The first is considered the most accurate indicator of the content of mineral salts in bone tissue.
The second is no less important, since its correlation with the risk of fractures is very high, so this index has great prognostic value. Interpretation of densitometry results may also contain one more parameter - volumetric mineral density of tissues, but it is used less and less. This is due to the fact that it is quite difficult to detect and often in order to obtain such a parameter it is necessary to use a special type of computed tomography and use quite expensive methods of data processing.
What is the procedure
The densitometry procedure is non-invasive, that is, it occurs without disturbing the skin (without cuts or punctures). Simply put, this is an x-ray or ultrasound of the bones. Special sensors recognize bone structures and transmit data about them to a computer. The latter performs calculations and displays the following data on the monitor:
- relative bone density;
- thickness of the cortical layer;
- spatial structure of bone tissue, etc.
As a rule, doctors prescribe an examination of the lumbar spine, as well as the femoral neck: fractures in these parts of the skeleton are especially dangerous. If a diagnostic need arises, the density of the entire skeleton is assessed. When it is necessary to determine bone density prophylactically, if there is no disease yet, they resort to ultrasound examination of the heel bone as the most indicative place (this bone is primarily exposed to osteoporosis).
Indications
Densinometry is performed when osteoporosis is suspected, as well as as a preventive examination associated with this disease.
This type of examination is used to determine:
- The amounts of minerals in any one of the bones or in the entire skeleton.
- General condition of the spine.
- The presence of osteoporosis or osteopenia (a disease characterized by a slight decrease in calcium content in bone tissue), the degree of development of the pathology.
- Fractures of bones and vertebrae.
That is, undergoing densitometry makes sense for any person who is at risk of developing osteoporosis. This is especially true for people exposed to risk factors.
The list of these factors is presented:
- Metabolic disorders.
- Pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancies.
- Diseases of the spine (spondylolisthesis, osteochondrosis), injuries.
- Endocrine diseases - hypothyroidism, diabetes, pathologies of the parathyroid gland.
- Long-term use of hormonal and other drugs that remove calcium.
- Some neurological disorders.
- Recurrent fractures.
- Rheumatism.
- Poor nutrition, frequent adherence to strict diets.
- Low body weight, alcohol abuse and smoking.
Densitometry of the lumbar spine and femoral neck can provide a 10-year prognosis for fracture and can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
When conducting such an examination on a child, it is possible to determine whether there is enough calcium and phosphorus in his body so that the child’s body can cope with intensive bone growth.
The amount of calcium in the bones after 30 years begins to decrease over time, so from about 40 years of age you need to control this indicator.
How often can densitometry be done? It should be carried out once every 2 years. Thanks to screening examinations, osteoporosis can be detected and treated in a timely manner. This examination regimen is recommended for women over 30 years of age who have close relatives susceptible to osteoporosis. Men should be screened for prevention starting at age 60.
Types of examination
Most often, ultrasound densitometry and x-ray are performed. One or another diagnostic method is chosen taking into account the location of osteoporosis foci and its severity. For the purpose of preventive examination or in the initial stages of pathology, the first procedure is used; in more serious cases, X-ray densitometry of bone tissue is performed.
Sometimes, in unclear or complex cases, they resort to conventional radiography, and can also perform scintigraphy and photon densitometry.
Osteodensitometry, or Strength Test
Let's look at what osteodensitometry is. This is an X-ray method for determining the mineral density of bone structures and the proportion of fatty tissue in the body. X-rays pass freely through soft tissue (skin, fat, muscle), but are absorbed in denser formations (bones). The rate of absorption of rays by the bone is read by sensors and forms the basis for calculations of the mineral density of various parts of the skeleton. The standard for evaluation is the density (g/cm2) of the cast model of the lumbar vertebrae. Other names for the test are DEXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
Osteodensitometry is the “gold standard” for modern diagnosis of osteoporosis. The study has higher accuracy compared to ultrasound densitometry and clearly shows the difference in bone density between the patient and a healthy person.
The procedure is performed as follows. The patient is placed on a table with a “sleeve” for 10–30 minutes. Parts of the spine (or the entire spine), hip joints or the entire skeleton are scanned.
The X-ray densitometry apparatus provides accuracy with an error of no more than 1%. Such devices are calibrated using a cast of the lumbar vertebrae. This impression is characterized by a certain density number, which depends on the material of the impression. The accuracy of the results obtained does not depend on the densitometer, but only on the immobility of the subject throughout the measurement and on the experience of the personnel.
The principle of operation of the device is based on the method of photon absorptiometry - determining the severity of attenuation (absorption) of X-rays by tissues of different densities. The densitometer emits rays of two energy levels - short-wave (soft) and long-wave (hard). It is the latter that are characterized by high penetrating ability and create a high-quality, clear image.
Note: the dose of radiation received by the patient is negligible - approximately 1/10 of the radiation from a regular chest x-ray.
X-rays, passing through the body, end up in the receiving device. Then a special program calculates bone density, the proportion and volume of fatty and lean tissue. The area of the surface being studied is assessed by the operator of the X-ray machine.
In this way, densitometry of the spine and hip joints is performed. To work with peripheral bones, a mobile unit is used that delivers minimal radiation doses (no more than 0.03 m3v). It is allowed to carry out examinations with its help directly in the doctor’s office.
Note: for timely recognition of osteoporosis, densitometry of the femoral neck and lumbar spine is performed.
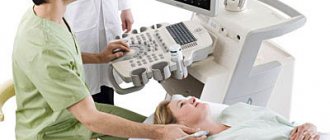
Ultrasound densitometry
Mineral density is also measured by bone absorption not of X-rays, but of ultrasound. Density is calculated, bone microstructure, thickness and density of the cortical layer are visualized. Ultrasound densitometry (US densitometry) is usually prescribed to women over 40 years of age and those who have entered the menopausal period.
The heel bone is examined: age-related metabolic changes occur primarily in it. In women, the density figures in the bones of the heel and in the bones that make up the hip joint are almost the same.
Note: Ultrasound densitometry can be performed frequently and repeated after a short period of time, since there is no radiation exposure during ultrasound.
The negative aspects of this method include the possibility of assessing density only in peripheral bones - in the calcaneus, tibia. In addition, the method does not give such accurate results compared to the x-ray procedure, and it also cannot be used to determine the severity of osteoporosis.
On the other hand, ultrasound has a significant advantage over x-ray determination of bone tissue: pregnancy and lactation are not an obstacle to performing the study, and it is also possible to examine people who are prohibited from even insignificant doses of x-ray radiation. In addition, ultrasound densitometry is performed faster and does not cause any discomfort (no need to remain motionless for 20–30 minutes).
In general, the ultrasound method is well suited as a primary examination and for preventive purposes. But in the future, especially if the bone mass is reduced, the patient is sent for X-ray osteodensitometry to get more accurate results.
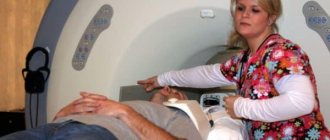
Computed and magnetic resonance imaging
Let's look at what computer densitometry is and how it differs. In principle, this is a computed tomography scan that gives the result in the form of a layer-by-layer image of the bone. The latter is a definite advantage compared to other methods of assessing the structure of bone tissue. In addition, the layer-by-layer image can be transformed into a more visual three-dimensional model.
However, due to its high cost, CT remains in the arsenal of additional methods. People turn to her if they need detailed information about the condition of the bones.
A patient undergoing CT densitometry receives a small dose of radiation, 50 Sv.
The advantages of computer osteodensitometry include high accuracy, the ability to examine any part of the human body and determine the condition of not only bone structures, but also muscles and subcutaneous fat. Disadvantages: the high price for such an examination, moreover, it can only be performed in a hospital setting.
How is MR densitometry done? This is a measurement of bone density using nuclear magnetic resonance. It is performed with an MRI scanner and does not contain an X-ray emitter. Different models of tomographs generate magnetic fields of different strengths. For bone tissue densitometry, this parameter must be at least 1.5 Tesla (this is a fairly powerful MRI scanner).
The method is characterized by absolute safety (no x-ray exposure), as well as speed of implementation. 20 seconds - and the image of the cross section of the body is ready!
However, MRI is a very expensive test. The operator must also manually set the boundaries of the study area.
Equipment for research
Medical instruments for examining bone tissue are represented by two devices:
- Ultrasound densitometers using ultrasonic irradiation;
- X-ray densitometers with X-ray irradiation.
Advantages of ultrasonic devices:
- safe examination;
- quick examination;
- compact and mobile devices;
- there is computer software with special programs;
- the examination can be carried out in any room;
- affordable cost of the device.
An ultrasound densitometer does not provide the most accurate information.
Frequently used models of ultrasound densitometers:
- Sonost 3000 device, made in Korea: equipped with a monitor and thermal printer, interface based on the latest Windows models;
- McCue CUBA Clinical device, made in the USA: it is characterized by high examination accuracy, can be connected to a computer with a printer if there is a special program;
- Omnisense 7000 device, made in Israel: equipped with a screen, main unit, probes for examining different bones.
Advantages of X-ray densitometers:
- high-precision measurement;
- direct examination of the hip joints;
- examination of the lower back, the most accurate method for determining the presence of osteoporosis;
- examination of large sections of bones.
Disadvantages of devices:
- patients receive x-rays;
- a special room is required to install the device;
- Expensive price of an x-ray densitometer.
The most popular models of X-ray devices:
- Norland ELITE installation , manufactured by Norland Medical Systems: the largest device in the world, equipped with modern software;
- installation Norland XR46 , manufactured by the same company: gives accurate measurements with calibration of the weight of different tissues, there is a positioning system with an angle of rotation;
- LUNAR iDXA installation : equipped with a program for examining children, studying the body index, analyzing the condition of bone tissue;
- The DEXXUM 3 device , produced by the South Korean company OsteoSys, conducts research using the dual-energy absorptiometry technique, an important advantage is the software in Russian.
X-ray and ultrasound densitometers of various manufacturers are successfully used in large diagnostic centers, medical departments at large manufacturing enterprises. Their choice and price range allows a medical institution to obtain a device that will suit the needs of an enterprise, city, or region.
When and who needs densitometry?
For preventive purposes, in order to detect osteoporosis at the earliest possible stages, bone densitometry is indicated for all women 65 years of age and older, and for men after 70 years of age.
Situations when a doctor can prescribe such a diagnosis:
- early, before 45 years of age, menopause (due to removal of the ovary, part of it, or for other reasons);
- low body weight in men;
- the presence of even one fracture that occurred due to a weak impact (for example, a fall from one’s own height);
- if the patient suffers from a pathology that causes calcium deficiency in the body or reduces bone density;
- taking medications that have the effects described above (steroids, contraceptives, anticonvulsants);
- a history of two or three pregnancies, childbirth after a short break and long-term breastfeeding;
- pathology of endocrine organs - dysfunction of the thyroid, parathyroid glands, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, insufficiency of pituitary function, diabetes mellitus, hypothalamic syndrome, dysfunction of the testicles and reduction in the synthesis of male sex steroids;
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract - reduction in stomach volume, low absorption of vitamins and microelements due to damage to the intestinal mucosa, chronic liver diseases, including failure;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- blood diseases - lymphoma, leukemia, myeloma;
- prolonged stay on bed rest (longer than 2 months), on a strict diet;
- sedentary, motionless lifestyle;
- osteoporosis in close blood relatives;
- tendency to dizziness and falls.
In these cases, densitometry should be done every three years. If it shows the presence of deviations, then they switch to the annual examination schedule.
Bone density analysis is also required during the treatment of osteoporosis - to monitor the achieved indicators.
Is densitometry prescribed for children? Yes, if the child received a fracture “suspicious” of osteoporosis - for example, he simply stood and fell for any reason, but without acceleration. Children may also have risk factors for osteoporosis. These are inflammatory bowel diseases (impair the absorption of calcium, phosphates, vitamins), systemic pathology of connective tissue (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus), anorexia (poor nutrition also flushes calcium from the body). If a child has been taking hormonal medications for a long time (for example, for asthma), diuretics or anticonvulsants (children with epilepsy have been taking them for years), he also needs to have his bone density determined.
However, such diagnostics for children has a number of limitations. The densitometers used in our country have software written for children over 5 years old - younger children cannot be examined. You need to look for a medical center where there is a device with a program designed specifically for small children.
Preparation and methodology
Ultrasound densitometry requires absolutely no special preparation. In the case of a radiation procedure, the doctor will explain to the patient how to properly prepare. 24 hours before the scheduled procedure, you should stop taking medications that contain calcium. It is imperative to inform the diagnostician if this patient has recently undergone radiation examinations using a contrast agent. You need to be determined to be as motionless as possible during the procedure and maintain the position specified by the doctor.
It is important to avoid calcium-based medications
The examination usually takes 30-40 minutes. The subject is asked to position himself correctly on the diagnostic table, under which there is a radiation source, and above it a device that records the result. During a stationary examination, a special sensor is moved along the body, it measures radiation levels, transfers it to computer equipment, analyzes and displays the result.
If equipment consisting of one block is used, then the part of the body being examined is placed in a special apparatus, and the result is given after processing by a computer program. To improve image quality, the limb may be immobilized or the patient may be asked not to breathe for a period of time. Having understood what densitometry is, it becomes obvious that this examination should be seriously considered by all those who are exposed to factors that increase the likelihood of developing osteoporosis at any age.
Preparation for the diagnostic procedure
The ultrasound version of densitometry is done immediately, without any preparation, directly in the doctor’s office. In the case of osteodensitometry, you need to prepare:
- One day before, you should give up any medications and vitamins containing calcium. Otherwise, it is possible to obtain false results from which conclusions cannot be drawn and treatment cannot be prescribed.
- The day before, you need to make sure that there are no metal elements on your clothes. It should be comfortable and not tight-fitting.
No special diet is needed.
Before the procedure, warn your doctor:
- if there is even a suspicion that you may be pregnant;
- if within the next two weeks you had an X-ray examination with the introduction of contrast (let's say you drank a barium mixture) or an MRI with contrast.
Contrast that is not completely removed from the body can cause false densitometry results. Perhaps you should abstain from it for a while - your doctor will give specific advice.
How much does the procedure cost?
The cost of the service depends on the method of execution and the scope of the study. Ultrasound bone densitometry is the most cost-effective procedure. The price of the study does not exceed 2000 rubles. Computer and magnetic resonance osteodensitometry are expensive. The cost of procedures reaches 9,000 rubles.
When examining individual areas, examinations of the hip joints and spinal column are expensive. The average cost is 4,000 rubles.
| Region | Average cost (in rubles) |
| Moscow | 2000–9000 |
| Saint Petersburg | 1500–9000 |
| Novosibirsk | 1500–6000 |
| Kazan | 1600–6200 |
| Ekaterinburg | 1500–4700 |
Osteoporosis remains a severely disabling disease. Lack of timely treatment can result in complete loss of the ability to move. Medicine can stop degenerative processes or even cause regression. The main problem in this case is the lack of early diagnosis.
Bone densitometry is a simple, accurate and convenient method for identifying osteoporosis and monitoring treatment. A large number of methods allows you to select a study that will be safe and informative for a particular person.
If you have experience with bone densitometry, please share it in the comments. Be healthy.
How is densitometry performed?
First of all, the patient is invited to take a place either on the table (if X-ray densitometry is prescribed) or on the couch near the ultrasound machine. Osteodensitometry is always performed in a special room.
First, the patient's data is entered into the densitometer's memory - passport data, as well as age, height and body weight. The device (or rather, its program) will compare the last three indicators with the norms of bone mineral density.
The main condition for successful osteodensitometry is maintaining immobility for 15–20 minutes. Even the smallest movements can worsen the result. The patient should take a comfortable position depending on the area to be examined. A small sensor is brought into contact with the skin and transmits radiation that reaches the bone. The indicators appear on the screen.
When scheduling an examination of the lumbar region, the patient can be placed on his back (direct projection) or on his left side (lateral).
When examining the femoral neck, the patient is placed on his back, his legs should not be bent. The leg being examined is placed straight, the foot is turned inward by 20° - it should be perpendicular to the lower leg and the couch.
If the area of interest is the forearm, the patient is seated and his hand is placed on the machine table.
For children, there are several features of this procedure. They examine either the entire skeleton or the lumbar spine. The child is placed on his back, arms along the body, lower limbs straight. The top point of the head should be 1.5 cm lower than the starting point of scanning.
The patient must remain completely still throughout the scan.
Note: in order to obtain reliable results on the effectiveness of treatment, the diagnostic procedure must be repeated on the same densitometer.
The conclusion based on the examination results is made only by the doctor. The device program is not able to take into account the height of the affected vertebrae, vertebral fusion, “extra” vertebrae, additional ribs, shape abnormalities that appeared during life, or changes in the area of study.
When carrying out the procedure, children need to remember that the bones of their skull are very rich in calcium salts, so the mineral density of this area is not taken into account in the densitometry results.
Ultrasound densitometry takes very little time and is usually carried out with a sensor. The surface of the body is scanned, treated with a special gel for ultrasound research.
Ultrasonic osteodensitometry technique
Ultrasound densitometry does not require special preparation on the part of the patient.
How densitometry is performed using an ultrasound machine depends on the method chosen by the doctor: water or dry.
In the first option, the patient’s limb is immersed in a container with distilled water; in the second, a special gel is used to improve contact with the sensor.
Using an ultrasonic densitometer, the doctor examines the limb, the data from which is displayed on the device’s screen, where it is studied. At the end of the procedure, a conclusion about the condition of the tissue is issued.
Interpretation of the results obtained
In conclusions on densitometry, three parameters are used:
- bone density, g/cm2;
- Z-score;
- T-test.
The last two are calculated by comparing the patient’s data with the standards stored in the device’s database. These criteria can be deciphered as follows:
- Z-score – comparison with the average bone density in a healthy person (same gender and age);
- T-criterion - comparison with the average bone density in a healthy person 30–35 years old (same gender).
The scope of use of these criteria is different. Using the Z-criterion, bone density is assessed in children, young people under 20 years of age, fertile (childbearing) women, and men under 50 years of age. The T-criterion allows you to determine bone density in men after 50 years, women in the perimenopausal period, as well as postmenopause.
The result of densitometry - both criteria - is assessed on a single scale (see Table 1).
Table 1. Values of densitometric criteria Z and T, in points
| Range of values, in points | Conclusion |
| 0…–1,5 | Normal |
| –1,5…–2,5 | Osteopenia (low density) |
| -2.5 or less | Osteoporosis (extremely high risk of fractures) |
If we are talking about a child, then it is impossible to make a diagnosis of osteoporosis based only on a densitometric report. After all, the bones of a child’s skeleton have not yet completed their formation.
When interpreting indicators in adults, one should not lose sight of the fact that bone density after 45 years normally decreases by 12–15%.
If the score of the Z- and T-criteria is higher than normal, this may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the bones of the spine, compression fractures, single or multiple, curvature of the spinal column, as well as vascular calcification.
If the criteria deviate (both above and below normal), additional examinations are indicated - biochemical blood test, radiography, bone biopsy.
Decoding the research results
Normally, when analyzing a graphic image, the bone has an almost uniform structure and white color. All anatomical landmarks are preserved. When foci of disorganization occur, you can see clearing in certain parts, structural disturbances, and pathological fractures.
The severity of manifestations depends on the stage of the disease. At the beginning of the disease, only a change in the bone pattern can be seen (dark lesions indicate an increase in tissue transparency). In the terminal stages, disorders of the bone structure occur - uzura (“eaten away” contours), pathological damage to the skeleton (compression fractures of the vertebrae, calcaneus, femoral neck).
During the research process, two main parameters are measured and analyzed:
- BMC – bone mineral content (in grams);
- BMD – bone mineral density (grams/sq. cm).
Parameters are assessed according to basic bone density criteria:
- “T” score is the ratio of the patient’s data to the average statistical indicator. Normally, the value ranges from +2 to -0.9.
- The "Z" score is a more objective parameter. It shows the correspondence between the patient's data and normal values in a specific gender and age group.
At the beginning of the pathological process, the “T” criterion ranges from -1 to -2.5. A value below -2.5 indicates progression of the disease and requires urgent correction.
When not to do densitometry
There are no contraindications to ultrasound measurement of bone density, and there is only one absolute contraindication to X-ray densitometry - pregnancy.
It is better to refuse the examination also in the following situations:
- the spinal column has a strong curvature, the vertebrae have significantly changed their shape;
- there is a hip joint prosthesis;
- there is a non-united fracture, serious joint diseases;
- there are metal clamps used in osteosynthesis; pacemakers;
- the patient is immobilized (paralyzed), which means he will not be able to take the necessary position;
- the patient's height is more than 196 cm;
- The patient's body weight is more than 120 kg.
If there are such relative contraindications, it is better to limit yourself to ultrasound scanning of the forearm bones.
Contraindications
Dystrophic changes in the spine
X-ray examination of the spinal column and femoral neck is not carried out in the following cases:
- pronounced curvature of the spine;
- severe deformation of the vertebrae;
- existing hip prostheses;
- unhealed fracture;
- late stages of articular pathologies;
- pregnancy;
- if the patient has undergone osteosynthesis - connecting bones with metal clamps.
Information: for densitometry, there are restrictions on height and weight: the procedure cannot be done if you are over 196 cm tall and weigh over 120 kg.
If the above contraindications are present, the bones of the forearm are scanned. X-rays are absolutely contraindicated for pregnant women.
Densitometry on a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is not done for people who have pacemakers or any metal implants.
Which examination is preferable: ultrasound or x-ray?
Ultrasound densitometry is quite suitable for making a diagnosis for the first time. If pathological changes are found during this procedure, then they turn to osteodensitometry. This test accurately identifies the location and degree of osteoporosis.
The prerogative to choose the method of assessing bone density belongs to the doctor. At the same time, he focuses on the indications and the required degree of safety for a particular patient (see Table 2).
Table 2. Comparison of some parameters of ultrasound and X-ray densitometry
| Parameter | Ultrasound procedure | X-ray densitometry |
| Mechanism | Reflection of ultrasound on bone tissue | Absorption of X-rays by bone tissue |
| Detection of osteoporosis lesions | In the initial stages | At advanced stages |
| Duration, min | 3–5 | 5–10 |
| Safety | Safe | Low doses of radiation |
Densitometry of the femoral neck and lumbar vertebrae allows predicting the occurrence of future fractures. Using this procedure, periodic monitoring of osteoporosis treatment is carried out, and, if necessary, changes in doses or drug therapy regimens.
Purpose of diagnosis
Densitometry can be performed in various areas of the musculoskeletal system, but most often the diagnosis of the spinal column, as well as the area of the knee, shoulder and hip joint tissue is performed.
Carrying out computer or complex densitometry allows you to obtain more complete information in comparison with conventional blood tests and even x-rays. Let's take a closer look at the varieties of this diagnostic, what it is, how it is carried out, and how to decipher the data.
Using complex densitometry, it is possible to determine:
- Osteoporosis of bone tissue of varying degrees.
- At what level is the bone structure density?
- How many mineral compounds are present in the patient’s bones in any part of the musculoskeletal system?
- Accurately localize the spinal fracture and consider its condition as a whole.
- To clarify the diagnosis of bone pathologies.
- To establish a further prognosis for the formation of osteoporosis, to determine the presence of a risk of disease progression.
- Evaluate the effect obtained from the treatment.
The manipulation is carried out without anesthesia; it is considered harmless, since there is no exposure to harmful rays on the patient’s body. During the procedure, a person is exposed to ultrasound or x-rays. The information is read by special sensors and transmitted to the computer. Then, using a special program, the level of density of the patient’s bone structure is determined.
Thanks to computer densitometry, it is possible to detect osteoporosis at an early stage of development. Under the influence of irradiation, even the presence of minor abnormalities in the bone structure can be detected (the procedure allows you to determine a 2% loss of calcium, which indicates that the diagnosis is highly accurate).
How much will you have to pay for the examination?
The most cost-effective measurement of bone density is the ultrasound method. It can be done not only in diagnostic centers, but also in a clinic. While X-ray osteodensitometry is carried out only in hospitals or in general medical institutions, in specially designated and equipped rooms. Accordingly, the cost of this research will be higher.
The price ranges from approximately 800 to 6500 rubles. It depends on the location of the osteoporosis foci and the type of specific joint. Let’s say an examination of one joint will cost about 1000–1500 rubles. If it is necessary to evaluate the condition of two joints (or more), the cost will be from 2,500 rubles.
For complex diagnostics, when they are not limited to densitometry, but also perform computed tomography, the costs will increase to 5000–5500 rubles.
The most expensive, of course, will be a full examination of the skeletal bones, for which you will have to pay about 4,000–5,000 rubles.
Where can I take the study?
A doctor can also determine the stages of osteoporosis using densitometry. The study can be carried out in a public or private clinic. In the first option, under the compulsory health insurance policy, if there is a referral from a therapist, diagnostics are carried out free of charge. The price in a private center depends on the level of the hospital and the type of procedure performed:
- ultrasonic – 700-2000 rubles;
- X-ray – 1300-3000;
- combined with the use of a tomograph – 5000;
- absorption photon – 3600.
Article on the topic: Bloody discharge from the ear - causes, diagnosis and treatment methods
Video on the topic
So, in order not to miss the formidable and gradually developing, unnoticed disease - osteoporosis, you need to know about age-related thinning of bone tissue. It occurs in absolutely everyone, differing only in the rate of progression. It is very important not to delay the first bone density assessment, having it done immediately after 40 years. This will allow timely measures to be taken to slow down this process. The sooner the use of means to combat bone loss begins, the cheaper and simpler these means will be.
X-ray variety
Two types of densitometry are practiced:
- ultrasound procedure;
- X-ray examination.
The ultrasound method is an examination without the use of rays. Due to the complete safety of the procedure, this type of densitometry is approved for frequent use even by pregnant women and mothers during lactation .
Such a study is practiced using a special densitometer, which can measure the speed of ultrasound through human bones. The indicator is taken by sensors and processed in a computer program.
Most often, the heel bone is examined with ultrasound.
Advantages of ultrasound diagnostics:
- Duration - no more than fifteen minutes.
- No harmful radiation or other negative effects on the body.
- Availability.
- Accuracy of the diagnostic procedure.
- No special preparation is needed.
- The ability to conduct research, both for primary diagnosis and to monitor already carried out treatment therapy and evaluate its effectiveness.
If the doctor is unable to obtain sufficient information from an ultrasound examination of the bones, X-ray densitometry is performed.
A more accurate diagnostic method is x-ray densitometry. During the procedure, X-rays are directed at a person's bone tissue. They calculate the amount of minerals in bone tissue to determine its density.
X-rays can reveal even minor abnormalities in the bones. Densitometry produces much less radiation than conventional x-rays, so the negative impact on the body is minimal.
X-rays are most often used to examine the bone density of the spine, wrists, and hip joints. This procedure can also be carried out for other areas of the human musculoskeletal system.
Due to the fact that this type of densitometry still exposes a person to radiation from X-rays, it is not recommended to carry it out too often.
It is impossible to say for sure which is better: ultrasound or x-ray densitometry, since both types of procedures have their pros and cons. However, examining bones using X-rays is considered a more informative method.