Electrocardiography is an accessible and informative procedure for diagnosing cardiac pathologies. The essence of the method is to record electrical impulses, the occurrence of which is due to the rhythmic alternation of contractions and relaxations of the heart muscle over a certain time range.
An electrocardiograph (a special medical device) records impulses coming from sensors mounted on the body and converts them into a graph. Such a graphic image is called an electrocardiogram, and is subject to further decoding by a cardiologist. Since ECGs are performed in hospitals and at home, there are stationary and portable cardiographs.
The main components of the device are:
- electrodes placed on a person’s arms, legs and torso;
- switch-regulator;
- signal amplifier;
- filter against network interference.
Modern cardiographs have high sensitivity to the bioelectrical activity of the heart muscle and accuracy in transmitting impulse oscillations.
How is an ECG performed?
An electrocardiogram is performed at least two hours after eating or smoking.
Before performing an ECG, you need to rest and calm down for 15 minutes. To record an electrocardiogram, electrodes are placed on the skin in the area of the lower legs, forearms and chest. To improve electrical conductivity, the skin is lubricated with a special gel.
In emergency situations, an ECG is recorded without any preparation.
Electrocardiography or ECG of the heart is a test in which a device senses the electrical activity of the heart. ECG results are a graph, usually written on graph paper as a curve, showing changes in voltage between two points over time.
Electrocardiography is a quick, cheap and easy test for people that provides important information about heart function. Therefore, it belongs to the basic medical examinations.
Many people know which doctor does an ECG. An electrocardiogram is performed by a cardiologist, who also interprets it. Today, cardiologist services are available online, where it is also possible to evaluate the results of the examination - that is, calmly go to the page - and decipher your cardiac activity!
An ECG is a necessary examination if heart disease is suspected. Electrocardiography is used in the diagnosis of ischemic changes in the heart muscle, i.e. changes from lack of oxygen, the most serious manifestation of which is the death of heart cells due to lack of oxygen - myocardial infarction.
In addition, ECG analysis may show arrhythmia, an abnormal heart rhythm.
Conclusion The ECG also reveals dilatation of the heart in case of heart failure or pulmonary embolism. A cardiogram is usually performed as part of a preoperative examination before a planned procedure under general anesthesia, or as part of a general examination.
There is no need to follow any special regime before the examination. All that matters is calmness.
Pathological disorders of the heart
If the final study data contains changed parameters, this is a reason for a more detailed examination of the patient. There are several types of deviations in ECG results:
- borderline - some indicators slightly do not correspond to the norm;
- low-amplitude (decrease in the amplitude of the waves in all leads) – characterizes myocardial dystrophy;
- pathological - cardiac dysfunction requires immediate medical attention.
However, not all altered results should be taken as evidence of serious problems with the functioning of the heart muscle. For example, a reduction in the horizontal distance of teeth and segments, as well as rhythm disturbances, can be recorded after physical and psycho-emotional stress. In such cases, the diagnostic procedure should be repeated.
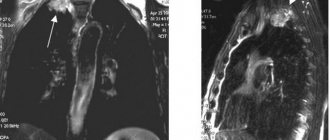
The photo shows an example of a cardiogram with deviations - ventricular extrasystole
Only a qualified specialist can “read” an ECG and draw appropriate conclusions! An inexperienced patient should not independently diagnose the disease and take medications. In the table we indicate an approximate interpretation of pathological electrocardiography:
| Deviations | Disease, pathology | Interpretation |
| Heart rhythm disturbance | Bradycardia | Pulse less than 60 beats/min, PQ segments> 0.12″, P wave in N (normal) |
| Tachycardia | Heart rate up to 180 beats/min, P wave directed upward, QRS> 0.12″ | |
| Changing the position of the EOS (electrical axis of the heart) | Bundle branch block | The S wave is highly elevated relative to R, the axis is deviated to the right by >90° |
| Left ventricular hypertrophy – observed with pulmonary edema and infarction | The R and S teeth are very high, the axis is deflected to the left from 40° to 90° | |
| Cardiac conduction disorders | AV I degree (atrioventricular block) | Duration of the PQ interval >0.2″, the T wave changes with the ventricular complex |
| AB II degree | PQ is constantly increased and completely replaces ORS | |
| Complete AV block | Change in atrial systole, identical sizes of P and R waves | |
| Other pathological changes | Mitral valve prolapse (loss) | The T wave is directed downward, QT segment prolongation and ST depression are observed |
| Underfunction of the thyroid gland – hypothyroidism | Bradycardia, T wave is flat, PQ segment is lengthened, QRS is low | |
| Ischemia | T angle is sharp and high | |
| Heart attack | The ST segment and T wave are dome-shaped, the height of R is increased, the Q is shallow |
Preparation rules
Preparation for an ECG is usually not required, but to obtain reliable data the patient should take into account some features. These include:
- the patient needs to tune in and not worry;
- before the procedure, you should not apply any cosmetic or medical creams, ointments, or gels to your body;
- clothing should be comfortable; women are not recommended to wear nylon tights or stockings, as they will need to be removed;
- You should avoid drinking large amounts of food and liquid immediately before the procedure.
Important! Patients suffering from severe shortness of breath are advised to sit rather than lie down during testing.
ECG in pediatrics
ECG is a non-invasive, painless and safe method, performed within a short period of time. These properties allow the study to be widely used in children.
In children, an ECG is used to diagnose:
- congenital heart defects, blood vessels (first months, years of life);
- inflammation of the membranes of the heart;
- rheumatism;
- vascular dystonia;
- cardiomyopathy.
A referral for examination to a child is given by a local pediatrician or a specialist (pediatric cardiologist, rheumatologist). For a child, the study is carried out using children's electrodes, for an older child - as in adults. It is important that the child is calm during the procedure and on an empty stomach.
Common mistakes when recording an ECG
Common mistakes that lead to distorted ECG results
Unfortunately, when recording a cardiogram, errors are common both on the part of preparing patients for the procedure and on the part of medical workers when carrying out the ECG registration algorithm. The most common errors leading to distortion of ECG results and the formation of artifacts are:
- Incorrect application of electrodes: incorrect placement, rearrangement of electrodes, incorrect connection of wires to the device can distort the ECG results;
- Insufficient contact of electrodes with the skin;
- Patient neglect of preparation rules. Smoking, overeating, drinking strong coffee before the procedure, or excessive physical activity when taking a resting ECG may give incorrect data about the electrical activity of the heart;
- Trembling in the body, uncomfortable positioning of the patient, tension of individual muscle groups in the body can also distort the data when recording an ECG.
In order for the ECG results to be reliable and truthful, healthcare workers need to clearly understand the algorithm of actions when taking a cardiogram and the technique for conducting it, and patients must approach the study responsibly and follow all the rules and recommendations before conducting it. It should be noted that ECG has no contraindications or side effects, which makes this research method even more attractive.
Making an appointment with a doctor
The information published on the site does not constitute a recommendation for use and is intended for informational purposes only.
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a technique for studying the electrical activity of cardiac myocytes, carried out using an electrocardiogram recording. The muscle fibers of the heart have an electrical potential, which is captured by special electrodes during the procedure. The result is a record called a cardiogram, which reflects the total electrical activity of the heart.
Registration of a cardiogram is usually carried out by nursing staff, but a referral for an ECG is given by a doctor of any specialty. Most often, the need to undergo the procedure arises in the following cases:
- carrying out a preventive examination (medical examination, examination upon entry to work);
- suspicion of various heart diseases;
- referral for planned surgical treatment or planned hospitalization;
- ECG registration for pregnant girls and women.
Electrocardiography is carried out as part of a medical examination, which all people over 18 years old undergo every 3 years. This procedure is necessary when applying for certain types of work (driver, pilot, etc.). The study should also be performed during pregnancy. Usually, the doctor orders an ECG when a pregnant woman is registered and in the third trimester.
Electrocardiography is mandatory if cardiovascular diseases are suspected. An ECG can reveal:
- ischemic changes (including myocardial infarction);
- rhythm and conduction disturbances (sinus tachycardia or bradycardia, paroxysmal tachycardia, extrasystoles, heart block, etc.);
- signs of hypertrophy and overload of various parts of the organ, etc.
Electrocardiographic examination is carried out not only for adults, but also for children. For example, this procedure is mandatory for a child aged 1 year for the purpose of early detection of heart disease. For all children it is carried out during planned hospitalization.
Electrocardiography is an absolutely safe research method, therefore, if necessary, even infants are given an ECG. Both adults and children can undergo this procedure without a doctor's referral. In this case, the research will be paid.
Only a doctor certified in functional diagnostics can interpret ECG results.
Recording an ECG does not require special preparation. Immediately before the test, it is necessary to avoid heavy physical activity, drinking caffeinated drinks and smoking cigarettes, as this usually leads to an increase in heart rate (HR).
If you are taking any medications, you must notify your doctor before recording an ECG.
ECG registration is carried out in the supine position. The patient needs to free the ankles, wrists and chest from clothing and jewelry, since these are the areas where the electrodes are applied. Four large clothespin-shaped clothes in red, yellow, green and black colors are attached to the right and left arms, left and right legs respectively.
Six small electrodes (usually suction cups) are placed on the chest. The first - on the fourth intercostal space along the right edge of the sternum, the second - on the fourth intercostal space on the left edge of the sternum, the fourth - along the midclavicular line in the fifth intercostal space, the third - in the middle between the second and fourth.
Electrode application diagram
Recording a cardiogram takes less than one minute and occurs automatically. After the procedure is completed, the electrodes are removed and the patient can stand up. The tape obtained during the study is sent to the functional diagnostics doctor. The results of the ECG can be found only after deciphering the electrocardiogram.
What is electrocardiography (ECG)
An electrocardiogram records electrical signals in the heart.
This is a general test used to identify problems and monitor the condition of the heart in various situations, as an ECG is done in the functional diagnostic room, in ambulances, and at the patient’s home. Electrocardiographic examination is non-invasive, painless and gives quick results. During the test, sensors (electrodes) are attached to the limbs and chest and remain for a few minutes, which usually does not cause discomfort.
Each heartbeat is triggered by an electrical impulse, and an electrocardiogram records the timing and strength of these signals as they travel through the myocardium. The device for recording electrical impulses is called a cardiograph, it has several terminals and electrodes that collect information from 12 different areas on the skin of the chest and limbs. Electrical activity is recorded as waves on a graph, with different patterns corresponding to each electrical phase of the heart rhythm.
An ECG graph is a graphical representation of changes in the electrical potential of the heart.
Not only patients with complaints, but also healthy people are prescribed an ECG. Why is this procedure done and what can it show? Using this research method you can determine:
- Regularity and heart rate.
- Chronic and acute myocardial damage.
- Disturbances in the metabolism of potassium, magnesium and calcium.
- The cause of pain in the heart area is whether it is caused by the work of the heart or, for example, by a pinched nerve.
- General condition and thickness of the myocardial walls (which may be normal or increased).
- The condition of an electrical pacemaker implanted in the heart.
What is a heart ecg (electrocardiogram), how it is done, you will learn from this video. Have a nice time everyone.
Electrocardiography is the main diagnostic method in cardiology. The technique for taking an electrocardiogram (ECG) is presented in this video clip. You should pay close attention and remember the sequence of placement of the electrodes on the limbs and chest.
Each of the segments of difference between the voltage of the electrical impulses of the cardiographic circuit is called a lead.
- red electrical conductor N1 with a negative charge is connected to the right hand;
- yellow conductor N1 with a positive charge - to the left hand;
- green electrical conductor N2 with a negative charge - on the right hand and with a positive charge (N2) - on the left leg;
- electrical conductor N3 - to the left hand (-) and to the left leg ( ).
The right leg is characterized by an indication close to a conventional zero, therefore the voltage level of the blood flow from it is not recorded; the right leg is used as grounding.
AVR, AVL, AVF - single-pole leads, proportional to the average voltage of all electrical conductors (or two out of three according to the Goldberger system).
Recording an electrocardiogram is always included in routine therapeutic examinations, even in the absence of complaints of pain in the heart area. The risk group includes age groups over 40 years and the presence of relatives with heart muscle diseases. It is also advisable to do an electrocardiogram when planning pregnancy.
The procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- severe pain in the spine;
- preoperative examination;
- kidney disease, hypertension, hypertension;
- increased hemoglobin;
- suspicion of plaque formation;
- dilatation of the superficial veins of the lower extremities;
- other indications as determined by a specialist.
It is important to note! Irregular heart rhythm is typical for a completely healthy child, but is a sign of pathology in an adult.
Important! An ECG can be prescribed to a child from birth; currently, in maternity hospitals, an electrocardiogram is done for preventive purposes before discharge. An ECG does not cause any harm to a child.
For children from birth to 10 years of age, electrocardiography is performed in a special way; the main differences lie in the methods of connecting the electrode conductors. The rheographic electrode conductor for examining children consists of an alloy of copper, nickel, zinc with a diameter of 2 square meters. cm (for newborns - 1 sq. cm), and electrical conductors for fixation on the chest area are equipped with rubber fasteners.
The child is placed on a treatment table equipped with an insulating mattress. The areas of skin intended for attachment of electrodes are moistened with a gel with high electrical conductivity. Flexible lead plates with a tight fit are attached to the baby. Specialized chest leads (needle electrode conductor) are used for low skin conductivity.
After this, the usual recording of the electrocardiogram begins.
A child's ECG contains five to six teeth and three segments, which are located on an isoelectric tape. The main teeth are: P, Q, R, S, T. The “U” tooth appears extremely rarely before the age of 10 years, so basically the electrocardiogram consists of five teeth.
In a healthy child, the PQ area is located between P and Q, and the ST area is between the end of the fifth tooth and the beginning of T, the TP area begins at point T and reaches P.
The main straight line represents a state of rest. This is an isoelectric straight line, or a line of zero potential. The cutting gap has no difference in potential; all cells at this moment are motionless. The line is indicated by sections T and P, in which the end of the tooth T is connected to the initial section P.
The child’s ECG is divided into three segments:
- the first section starts from the P tooth and reaches the Q point and corresponds to atrioventricular conduction;
- the second interval is from Q to the end of the T wave, this segment is called the ventricular complex;
- the third segment is an isoelectric line that connects the end point of the T wave with the starting point of the next P wave and corresponds to the state of rest.
The starting point of the T wave determines the transmission of excitation from the atrium. The length of the clove corresponds to the time interval of the irritable reaction until the condition stabilizes. This is a segment that has a round or sharp small tooth with a positive amplitude.
The duration of this segment in the ECG of a child under 10 years of age does not exceed the time indicator of 0.1 seconds. The direction of the line of irritation runs from the right side up, then to the left and down, all directions have a positive charge, only in the third segment can they change to negative or bilateral (-), this is not a pathology.
Atrioventricular conduction on the ECG is parallel to the heart rate pulsation frequency. In children from birth to 10 years of age, the atrioventricular impulse is much shorter than in adults. The time interval of the pulse amplitude in newborns is 0.14 seconds, in infants up to one year old - 0.16 seconds, in children 10 years old - 0.18 seconds.
Main features of deciphering an ECG for a child:
- the electrocardiogram shows a predominance of the right ventricle;
- the brevity of the intervals increases and decreases depending on the age of the child;
- the size of the atrium is higher than that of an adult;
- a negative T wave is normal;
- respiratory and sinus arrhythmia;
- migration of the rhythm source within the sinus node or atrium;
- with the chest lead, a deep Q wave is possible in the third lead;
- partial block of the bundle branch.
Important! Many indicators of a child’s cardiogram are characterized by an increased heart rate and an enlarged size of the cardiac lobes; this is not a deviation from the norm.
What can be seen on a cardiogram
Electrical cardiography is a method that is quite widely used in modern medical practice. The procedure allows you to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system in a short time, which allows you to select the necessary treatment for the patient and prevent the development of complications.
Using the described method, doctors can recognize the following diseases in a person:
- hypertrophy of the heart. This condition is indicated by such ECG changes as an increase in the interval of impulse conduction, a change in the cardiac electrical axis, and a violation of the amplitude of the waves. Hypertrophy occurs due to overload of the heart parts against the background of hemodynamic disturbances;
- IHD, angina pectoris. In this case, the cardiogram will show a violation of the QRS complex, depression of the S-T segment, a change in the T wave;
- arrhythmia. Arrhythmias of various origins are accompanied by disturbances in the heart rate. The cardiogram will show changes in P – Q, R – R, Q – t complexes.
In addition, electrical cardiography allows us to identify various heart defects, aneurysms of the heart muscle, inflammation of the myocardium and many other pathologies. You can read more about interpreting ECG for various diseases here.
Electrocardiography at home
Cardiac pathologies are quite common, especially in elderly patients. Sometimes it is difficult for a person to visit the hospital on his own, so in some cases an ECG is performed at home to obtain a cardiogram.
The peculiarity of the procedure is that diagnostics are performed using special portable equipment. Modern portable devices provide accurate data and are not much inferior to stationary devices.
ECG at home is performed using special portable devices
In addition, conducting a session at home is indicated for people for whom physical activity and travel to the clinic are contraindicated. Many portable devices are equipped with printers, which makes it possible to immediately print out a cardiogram and establish a diagnosis.
Electrocardiography is a widely used diagnostic method that allows timely detection of various cardiovascular pathologies. A cardiogram provides clear information about the state of the myocardium, the functioning of the cardiac ventricles, and the conductivity of electrical impulses. Correct diagnostics and competent interpretation of the results ensure the diagnosis and selection of the necessary treatment.
What kind of doctor does an ECG in a clinic?
When making an appointment with a doctor, we expect qualified assistance - a correct diagnosis and prescription of effective treatment. Often, an inspection and survey alone is not enough. For better treatment, the doctor prescribes tests and the necessary types of instrumental diagnostics.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DMxsY4eVrHk
A relatively inexpensive but valuable method in cardiology is ECG (electrocardiography). A referral for examination can be issued by a local internist and a specialist - a cardiologist, rheumatologist, or endocrinologist. Using the information obtained from an ECG, all deficiencies in the functioning of the heart are assessed and areas of impaired blood supply are identified. They also undergo electrocardiography for the purpose of early diagnosis of vascular and heart diseases.
If you feel pain in the chest, increased heart rate after a slight exercise, arrhythmia (irregular rhythm), increased blood pressure or shortness of breath, increased sweating and a feeling of weakness, you should consult a doctor and ask to be examined and have an ECG.
Indications for ECG in childhood
A children's cardiogram shows abnormalities such as congenital and acquired heart defects, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, heart block, myocarditis, failures of myocardial metabolic processes and other conditions.
In childhood, indications for an ECG are:
- heart murmurs;
- upcoming surgery;
- transmission of diseases of infectious origin;
- admission to kindergarten or school;
- before admitting a child to a sports section.
A cardiologist interprets the cardiogram. In this case, the characteristics of the child’s body are taken into account. Children over 3 years of age may be prescribed a stress ECG.
How to do an ECG correctly: preparation and conduct of the procedure
When making an appointment for diagnostics, the question arises: “Which doctor does the ECG?” The procedure is usually performed by a nurse with special training. The result of the study is deciphered only by a functional diagnostics doctor who has the first specialization - a cardiologist. An ECG examination can be performed by a cardiologist if equipment is available in the office or when called at home.
It is recommended to conduct the examination two hours after eating, and you should not smoke 2 hours before the procedure. The procedure begins after the patient has calmed down or rested for at least 15 minutes. In emergency situations, no preparation is carried out, and the examination is done immediately.
Electrodes are placed on the skin in certain places - in the chest, forearms and lower legs. The skin is lubricated with gel to improve electrical conductivity. Therefore, take a shower before the procedure and do not use body cosmetics.
For those who do not know how to do an ECG correctly, do not worry: conducting electrocardiography does not require special training. However, some nuances still exist. It is advisable to refrain from eating heavy food 2 hours before the procedure.
Also, do not be nervous, play sports, drink energy cocktails or alcohol, as well as strong coffee or tea. Before the examination, women do not need to apply lotion or cream to the body; they should remove any jewelry from the wrists and chest area: bracelets, rings, chains, etc.
The chest electrodes have a special suction cup that is attached to the body due to the vacuum created. The specialist taking the readings knows very well how to do an ECG correctly, so it is unlikely that he will be able to confuse the wires connecting the suction cups to the device.
Before starting work, the device must be warmed up (3-5 minutes is enough). After this, the position of the recorder pen is adjusted, giving a calibration signal by turning on a special button.
There are no contraindications for conducting an ECG - the study can be performed even on infants.
In this case, the procedure for collecting data from a child is similar to that carried out by adults. Only the result will be different - for example, babies have a higher heart rate.
Some children are afraid of all people in white coats, so they can be very nervous before the procedure. Before it starts, parents should relieve stress in their children - give them a favorite toy, show a funny picture or photo (you can do it on your phone). An older child can be told about the study in advance and shown in a playful way how to do an ECG correctly.
The examination procedure may be difficult for those with complex chest injuries, high obesity, or excessive chest hair - in this case, the electrodes will not adhere tightly to the skin and the examination result will be distorted. The presence of a pacemaker will also lead to incorrect results.
Transesophageal examination cannot be performed in the presence of tumors or other diseases of the esophagus. ECG with stress is contraindicated in acute infectious diseases, chronic heart failure, coronary heart disease, complex rhythm disturbances, and in the acute period of myocardial infarction. Also, you should not do this if there is an exacerbation of diseases of other body systems - urinary, respiratory, digestive.
Additional types of research
In addition to the standard method, Holter monitoring and stress ECG are widely used in medical practice. These types of diagnostics make it possible to record cardiac impulses over a longer period of time or during physical activity.
Holter monitoring is used to assess cardiac activity over a 24-hour period or a longer period. The method involves attaching electrodes and a special battery-powered device to the human body. After this, the patient is asked to lead a normal lifestyle for 24 hours. Sometimes the specialist may ask the patient to do physical exercises.
During the study, a person needs to record data in a special diary. Here he must indicate what exactly he did, whether there were any worries or physical activity. After the procedure is completed, the electrodes are removed from the body, and the data from the device is printed in the form of a cardiogram.
Holter monitoring allows you to assess the condition of the heart over a long period of time
Normally, the cardiogram will show the following values:
- heart beats during wakefulness - from 60 to 100 per minute;
- heart beats during sleep – from 40 to 80 per minute;
- changes in heart rate when changing activities;
- ventricular extrasystoles are not observed normally. Up to 200 pieces are allowed;
- QT interval – women – 340 – 430 ms, men – 340 – 450 ms.
Important! In some cases, a deviation from the norm is considered acceptable, which depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
During a stress ECG, the patient must perform various physical exercises. This helps evaluate the functioning of the heart muscle at rest and during exercise.
Read more:Holter ECG - what is it?
- serious heart defects;
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiac congestive failure;
- severe forms of unstable angina;
- inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle;
- stage 3 hypertension;
- the presence of blood clots in the vessels;
- patient's pacemaker.
During the study, the doctor asks the patient to perform physical activity for 60 seconds. At rest, a person's heart rate ranges from 60 to 90 beats per minute. After squats, this amount should increase by no more than 20%.
An increase in heart rate to 30–50% indicates the presence of any cardiac pathologies. Coronary heart disease may be indicated by changes in leads V 4, 5, 6 in the form of horizontal depression of the ST segment. The same changes can be observed in coronary insufficiency. With unstable angina, the cardiogram shows a distortion of T waves and a displacement of the T wave.
A specialist should decrypt the data. Based on the data obtained, the doctor selects the necessary treatment.
Decoding the final data
ECG results are considered the basis for diagnosing cardiovascular pathologies. When interpreting them, such indicators as the systolic (stroke) volume of blood, which is pumped into the ventricles and released into the great vessels, the minute volume of blood circulation, and the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle in 1 minute, are taken into account.
The sequence algorithm for assessing the functional activity of the heart consists of:
- Studying the rhythm of contractions - assessing the duration of intervals and identifying disturbances in the conduction of electrical impulses (blockade).
- Analysis of ST segments and detection of pathological Q waves.
- Study of P waves reflecting atrial contraction.
- Study of the walls of the ventricles in order to identify their compaction.
- Determination of the electrical axis of the heart.
- Study of T waves, reflecting repolarization (restoration) of muscle tissue after contractions.
ECG analysis consists of the main indicators, schematically depicted on a graphic tape: elevations or depressions with sharp ends above a straight line - teeth; segments that connect the teeth - segments; distance from tooth to segment – interval
After analyzing the characteristics of the cardiogram, the attending physician has an idea of the clinical picture of cardiac activity, for example, a change in the width of the intervals and the shape of all convex and concave teeth is observed when the conduction of the cardiac impulse slows down, a mirror-inverted curve of the T wave and a decrease in the ST segment indicates damage to the cells of the muscle layer hearts.
When interpreting an ECG, contractions of the heart muscle are assessed by studying the amplitude and direction of their electric fields in 3 standard leads, 3 enhanced (unipolar) leads, 6 leads from the chest area - I, II, III, avR, avL and avF . Based on the results of these elements, the electrical axis of the heart is assessed, the location of the heart and the presence of disturbances in the passage of electrical impulses through the heart muscle (blockades) are assessed.
Normal cardiogram of an adult
It is impossible for the patient to “read” a graphic image correctly without the appropriate knowledge. However, you can have general information about the main parameters of the study:
| Index | Norm | Description |
| Ventricular QRS complex | 0.06 – 0.1 seconds | Reflects ventricular depolarization |
| P wave | 0,07″ – 0,12″ | Shows atrial excitation |
| Q wave | 0,04″ | Displays the completion of processes that occur in the ventricles |
| T wave | 0,12″ – 0,28″ | Characterizes the processes of recovery of the ventricles after their contraction |
| PQ interval | 0,12″ – 0,2″ | Shows the time it takes for impulses to travel through the atria to the middle layer of the ventricular walls |
| HR (heart rate) | 60 – 90 beats/min | Displays the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle |
Normal ECG of a child
The location and duration of the segments comply with generally accepted standards. Some study indicators depend on age:
- the electrical axis has an angle from 45° to 70°, in a newborn baby it is deviated to the left, until the age of 14 it is located vertically;
- heart rate is sinus, in a newborn up to 135 beats/min, in a teenager – 75-85.