Laparoscopy has become a widespread method in surgery and gynecology. The operation involves the surgeon making small holes in the person's body instead of the traditional large incisions that leave noticeable scars. The idea that a doctor will cut the body is terrifying, but if laparoscopy is prescribed, anesthesia will “switch off” the person from consciousness or create the effect of complete anesthesia. The article describes in detail what anesthesia is used to perform laparoscopy, how local anesthesia differs from general anesthesia, and what types exist. Remember! Anesthesia for laparoscopy is selected only by an anesthesiologist on an individual basis.
Indications and contraindications for use
Under anesthesia, it is possible to achieve deep pain relief, relax the muscle fibers of the peritoneum, and also provide access for mechanical ventilation.
Epidural anesthesia or combined anesthesia, which involves a combination of regional anesthesia with intravenous sedation, can be used. This type of pain relief is appropriate for severe anxiety or fear of an upcoming intervention (for example, during gynecological operations).
Contraindications to general anesthesia:
- psychoneurological diseases in the acute stage;
- recent myocardial infarction;
- acute coronary syndrome;
- decompensated heart failure;
- serious respiratory diseases.
Local anesthesia is not carried out if the last time an allergic reaction to the administration of a local anesthetic occurred.
Indications for laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopy is performed both for diagnostic purposes (during examination of organs) and for the treatment of detected inflammations. It is prescribed when it is impossible to determine the disease using ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance therapy, etc.
Indications for laparoscopy:
- Gynecology. Used to determine infertility, if a tumor is suspected in the uterus and its appendages. In emergency cases of damage to the internal genital organs of a woman; threat of tubal pregnancy; inflammation.
- Surgical diseases. Acute diseases in the abdominal cavity that have unclear symptoms (pancreatitis, appendicitis).
- Jaundice. To determine the type of disease (hepatic or subhepatic form). Investigation of the cause of disruption of the normal flow of bile.
- Complex or closed injuries to the abdomen, head and limbs. In particular, laparoscopy is performed on persons with alcohol and drug intoxication, coma and traumatic shock. The procedure is prescribed to eliminate the risk of internal bleeding, limb injury and peritonitis.
- Various wounds in the abdominal cavity, ascites with unclear symptoms. The degree of organ damage, the presence of bleeding and inflammatory processes are diagnosed.
- Peritonitis after surgery with vague clinical symptoms.
- Tumors. Clarifying the diagnosis, establishing the boundaries of the tumor, determining metastases to other organs.
Diagnostics using laparoscopy allows you to clarify the patient’s diagnosis.
Under what anesthesia is laparoscopy performed and its types?
The doctor decides under what anesthesia the patient will undergo laparoscopy after analyzing the general condition of the patient, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. General anesthesia is used in most cases. Laparoscopy is rarely performed under local anesthesia, since this is an ineffective method that is used only as additional pain relief. The following types of anesthesia can be distinguished:
- Intubation endotracheal anesthesia. This type involves tracheal intubation and the introduction of medications into the patient’s respiratory system through a special mask with a tube.
- Inhalation. The patient inhales narcotic drugs that cause anesthesia in the form of vapor or gas.
- Intravenous. This type is used for short interventions, by administering the drug intravenously.
- Spinal. An anesthetic substance is injected into the subarachnoid space.
Local anesthesia is preferred for simple therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Often during laparoscopy, the epidural (injection of an anesthetic into the spine) or conduction (injection of a drug into the area of the nerve trunk) method is used. Epidural anesthesia is used when it is necessary to perform laparoscopy on people with pathologies of the respiratory system, heart or blood vessels.
The period of rehabilitation of a patient after laparoscopic intervention depends on the age category of the patient, the area of surgical intervention, the presence of somatic diseases and general health. A person must definitely take into account what can be eaten after general anesthesia or other important nuances.
Application of anesthesia
Anesthesiologist performs endotracheal anesthesia
The main method of pain relief during endoscopic operations on the abdominal organs is endotracheal anesthesia. This type of anesthesia makes the operation as safe as possible for the patient, and also creates comfortable working conditions for the operating team:
- The patient feels absolutely no pain and retains no memory of the operation. The surgeon does not have any time restrictions and knows that the anesthesia cannot suddenly disappear.
- Carrying out artificial ventilation facilitates abdominal operations due to the ability to control breathing.
- The drugs used allow achieving good results with a low risk of side effects. It is most optimal to use the latest generation of inhalation drugs - Isoflurane, Sevoflurane, etc.
Such features of the use of general anesthesia during operations make the procedure safe and highly effective, which certainly has a positive effect on the patient’s health.
When performing laparoscopy, inhalation techniques are used for short operations
Thus, anesthesia is most often used during laparoscopy for the purpose of pain relief. Carried out by intravenous administration of drugs, using a mask or tracheal intubation, it allows you to achieve high safety and optimal conditions for pain relief.
Preoperative preparation
The type of anesthesia is selected only by an anesthesiologist. Before the operation, he assesses the patient’s condition and corrects identified life support disorders. This is necessary to ensure that surgical interventions take place with minimal risk of complications.
If preparation for surgery is carried out as planned, then the patient must examine in detail various organ systems. To do this, the attending physician or anesthesiologist will prescribe tests that he needs to take:
- Blood chemistry.
- Functional tests showing the state of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, the functioning of the central nervous system, as well as the functionality of the excretory system.
- Narrow-profile instrumental studies (ultrasound, gastroscopy, angiography, CT, MRI).
In urgent patients, not only is the use of anesthesia before laparoscopy very different, but the preparation for it is minimal.
Specifics of laparoscopic operations
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a surgical method that allows diagnostics and surgical treatment of the abdominal and pelvic organs through small incisions in the anterior abdominal wall. The main advantages of laparoscopic interventions: low trauma, quick recovery, less pain, absence of large postoperative scars after the intervention, the object can be viewed from different angles using a camera.
To perform such an operation, surgeons use special instruments and equipment:
- Laparoscopic stand: monitor, video unit, “cold light” source, insufflator (a device that supplies gas to raise the abdominal wall), electrosurgical unit, instruments.
- Endoscope (laparoscope): telescopic tube with a lens system.
- Video system, fiber optic light guide.
How is anesthesia administered during laparoscopy?
General anesthesia, which is widely used in general surgery, involves complete loss of consciousness and sensitivity of nerve endings. Throughout the laparoscopic procedure, the anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s reaction to anesthesia and also maintains his vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure).
Drugs are administered intravenously through a catheter or by inhalation of inhaled drugs through a breathing apparatus or a combination of both. The anesthetic is administered in different dosages at different stages of anesthesia and the course of the operation, and its concentration depends on the general condition of the patient. More painful stages during surgery require a greater depth of anesthesia.
In addition to general, regional or local anesthesia, the use of sedation is practiced in medical practice. This is the simplest type of anesthesia, which is performed during minimally invasive procedures (colonoscopy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging studies) to protect the patient from discomfort and allay his fears.
Features of anesthesia
Anesthesia for laparoscopy is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. Before deciding which type will be used, the anesthesiologist studies the medical history and evaluates the patient’s body according to the following parameters:
- urgency of the operation,
- the severity of the upcoming intervention,
- indicators of analyzes and research,
- presence of chronic diseases,
- arterial pressure.
The most commonly used surgical interventions are performed under general anesthesia (artificial disconnection from consciousness, immersion in sleep). If the situation is quite mild, the surgeon may decide to use local anesthesia (operating with the patient awake).
Despite the fact that many patients are afraid of the intervention due to the fact that they will have to observe the progress of the operation, local anesthesia is safe for the body, since the risks of complications are reduced, the body recovers earlier, and patients go through the recovery period more easily. Don't worry, be afraid, or panic.
Possible complications after anesthesia
After general anesthesia, the following complications are most often observed:
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the throat;
- tremor;
- disturbance of spatial orientation or confusion;
- headache;
- back pain, lower back pain, myalgia.
Sometimes the anesthesia used during laparoscopy can cause infections of the respiratory system, trauma to the oral cavity, which provokes the insertion of a tube during intubation, as well as disorders of the nerve innervation. The need for tracheal intubation can cause all sorts of airway injuries.
Any type of anesthesia during laparoscopy requires the presence of an anesthesiologist who will monitor the patient’s condition. If the laparoscopic intervention was simple and short, then the patient quickly and easily recovers from anesthesia and recovers.
Preparing for pain relief
In order for the patient to recover from laparoscopy without consequences, the following rules must be followed:
- A preliminary examination of the functioning of internal organs, especially the heart, is carried out, blood and urine tests are taken.
- Inform the doctor about the medications used, because some groups are incompatible with anesthetic (painkiller) medications.
- The body is cleansed using laxatives and enemas the day before surgery according to a scheme discussed with the doctor.
- On the eve of the operation, eating after 18 pm is excluded (exclude food 17-24 hours before the appointed date) and drinking water after 22 pm.
- You must follow a diet for the entire week before surgery.
- Laparoscopy is performed on an empty stomach; it is strictly forbidden to eat or drink drinks directly on the day of surgery.
As a rule, a patient who follows all the recommendations recovers from anesthesia painlessly, quickly and does not experience any unpleasant consequences.
How is laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst performed?
The need to remove a cyst laparoscopically arises in the following situations:
- detection of endometriotic or dermoid cysts;
- significant size of the formation in the ovary;
- danger of cyst rupture or twisting;
- active growth of education;
- the risk of the cyst degenerating into a malignant tumor.
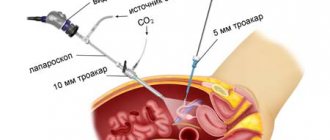
To perform laparoscopy efficiently, several incisions (punctures) are made in the anterior abdominal wall, one of which is located slightly below the navel. Through this incision, a special needle called a cannula is inserted into the abdominal cavity. After this, carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity, which helps straighten the tissues for more convenient surgical procedures. In addition to the main cannula, it is necessary to use additional instruments (thoracars), for which a couple more incisions are made on the sides of the abdomen (3 or 4 punctures may be provided).
When the preparatory procedures are completed, a miniature video camera is inserted into the abdominal cavity, through which the actions performed in the ovarian area are monitored. Internal organs are displayed on a monitor connected to a video camera. With laparoscopy, it is possible to efficiently excise the cyst without damaging healthy tissue, despite the minimal visibility during the operation. First, the cyst is cut off, after which the pathological tissue is carefully removed through the incisions made. Sometimes removal of the cyst is only possible simultaneously with complete removal of the appendage.
At the end of the surgical procedures, gas is released from the abdominal cavity using a special device, after which sutures and a sterile bandage are applied. Sometimes, to ensure the drainage of the pathological inflammatory contents of the cyst, a drainage tube is left in place for a day.
Today, laparoscopy is positioned as the simplest and most painless method of surgery, although such a procedure requires maximum precision and accuracy. The duration of surgical intervention is determined by several criteria, including: the size of the ovarian cyst, the presence and severity of the inflammatory process, tissue necrosis (if the indication for surgery is torsion of the pedicle). The average is about 3-4 hours. This takes into account preparation for the operation, administration of anesthesia and recovery from anesthesia, which can be given in several ways.
Situations when laparoscopy is not applicable
Laparoscopic surgery and the anesthesia used for it are contraindicated in the following situations:
- The presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system in the acute stage.
- Respiratory diseases, colds and acute respiratory viral infections (after recovery, a recovery period of at least a month is required).
- Physical exhaustion.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Presence of oncology of the reproductive system or suspicion of it.
- The presence of adhesions in the pelvic area.
- Severe obesity.
Possible complications
- Gas embolism (blockage of blood vessels with gas bubbles).
- Thrombosis of deep veins, pulmonary artery.
- Pneumothorax (accumulation of air in the pleural cavity).
- Cardiovascular problems (arterial hypertension, heart rhythm disturbances).
- Gastroesophageal reflux (return of stomach contents into the esophagus).
- Puncture of the dura mater.
- Headaches and back pain after the intervention.
The choice of drug used for anesthesia directly depends on the purpose of the operation, age, and condition of the patient. It is important to take into account the specific effects of a particular drug on body systems. The likelihood of developing complications after anesthesia during laparoscopic interventions is minimal.
We recommend reading: anesthesia in dentistry
Types of anesthesia
Among the anesthetic drugs recommended for use during laparoscopy are inhalation and non-inhalation anesthetics. The first group includes nitrous oxide, fluorothane or halothane, desflurane, isoflurane. Non-inhalational anesthetics are propofol, calypsol or ketamine, relanium, midazolam, droperidol. The choice of drug is made by an anesthesiologist based on the complexity of the planned intervention and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. The effectiveness of inhalational and non-inhalational anesthetics is equivalent when removing an ovarian cyst.