Essence of the study
The principle of MRI is nuclear magnetic resonance. During the diagnostic process, the tissues and organs of the human body are exposed to magnetic waves controlled by a high-power constant magnetic field.
The reaction of hydrogen atoms observed in response to the influence of waves is displayed in the form of an electromagnetic response, which is subsequently used as a result.
MRI
Indications and limitations for MRI diagnostics
The reason for performing an MRI of the leg is often a chronic rheumatoid disease or loss of vascular tone and the formation of deposits in their cavity. Other indications for magnetic tomography include:
- pain in the local area after completing the treatment course;
- loss of sensation in the limbs;
- bone or soft tissue injuries;
- slow bone regeneration, formation of a false joint, hemorrhage, tendon damage;
- suspicion of a tumor, metastasis and control over the condition of an oncology patient;
- limitation of limb mobility;
- symptoms of thrombosis;
- pathologies of the blood vessels of the legs;
- the need for research before and after surgery.
The list of contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging is not wide. Among the absolute restrictions:
- the presence of electronic devices and metal objects (shards, bullets, prostheses, clips, etc.) in the patient’s body;
- the patient’s inability to maintain body stillness;
- human body weight more than 150 kg;
- The diameter of the widest part of the human body is more than 150 cm.
The procedure using contrast is not performed on pregnant and lactating women, people with renal failure, or those suffering from intolerance to gadolinium-based drugs.
When should you avoid an MRI?
Among the contraindications to the use of the diagnostic method under consideration are:
- Predisposition to allergic manifestations. In some cases, the injected contrast agent may cause an undesirable response from the body. Therefore, first the doctor suggests an allergy test.
- The presence of neuropsychic disorders associated with fear of closed spaces. The identification of such a feature is due to the need for the patient to be in a closed chamber during diagnostics.
- The presence of metallic foreign particles inside the patient. Such items are therapeutic components that complement the vitality of individual organs in the form of implants, valve septa, and hearing aids.
- Beginning of pregnancy. The first months of a baby's development in a woman's womb do not allow for an MRI procedure.
- Lactation. Breastfeeding of the infant is stopped for at least 24 hours after contrast exposure.
- Excess body weight of the patient exceeding 130 kg.
- Damage to the urinary organs and other chronic diseases of the kidneys and liver.
If the patient has no contraindications, it is strongly recommended to prepare responsibly for the examination.
What does an MRI of the legs show?
As a result of an MRI scan, a specialist diagnoses one of the following pathological conditions:
- tumor processes;
- joint atrophy;
- inflammation of joint tissue;
- bone pathologies;
- diseases of large elements of the vascular system of the legs;
- stretching or thinning of blood vessels;
- vein thrombosis;
- abnormal phenomena in tissues;
- hemangioma;
- degenerative processes in joints;
- angiosarcoma;
- abnormalities in the structure of the vascular network.
Diagnosis is also carried out in relation to individual areas of the lower extremities - thighs, legs, feet.
Hip MRI results
Magnetic tomography of the local area evaluates the soft tissues and the entire hip joint. During the scan, the doctor reveals:
- malignant tumor processes, signs of metastasis;
- dislocation, sprain;
- factor in the formation of joint dysplasia;
- location and degree of development of oncology;
- osteomyelitis;
- septic arthritis.
MRI helps to control the process of restoration of damaged anatomical structures of the local area and see the result of the operation.
What will an MRI of the leg show?
Pathologies in this area are the most difficult to diagnose. For this reason, a contrast agent is often used. During MRI, the condition of the bone tissue of the ankle joint, cartilage, ligaments, and adjacent joints is determined.
The images obtained after the study help to identify pathologies of tendons and muscle tissue and diagnose the inflammatory process in the local area.
What does a foot photograph show?
We are talking about diagnosing the most injury-prone area of the leg. During an MRI scan, the doctor can confirm the development of the following pathologies:
- heel spurs;
- arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- plantar fasciitis;
- tumor processes;
- flat feet;
- Northern diseases;
- diabetic foot, etc.
This type of diagnosis helps to assess the condition of the ligaments, muscles, bone tissue, and small joints. The picture also shows the ankle joint.
MRI results of soft tissues of the legs
MRI of the soft tissues of the extremities helps to draw a conclusion about the condition of the buttocks, soft tissues of the foot, and lower leg.
The focus is on the muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, venous apparatus, fat layer and joints of the leg.
Diagnosis of the gluteal zone provides information about the condition of the piriformis muscle and blood vessels.
The following types of formations in the soft tissues of the legs are often diagnosed using magnetic resonance imaging:
- fibrosarcoma is a tumor of a malignant nature, localized in the muscle tissue of the femur, therefore it rarely leads to discomfort in movements and the manifestation of obvious symptoms, it is diagnosed randomly;
- lipoma is a common formation located in the fat layer and rarely develops into a malignant tumor;
- hemangioma is a benign neoplasm, which is a node several centimeters in size. In some cases it transforms into oncology.
MRI of the vessels of the lower extremities - examination results
The influence of external unfavorable factors stimulates the development of pathologies in the process of blood circulation of the extremities. To determine the root causes of the phenomenon, MRI diagnostics of the veins is performed, which reveals:
- vasculitis;
- expansion of arterial walls;
- atherosclerosis due to cholesterol deposits;
- narrowing of the vascular lumen;
- ischemia;
- blood clots in the vessels of the legs.
Preparatory stage of MRI
No special preparation is required for the upcoming procedure. The patient can eat and drink liquids at his own discretion. The only limitation: in case of contrast scanning, it is recommended to refrain from eating 4 hours before the MRI.
You should take a medical referral, an outpatient card and the results of previous studies with you to the diagnosis. Before entering the office, the patient will have to remove metal objects and devices. On the eve of the examination with contrast, you must undergo an allergy test to the drug.
How is MRI of the veins of the lower extremities performed?
This procedure does not apply to emergency examination methods, therefore it is performed in the clinic by appointment with a specialist. After making an appointment, you should once again clarify the date and time of the examination and subsequently arrive on the appointed day without delay.
Upon arrival for the examination, the patient will be required to fill out a form, thereby confirming that at the time of the MRI they do not have metal implants or medical clips. After which you need to draw up an agreement for the provision of medical services, which can take up to 10 minutes. At this stage, you can ask about the exact cost of the procedure and ask other questions.
Before starting the diagnosis, the patient must remove any metal objects (jewelry, glasses, dentures, etc.) and change into a special suit. Those who do not wish to wear a medical uniform can bring their own change of clothes from home. But in this case, you should again pay attention to the presence of any metal inserts in it. They shouldn't exist.
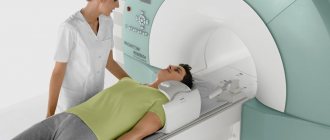
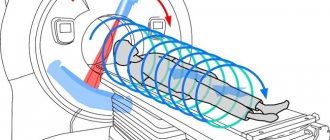
After which the patient will be directed to the tomograph, where a retractable table specially designed for scanning is located. Devices can be open or closed. The first one looks like a pipe or a cocoon, the second one looks like a leaf that will hang over the patient.
As soon as the patient lies on the table, he can be fastened with special belts. This is necessary in order to fix its position and keep the body still during scanning. After turning on the tomograph, special sounds will be heard; if desired, the patient can plug his ears with silicone earplugs in advance. The procedure itself can take from half an hour to an hour.
Progress of MRI examination of legs
Algorithm for MRI diagnostics:
- The patient enters the office, changes clothes and lies down on the movable table of the apparatus.
- The specialist secures the patient’s limbs and head with special belts.
- If a contrast examination is to be performed, the person is injected with a substance and waits for some time until the drug accumulates in the local area.
- After the table moves inside the tunnel, the tomograph ring begins to move in the examined area.
- During the diagnostic process, the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. The procedure lasts about 20 minutes. If contrast is used, this time doubles.
- As soon as the equipment finishes working, the patient gets up, changes clothes and leaves the office.
Carrying out the procedure
The MRI machine is a hollow capsule. The position for diagnosis is the supine position. If necessary, the doctor will indicate the rotation of the body. The specialist fixes the subject with a fastening device, ensuring complete immobility of the body. The device produces very loud sounds, so the patient is asked to use headphones. The patient remains in the scanner department for the required time, usually varying around 35-45 minutes.
Deciphering the image and diagnosing it based on the results obtained takes some time. After a couple of hours, the patient already receives a detailed analysis of the state of the vascular system of the extremities. Based on the description and provided medical facts, the doctor will prescribe the treatment necessary for the patient.
An important issue that worries every patient is the price of such a popular procedure. Today, MRI is part of the basic list of medical services provided under the compulsory health insurance policy. Therefore, a referral from a doctor gives the right to a free examination in a hospital setting. In case of self-referral to a private clinic, the patient must pay according to the institution’s price list.
Advantages and disadvantages of MRI scanning
The advantages and disadvantages of the described technique are presented in the table below:
| Pros of MRI | Cons of MRI |
| - no radiation exposure to the body | - relatively long diagnostic period |
| — obtaining accurate and high-quality images | — the impossibility of a thorough examination of the tissues of hollow organs (bladder, etc.) |
| — obtaining images of the organ in different projections | — impossibility of diagnosing persons with metal elements and medical devices implanted into the body |
| — diagnostics of women during pregnancy, small children | - the need to remain in a stationary position throughout the entire scanning period |
| - painlessness | - high price |
General characteristics of the study area
Limbs are appendages of the body that are responsible for motor function. In humans, these include the arms and legs. The functionality of the limbs is possible not only due to muscles, bones, several types of tissues, but also blood vessels. These are elastic tubular formations that penetrate all parts of the body and are responsible for moving blood throughout the body. The blood flow diagram looks like this: blood flows to organs and tissues through arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and from them it goes to the heart through venules and veins.
Blood vessels are located throughout the body, but each of them differs in tissue composition, diameter and functional characteristics. Let us examine in more detail the main types of elastic tubes. Arteries are vessels through which blood moves away from the heart. They are characterized by thick walls containing muscle, collagen and elastic fibers. Arteries are as flexible as possible and can expand/contract depending on the amount of blood. The blood circulating through the arteries is saturated with oxygen. The only exception is the pulmonary artery, through which venous blood flows.
Content:
- General characteristics of the study area
- The principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
- Indications/contraindications for MRI
- Preparation and methodology
In the extremities, blood circulates through the following arteries: digital, radial, brachial, axillary, dorsal digital, arcuate, anterior/posterior tibial, peroneal, popliteal, femoral.
Arterioles are small arteries that precede capillaries. The vascular wall of the arteriole consists of muscle fiber. This allows the vessel to change the size of the lumen and provide resistance. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. There are about 40 billion of them in the human body. Through the capillary walls, oxygen and nutrients pass from the blood into the cells, and carbon dioxide and other waste products pass from the cells into the blood.
Venules are small blood vessels that are responsible for the circulation of blood with an abundance of waste products and a lack of oxygen from the capillaries to the vein. Veins are vessels through which blood moves to the heart. The walls of veins are much thinner than the walls of arteries, they have fewer elastic elements and muscle fibers.
In the extremities, blood circulates through the following veins: palmar digital, ulnar, lateral saphenous, median, medial subcutaneous, axillary, dorsal digital, anterior/posterior tibial, lesser saphenous, popliteal, femoral, greater saphenous.
What alternatives are there?
Alternative techniques for magnetic tomography of the legs include:
- ultrasound examination with Doppler sonography;
- ;
- CT angiography;
- X-ray.
The choice of a particular procedure depends on the medical history and diagnostic goals. Angiography cannot be equated to ultrasound with Doppler sonography.
In the latter case, the doctor assesses the blood flow, but it will not be possible to fully examine the vessels of the lower extremities using ultrasound.
For this reason, the technique is used extremely rarely. Computed tomography is often prescribed instead of MRI if there are characteristic objects and devices in the patient’s body.
CT
If it is necessary to examine exclusively the vessels of the legs, angiography is used. X-rays are recommended in cases where a specialist suspects pathology of the bone tissue or joints of the diseased legs.
What does it show
MR scanning of the soft tissues of the veins of the upper and lower extremities allows you to visualize the structure in all details. If the venous bed is functioning normally, then the image will clearly display:
- Correct size and shape of vessels.
- No developmental defects.
- Clean vein lumens, without wall deformations.
- No neoplasms.
In the presence of pathological processes, the procedure will detect:
- Anatomical anomalies in the structure and location of the venous bed.
- Disturbances in the structure of connective tissues.
- Signs of inflammation of blood vessels and soft tissues.
- Violation of the integrity of the veins.
- Thinning and stretching of the walls, indicating an aneurysm of the vein of the limb.
- Thrombophlebitis and vein blockages.
Conclusion
MRI of the lower extremities is one of the most informative diagnostic methods.
The technique determines pathologies of various anatomical zones (hips, legs, feet) even in the initial period of disease development.
The procedure is painless and safe for health, and can be performed on pregnant women and small children. In some cases, a contrast agent is used, the use of which cannot exclude the possibility of an adverse reaction.
There are a number of contraindications to the examination. The following are considered as alternative diagnostic techniques in medical practice: ultrasound with Dopplerography (rarely used), CT, radiography and angiography.
Indications
The patient can independently apply for examination to the MRI center for the purpose of prevention and timely diagnosis of pathological disorders of venous blood flow in the upper and lower extremities.
If he has a genetic predisposition to such diseases and/or experiences the following symptoms and conditions:
- Numbness of the arms and/or legs.
- Changes in the condition of the skin (ulcers, capillary networks).
- Swelling of the limbs.
- The presence of vascular pathologies of the lower/upper extremities in close relatives.
- Other hardware research methods showed signs of blood vessel disease.
MRI is also performed to clarify indicators for the following diagnoses:
- Takayasu's disease.
- Thrombosis of the veins of the extremities.
- Aneurysm.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Injuries of the extremities affecting the structure of the venous bed.
MRI helps determine the need for surgical intervention or select appropriate treatment, as well as monitor the results of conservative and surgical therapy.