandular fibrous polyp of the cervical canal.
- Serosocervix. With this disease, inflammatory fluid accumulates in the CB.
- Suspicion of hematocervix – accumulation of blood in the area of the central circulation.
- For chronic cervicitis.
- If cervical atresia is suspected.
- If the patient complains of discharge with an unpleasant odor or tint, itching, redness of the genitals.
- If a woman experiences pain in the lower abdomen.
- When copious mucous or purulent secretion appears.
These signs in gynecology, as a rule, indicate the presence of certain diseases in a woman. Often the described symptoms occur against the background of an inflammatory process, with a decrease in immunity, and also due to intestinal microflora entering the vagina.
If the patient has no complaints, a smear is taken once a year during a routine examination by a gynecologist. Sometimes an analysis is performed to monitor the state of the microflora while taking antibiotics.
Cytological examination of scrapings from the cervical canal (endocervix, 1 glass)
Examination of cervical scraping (endocervix, 1 glass)
- carried out for the purpose of diagnosing changes in the epithelium of the endocervix and diagnosing early precancerous diseases and cervical cancer. The endocervix is the canal of the cervix.
Cytological examination of cervical scrapings has helped save the lives of millions of women, since with this method it is possible to detect pre-cancer or cervical cancer while it is still curable.
Risk factors for developing cervical cancer:
- infection with human papillomavirus (oncogenic serotypes HPV16, HPV18, HPV31, HPV33, HPV45, etc.);
- smoking;
- chlamydial or herpes infection;
- chronic inflammatory gynecological diseases;
- long-term use of contraceptives;
- several births;
- family history of cervical cancer;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- insufficient intake of vitamins A and C from food;
- immunodeficiencies and HIV infection.
Screening women aged 25–64 years at 5-year intervals can lead to an 84% reduction in mortality, and screening 25–63 year-olds at 3-year intervals can lead to a 90% reduction in mortality.
The risk of developing invasive cancer is 5 to 10 times higher in women who have never been screened. It is recommended that women who are sexually active undergo a smear for oncocytology annually during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
Indications:
- screening and diagnosis of precancerous and cancerous diseases of the cervix.
Preparation
In women of reproductive age, it is advisable to take a smear for examination no earlier than the 5th day from the start of the menstrual cycle or no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
24 hours before collection, you must stop using vaginal medications, spermicides, lubricants, and avoid sexual intercourse. You should not douche the day before your smear test.
If there is a visual pathology on the cervix, a smear should be taken regardless of the above factors.
Recommendations for passing the study
With regular preventive examination of all women over 25 years of age (it is recommended to take the test annually).
When examining girls under 25 years of age who are sexually active.
Starting from the age of 25 years, cytology must be taken every 2 years. If the next smear for atypia reveals any undesirable changes, then subsequent examinations will need to be carried out more often: 1–2 times a year (depending on the changes detected).
Interpretation of results
I. Amount of material.
- The material is complete (adequate) - a smear of good quality, containing a sufficient number of appropriate cell types.
- The material is insufficiently complete (insufficiently adequate) - the material does not contain endocervical cells and/or metaplastic cells, squamous epithelial cells are in insufficient quantities or the cellular composition is poor.
- The material is defective (inadequate) - it is impossible to judge from the material the presence or absence of pathological changes in the cervix.
II. Interpretation of results.
- The cytogram is without features
- epithelial cells are within normal limits, the cytogram corresponds to the age and normal. - Inflammatory changes in the epithelium -
an increased number of leukocytes; during infection - a significant number of cocci and rods. It is possible to detect infectious agents (indicating the pathogen), for example Trichomonas, yeast. - Suspicion of malignancy.
- Individual malignant cells.
- A large number of malignant cells, malignant neoplasm.
- If minimal changes are detected or if a malignant formation is suspected, it is recommended to conduct testing for oncogenic serotypes of the human papillomavirus.
Only your gynecologist can adequately interpret the results of cytology.
Do not rush to interpret the smear results yourself, as some data may unduly frighten you. What can influence the result?
- In girls under 20 years of age, false-positive results are possible due to changes in the epithelium due to transient hormonal disorders.
- The preparation was not carried out properly: smears were taken during menstruation and are represented by a large number of endometrial cells and blood; the preparations contain spermatozoa; the smear is contaminated with spermicidal and antibacterial creams, lubricant from condoms, ultrasound gel; Before the collection of cytological material, a bimanual examination was performed (contamination of the material with talc).
- The conditions for obtaining the material and preparing the drug were not met.
Preparing for analysis
No special preparation is required before the procedure. There are also no contraindications to this type of diagnosis, except for a woman’s menstruation. If the situation is urgent, a smear may be prescribed during monthly bleeding. The optimal time to take a smear from the cervical canal is considered to be the middle of the cycle, that is, from 10 to 20 days after the start of menstruation. Before taking a smear, it is recommended:
- Refrain from sexual intercourse with your partner.
- Stop taking antibacterial drugs 2 weeks before the examination. If taking such medications is necessary, you must inform your gynecologist about this.
- Avoid candles, lubricants, and scented gels for intimate hygiene.
- You need to urinate no later than 2 hours before the procedure. This is due to the fact that urine washes away pathogens.
- You should not douche before going to the hospital.
- In the morning before taking a smear, you are allowed to wash yourself with warm water using baby soap or neutral gels for intimate hygiene.
- You cannot eat salty foods (herring, marinades, etc.) or drink alcoholic beverages.
These simple tips will help you get the most accurate results during your research. Some patients try to improve the result of the smear by douching the day before the procedure. Under no circumstances should this be done. This may prevent the detection of dangerous pathogens. A woman should understand that untimely detection of gynecological diseases can lead to the development of severe complications.
If questionable results are obtained (with an increase in leukocytes without identifying pathogenic microflora), doctors may prescribe a repeat test after some time.
How to prepare
There is no need to do anything special, the biomaterial is taken on days free from menstruation, but in emergency cases it is possible in the first days of the cycle. As a rule, to get tested you need to visit a doctor from days 9 to 21 of your cycle.
Before visiting a doctor you must:
- Avoid intimate relationships during the day;
- Do not take antibiotics or similar medications for two weeks before the procedure. If treatment needs to be continued, the doctor should be notified;
- Candles, lubricants and aromatic intimate hygiene products should not be used;
- 2 hours before your visit to the doctor, do not go to the toilet in small quantities so that the smear is reliable. Otherwise, any microflora in the urethra will be washed away;
- Don't douche! You can only wash your private parts with warm water. Douching will wash away all microflora from the vagina and cervical canal; this method is used in cases where they want to improve the result of the study, but there is no benefit from it, it is biased.
When receiving an ideal analysis, you can miss the disease, and the doctor does not need an empty result, the main thing is the woman’s health. You need to take a smear in good faith, not to spread the disease, which is then more difficult to treat and more expensive.
In cases where the level of leukocytes is high and the pathogen has not been identified, a repeat smear is taken with provocation. On the eve of the test, you need to drink beer with herring or pickled cucumber, and eat smoked meats.
How to take a smear
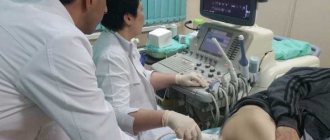
The procedure for taking a smear does not require special equipment or any special conditions. The sampling is performed in a gynecological office on a chair. The analysis time takes no more than three minutes. The session is painless for the patient. In this case, the doctor must use sterile instruments and gloves. Technique:
- The patient lies down on the gynecological chair.
- A special speculum is inserted into the vaginal area to reveal the cervix.
- Biological material is collected from the cervical canal using a cotton swab, brush or spatula.
- A smear is also taken from the urethra and vagina (each test is collected with a separate instrument).
You might be interested in: Is it possible to cut your hair during pregnancy?
When examining a smear for bacteriological culture, the result will have to wait at least 5 days. This is due to the fact that this is the time it takes for bacteria to grow and identify.
Taking analysis
To take tests and examine the cervix, the doctor uses special gynecological kits, which are a sterile kit; depending on the type, it can be used to take biomaterial for culture, a smear from the cervical canal, or do a colposcopy.
To visually examine the cervix, you need a Cusco speculum. The device is disposable, transparent, made of polystyrene, already sterile. Before performing manipulations, the doctor must wear medical chainmail gloves. They are excellent at protecting hands from cuts, since patients may be infected, but they provide virtually no reduction in sensitivity. It is recommended to wear them over ordinary latex medical gloves.
The kit includes a cervical brush, which is used to take a smear from the cervical canal. It is a handle with an attachment, the attachment is a brush, its bristles are of different lengths, made of plastic. It allows you to painlessly take a smear from the surface of the mucous membrane of the urethra, cervical canal and vagina.
Each type of analysis requires a separate sterile accessory! After collecting a smear, the contents of the brush are distributed over a glass slide and labeled:
- V – vaginal contents;
- C – cervical canal;
- U – urethra.
When the glass is completely dry, it is sent to the laboratory for testing.
After 24 hours, the result can be obtained; it is valid for 10 days; if they have already passed, you will have to take the test again. If you need to undergo a gynecological procedure, for example, inserting an IUD, you need to go to the doctor without delay, otherwise you will have to postpone the main procedure.
When doing bacterial sowing, you will have to wait at least 5 days for the result; it won’t work faster, since bacteria and microflora need to be grown, and this will take time.
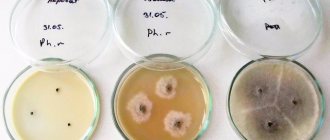
Tank culture from the cervical canal
Bacteriological culture is carried out if the patient is suspected of having diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms related to bacteria. In this case, fragments of the epithelium are sent to the laboratory for examination.
Indications for taking a smear are as follows:
- Planning to conceive a baby.
- Detection of an inflammatory process in the genital area.
- Infections of the uterus and vagina.
- Detection of pathogenic microflora when taking a smear from the vagina and urethra.
- Increased level of leukocytes in the urine.
- The presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the female genital area.
Using a smear from the cervical canal on a culture tank, you can identify pathogens such as chlamydia, trichomonas, gonococci, fungi, enterococci and others. A smear is considered the most informative diagnostic method for identifying dangerous sexually transmitted diseases. Upon receipt of research data in gynecology, they are deciphered and a further treatment strategy is selected.
Methodology
A scraping from the cervical canal is taken by the gynecologist using an Eyre spatula. For research, it is necessary to take cells from the mucous membrane of the exocervix.
A special gynecological instrument - the Eyre spatula, or curette - is very convenient to use. In modern clinics, an endobrush is used for such a medical procedure, which allows you to quickly obtain the required amount of biological material for laboratory examination. In addition, for optimal visualization of the process of material removal, gynecologists use a Cusco mirror. This is a reusable or disposable medical instrument. Available in various designs and sizes. The Cusco speculum helps to examine the condition of the cervical mucosa.
After this, the doctor transfers a small amount of mucus from the cervical canal onto a glass slide and sends the sample to the laboratory. The specialist must attach a note to the glass containing the patient’s data. No additional anesthesia is required during scraping, as the procedure is usually painless and takes a few seconds.
Endocervical cysts
Similar neoplasms in gynecology occur in many patients who have already given birth, after 35-45 years. Most often cysts are benign. In nulliparous girls, such formations are extremely rare.
The causes of the cyst are the accumulation of mucus, which, under the influence of any provoking factors, cannot come out.
Why does pathology develop?
More often, the problem develops against the background of injuries to the mucous layer. Factors that provoke a cyst may be the following:
- Birth of a child. During childbirth, damage to the endocervix often occurs, which causes formations to appear in this area.
- Ectopia or erosion. Here, the outflow of mucus is disrupted due to blockage of the canal by dead cells during the healing of erosion.
- Endometriosis. Pathology occurs due to the entry of mucosal cells into the cervical canal.
- Inflammatory diseases in the area of the internal genital organs.
As already mentioned, endocervical cysts are extremely rare in children and nulliparous women.
Symptoms
Many gynecological diseases affecting the female genital organs cause similar symptoms. Because of this, you cannot diagnose them yourself. The presence of an endocervical cyst may be indicated by the following manifestations:
- Menstrual irregularities. Failures arise due to the narrowing of the Central Committee.
- Feeling of pressure and fullness in the lower abdomen.
- Discharge with a rusty or red tint after sexual intercourse.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increased temperature (observed in case of infection).
- Inability to get pregnant.
To identify pathology, the patient is prescribed a study of the cervical canal. Normally, the size of the cervix should be 2-3 mm. The cavity of the cervix should be filled with homogeneous mucus.
If the Central Committee is expanded, this indicates the presence of certain problems. If cancer is suspected, a woman is prescribed a special examination.
Treatment
During diagnosis in gynecology, cervicoscopy, cervicometry and ultrasound are used, as well as cervical biopsy and PCR. After detecting small formations that are not harmful to health and do not interfere with conception, doctors choose observational tactics. In this case, the patient must undergo regular preventive examinations. For larger cysts that carry pathogenic flora and interfere with conception, the following treatment methods may be prescribed:
- Radio wave therapy.
- Cryotherapy.
- Laser treatment.
- Scraping.
- Full surgical intervention.
The type of treatment is selected depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the size of the cyst and some other factors.
What does it mean if the cervical canal is closed?
Sometimes at an appointment with a gynecologist, patients hear that the passage to the uterus is closed. Is this the norm? Not always. Sometimes this may indicate the following pathologies:
- The presence of two cervical canals.
- Overgrowth of the Central Committee.
If it is closed, this means it is closed. This indicates a disruption in the normal communication between the vagina and the uterine cavity. However, any signs may be absent for a long time. If the pathology is observed in adolescence, the girl does not have monthly bleeding during puberty.
You might be interested in: False bellies to simulate pregnancy
Treatment of the disease in gynecology in nulliparous women is carried out using hormonal drugs. To artificially open the canal, bougienage is performed. In this case, the expansion of the passage is performed with a special instrument under general anesthesia. After medical manipulations of this type, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
Interpretation of cytological examination of cervical smears
Scraping can be considered a standard method of gynecological examination. We explained above what the cervical canal is.
After entering the laboratory, the material is examined under a microscope. This is a rather complex process that takes from 1 to 8 days.
If the result is positive, there is no need to panic, because it does not mean that the patient has cancer. Therefore, it is very important to correctly decipher the results. In modern medical practice, pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal are divided into several classes:
- the number 0 means that the biomaterial is unsuitable for research and scraping must be repeated;
- number 1 indicates that the studied cells are normal, no pathological abnormalities were identified in the patient;
- number 2 means that the biomaterial contains a small number of atypical cells, and the disease is at an early stage of development;
- number 3 is an alarming symptom that signals cervical dysplasia;
- number 4 – first precancerous degree;
- number 5 is the most dangerous because it indicates the presence of cancer.
Cytological examination of cervical smears should be interpreted only by a highly qualified specialist.
The cervical canal is open
In nulliparous patients, the cervical canal has a length of no more than 4.5 cm and a diameter of no more than 8 mm. After the baby is born, the canal takes the form of a slit (linear). There are traces of tears on it, which is not a pathology. Now the hole does not close tightly. That is, normally the width of the lumen should not exceed 6-8 mm. If the hole is open by more than 8 mm, this serves as a reason for ordering an additional examination.
Dilation poses a particular danger in gynecology during pregnancy. In this case, the woman is exposed to the following risks:
- Threat of miscarriage in the first trimester. Additional signs include uterine hypertonicity and fetal abruption.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This condition often causes spontaneous abortion.
- Spontaneous abortion or premature birth.
Doctors identify such reasons for the opening of the CB as the presence of cysts and other formations in this area, endometriosis, tumors, cervicitis (inflammation of the epithelium) and others.
Treatment tactics directly depend on the factors that provoked the pathology.
Cytogram concept
This type of diagnosis in gynecology involves examining a smear from the central cerebral cortex. With its help, the process of inflammation in the patient can be detected. Its causes are often the following conditions:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases, including trichomoniasis, chlamydia, human papillomavirus, genital herpes, etc.
- Vaginitis of atrophic nature.
- Contraception in the form of an intrauterine device.
- The period of bearing a baby.
- Treatment with certain medications.
- Undergoing radiation therapy.
The inflammatory process should be treated in accordance with the reasons for its development. Therapy methods are selected exclusively by a specialist and only after a full medical examination.
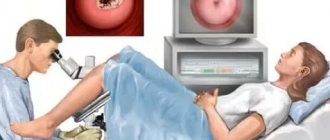
How the analysis is done
A smear is taken during an examination by a gynecologist for the purpose of subsequent cytological examination (PAP test, Papanicolaou test). It is a biological material scraped from the mucous membrane of the cervix. Subsequently, the sample is carefully examined using a microscope. The action allows you to quickly but reliably detect the beginning of cellular changes. In 9 out of 10 cases, they unmistakably indicate the development of cancer or a high predisposition to it.
Cytological examination of a smear is aimed at achieving two goals simultaneously. The first is the detection of cancer tumors at the initial stage of their development. The second goal is to establish the vaginal microflora and identify its violations.
Cytological examination of a smear from the cervix
Separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal
Many women are interested in what RDV or separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and CD is in gynecology. This technique is carried out for several purposes:
- Perform diagnostics. RDV allows you to take biological material for laboratory research in pathologies such as cancer, sarcoma and others.
- Treatment. The method is used to remove various tumors in the cavity of the reproductive organ and cervical canal.
Among the indications for separate diagnostic curettage in gynecology are hyperplasia of the female genital organs, uterine bleeding, endometritis, fibroids, tumors, polyps, fetal freezing, uterine synechiae and other conditions. In pregnant women, this study is carried out with extreme caution.
RDV is performed under local or general anesthesia, which depends on the scope of the intended intervention. The session lasts, as a rule, no more than half an hour. First, a scraping is taken from the cervical canal, then from the cavity of the reproductive organ. The samples are placed in different tubes and sent to the laboratory for further testing.
Preparation
To conduct an analysis from the cervical canal, a woman does not need to be specially prepared. This procedure can be performed by a gynecologist during a routine examination in the chair. This diagnosis is absolutely painless and does not cause the patient any discomfort or discomfort.
Nevertheless, there are several recommendations, adherence to which will help to obtain the most reliable results of this laboratory diagnosis of epithelial cells.
A few days before taking a scraping from the cervical canal, a woman is prohibited from douching. It is recommended to wash only with boiled water, without using soap or other detergents. For several days before the test, you must avoid intimacy. This will help preserve the natural microflora in the vagina, making the analysis more accurate. A few hours before taking a scraping, a woman should not go to the toilet.
What does a smear show?
After taking a smear from the area of the uterus and CC, the obtained research results in gynecology are divided into several degrees. Let's look at the decoding in the table.
| There are no deviations from the norm in epithelial cells, no changes were detected | The patient is healthy |
| Changes are detected in the structure of cells taken for analysis | This result indicates the presence of an inflammatory process |
| Cells with modified nuclei are detected | Here the gynecologist may suspect an oncological process |
| Cells with modified nuclei are present in large numbers | There is every reason to suspect cancer. Other diagnostic techniques are used to confirm the diagnosis |
| A large number of modified cells | This result indicates a severe degree of cancer |
The interpretation of the analysis is carried out only by a doctor. The specialist gives an objective assessment of the woman’s health, taking into account the data obtained during the implementation of other diagnostic techniques.
In addition to testing for oncology, a smear from the vagina and cervical canal can reveal other pathologies:
- HPV or human papillomavirus.
- Candidiasis.
- Chlamydia.
- Gonorrhea.
- Trichomoniasis.
- Herpes infection.
- Cercivit.
- Vaginitis and others.
The decoding of the results is carried out exclusively by a specialist, since it is quite difficult for a person who does not have sufficient knowledge to understand the designations given by the laboratory.
Decoding
The interpretation of the results obtained should be carried out exclusively by a qualified specialist. As a rule, decryption takes at least 8 days.
Cytology test results may be positive or negative. As a rule, the second option assumes the absence of any abnormal changes in cellular structures. The cells do not change, and there is no pathogenic microflora in the biomaterial.
A positive scraping test indicates the presence of abnormal cells in the scraping. Atypical elements may differ from each other in size and shape. If such a result is obtained, the specialist will refer the patient for a repeat procedure. Additionally, a biopsy, colposcopy and human papillomavirus test may be prescribed.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
In addition, venous blood must be donated for a detailed analysis.
In the case when a doctor reports poor cytology, this does not always indicate the development of an oncological process. The main thing is to know how to correctly interpret the results of a laboratory test.
Modern medicine suggests several classes, one of which will include a pathological change in the female body, in particular, in the cellular structures of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
Experts distinguish 6 main groups:
- zero – the material taken during the diagnostic examination is unsuitable for further research, the procedure must be repeated;
- first , the studied cellular structures are in a normal state, which is why there are no pathological abnormalities;
- second , the biological material contains a small number of abnormal cells, which indicates that the pathological process is at the beginning of its formation;
- the third - indicates more serious signs, in particular, indicates the presence of cervical dysplasia (this disease has a predisposition to progression, which can threaten not only the health, but also the life of the patient);
- fourth – is regarded as a precancerous condition (if grade 4 is detected, the specialist will prescribe the woman an additional diagnostic examination and select the most effective tactics of therapeutic measures);
- fifth - this class is among the most dangerous, since it indicates the presence of an oncological process.
Smear cytology: interpretation
Cytological examination of CD in gynecology is carried out if various pathologies are suspected in the patient. In this case, special terminology is often used. The concepts and their definition can be seen in the table.
| CBO | Indicates that the woman’s cervix is in a state without visible changes |
| Cytogram of inflammation | Indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the area of the central circulation |
| Dysplasia | Indicates a threat of cancer development |
| Metaplasia | Indicates the presence of replacement of one type of cell with pathological ones |
| Leukoplakia | There are changes, but there is no talk of cancer yet |
| Proliferation | Cell division occurs at an accelerated pace |
| Leukocyte infiltration | Hanging white cell count |
| Koilocytes | Detection of cells associated with HPV |
You might be interested in: 20 weeks pregnant
If questionable results are obtained, the girl is referred for additional research methods. This allows you to make the correct diagnosis and select the necessary treatment.
If the gynecologist has doubts about the data obtained, the woman is referred for additional medical research. The patient is prescribed extended smears for sexually transmitted diseases, ultrasound and other diagnostic methods.
Norms
There are certain medical standards that the analysis of cervical scraping in a healthy woman must comply with. In laboratory analysis, the visible zone must contain epithelial cells. In a healthy patient, they can be either single-layer cylindrical or multilayer metaplastic. Pathological changes most often occur in the stratified epithelium, to which the physician must pay attention.
Diagnosis of scraping is a standard procedure that is performed in any antenatal clinic or gynecological clinic. In a public medical institution, the study is free, and in a private one it is paid. However, contacting a private medical institution has its advantages - you will receive the test result as quickly as possible.
The cytology test can be positive or negative. In the second option, no pathological changes in the cells were detected. Their structure remains unchanged; there is no pathogenic microflora in the biomaterial.
Positive cytology of the uterine scraping indicates that abnormal cells are present in the patient's genitals. Atypical elements can have different shapes and sizes. If this result occurs, a re-examination is recommended. The gynecologist may also prescribe additional methods for diagnosing gynecological diseases:
- HPV test;
- Biopsy;
- Colposcopy.
The patient also needs to donate blood from a vein for a detailed analysis. All these diagnostic methods will allow doctors to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the most effective treatment.
What is CD stenosis
In gynecology, there is such a thing as stenosis of the cervical canal. This condition implies an acquired or congenital pathology, accompanied by narrowing or complete obstruction of the cervical canal.
Causes
Among the reasons for the narrowing of the endocervix, the following provoking factors should be mentioned:
- Chronic inflammatory process in this area.
- Injuries to the central circulation during childbirth or gynecological procedures.
- Decrease in the level of female hormones during menopause.
- The presence of neoplasms in this area.
These are just some of the reasons that can cause pathology. Sometimes a congenital form of stenosis occurs in girls.
Symptoms
Cervical canal stenosis in women of childbearing age is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of monthly bleeding. Some patients experience pain in the lower abdomen and general malaise. In the middle of the cycle, slight spotting with an unpleasant odor may occur.
Sexual intercourse is often accompanied by painful sensations. If the canal is overgrown, large quantities of blood accumulate in the uterus, this is often perceived as neoplasms in it. In addition, there are difficulties with conception.
Possible complications
The main danger of cervical canal stenosis in gynecology is considered to be female reproductive failure. This occurs due to the inability of sperm to pass through the cervix. If pregnancy occurs, there is a high risk of fetal death or spontaneous abortion.
Treatment methods
Treatment of stenosis in gynecology is indicated for girls with obstruction of menstruation and the impossibility of conceiving a baby. If the pathology is not accompanied by visible symptoms, the doctor often chooses observational tactics. In this case, a woman must undergo a routine ultrasound scan at least twice a year. Treatment of stenosis is carried out using several methods. Among them are:
- Bougienage of the Central Committee. The narrowing is eliminated using a special medical instrument - a bougie. Therapy is carried out over several weeks with periodic replacement of the bougie with a larger diameter instrument.
- Surgery. Laser or radio wave therapy is used here. Only in severe cases is full-fledged surgical intervention used.
The prognosis for a patient with cervical canal stenosis depends on the disease that provoked the narrowing.
Timely treatment helps to cope with the problem and prevent various complications.
Degrees of vaginal cleanliness: explanation
An important indicator in gynecology when taking a smear is the degree of vaginal cleanliness. The decoding can be seen in the table.
| Degrees | Decoding |
| I | The smear contains a large number of useful Doderlein bacilli, as well as a small amount of squamous epithelium. This state of the vaginal microflora is typical for completely healthy women. |
| II | The smear reveals a small number of cocci (small round bacteria), but the beneficial Doderlein bacilli predominate. The second degree of vaginal cleanliness is not a sign of disease and is observed in many healthy women |
| III | The smear contains a small number of vaginal bacilli, but cocci predominate and an increased number of leukocytes is observed. The third degree of vaginal cleanliness is an unfavorable sign and indicates the presence of an inflammatory process |
| IV | Useful Doderlein sticks are practically absent from the smear. The fourth degree of vaginal cleanliness indicates bacterial vaginosis, accompanied by inflammation |
The third and fourth degrees in gynecology indicate the presence of certain diseases in the patient, which requires further medical examination.
Prevention of female diseases
Gynecologists insist that to reduce the risk of developing various pathologies of the cervix and cervical canal, a woman must follow simple rules of prevention. These include the following recommendations:
- Regular visits to the gynecologist.
- Carrying out cytological studies.
- Timely treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- We must try to prevent artificial termination of pregnancy. For this purpose, contraceptive methods such as condoms, cervical cap, pills, etc. are used.
- It is important to respect the culture of sexual life.
- If the menstrual cycle is disrupted, it is imperative to look for the reasons.
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene.
- If any complaints regarding women's health occur, it is important to immediately contact a gynecologist.
These simple rules will help you stay healthy and prevent dangerous diseases such as cancer. Every girl should remember the importance of preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
If there are no complaints, a visit to the doctor should be made once a year. If there are any problems, the doctor himself selects a schedule for visiting the hospital. Under no circumstances should inspections be skipped. It is necessary to take the prescribed tests and strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations. Take care of yourself and be happy.
Methodology
The scraping is taken by a gynecologist. It is necessary to remove mucosal cells from the exocervix for analysis. For this purpose, a special gynecological instrument is used - a curette or an Eyre spatula. In modern clinics, endobrush is used for this procedure. It allows you to quickly obtain the required amount of biomaterial for laboratory research.
Cervical smear. Source: dailyexcelsior.com
Previously, the gynecologist examines the patient on a chair using gynecological mirrors. During this procedure, biomaterial is collected for bacteriological examination.
A small amount of mucus is transferred to a glass slide and the finished sample is sent to the laboratory. The doctor must securely attach a note to the glass containing the patient’s data (age, last name, date of last menstruation, preliminary diagnosis). No additional anesthesia is required during this procedure. It is completely painless and takes a few minutes.
A laboratory technician examines the scraping under a microscope. The detection of atypical cells in the analysis can signal the development of dangerous diseases such as dysplasia, pseudo-erosion, leukoplakia, infectious or inflammatory pathology, cancer or a precancerous condition. If a disease is detected, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment, and after the end of the course of therapy, the procedure is repeated.