In multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheath of nerve fibers is destroyed. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central and peripheral nervous systems. A person gradually loses vision, the ability to speak, voluntary movements, control over the pelvic organs and many other brain functions. Signs of pathology can appear and disappear long before a persistent deterioration in health. It takes 2-3 years from the first alarming symptoms to diagnosis.
Foci of multiple sclerosis on MRI are visible at any stage, including the initial stages. Scanning reveals changes of varying degrees of age: from “fresh”, accompanied by neurological deficit, to “old”, in which clinical manifestations have already regressed. For successful treatment, it is important to be examined as early as possible.
Why is this method used?
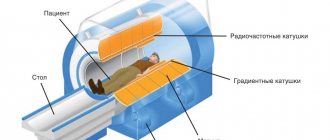
The principle of operation of the method is to influence hydrogen atoms in the patient's brain and spinal cord .
The particles change their position and line up under the influence of the magnetic field. The atoms contribute to the oscillation of the pulses. The device reads information, which is converted into a three-dimensional black and white picture.
MRI is suitable for detecting demyelinating diseases because it better visualizes soft tissue, cartilage, and blood vessels. Computed tomography is used to examine the skeletal system and recent lesions in the brain.
A special feature of MRI is the absence of radioactive radiation . This means that the study is safe. If the need arises, it can be performed many times in a short period of time.
Unlike magnetic resonance scanning, CT gives a greater radiation dose to the body.
To summarize
To make a correct diagnosis, you cannot limit yourself to one MRI examination. Remember that any analysis is only half the battle. You need a competent specialist who can properly interpret your diagnostic test results. Diagnosing multiple sclerosis is a complex, multi-step procedure, and to get practical advice from a doctor, you will have to go through more than just an MRI scanner. Conclusion MRI is only a very powerful aid for the doctor, but nothing can replace medical experience.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
The doctor prescribes an MRI if the following symptoms of the disease are present:
- occasional dizziness;
- unsteadiness of gait and loss of balance;
- a sharp decrease in vision in one eye;
- reduction of visual fields;
- non-perception of any color;
- feeling of numbness in the limbs;
- development of pelvic disorders (frequency or retention of urination, impotence);
- movement disorders - muscle weakness, awkwardness of movements.
However, in some cases, magnetic resonance imaging is prohibited . It may harm the health of the subject or provide distorted scan data. Doctors divide contraindications into absolute and relative.
The first group includes:
- Metal objects that are inserted into the patient's body.
- Presence of a cardiac or neurostimulator.
- Cochlear implant.
- Prostheses or metal structures.
- Fixed bracket system.
- The weight of the subject exceeds 120 kg.
The second group includes such contraindications associated with temporary health problems of the patient during the MRI.
Once he receives treatment or a certain period has passed, a diagnosis can be made. These include:
- Heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
- Carrying a child (1st trimester).
- Exacerbation of severe chronic diseases.
Description of methods
The patient may have a scan without contrast or with a dye . The doctor, based on the patient’s complaints, clinical picture and research methods, selects the most appropriate method.
No contrast
It is used to identify pathological foci in brain tissue. Advantages of the method compared to contrast research:
- Possibility of use in case of severe kidney disorders and allergic reactions to the components of the dye.
- Lack of special preparation before scanning.
- Takes less time for inspection.
- It is recommended for use in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of gestation, since contrast is prohibited at any stage of pregnancy.
- The cost of the study is lower.
With gadolinium salts
Gadolinium salts are used for diagnosis. It is classified as a lanthanide metal. The substance has an important property: it accumulates in areas of increased blood supply.
Among the gadolinium salts used are:
- linear connections (Optimark, Omniscan);
- macrocyclic (Gadovist, Dotarem).
The volume of contrast is calculated individually. It depends on the mass of the test subject.
The substance enters the bloodstream and quickly reaches the brain tissue. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging identifies areas of nerve fiber destruction in these organs.
Specificity of the method
Specificity is the ability to determine, using one research method, whether a person has a specific disease or not. In this sense, it cannot be argued that MRI features are specific only to multiple sclerosis. A similar picture may occur with Binswanger's disease, tumors, leukoareolysis and other conditions. To increase reliability, contrast is used; lesions tend to accumulate it. Diagnostics with contrast increases the accuracy of the examination.
The drug Magnevist is used as a contrast, which is administered intravenously using a flexible catheter. Such a study is performed only in a hospital; the presence of an intensive care unit is required. As the demyelination process intensifies, the blood-brain barrier that separates the brain from the general bloodstream becomes permeable. Areas of inflammation and edema actively accumulate contrast, revealing new growing lesions. The activity of the lesion is judged by the degree of contrast accumulation.
Analogues of Magnevist are the drugs Gadovist and Omniscan.
MRI has proven itself to be excellent in examining the posterior cranial fossa, which is inaccessible to other methods. Modern complexes have the technical ability to perform three visual slices, which allows one to obtain a three-dimensional (3D) visual picture of the brain. It is also possible to distinguish sites of myelin destruction from sites of swelling caused by the inflammatory process.
Radiologists distinguish two variants of the process: acute and chronic. For an acute process, visual signs are similar to a tumor process and to acute disseminated (scattered, widespread) encephalomyelitis. In a chronic course, the lesions are located under the cerebral cortex and in the area of the visual thalamus in the gray matter.
There is also an option in which there are many lesions, but they are small and located in atypical places.
MRI monitoring is promising, in which “pulsating” lesions can be seen. If you constantly do control studies, you can see that the lesions are continuously changing shape, outline and location. Some disappear, others appear. At the same time, the clinical picture (what worries a person) can remain unchanged for a long time.
Patient preparation and procedure
Before the scan, the diagnostician tells you how to behave during the examination . He warns that the device is quite noisy and suggests putting on headphones. The doctor shows the panic button that the patient presses when his health worsens.
Description of the brain MRI procedure for multiple sclerosis:
- The patient is placed on a tomographic bed.
- The chest and limbs are secured with straps to ensure immobility of the subject.
- When a scan is done with contrast, the doctor injects it into a vein. The catheter must be in place throughout the entire examination.
- The patient is placed in a tomograph. An inspection is being carried out.
- At the end of the procedure, the doctor removes the belts. Then he reads the tomogram, making a conclusion.
Tomography does not require special preparation from the patient . Before scanning, you must remove metal objects: watches, jewelry. You will also need to leave electronic key cards and a smartphone.
Before magnetic resonance imaging with contrast, the doctor does a test for the development of an allergic reaction. Some patients suffer from intolerance to the components of the dye.
How is the procedure done?
Brain MPT procedure
painless and does not require special preparation. The average duration is 30 minutes. For examination, the patient lies down on the retractable table of the device in a stationary position. The table then slides inside the cylinder of the scanning machine.
The tomograph takes many pictures in various projections and modes. After the procedure, the specialist will be able to see the result on the computer and begin decoding.
Statistics on the localization of disease foci in the brain
In multiple sclerosis, pathological changes have a symmetrical distribution and usually affect the same structures.
Their typical location, revealed on MRI images:
- periventricular region;
- corpus callosum;
- isolated lesions in the white matter;
- cerebellum;
- brain stem;
- cerebral cortex.
What else is important to know about multiple sclerosis:
- what is the reason for the development of the disease, what are its early manifestations;
- what types and forms the disease has, what diseases are similar to MS and in what ways;
- Is the disease hereditary and can it become a contraindication for bearing and giving birth to children?
Brain diseases detected on MRI
What other diagnoses can be confirmed or made for the first time based on MRI results?
Tumor
In photographs, it will differ in color from healthy tissue; most often it appears as a lighter area with uneven contours. Such a formation can displace other brain structures. If a tumor is detected, additional studies may be required to determine its nature and monitor its growth. In particular, additional MRGs of the brain may be needed to monitor the dynamics of its growth.
Stroke
During a stroke, some areas of the brain suffer from hypoxia, that is, from a lack of oxygen. Because during an attack, the vessels of the head spasm, oxygen-rich blood stops flowing. Depending on the duration of the attack, the degree of hypoxia will vary. In the most severe cases, some areas of the brain may die.
The area of the brain affected by hypoxia will appear lighter in the image than healthy areas of the brain. It can be visually distinguished from a tumor, because this zone corresponds to the innervation of one of the affected cerebral arteries.
If a vessel ruptures during a stroke, a hematoma will be visible on the image. In the photographs, its shade is darker than the healthy area.
Multiple sclerosis
This is a disease in which some nerve fibers lose their outer layer. Because of this, the conduction of impulses through them from the brain to all limbs and internal organs deteriorates. Therefore, with multiple sclerosis, it is difficult for a person to control his body.
Foci of the disease appear on photographs as light areas. They can be found in any part of the brain. Their number can be anything from one to several dozen. If there is only one formation, it can be confused with a neoplasm. But unlike a tumor, the affected areas in multiple sclerosis do not compress or deform other parts of the brain.
Hydrocephalus
This disease is also called dropsy. This is an expansion of the cavities of the ventricles of the brain. Since their volume is larger than normal, they will compress the brain, interfering with its normal functioning. If the patient's condition is not controlled, subsequent brain injuries can be fatal.
Brain gliosis
Brain gliosis (as doctors more often say) is not a disease, but rather a condition of the brain, which is characterized by disruption of the central nervous system. With gliosis, brain neurons die. This condition is a consequence of prolonged hypoxia or stroke. In this case, scars are visible in the photographs.
Anomalies of brain structure and development
If the patient has congenital pathologies, they will be visible in the photographs. Their severity and impact on the patient’s health will be judged by the attending physician. In many cases, such anomalies are either corrected surgically or do not affect the patient’s well-being.
Vascular atherosclerosis
In the photographs, this disease looks like a narrowing of the vessel, as if it was pinched. There is less contrast penetration in this area, so this area appears lighter on the image.
Hypertensive angiopathy
This is an expansion of the perivascular spaces, that is, the appearance of edema. In the image you can see round or oval areas with a clear border next to the vessels.
Aneurysm
This is the thinning of the vessel wall due to its expansion. An aneurysm can rupture at any time. Therefore, such conditions are extremely dangerous and require immediate consideration at a consultation.
Malformation
This is a pathology of the vascular bed, it refers to congenital pathologies. The images show that the vessels, which are located radially, converge towards the center.
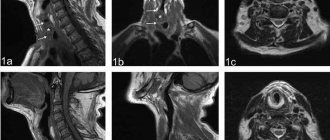
Signs and picture of the disease in the picture
A characteristic manifestation of multiple sclerosis in photographs is the identification of multiple small foci in the substance of the brain and spinal cord. They look like areas of clearing in the picture.
In addition, on tomograms the doctor sees the following changes:
- "Dawson's Fingers" This is demyelination (destruction of myelin fibers) of the white matter of the brain. Pathological formations have an oblong shape and are located along the small cerebral veins perpendicular to the lateral ventricles.
- Strengthening the signal from lesions after the injection of a dye.
- Multiplicity of lesions and their localization in the periventricular region.
If the patient does an MRI 3 months after the clinical debut, the doctor will detect the following changes:
- Multiple lesions that accumulate contrast.
- The areas of clearing are tightly adjacent to the cerebral cortex, affecting the arcuate fibers.
What do multiple sclerosis lesions look like on an MRI image?
Are there any complications possible after the examination?
Like any other medical procedure, magnetic resonance imaging does not exclude the development of negative consequences. However, you need to understand that they rarely occur.
Complications may arise if the patient does not inform the doctor about the metal objects in his body. Otherwise, he risks serious damage to organs and structures at the site of contact of objects.
If the subject has a pacemaker inserted, the tomograph may disrupt the operation of the device, which can also end in disaster. When contrast is administered, an allergy may develop, including anaphylactic shock.
To avoid such consequences, it is necessary to strictly follow the rules of preparation for the procedure. You should definitely tell your doctor about metal objects inserted into your body.
MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic test that is widely used to confirm multiple sclerosis. Often, specialists perform scans with contrast. The method is informative, reliable and safe for the subject.
Signs of multiple sclerosis
Some of the first symptoms are loss of vision, paresis, paralysis, weakened sensitivity of the limbs and other parts of the body, and impaired coordination of movements. A person may have the feeling that there is “frozen” on the face, or that the leg or hand is “not his.”
With the development of multiple sclerosis, the following is observed:
- a sharp decrease in performance, mental functions, concentration;
- sudden dizziness for no apparent reason;
- speech problems;
- unilateral decrease in vision up to blindness (impairments appear and disappear);
- problems with coordination of movements;
- impaired motor skills of the hands (the patient finds it difficult to do small work, handwriting noticeably deteriorates, etc.);
- convulsions and non-convulsive epileptic seizures;
- complete or partial paresis of the limbs;
- disturbance of urination, bowel movements, and genital function;
- pain without a clearly defined focus
- anxiety, sudden mood swings, etc.
If several symptoms from the above list appear simultaneously, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The appearance of causeless dizziness may be one of the signs of MS