Synonyms: Fibrin degradation fragment, D-dimer, Fragment D-dimer, Fibrin degradation fragment.
Scientific editor: M. Merkusheva, PSPbSMU named after. acad. Pavlova, medical practice.
D-dimer is a protein fraction, the result of fibrin breakdown during the process of dissolving blood clots (fibrinolysis). D-dimer is considered a fairly informative indicator of thrombus formation, since the mechanism of its production starts simultaneously with the process of thrombus formation.
The D-dimer test allows you to evaluate two factors in combination: coagulation (blood clotting) and fibrinolysis (dissolution of clots). The marker makes it possible to promptly detect an imbalance between them in the case of diseases of the circulatory system (varicose veins, thrombophilia, pulmonary embolism, etc.).
What do we know about D-dimer?
What does it represent?
D dimer is a protein molecule that has some relation to the blood coagulation and anticoagulation system.
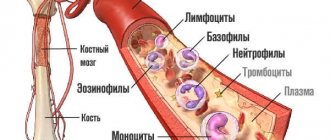
So, the process of blood clotting begins. One of the stages of blood clotting is the formation of an intermediate substance - thrombin. Thrombin promotes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. This point is worth dwelling on in more detail.
Fibrinogen is a protein molecule consisting of several peptide chains. Under the influence of thrombin, 4 fibrinopeptides are cleaved: 2 fibrinopeptide A and 2 fibrinopeptide B. As a result, fibrin monomers are formed, which make up the insoluble fibrin polymer molecule. This polymer is a clot that prevents blood flow.
The fibrinogen molecule has D and E regions. By connecting with each other, they form a strong network of monomers, forming a polymer complex.
In response to the formation of a clot, the body starts the reverse process - the breakdown of fibrin. This process is called fibrinolysis.
The process of fibrin breakdown is triggered by plasminogen. It is activated in response to fibrin formation. Plasminogen is the precursor of plasmin. Plasmin “cuts” the network of fibrin polymers into various sections - products of fibrin degradation. These include the D dimer.
That is, the mechanism that can explain where D-dimer comes from in the body looks something like this:
- thrombin triggers the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin;
- as a result of fibrin formation, the fibrinolysis system is activated;
- During the breakdown of fibrin, various products are formed, which include D-dimer.
What functions does it perform?
D-dimer has no specialized functions in the body. However, this indicator has great diagnostic value; it indicates at what level the processes of clot formation and its splitting occur.
After D-dimers are formed during the breakdown of fibrin, they circulate in the bloodstream for 24 hours and are then excreted from the body. This allows this indicator to be used to assess the body's ability to form blood clots.
Historical facts about D-dimer
D-dimer was first described back in the seventies of the twentieth century. However, the practical use of this indicator to assess the risk of blood clots began only in the nineties.
Blood D-dimer levels
In men
The blood levels of D-dimer in males generally remain stable over time. Reference values for D-dimer levels can be given in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml), or even in fibrinogen equivalent units (FEU). Based on the fact that the units of measurement can be different, the reference values are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Reference values for D-dimer levels in the blood.
| Index | Reference values | ||
| D-dimer | mg/l | ng/ml | µg FEE/ml |
| Less than 0.5 | 110 — 300 | 0 — 0,55 | |
There is evidence that D-dimer levels increase with age. For the most part, this applies to older people.
In children
D-dimer is determined in the blood for the purpose of diagnosing disorders of the hemostatic system and assessing the risk of thrombosis. As a rule, this pathology rarely occurs in children. Therefore, it is not advisable to determine the level of D-dimer, and therefore there are no standards as such separately for children.
In women at different periods of life
For women, the values of norms change slightly at different periods of life. This is especially true during pregnancy. For example, before pregnancy, acceptable levels of d-dimer are no more than 500 ng/ml. In the first trimester, the upper limit of the norm is 950 ng/ml, in the second trimester the norm is 320 – 1200 ng/ml. In the third trimester, the upper limit of normal can reach 1500 ng/ml.
Example values are given here to show how much the normal range can vary. In each laboratory, depending on the method used and the manufacturer of the reagents, reference values may vary.
The presence of rheumatoid factor in the blood can lead to increased D-dimer levels. Therefore, it is worth informing your doctor about various conditions. It is difficult to guess which of them may have an impact and which may not.
You can easily track your D-dimer levels, as well as any others, with the free Ornament smartphone app . This is an aggregator of medical research results that helps to store and systematize the results of medical tests. The ornament processes more than 3,000 biomarkers, including very rare ones. By creating an account in Ornament, you will be able to maintain not only your “medical statistics”, but also make separate profiles for each family member.
Ornament is very easy to use. To enter data into the application, just take a photo of the form with the results from the laboratory. Digitization and processing of information will take an average of 20 minutes, after which the result of the analysis will be entered into the database and displayed in several sections of the application at once.
Firstly, you can always find this analysis by date of entry and name. Secondly, each of its indicators will be built into the corresponding dynamics graph. For example, after taking several blood tests, you will be able to see how all its indicators changed from one time to another. Thirdly, new data will immediately be reflected in the assessment of organs and body systems on the “Health” tab.
If all biomarkers are normal, the graphs will be green, and in the “Health” section there will be only fives. Scores above four indicate good health. But still, if yellow areas appear on the diagrams, you should consult your doctor. Or at least ask for advice in the “Community” section - there are users with medical education there.
And you can download this wonderful Ornament application for free both in the AppStore and in the PlayMarket.
Treatment
Before prescribing treatment, if the doctor sees a need for it, the woman is sent for a consultation with a cardiologist, nephrologist and therapist. A detailed analysis of all blood clotting indicators is performed - a coagulogram. If necessary, a woman is recommended to consult a hematologist. After which the question of the presence of a specific pathology is resolved, and ways are sought to provide assistance to the pregnant woman.
To normalize blood clotting, special drugs are prescribed - anticoagulants. Most often these are “Nadroparin calcium” (“Fraxiparin”) and “Reopoliglyukin”. “Nadroparin calcium” in the form of injections is placed in the stomach, in the area of the umbilical ring. There is no need to be afraid of the procedure; thin and small needles, also called insulin needles, are used for injections. The expectant mother will not feel severe pain during the injection. After the injection, a slight burning and tingling sensation may be observed at the injection site.
"Reopoliglyukin" is administered as part of droppers in a day hospital or in a hospital inpatient setting. The drug helps the process of resorption of blood clots, cleanses blood vessels, and restores normal blood circulation in them. A course of treatment usually helps lower D-dimer levels to normal levels for pregnancy.
Women are usually prescribed B vitamins, as well as vitamin K.
If the disorder is detected in the early stages, special attention is paid to taking folic acid, a deficiency of which can also become one of the reasons for the increase in D-dimer in the blood
Excessive physical activity, insufficient sleep, emotional distress and stress are strictly contraindicated for a woman. Moderate physical activity is encouraged - exercise and walking will be beneficial as a good means of preventing thrombosis.
Do not be alarmed if your obstetrician-gynecologist advises you to visit a geneticist. Typically, such advice can be heard by pregnant women whose close relatives have problems with blood vessels, if they have been diagnosed with strokes or heart attacks. A consultation with such a specialist is needed to more carefully calculate the likelihood of hereditary pathology in a woman and her child, this will allow doctors to choose the right tactics for managing pregnancy and delivery.
In the 90s of the last century, a blood test for D-dimer appeared. It is indispensable when examining patients for various thrombotic disorders. Let's look at what a D-dimer is and what its features are.
Indications for referral for analysis
D-dimer is one of the early markers of blood clot formation. Therefore, knowing its level in the blood, we can guess what state the coagulation system is in and whether there is a tendency to thrombosis.
Hypercoagulation is a state of the body when the blood coagulation system prevails over the anticoagulation system.
The main reasons for referral to determine D-dimer levels are:
- diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome;
- with symptoms of vein thrombosis, for example, swelling, pain, pallor of the skin in the area of the formation of a blood clot;
- diagnosis of thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries. Symptoms indicating this may include shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood;
- monitoring the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy.
When the level of D-dimer in the blood is within the reference values, this indicates that there are no blood clots in the vessels at the moment. This analysis is only the initial stage of diagnosing the hemostatic system.
The reliability of the result depends on the preparation
Deviation from the norm
To identify pathology, only exceeding standard values is important. Low D-dimer levels in a pregnant woman are not clinically significant
Therefore, the conclusion “D-dimer is reduced” is incorrect.
A high level of this marker is an indicator of increased thrombus formation in the body of a pregnant woman. The reasons for an increase in D-dimer may be:
- Diabetes. In this case, the pregnant woman has damage to the inner layer of blood vessels and an increased tendency to intravascular thrombus formation.
- Chronic kidney diseases. In a condition called nephrotic syndrome, there is also an increased tendency for blood clots to form in the vessels.
- Preeclampsia. The old name for this disease is “late toxicosis.” This pathology in obstetrics and gynecology is one of the most severe. It is characterized by increased blood pressure, the presence of protein in urine analysis and the occurrence of edema. Increased thrombus formation is also characteristic of this disease.
- Heart failure. With this disease, there is stagnation of blood in one of the circulation circles. This predisposes to the development of blood clots.
- Heart defects. If there are changes in the heart valves, D-dimer levels may also increase.
- Multiple pregnancy (pregnancy with twins, triplets, etc.);
- Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities (DVT). This pathology often develops against the background of varicose veins in the legs. Characteristic manifestations of this disease are the development of swelling of the lower limb, its blueness and severe bursting pain.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE). This pathology often complicates DVT. It is due to the fact that a blood clot breaks off from the wall of the vein, is carried by the bloodstream and clogs the pulmonary artery. As a result, the blood supply to the lungs is disrupted, acute pulmonary heart failure develops, and in severe cases the patient dies.
- Myocardial infarction. A heart attack occurs when a blood clot forms in a coronary (heart) artery, which can also cause D-dimer levels to rise.
- Ischemic stroke. This condition is similar in its development mechanism to myocardial infarction. Only the blood clot forms not in the coronary vessels, but in the cerebral vessels.
- Premature placental abruption. This pathology is extremely dangerous. It consists of separating the placenta (baby place) from the inner surface of the uterus before the due date. This is accompanied by severe pain, bleeding from the genital tract, disruption of the vital functions of the fetus, including its death.
- Systemic (rheumatological) diseases. These diseases affect several organs and their systems at once. These include systemic scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
- Malignant neoplasm. A number of malignant tumors lead to increased thrombus formation. It is worth noting that the tumor may not manifest itself for a long time, and may appear for the first time only during pregnancy.
- Recent injuries and surgical interventions. In these situations, blood clots will form in the body, which are necessary to stop obvious or hidden bleeding that inevitably occurs after surgery and injuries.
The above diseases are not all pathologies that lead to an increase in D-dimer levels.
Tips for preparing to donate blood for D-dimer testing
The material for testing D-dimer levels is blood. Most often, venous blood is suitable for this. Sometimes there are some factors that can affect the value of the indicator. To prevent this from happening, it is important to properly prepare for the study.
- It is best to take a blood test on an empty stomach. Before determining your D-dimer level, you are advised to abstain from fatty foods for 24 hours.
- It is recommended to refrain from smoking 1 to 2 hours before blood collection.
- Physical and emotional stress can distort the results of the study. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to this when preparing for analysis.
- If the patient is taking any medications, it is worth informing the attending physician. A number of medications can lead to overestimation or underestimation of indicators.
The patient’s main task is to follow a number of simple rules. Then everything depends on the medical personnel: how to properly collect blood and prepare it for analysis.
Possible complications
- Thrombosis. Blood clots form in the lumen of intact vessels. They often accompany varicose veins of the legs. Thrombosis can also be arterial.
- DIC - disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome - is a serious condition in which the normal course of processes in the hemostatic system is disrupted and the vascular bed is filled with many blood clots. It can occur as a complication of blood poisoning, after severe injuries, surgical interventions, or previous infections. If left untreated, fibrin reserves are depleted, the blood does not clot, and the patient may die from uncontrolled blood loss and damage to internal organs. Determining the level of D-dimer allows you to prevent complications in time.
When and where to take it?
The doctor who issued the referral must inform the patient about when to donate blood in order to determine D-dimer. Based on practice, blood is usually donated on an empty stomach, and this is most conveniently done in the morning.
Blood to determine the level of D-dimer can be donated at a clinic at your place of residence. You can also find a private laboratory that does coagulation blood tests. Information can be obtained in advance, for example, by calling before the patient contacts this laboratory.
Methods for determining D-dimer in blood
The price of the analysis is determined by what equipment and reagents are needed to determine it.
When a D dimer test is prescribed, the blood level can be determined by the following methods:
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) - this method is characterized by fairly high sensitivity, so it is better than others, but it is difficult to use in emergency conditions;
- latex agglutination - this method is quite simple, which allows it to be used in emergency conditions, however, the disadvantage of this method is the possibility of distorting the results in the presence of rheumatoid factor;
- other immunological methods - immunochromatography, immunochemiluminescence.
Immunological methods are among the more accurate, as they are based on the use of monoclonal antibodies. They provide a specific interaction with the desired substance. These methods can also detect low protein concentrations in the blood. But this requires expensive equipment, which is a disadvantage of these methods.
With IVF
Not everyone manages to get pregnant naturally, so some use IVF. This procedure is preceded by superovulation - artificial stimulation of the maturation of several eggs for more successful fertilization. A large amount of hormones is introduced into the body, but this is fraught with the occurrence of thrombosis. For this reason, D-dimer is so necessary for IVF. Tests are also carried out after the procedure is completed, since there remains a risk of ovulation of new eggs. In addition, after the embryo is transferred to the uterus, this figure may increase.
- How to treat cervical osteochondrosis
- How to salt salmon tasty and quickly
- Size chart for children's shoes in the table. Matching foot length and age
Analysis transcript
Conditions when D-dimer increases
The detection of D-dimer above reference values indicates conditions accompanied by increased fibrin formation and high plasmin activity.
A slight increase in the concentration of D-dimer in the blood can be observed with:
- minor injuries;
- cardiovascular diseases (myocardial infarction);
- infectious diseases;
- malignant neoplasms;
- pregnancy;
- surgical intervention.
There are also a number of pathologies in which the level of D-dimer in the blood will be significantly higher than the reference values:
- early stage of DIC syndrome;
- pulmonary embolism (D-dimer is a highly sensitive indicator);
- blood clots in the veins;
- blood clots in the arteries.
D-dimer only indicates whether or not there is a blood clot in the vessels. But in order to determine its localization, other research methods are needed.
Sometimes there are false negative results: the thrombus formation process is increased, but the D-dimer is within acceptable values. This occurs when the size of the blood clot is very small or there are disturbances in the plasmin system.
Conditions in which D-dimer levels are low
When the D-dimer level is within acceptable values, this means that the patient does not currently have blood clots in the body. Looking at the numbers of reference values, you can see that there is not always a lower limit. When D-dimer is not detected, or its concentration is so low that it is difficult to detect, this indicates that the body does not currently have a tendency to form blood clots.
That is, the detection of low concentrations of D-dimer does not have important diagnostic value.
Advantage of the test
Determination of D-dimer - a quick and affordable test
Diagnosis of hemostasis using D-dimer has been used since the 1990s, and during this time it has established itself as a highly effective technique for quickly determining thrombus formation processes in the circulatory system.
To identify thrombosis and concomitant diseases, there are various methods: contrast angiography, ultrasound Dopplerography of veins, lung scintigraphy and other techniques. But these studies are not available to every clinic, and do not always accurately determine the presence of blood clots.
Tests based on blood samples that diagnose other markers of the hemocoagulation system take significantly longer to reveal results. For example, diagnosing fibrinopeptide requires excluding all cross-reacting fibrinogen from the plasma sample.
Another advantage of the D-dimer test is that it is independent of the blood sample collection technique. Also, the result is not affected by platelet admixture, which accompanies the diagnosis of other indicators.
A distinctive feature of D-dimers is their resistance to decay; the duration of circulation of molecules in the bloodstream is about 300 - 400 minutes.