- What does a liver CT scan show?
- CT with contrast
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Preparing for the examination
- How is the procedure performed?
- Decoding the results
- How often can you do it
Liver CT is a modern, informative and non-invasive examination method that allows you to obtain information about the structure, blood supply, and functioning of the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
Computed tomography of the liver allows you to obtain images that represent layer-by-layer sections of tissues and organs of the area under study. During one examination, from 100 to 300 images can be obtained, depending on the thickness of the sections. The thickness of the tissue sections of the area under study can be from 1 mm and is set manually by the doctor using the tomograph settings. All this makes it possible to identify even small tumors and notice pathological changes in tissues at the earliest stages of disease development.
It should be understood that ultrasound can be used to examine the liver with approximately the same level of information content. Ultrasound examination is more affordable and does not have any harmful effects on the human body. CT is used in cases where the use of ultrasound is difficult due to the patient’s excess weight or there are pathological changes in the liver that are not clearly visible on the screen of an ultrasound diagnostic device.
What is CT scan of the liver
Computed tomography (CT) is a special research method that can be used to obtain a three-dimensional image of an internal organ. During the examination, a person is irradiated with special electromagnetic rays in several planes, which makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image.
Often, a special contrast material is injected into the patient's body, which allows for a clearer image, which makes the study more accurate.
CT scans can be used to examine the liver. With its help, it is possible to identify liver pathologies even at an early stage of their development. Typically, a liver CT scan is prescribed by a doctor if a serious pathology is suspected or if other diagnostic methods do not provide a high-quality result.
A liver CT scan performs three tasks:
- Detection of structural liver disorders;
- Determining the cause of such violations;
- Making a diagnosis and developing treatment methods.
What is computed tomography
A CT scan of the liver is a procedure in which the abdominal organs are exposed to x-rays. A tomograph is a device that resembles an arch and sends rays evenly from all sides.
As a result of the difference in their absorption and refraction by tissues and internal organs, a clear two-dimensional image appears on the monitor screen.
Tomography can be carried out in two ways:
- using a contrast agent, which additionally highlights the contours of organs and formations;
- without contrast is a standard procedure that does not require special preparation.
A more modern diagnostic method is PET (positron emission tomography). Unlike MRI and CT, this method provides a three-dimensional image, which makes it possible to more clearly visualize tumors, inflammatory processes and other pathologies.
Although this procedure allows for better examination of internal organs, it is rarely practiced.
Indications
Typically, a liver CT scan is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- Aching, pressing pain in the liver;
- Pain and feeling of heaviness in the right hip area;
- Nausea and bloating;
- Feeling of bitterness and metallic taste in the mouth;
- Change in color of stool and urine;
- Weakness and fatigue.
If the patient has most of the above symptoms, then a computed tomography scan will help confirm or refute one of the following diagnoses:
- Tumor or presence of metastases in the liver;
- Mechanical damage and/or inflammation;
- Damage to blood vessels and/or internal hemorrhage;
- Jaundice;
- Cirrhosis;
- Some types of dystrophy.
In some cases, a CT scan is performed before a major operation, when it is very important for the doctor to know the appearance of the liver.
A computer examination is also carried out to assess the effectiveness of treatment. If the CT scan shows that the treatment was ineffective, the doctor may change the treatment method.
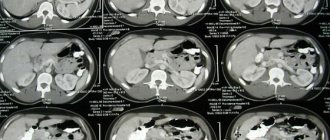
What is visible on CT scans with contrast
Decoding of the received data is carried out by a radiologist after completion of the procedure. For each parameter under study, a standard has been established. CT scan shows abnormality.
- A CT scan with contrast clearly shows the organ, its shape and size. An increased size indicates possible cirrhosis.
- The fat capsule, lobar structure, and organ density are examined. Density is an important parameter for detecting diffuse changes.
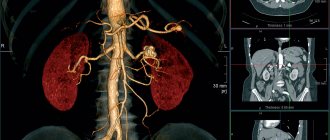
- On a CT scan, you can clearly see the vessels and bile ducts penetrating the tissue of the organs. It is considered almost impossible to examine the condition of blood vessels without contrast.
- Dilated bile ducts indicate the possible presence of obstructive jaundice.
- Benign tumors are characterized by slow growth, small size, and the presence of clear and even, sometimes wavy, outlines. The contrast agent accumulates poorly.
- Hemangioma is determined by the nature of the distribution of the contrast agent.
- A cyst is a benign formation that is common. A single cyst has liquid contents and is located in the lower right part of the organ. Polycystic disease is characterized by multiple cysts located throughout the organ.
- Malignant tumors are usually characterized by large sizes, accelerated growth, and the presence of uneven, bumpy outlines. The contrast accumulates intensely.
- Liver cancer often occurs as a consequence of cirrhosis, which can be caused by hepatitis C, B, and alcohol addiction.
- The presence of abdominal cancer often gives metastases to the liver. Diagnostics is mandatory before prescribing chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Abdominal oncology
Contraindications
In general, CT is quite safe. However, it should be remembered that during the examination a person receives radiation exposure, so tomography should not be used too often so that the person does not develop radiation sickness. There are also other contraindications in the presence of which CT of the liver cannot be performed:
- Pregnancy (radiation exposure may affect fetal development);
- Age up to 14 years (rays can negatively affect the development of internal organs and bones);
- Excess body weight (most devices have a maximum permissible load level of 150 kg).
It should also be remembered that during a CT scan, contrast is usually injected into the body to improve the quality of the examination. However, it should be remembered that in some cases its use may be contraindicated:
- Serious kidney and liver diseases;
- Allergy to contrast agent components;
- Diabetes mellitus (in some cases).
Operating principle of CT
Computed tomography is based on the principle of absorption of X-rays by various tissues. The method is similar to conventional X-ray diagnostics, but the diagnostic capabilities of computed tomography are broader; in addition, modern innovative devices and the ability to process the information received provide almost limitless opportunities for examining internal organs.
Until recently, specialists had to work on outdated 16-slice tomographs. And at the time of scanning, the person had to hold his breath for a short time. The radiation exposure was much higher than with modern and improved devices. New tomographs gradually replaced the first devices, which were dangerous to human health. Today, outdated technology has been replaced by sophisticated multi-slice scanners, which are distinguished by high quality visualization of the organs and tissues being studied and minimal radiation exposure to the body.
During the examination, the X-ray tube rotates continuously, records data and processes information. The multispiral unit rotates slowly at different angles, so the X-ray radiation used passes through all structures of the human body. The rays are converted into electrical signals, and the diagnostician receives high-quality images showing the condition of internal organs, including bones and blood vessels.
The doctor enters the obtained data into a modern computer, where they can be stored for a long time in a systematized and convenient form. If desired, specialists use previously obtained information to conduct a comparative analysis of one or a series of images and evaluate the effectiveness of the drug therapy used.
During radiography, images of tissue appear on film. During a CT scan, X-ray radiation is supplied from different places, the device records the intensity of its absorption in specific areas of the study, after which the specialist receives pictures and interprets the images.
Preparing for a CT scan of the liver
To get correct results, you need to properly prepare for a CT scan. Preparation begins 3-4 days before the examination. The patient must have blood and urine tested, since CT scans are almost always performed using contrast material, so it is important to rule out allergies.
You should refrain from eating and drinking 6 hours before the examination, since the CT scan must be performed on an empty stomach.
Before performing a CT scan, you also need to choose the right clothing without metal inserts or threads, since metal can “leave a shadow” on the volumetric image, which will make the examination results useless from a diagnostic point of view.
When CT is not done
Contraindications to MSCT and SCT without contrast:
- pregnancy (regardless of trimester);
- obesity (body weight more than 150 kg).
Pregnant women should not undergo CT scans with contrast agents. X-ray radiation, even in a small volume, harms the growing body, so CT scans are prescribed for children only in exceptional cases. Absolute contraindications for liver CT with contrast are:
- severe form of diabetes mellitus;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- intolerance or allergy to contrast media;
- bronchial asthma;
- acute heart failure;
- the patient’s weight exceeds the permissible load on the tomograph;
- renal failure;
- multiple myeloma (a type of blood cancer).
It is dangerous to do a liver CT scan if the creatinine value exceeds 130 µmol/l, which indicates a critical condition of the kidneys. In this case, MRI is chosen as a diagnosis. The procedure is postponed for 6 days if the patient has undergone an X-ray of the stomach or intestines with barium.
Preparation for the procedure
If a CT scan without contrast is planned, preparation is to prevent gas formation in the intestines. Flatulence can distort the results, so 3 days before the procedure, doctors recommend avoiding carbonated drinks, alcohol, fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, peas, beans, rye bread and other foods that contribute to the formation of gas bubbles in the intestines.
2 hours before a liver CT scan, you should refrain from eating and drinking. Before the procedure, physical and psycho-emotional stress should be avoided. If you are planning to examine a child under the age of 7, it is important to check with the doctor how the procedure will be carried out - with or without anesthesia. General anesthesia is given on an empty stomach, so the baby is not allowed to eat or drink 12 hours before the CT scan.
Preparing a patient for a CT scan of the liver and gallbladder with contrast, in addition to the general rules, requires additional actions:
- 2 days before CT, you should stop taking medications that have increased toxicity to the kidneys - NSAIDs, antibiotics;
- Do not take diuretics per day.
You can resume taking medications no earlier than 2 days after the examination. On the eve of the procedure, the patient is prescribed a laboratory blood test (biochemistry) and a Reberg-Tareev test. If the test results are normal, the patient is ready for examination.
If a person has contraindications to a CT scan, but the diagnosis is necessary for health reasons, he is given special medication preparation. For such patients, the doctor prescribes steroid hormones, drugs that suppress the secretion of gastric juice, antihistamines, drip administration of Ringer's solution, and saline.
Progress of the procedure
Typically, liver tomography is done as follows:
- The person puts a special robe on the body without metal threads or inserts, and then lies down on the tomography table;
- A nurse administers a contrast agent to a patient using a syringe.
- After this, the doctor and nurse turn on the tomograph and leave the room. They watch the progress of the inspection from another room through glass.
- The doctor can use loudspeakers to communicate with the patient. Headphones should not be used for this as they may distort the transmission of the tomographic beams, rendering the examination results useless.
- When the patient has taken the desired position, the doctor turns on the examination mode, during which a special disk emitting electromagnetic rays begins to move in the tomography machine. To obtain an accurate image, the patient must remain completely still for 30-40 minutes. Optionally, the patient may be given sedatives if he cannot remain still for such a long period of time.
- All results are processed using a special computer program and saved to a hard drive for storage.
How is the examination carried out?
Before the procedure, the patient will be asked to remove clothing and accessories that have metal fasteners or trim elements located in the abdominal area. Metal parts can leave shadows on images and thereby complicate diagnosis.
To conduct a liver examination, the patient is placed on a retractable tomograph table in a supine position. Your hands will need to be placed behind your head. You will have to lie still for 15-30 minutes, so it is advisable to choose loose-fitting clothing for the procedure. To avoid distortions in the images from voluntary and involuntary movements, the patient’s body is fixed using special pillows and belts.
The medical staff positions the patient's body inside the tomograph so that the area being examined is at the same level as the machine's scanner. Before turning on the CT scanner, technicians and nurses leave the room in which the machine is installed to avoid exposure to radiation.
A doctor or nurse constantly monitors the patient through a special window from an adjacent room. The patient can always contact the nurse using voice communication or a special “panic button”. During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to hold his breath for 1-2 seconds in order to prevent displacement of organs during breathing and to obtain clearer and more informative images.
Benefits of CT
CT has many advantages:
- Three-dimensional images are very accurate and detailed, so CT can be used to diagnose diseases at both late and early stages of development.
- Using a three-dimensional image, you can establish the presence of a disease and understand the reasons that led to its appearance.
- The examination is completely painless, but the person will have to lie on the tomography table for about 30 minutes without moving.
How is the examination carried out?
Since CT scans of the liver are performed quite quickly, which is especially important in case of injuries, when doctors do not have time to conduct ultrasound and MRI, the procedure is easily tolerated by patients. Contrast is injected through a vein shortly before the examination. It is recommended to perform an allergy test first, so that unexpected reactions to the contrast agent used do not occur on the liver tomography. Depending on the type of tomograph used, the diagnostician may ask the patient to hold their breath for a while.
We suggest watching a video of how the CT procedure is performed so that you can see it clearly.
Harmful CT scan of the liver
Computed tomography is a moderately safe method of examining the liver. During the scan, the body is irradiated quite mildly, which cannot lead to any negative side effects. However, to monitor treatment, the doctor may prescribe tomography quite often: in this case, radiation will begin to accumulate in the body.
There is also a small chance that a person will become ill due to the introduction of contrast agents into the body, but preliminary tests can minimize the risk of allergic reactions.
The essence and advantage of the method
There are a number of types of computed tomography of the liver. Each of them has its own characteristics. The most popular method is contrast-enhanced CT, which involves the use of radiation in small doses, the introduction of a certain drug that enhances the contrast between healthy tissues and abnormal structures. The described type of diagnosis is used when it is necessary to obtain comprehensive information about the area under study. Contrast allows you to examine in detail the condition of the liver and gallbladder.
Execution technique
To perform a CT scan with contrast, the patient is given a contrast agent containing iodine. Drugs are divided into ionic and non-ionic.
Carrying out tomography
Ionic drugs include: diatrizoate, urografin, ioxaglate, metrizoate. The non-ionic group includes: omnipaque, iopromide, ultravist, ioversol, unigexol. Non-ionic substances are preferred since side effects with their use are extremely rare.
To perform the procedure, a bolus injection of the drug or a manual injection is performed. CT with bolus contrast is automated and involves drip administration of a substance.
The effectiveness of this type of research is determined by the following factors:
- volume of drug administered;
- drug concentration;
- speed of drug administration.
Providing the required level of staining between normal and pathological structures is determined by the degree of concentration of the substance and the rate of its administration. Slow administration of a substance with a weak concentration can cause diagnostic errors. For obese people, it is important to administer a larger volume of contrast agent. Thus, the volume of the administered drug should be calculated depending on the weight of the person being examined.
The radiation dose during examination of internal organs is 7-9 mSv (millisieverts).
Research stages
A study with contrast involves division into stages:
- Arterial stage. Lasts 30-45 seconds. During the stage, the X-ray density in the aorta increases sharply. Staining of pathological formations that have a strong blood supply occurs intensively.
- Redistribution stage. Lasts 2.5 minutes. Increases in the liver parenchyma (tissue). Formations with slow blood flow are visible against the background of intensely stained liver parenchyma.
CT scan
- Balance stage. Duration – 5-10 minutes. The difference in drug accumulation between normal and pathological structures is smoothed out. During this stage, the substance slowly accumulates in formations that are poorly supplied with blood and have connective tissue. Therefore, in order to view such formations, delayed tomograms are performed 10 minutes after the administration of the contrast agent is completed.
Thus, structures with increased blood flow are stained more strongly in comparison with the liver parenchyma, those with reduced blood flow are stained weaker or with a slight delay.
Interpretation of tomography of the liver and gallbladder
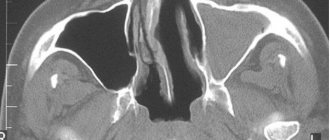
The density of the liver is normally greater on CT than the tissue of the pancreas, kidneys or spleen. Often the intrahepatic bile ducts are not visible on the tomogram. However, it is worth noting that due to the administration of intravenous contrast, the bile ducts are more distinguishable compared to the surrounding liver ducts. In a detailed study of the disease, the two main lobes of the liver are examined, and the condition of the edges of the organ is assessed.
Computed tomography of the gallbladder, like the liver, allows one to distinguish fairly small areas of damage.
The structure of the tissues of the liver and gallbladder is subjected to a mandatory meticulous examination. In the process of describing the images obtained, special attention is paid to this issue, since due to a lack of nutrients, the organ may stop performing its functions. More precise localization of lesions is revealed by the diagram of liver segments on CT.
The large vena cava into which the hepatic ducts flow is chosen as the basis for observation. Blood flows out through these vessels. In this case, the attending physician evaluates the condition of large vessels in the liver that collect venous blood from the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas.
Using fast-frame scanning with intravenous contrast, signs of liver cirrhosis can be quickly detected on CT. The width of the splenic and mesenteric veins is taken into account, the degree of narrowing or expansion of the lumen, filling defects, and the presence of a clot in the blood are studied. After a certain time, the dynamics and response of organs to the treatment received is studied.
After a CT scan of the liver, specialized specialists conduct follow-up monitoring of the patient. If gallstones are visible on a CT scan, urgent treatment and hospitalization are required.
How the research works
During the examination, the patient lies on a special table along which the tomograph ring moves. A liver CT scan does not cause pain or discomfort; the only inconvenience is that the patient must remain motionless throughout the examination.
In what cases is a CT scan of the liver with artificial contrast indicated?
When a conventional CT scan of the liver does not provide a clear clinical picture, contrast is used. A special preparation makes images more contrasty, allowing them to increase their clarity and resolution. Liver CT with contrast is often used to diagnose cancer, localize metastases, and determine the stage of cirrhosis.
Preparation
A CT scan of the gallbladder requires certain conditions to be met. Preparation consists of following a diet for 2 days before the procedure. Restrictions are imposed on products that contribute to gas formation:
- vegetables containing coarse fiber;
- carbonated drinks;
- dairy products;
- bakery products.
The evening before the test, you must avoid eating. Otherwise, the information content of the method will be questionable: the images will show darkening and spots from food lumps, which will be impossible to differentiate. Before this event, you should drink a laxative or do an enema. On the eve of the session, medications that block x-rays may be prescribed as a contrast agent. A few hours before the diagnosis, it is recommended to drink still water (2-3 l).
A mandatory condition for admission to such a diagnosis is the absence of metal jewelry and piercings on the body, since these items can distort the results of such an examination.