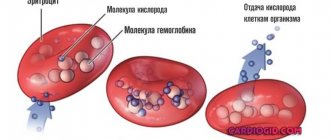
Fibrinogen is a soluble protein found in blood plasma. During metabolism, the protein loses its solubility and forms blood clots, falling out in the form of fibrin threads.
Thanks to this, the blood constantly has the ability to clot if the thrombosis mechanism is activated in a timely manner - the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin.
The level of fibrinogen in plasma is of particular importance, since this protein has an active effect in the fight against pathogenic microflora and avoids large blood losses. An increase or decrease in protein levels can trigger the development of dangerous diseases.
The role of fibrinogen protein in the body, synthesis
Fibrinogen is a colorless protein dissolved in blood plasma and takes part in the formation of the necessary blood clot after injury to a vessel, which is further processed into fiber. Whose threads intertwine and form a dense network. On which platelets fall and create a strong temporary patch to stop blood loss.
In addition to creating a protective blood clot, this protein performs the following tasks:
- Helps quickly restore damaged epidermis and damaged insides.
- It has a positive effect on the vascular system during inflammation and protects against infection.
- Helps dissolve harmful blood clots.
- Promotes the development of new capillaries.
- Participates in the joint work of blood cells with arteries.
Fibrinogen - what is it and what effect does it have on the female body?
Fibrinogen is a special protein that can dissolve in aqueous media. This compound is produced in liver tissue. This substance belongs to blood clotting factors. The renewal of this compound in the blood occurs in just 2-5 days. In the blood, the protein remains inactive. Only at the moment of need it is activated. At this time, the connection leads to the formation of a clot, blocking bleeding. Additionally, fibrinogen functions include:
- restoration of blood vessels affected by inflammation;
- regulation of the process of dissolving blood clots;
- participation in the creation of vessels;
- participation in the regeneration of damaged mucous membranes and skin.
Normal levels of this protein are extremely important for women. Good blood clotting is an important condition for the absence of complications during pregnancy and labor. In addition, fibrinogen is involved in the regulation of blood loss during menstruation. However, elevated protein levels contribute to the development of thrombosis and its dangerous consequences.
The norm of fibrinogen in women of different ages
| The normal level of fibrinogen in females is: | |
| up to 1 year | 1.3-2 g/l. |
| 2-6 years | 1.7-3 g/l |
| 6-14 years | 1.7-3 g/l |
| 15-25 years | 2-4 g/l |
| After 35 years | 1.8-4 g/l |
Protein norm for females: 2-4 g/l (grams per liter), but on critical days the indicators are often inaccurate, this is due to natural changes in the body when hormones temporarily increase the thickness and coagulability of blood to prevent major bleeding. Therefore, it is better to conduct research 3-5 days after the end of menstruation.
Reasons for increased fibrinogen levels above normal
Increased protein levels can be observed in patients taking medications containing steroid sex hormones. If its concentration is much higher than the permitted limits, then this indicates inflammation or some problems in the body.
For example:
- Acute inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- Oncology.
- Complicated hypothyroidism.
- Tissue death.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Peripheral artery disease.
- DIC syndrome (in the early stages of the disease).
- Amyloidosis.
- Pregnancy.
- Tuberculosis.
- Pneumonia.
Often this protein compound is temporarily higher than the permissible norm, this is influenced by the following factors:
- Critical days.
- Recent transactions.
- Fresh burns and wounds.
- Cold.
During pregnancy, the levels increase to 6.5 g/l - this is considered normal, since, in this way, the body is rebuilt for successful childbearing. If the protein concentration remains the same or decreases, then this indicates serious violations.
At different stages of pregnancy, the following data are generally accepted:
- Up to 3 months – 2.5-5 g/l.
- 3-6 months – 2.5-5.1 g/l.
- 6-9 months – 3.7-6.1 g/l.
Why is it rising?
The causes of increased fibrinogen can be temporary or permanent. So, in the first case, deviations in indicators may be associated with: 1. Stressful situations. 2. Bad habits. 3. Dehydration. 4. Pregnancy. 5. Retirement age. 6. Burns.
In the second case, the causes of hyperfibrinogenemia may be the following: • Stroke. • Diabetes. • Tuberculosis. • Oncology. • Postoperative period. • Hypothyroidism is a pathological condition associated with a chronic lack of thyroid hormones. • Flu, ARVI. • Pneumonia. • Amyloidosis is a failure in protein metabolism. • Myocardial infarction. • Rheumatoid arthritis.
Important! More often than not, excess levels are associated with physiological reasons, tuberculosis, and influenza.
Causes of low protein levels
Fibrinogen (the norm for women by age, the table of which is given in the article, may fluctuate slightly) in a healthy girl can increase or decrease, since the female body is very sensitive to hormonal changes.
For example, during menopause, due to a slowdown in the functions of the reproductive system, a decrease in protein may be observed, which is a natural phenomenon. Low levels of this protein indicate the inability of the plasma to produce the necessary blood clots during injury.
This is a rather serious violation, since too little blood, unable to clot at the right time, can cause great harm to the body. And fibrinogen, which does not reach 1 g/l, indicates health problems.
Reasons for decreased performance:
- Liver failure.
- Diseases of the digestive system in which vitamin K is not absorbed.
- Lymphoblastosis is benign.
- Toxicosis, in which the body practically does not absorb food, because of this, the balance of essential microelements is disrupted.
- Leukemia.
- Vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamins C and B).
- Hereditary fibrinogenopenia.
- Erythremia.
- Disease of the heart and blood vessels.
- DIC syndrome.
- Acute intoxication.
- Recent heavy bleeding.
- Alcohol addiction.
- Vegetarianism.
- Prolonged and uncontrolled use of blood thinning medications that contain Aspirin.
- Use of hormonal and anabolic drugs.
- Polycythemia vera.
- Consumption of fish oil.
Causes of deviations and methods of correcting fibrinogen levels
There are many factors that can provoke an increase in the level of this substance in a woman’s blood. To identify the pathology that caused the disorder, a comprehensive examination is required.
Often, such a disorder occurs in women due to hormonal changes during menopause. In this case, hormonal drugs are selected for the patient. In women during pregnancy, such a deviation may indicate a pathology of its course. In this case, additional studies are prescribed to assess the viability of the fetus and the risks for the woman.
The reasons for the increase in the level of this substance may lie in pathologies of an infectious and autoimmune nature, accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory process. Such diseases include:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- pneumonia;
- stomach ulcer;
- vasculitis, etc.
In addition, an increase in fibrinogen levels can occur against the background of various types of cerebrovascular accidents. The presence of a large amount of this substance indicates the presence of bleeding. Often such a disorder is detected in women who have a long history of smoking.
Burns and traumatic injuries to the skin can also cause an increase in protein levels. An increase in the amount of this coagulation factor is often observed during the acute phase of myocardial infarction. This problem often occurs in acute and chronic nephrotic syndrome. Recent surgery can create conditions for an increase in blood clotting factor levels.
Symptoms, danger of fibrinogen deviation from the norm?
Inflated indicators usually do not affect your well-being in any way; for this reason, this problem often goes unnoticed. Which is quite dangerous, since this indicates a high concentration of protein, which thickens the blood and complicates its movement through the veins.
In addition, it promotes the formation of harmful blood clots, which are able to move freely in the circulatory system.
This action is serious in 2 cases: a blood clot can block a large artery and then deform it. Or, on the contrary, he will move without difficulty, once hit in the heart. Where it will cause blockage of the valves, which will lead to its stop and inevitable death.
A high concentration of protein during pregnancy is quite dangerous, since very thick blood can cause the following disorders:
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis.
- Placental abruption and spontaneous miscarriages.
- Frozen fruit.
- Birth of premature babies.
- Formation of gestosis.
- Umbilical cord thrombosis.
Low levels of protein (not reaching 1 g/l) are dangerous due to internal hemorrhage, since any careless body movement can activate damage to large arteries, which can lead to serious health problems.
Symptoms and signs
Identifying problems with blood clotting is quite simple. A person's gum bleeding increases, and any awkward movements can provoke the appearance of subcutaneous hemorrhages. A person's skin is literally covered with bruises, although there is no mechanical damage preceding this.
When a minor abrasion or cut from a knife appears on the body, capillary bleeding develops, which in healthy people disappears independently after 2-3 minutes. When fibrinogen levels are low, the blood cannot stop for a long time. Bleeding occurs, which can lead to serious blood loss. This is extremely dangerous, since any household cut can cause death.
No less life-threatening are situations when, with an awkward turn or tilt, internal bleeding can develop, which causes death in the shortest possible time.
Therefore, if the above symptoms appear quite often, then it is necessary to take a clotting test.
When an examination is prescribed, features of a blood test for fibrinogen
To determine blood clotting, a special examination is prescribed - a coagulogram, which is prescribed if there are such indications:
- Before and after operations.
- Liver diseases.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Pregnancy.
- Uncertain pathological changes in the body.
- Suspicion of hemophilia.
- Use of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin, acenocoumarol).
- Bleeding.
- DIC syndrome.
- Constant miscarriages, stillbirths.
Content:
Everyone has had their blood tested at least several times in their life. Decoding the results of this study can tell us a lot: about the presence of infection, the development of pathological processes in the body, the correct functioning of internal organs, etc.
Fibrinogen is one of the most important indicators of blood clotting analysis. An increase in fibrinogen can lead to serious consequences, therefore, if there is a deviation from the norm, the cause should be immediately determined and a course of treatment prescribed. This article will help you understand and understand the main questions: “What to do if fibrinogen is higher than normal? What does this deviation mean and how does it affect the functioning of the body?
What can affect the results of the analysis?
Fibrinogen (the norm for women by age, the table of which is presented in the article, may change from time to time) during pregnancy increases to 6.5 g/l, since during this difficult time a complete restructuring of the body occurs, which is necessary for successful pregnancy and childbirth.
It is forbidden to carry out the examination on critical days, since the protein concentration will be inaccurate, since the blood is renewed during this period of time. The event is also undesirable during the hot season, because at this time the body often takes on fluids. This circumstance also increases the density of the plasma, which can have a negative impact on the results.
Since the quantity and quality of the prefabricated material can change under the influence of various changes in the body, to obtain accurate results you need to know that the use of medications and the following substances contribute to a decrease in protein:
- Androgens.
- Anabolic steroid.
- Anticoagulants.
- Antioxidants.
- Urokinase.
- Phenobarbital.
- Valproic acid.
Increase protein concentration:
- Emotional and physical stress.
- Overweight.
- Increased blood sugar and cholesterol.
- Use of oral contraceptives.
The article provides a table with fibrinogen standards in women by age.
The results of the study are considered invalid if the patient suffered from the following diseases during the manipulations:
- Syndrome of inflammation of the nasal mucosa (runny nose).
- Tonsillitis.
- ORZ.
- Acute respiratory viral infections.
- An infectious disease of the respiratory tract caused by the influenza virus.
What analysis is it determined by?
To determine the level of fibrinogen in the blood, a study such as a coagulogram is performed. To perform the analysis, blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach. You should stop taking medications and smoking. This may affect the analysis results.
It is not recommended to conduct the study if there are signs of a cold. This may affect the correctness of the result. Additionally, to assess the activity of this substance, blood tests such as ATCV and antithrombin 3 are performed. In the list of detected enzymes, fibrinogen is called Factor 1. Its content varies g/l.
Preparing for analysis, donating blood
Fibrinogen in the blood of women at different ages (according to the table) differs from each other, for example, if the levels reach 2-4 mg after 15 years, then this is considered normal. A higher protein concentration may indicate the presence of infections and viruses, while a lower concentration may indicate problems with the liver or a lack of vitamins.
For the most accurate examination results, the following rules must be followed:
- The activity must be done in the morning, 1-2 hours after sleep.
- The last meal should be 9-12 hours before collection.
- You need to get a good night's sleep before the test.
- Drinking coffee and alcoholic beverages before the event is prohibited.
- It is advisable to refrain from consuming nicotine for 2-2.5 hours.
- Immediately before the coagulogram, you need to drink 200-250 ml of purified or mineral water without gas.
- 15 minutes before the event, it is not advisable to be nervous and overexert yourself, and reduce physical activity to a minimum 2-3 days before the coagulogram.
The accuracy of the examination also depends on the professionalism of the laboratory itself. A patient taking a medication that affects clotting should notify health care providers.
What to do?
In the case where fibrinogen and fibrin in the blood are low, it is necessary to identify the cause. It is important to understand that changes in blood clotting functions are a consequence, and not an independent disease.
It is impossible to do this on your own, therefore, after deciphering the coagulogram, you need to contact your local physician, who will prescribe a more detailed examination.
Medicines
Drug treatment is selected individually, depending on what disease provoked the decrease in fibrinogen levels in the blood. Targeted therapy that can regulate the concentration of this protein is used in combination. This includes taking medications such as:
Tranexam - contains tranexamic acid, which is an inhibitor of plasmin activator, which promotes the destruction of fibrin. It is used for critically low levels of fibrinogen in the blood, when it is necessary to prepare a person for surgery, as well as during pregnancy and before childbirth. Available in tablet form. Positive dynamics are determined on days 5-8 of taking the medicine. Do not use if you are hypersensitive to tranexamic acid. May cause digestive tract disorders. Price – 200-650, depending on the dosage and number of capsules.
Dicinone - regulates hemostasis, normalizing blood clotting processes by increasing the amount of fibrin. It is used as the main medicine in the presence of bleeding, as well as as a prophylaxis in case of reduced coagulation. A contraindication is individual intolerance to the drug. After prolonged use, appetite may deteriorate and nausea may occur. Price – 650-750 rubles.
Vikasol - the drug contains a substance similar to vitamin K, which is synthesized by liver cells and is involved in the coagulation process. Normalizes the activation of fibrin, which increases coagulation. Not used in the presence of serious diseases of the digestive system, as well as in case of individual intolerance. Price – 115-160 rubles.
Aminocaproic acid - inhibits plasmin activity, which increases coagulation. It is well tolerated by the body, but to consolidate the results, it is necessary to use the drug in a course of at least 15-20 days. Contraindicated in the presence of individual intolerance and a tendency to allergies. Price – 40-80 rubles.
In cases where fibrinogen is reduced to critical levels and there is a serious threat to human life (especially during or after operations), a special solution is used - Plasmastabil-200. It contains components that are identical to plasma inclusions, which helps normalize hemostasis. It is administered by drip, which reduces the percentage of rejection by the body.
A positive effect is observed 30-45 minutes after administration of the medicinal solution.
Diet
Since food can influence the quantitative and qualitative composition of the blood, they can be used to stabilize low levels. To do this, it is necessary to exclude from the diet those foods that can reduce blood clotting. These include:
- fatty varieties of sea fish;
- raspberries;
- beets, especially boiled;
- flax oil;
- turmeric;
- cucumbers in large quantities;
- high consumption of green tea without sugar.
The menu should be formed from those products that stimulate the production of fibrinogen and activate the coagulation process.
These include:
- any types of meat, except fatty ones;
- legumes;
- young nettle;
- bananas;
- spinach;
- all types of cabbage, including sea cabbage;
- corn;
- persimmon;
- pumpkin.
Decoding the result
Fibrinogen (the norm for women by age, the table of which is presented in the article, can vary depending on the physiological state) in a healthy girl often fluctuates and this is influenced by many factors.
For example, on critical days, protein levels are unstable , which is explained by natural trends in the female body, when, under the influence of hormones, the density and coagulability of the plasma system temporarily increases to prevent major bleeding.
To decipher the result, 2 columns with numbers are used: 1 indicates the patient’s indicators, 2 indicates the required norm. If the protein concentration corresponds to the established values, then no clotting abnormalities were detected.
Prevention
If fibrinogen in the body is below normal, this means there is a high risk of bleeding and death. This is especially true for those patients who are undergoing surgery. In order to avoid negative consequences, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures, namely:
- Eat rationally, never depriving yourself of protein foods.
- Eliminate the possibility of prolonged fasting or mono-diets, which is why problems with the quality of the blood develop.
- Limit consumption of foods that lower fibrinogen levels.
- Lead an active lifestyle and spend more time in the fresh air.
- If you have any diseases, do not self-medicate, but adhere to the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Thus, low levels of fibrinogen contribute to the formation of various bleedings, which dictates the need to increase the amount of this protein in the blood.
This is possible with the help of medications, as well as dietary adjustments, but treatment is considered complete when the true cause is identified and eliminated. In critical situations, when it is not possible to search for causes and the probability of the patient’s death is high, special solutions are introduced that can control the plasma composition and trigger coagulation mechanisms.
Treatment of fibrinogen synthesis disorders
It is important to know that impaired protein levels should not become a reason for self-treatment. First you need to undergo a full examination and only after that therapy is prescribed, the main task of which is to eliminate the culprit that causes this pathology.
Drugs to stabilize protease levels
To regulate indicators, the following medications may be prescribed that affect the circulatory system:
- Antiplatelet agents - reduce blood clotting, due to which they have a preventive and therapeutic effect (Cardiomagnyl, Aspirin Cardio).
- Anticoagulants are chemicals and medications that inhibit the activity of the blood coagulation system and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Thrombolytics - aimed at restoring blood flow in the vessel due to the lysis of a blood clot inside the vascular bed (Batroxobin, Biostrepta).
- Fibrinolytics - cause the destruction of formed fibrin threads, they mainly contribute to the resorption of fresh (not yet undergone organization) blood clots (Thromboflux, Eberkinase).
To normalize protein mass at increased concentrations, a special diet that contains the following foods is very helpful:
- Onion.
- Beet.
- Tomatoes.
- Seafood.
- Cranberry.
- Raspberries.
- Green tea.
- Cocoa.
- Black chocolate.
- Chicken and turkey.
- Veal.
- Leguminous crops.
- Potato.
- Olive oil.
- Cabbage.
- Cherry.
- Bananas.
- Lemon.
- Buckwheat grain.
- Walnuts.
- Black currant.
- Eggs.
- Garlic.
- Dry red wine.
Eating such foods helps normalize and improve blood composition; in addition, they perfectly relieve stress and have a positive effect on the entire body.
Emergency reduction of fibrinogen concentration
If a low protein level is detected, therapy and the cause of such disorders must be started immediately.
Along with the treatment of the disease that activated these disorders, it is recommended to carry out targeted drug treatment to regulate indicators and prevent internal bleeding using the following medications:
- Aminocaproic acid.
- Transamcha.
- Etamzilat.
- Menadione sodium bisulfite.
Fibrinogen is a colorless protein mass that resides in the lymphatic system, which is formed in the liver and is renewed within 4-6 days. It is called plasma coagulation factor 1. The norm of this protein in women differs by age, as shown in a special table.
Author: Inessa Kalinovskaya
Why it might be downgraded and what it threatens
Now let's look at what it means if fibrinogen in the blood is below normal, and what are the reasons for the low levels.
The condition of plasma deprived of fibrinogen is called afibrinogenemia, and its deficiency is called fibrinogenopenia or hypofibrinogenemia. Such conditions can be congenital or acquired .
In the absence of protein, blood clotting does not occur, and with its deficiency, the clot turns out to be loose and crumbly.
A decrease in fibrinogen levels is associated with a dangerous hematopoietic disorder - DIC syndrome (disseminated intravascular coagulation), or thrombohemorrhagic syndrome, which can be fatal. DIC syndrome is observed in severe poisoning, acute infections, and malignant tumors.
The following conditions lead to a decrease in fibrinogen in the blood:
- liver pathologies with impaired organ function - cirrhosis, hepatitis, when the production of the substance is disrupted;
- deficiency of vitamins B12 and C;
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- penetration of amniotic fluid into the bloodstream during cesarean section;
- blood diseases - polycythemia, chronic myeloid leukemia;
- taking anabolic hormones (androgen-containing);
- snake venom, which, when entering the body, disrupts the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
Some foods increase the production of fibrinogen - bananas, potatoes, walnuts, spinach, cereals, cabbage. It is also useful to use infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs - nettle, St. John's wort, yarrow.
But diet and herbal medicines are prescribed only by a doctor based on the results of laboratory tests.